Contour stone bunds [Нигер]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Dieter Nill
- Редактор: –
- Рецензент: David Streiff
Cordons pierreux (French)
technologies_1616 - Нигер
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Технологии
Специалист по УЗП:
Dorlöchter-Sulser Sabine
Misereor
Германия
Специалист по УЗП:
Mamadou Abdou Gaoh Sani
mamadou.sani@giz.de
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive
Niamey
Нигер
Название проекта, содействовавшего документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive (GIZ / PROMAP)Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - ГерманияНазвание организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Misereor - Германия1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование данных, собранных ВОКАТ
Когда были собраны данные (на местах)?
01/07/2012
Составитель и ответственный(-ые) специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
2. Описание Технологии УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Технологии
Определение Технологии:
Contour stone bunds are erosion control structures and improve water retention and infiltration into the soil, resulting in an increased harvest.
2.2 Подробное описание Технологии
Описание:
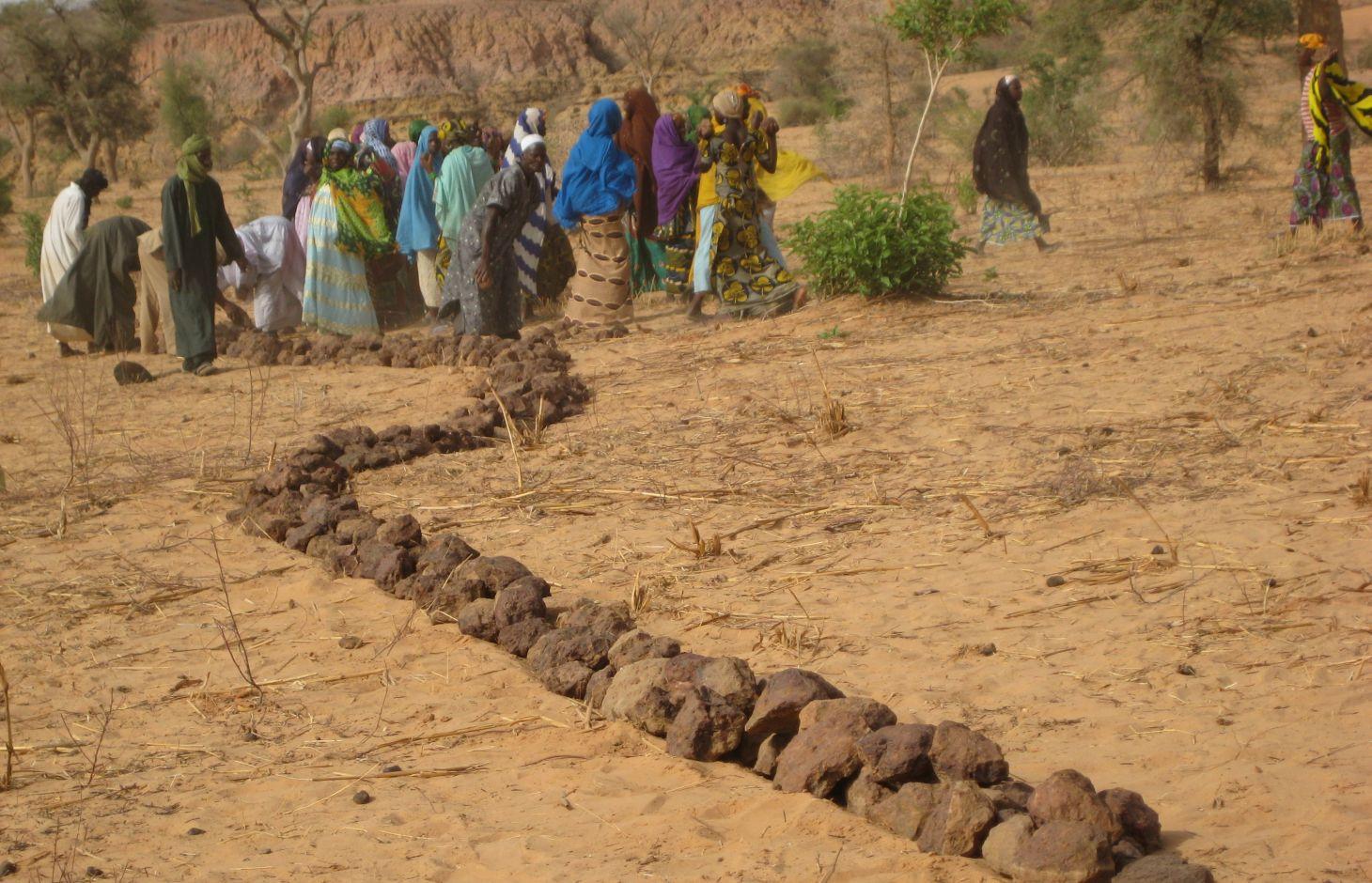
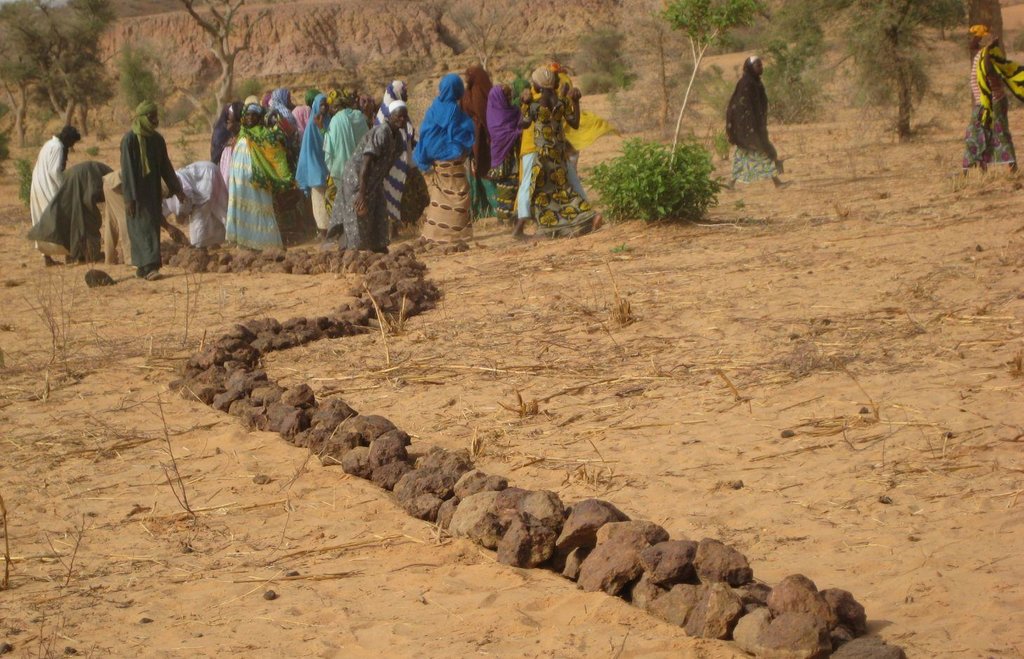
Contour stone bunds are erosion control structures built with quarry rock or stones in series of two or three. They are constructed in lines along the natural contour of the land after 10-15 cm of the soil has been removed from the line where they are to be built. They should be built to a height of 20-30 cm from the ground and spaced 20 to 50 m apart depending on the inclination of the terrain.
The best results are achieved when contour stone bunds are used in combination with biological measures (planting of grass, trees and hedges) and the use of organic fertiliser and mulching.
Purpose of the Technology: Contour stone bunds protect the land against sheet erosion caused by runoff. They form a barrier that slows down runoff and spreads it more evenly over the land. By slowing the flow of water over the land, it can seep into the soil and prevents the loss of rainwater. The bunds also act as a filter, trapping fine waterborne particles of soil and manure, resulting in a build-up of sediment and the formation of terraces. The seeds of grasses and shrubs are also trapped by the bunds, favouring the establishment of natural vegetation along the structure. This further stabilises the soil and the bunds and contributes to conserving the biodiversity of plants and small wild animals (monitor lizards, birds, snakes and other reptiles). If good vegetation cover is developed on the stone bunds, they also lower soil temperature and provide protection against wind erosion. Excess water filters through the bunds and infiltrates into the soil. When rainfall is erratic, the stone bunds contribute to conserving more moisture in the soil for longer, which helps to alleviate water stress during dry spells. There is evidence that bunds that have been in place for over 15 years have positive effects on yields.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: A minimum amount of upkeep is required, which essentially involves replacing stones dislodged by animals or water flow. The lifespan of a stone bund is over 20 years.
In order to optimise the positive effects of stone bunds, it is important to ensure that they are constructed closely following the natural contour of the land and in accordance with the established technical standards.
The means of transport required depends on the proximity of a quarry or a supply of stones (cart or lorry).
Natural / human environment: This technique is designed for cropland, but can also be used on forest/rangeland. It is suitable for areas in the Sahel and the Sudan with rainfall ranging between 300 and 900 mm/year and low-to-medium gradient terrain.
When rainfall is high, they protect the land in the event of heavy rain, a phenomenon that tends to increase with climate change.
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Технологию
2.5 Страна/ регион/ места, где применяется Технология, информация о которых собрана в данной Анкете
Страна:
Нигер
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Niger, Mali, Burkina Faso, Chad
Более точная привязка места:
Regions of Tillabéri, Filingué, Ouallam, Téra and Tahuoa
Map
×2.6 Сколько лет применяется данная Технология
Если год начала применения Технологии достоверно неизвестен, дайте примерную оценку:
- 10-50 лет назад
2.7 Внедрение Технологии
Укажите, как именно Технология УЗП была внедрена:
- через проекты/ внешнее вмешательство
Пояснения (тип проекта и т.д.):
Known as traditional method in some areas. Improved and up-scaled as part of numerous projects in many semi-arid countries. German Developmenmt Cooperation has used the technology from the 1980s onwards to combat desertification and improve natural resource management e.g. PDRT (Projet de développement rural de Tahoua - Tahoua Rural Development Project), PASP (Projet de protection intégrée des ressources agro-sylvo-pastorales Tillabéri-Nord - Project for the Integrated Protection of Agricultural, Forest and Rangeland Resources in Tillabéri-Nord) and several other projects of GIZ/KfW and other donors.
3. Классификация Технологии УЗП
3.1 Основные цели и задачи реализации Технологии
- снижение или предотвращение деградации земель, восстановление нарушенных земель
3.2 Текущий(-ие) тип(-ы) землепользования на территории, где применяется Технология

Пахотные угодья и плантации
- Однолетние культуры
Основные сельскохозяйственные культуры (товарные и продовольственные):
major cash crop: Ground nut
major food crop: Millet
other: Sorghum, cow pea and mangoes

Смешанное землепользование (пашня/ пастбища/ лес), включая агролесоводство
- Агро-лесо-пастбищное хозяйство
Пояснения:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): surface runoff, erosion by water and wind, fertility decline,
Nomadism: Yes
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Yes
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: Yes
Improved pasture: Yes
Other grazingland: agropastoralism
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: Yes
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, fruits and nuts, grazing / browsing, other forest products / uses (honey, medical, etc.)
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: farmers are mainly agropastoralists with some communities specialised on pure pastoralism
Constraints of common grazing land
Constraints of forested government-owned land or commons
3.3 Дополнительная информация о землепользовании
Обеспеченность водой участков, где реализуется Технология :
- богарные земли
Пояснения:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated and post-flooding
Число урожаев за год:
- 1
Поясните:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: August to October
Поголовье скота на единицу площади (если применимо):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 Категория УЗП, к которой относится Технология
- мероприятия по влагозадержанию и снижению эрозии почв на склонах
3.5 Распределение Технологии по площади
Охарактеризуйте пространственное распространение Технологии :
- равномерно-однородное применение на определенной площади
Если Технология равномерно применяется на той или иной территории, укажите ее приблизительную общую площадь:
- > 10 000 км2
Пояснения:
Large-scale areas have been protected in most Sahel countries. German Development Cooperation (BMZ/GIZ/KfW) for example has had several projects in Chad, Burkina Faso, Niger, Mali, Benin, which have applied stone bunds on around 800.000 to 1.000.000 ha since the 90ies.
3.6 Мероприятия УЗП, выполняемые в рамках Технологии

инженерные мероприятия
- И2: Насыпи, валы
3.7 Основные проблемы деградации земель, на решение которых направлена Технология

водная эрозия почв
- ВЭп: поверхностная эрозия/смыв верхних почвенных горизонтов
- ВЭл: овражная эрозия / оврагообразование
- ВЭд: косвенное воздействие водной эрозии

ветровая эрозия почв
- Эп: утрата плодородного слоя почвы

ухудшение химических свойств почв
- Хп: Снижение плодородия и уменьшение содержания органического вещества (вызванное не эрозией, а другими причинами)

биологическая деградация
- Бр: сокращение растительного покрова

деградация водных ресурсов
- Вуп: изменение объема поверхностного стока
Пояснения:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Unadapted landuse methods, reduced or abandoned fallow periods), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Neglect of fallow periods and crop rotation), droughts (due to heat waves and unreliable rainfall), population pressure (rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land), land tenure (insecure access to land and collectively managed communal land), poverty / wealth (very poor population)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (deforestation through overgrazing and fire wood collection), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (firewood collection), overgrazing (cattle, sheep and goats), change in temperature (Climate change: heat waves), change of seasonal rainfall (more variable onset of rain), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (more variable and intensive rains), wind storms / dust storms (frequent storms), floods (due to intensive rain storms), labour availability (some migration of men to nearby cities), education, access to knowledge and support services (high level of illiteracy)
3.8 Предотвращение и снижение деградации земель, или восстановление нарушенных земель
Укажите цель Технологии по отношению к деградации земель :
- восстановление/ реабилитация нарушенных земель
Пояснения:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Технические характеристики, мероприятия по практической реализации, вложения и стоимость
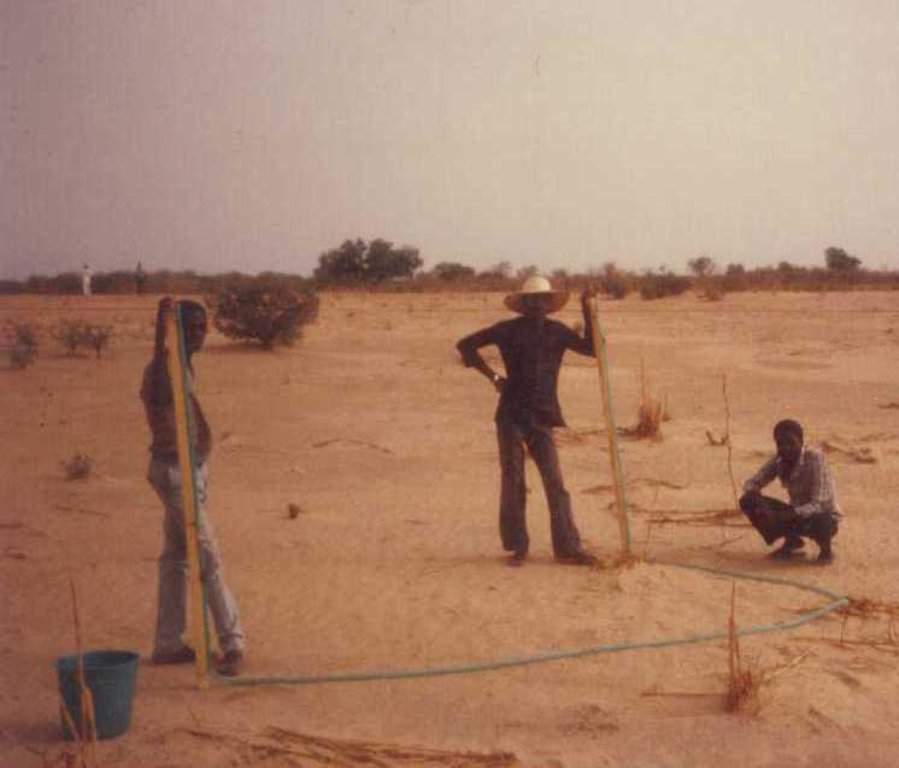
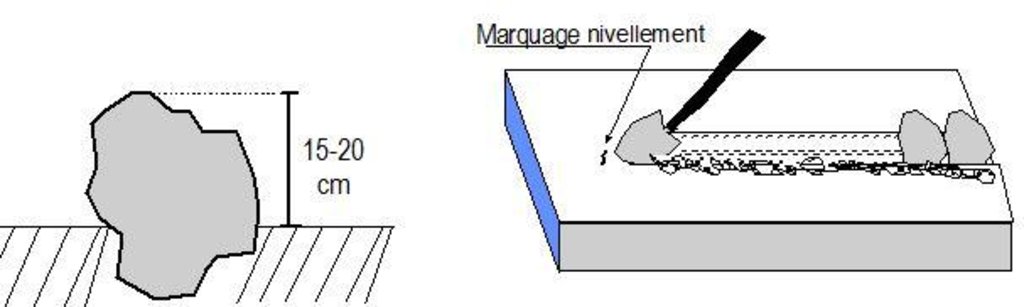
4.1 Технический рисунок, иллюстрирующий Технологию
4.2 Спецификация / пояснения к техническому рисунку
Contour stone bunds are built with quarry rock or stones in series of two or three. They are constructed in lines along the natural contour of the land after 10-15 cm of the soil has been removed from the line where they are to be built. They should be built to a height of 20-30 cm from the ground and spaced 20 to 50 m apart. The best results are achieved when contour stone bunds are used in combination with biological measures (planting of grass, trees and hedges) and the use of organic fertiliser and mulching.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, improvement of ground cover, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity)
Bund/ bank: graded
Spacing between structures (m): 20-50
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.2-0.3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.2
Material: Stone
4.3 Общая информация по необходимым вложениям и стоимости
Укажите денежные единицы, использованные для подсчета затрат:
- Доллары США
4.4 Мероприятия, необходимые для начала реализации
| Деятельность | Тип мероприятия | Сроки | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Levelling and marking out the contour lines | Инженерные | |
| 2. | collecting stones and loading them onto carts | Инженерные | |
| 3. | transporting the stones by cart | Инженерные | |
| 4. | constructing the bunds | Инженерные | |
| 5. | applying manure | Инженерные |
4.5 Вложения и затраты, необходимые для начала реализации
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Levelling and construction of bunds | ha | 1,0 | 19,32 | 19,32 | |
| Оборудование | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 1,95 | 1,95 | |
| Другие | Transport of stones | ha | 1,0 | 15,07 | 15,07 | |
| Общая стоимость запуска Технологии | 36,34 | |||||
4.6 Поддержание/ текущее обслуживание
| Деятельность | Тип мероприятия | Сроки/ повторяемость проведения | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Replacing stones dislodged by animals or water flow | Инженерные |
4.8 Наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат
Опишите наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат:
The exact cost per hectare of constructing stone bunds depends on the distance of the site from the quarry, the size of the quarry, the inclination of the terrain, which determines the spacing between the stone bunds, and the actual amount of stones transported in each lorryload. The prices below are provided as a guide.
Supply of quarry rock/stones: 24 m3 per 400 m of bund
Labour: 30 man-days per ha
• levelling and marking out the contour lines: 1 man-day
• collecting stones and loading them onto carts:
10 man-days
• transporting the stones by cart: 10 man-days
• constructing the bunds: 9 man-days
• applying manure.
Transportation by cart:
• 20 cartloads of stones
• 20 cartloads of manure (if used).
Transportation by lorry:
• 6 lorryloads (skip loader – 4.5 m3 per load).
Other costs: equipment (pickaxes, shovels, wheelbarrows, water-tube level, etc.).
5. Природные и социально-экономические условия
5.1 Климат
Среднегодовое количество осадков
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1000 мм
- 1001-1500 мм
- 1501-2000 мм
- 2001-3000 мм
- 3001-4000 мм
- > 4000 мм
Агроклиматическая зона
- полузасушливая
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Рельеф
Склоны (преобладающие):
- пологие (0-2%)
- покатые (3-5%)
- покато-крутые (6-10%)
- крутые (11-15%)
- очень крутые (16-30%)
- чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
- обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа:
- плато/ равнины
- гребни хребтов/холмов
- склоны гор
- склоны холмов
- подножья
- днища долин
Зона высотной поясности:
- 0-100 м над уровнем моря
- 101-500 м н.у.м.
- 501-1000 м н.у.м.
- 1001-1500 м н.у.м.
- 1501-2000 м н.у.м.
- 2001-2500 м н.у.м.
- 2501-3000 м н.у.м.
- 3001-4000 м н.у.м.
- > 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
Комментарии и дополнительные сведения по условиям рельефа/ топографии :
Landforms: Also footslopes and valley floors
Altitudinal zone: 200 m a.s.l.
5.3 Почвы
Средняя мощность почв:
- поверхностные (0-20 см)
- неглубокие (21-50 см)
- умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
- глубокие (81-120 см)
- очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта):
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
- тонкодисперсный/ тяжёлый (глинистый)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем горизонте:
- низкое (< 1%)
Если возможно, приложите полное описание почв или укажите доступную информацию, например тип почв, рH/ кислотность почв, ёмкость катионного обмена, содержание азота, содержание солей и т.д.
Soil texture (topsoil): Fine to medium (sandy to clayey loams)
5.4 Доступность и качество воды
Уровень грунтовых вод:
5-50 м
Доступность поверхностных вод:
средняя
Качество воды (без обработки):
исключительно для сельскохозяйственного использования (орошение)
Комментарии и дополнительная информация по качеству и количеству воды:
Ground water table: > 10 m
Availability of surface water: Surface runoff generated by limited but intense rainfalls
5.5 Биоразнообразие
Видовое разнообразие:
- низкое
5.6 Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Рыночная ориентация производства:
- натуральное хозяйство (самообеспечение)
- смешанное (самообеспечение/ товарное хозяйство
Доходы из других источников:
- 10-50% всех доходов
Относительный уровень достатка:
- очень плохой
- плохой
Уровень механизации:
- ручной труд
- тягловая сила
Пол:
- мужчины
Укажите другие важные характеристики землепользователей:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
(mostly poor households below poverty line).
Off-farm income specification: men migrate temporarily or permanently to cities for off-farm income, women and men seasonally carry out paid farm work
Market orientation of production system: Most households crop for subsistence (mainly for small agropastoralists) and surplus is sold on market (medium agropastoralists). Commercial markets: some vegetable growing and pastoralists.
Level of mechanization: Ox and donkey used for animal traction
5.7 Средний размер земельных участков, арендуемых или находящихся в собственности землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
- < 0,5 га
- 0,5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1000 га
- 1000-10000 га
- > 10000 га
Считается ли это мелким, средним или крупным хозяйством (по местным масштабам)?
- мелкое
Пояснения:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Also 1-2 ha
5.8 Собственность на землю, права на земле- и водопользование
Землевладелец:
- государственная
- общинная/ поселковая
Право землепользования:
- общинное (контролируемое)
- индивидуальное
Пояснения:
traditional land use rights prevail. On fields individual land use rights, communal rights on pasture and forest land (collection of wood and other products (fruits, medicinal plants))
Land ownership: Also individual not titled
5.9 Доступ к базовым услугам и инфраструктуре
медицинское обслуживание:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
образование:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
технические консультации:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
занятость (вне хозяйства):
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
рынки:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
электроснабжение:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
транспорт и дорожная сеть:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
водоснабжение и канализация:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
финансовые услуги:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
6. Воздействия и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Технологии УЗП в пределах территории ее применения
Социально-экономическое воздействие
Продуктивность
производство сельскозяйственных культур
производство кормов
риск потери продуктивности
Доступность и качество воды
потребность в оросительной воде
Доходы и затраты
сельскохозяйственные издержки
доходы хозяйства
Социальное и культурное воздействие
продовольственная безопасность/ самообеспечение
знания в области УЗП/ деградации земель
livelihood and human well-being
Комментарий/ пояснения:
There is evidence that 15 year old bunds still maintain their positive effects on yields. 40 % higher grain yields were measured on such bunds and there is no evidence to suggest that yields decline with time. In dry years, while unimproved land produces nothing, land protected by stone bunds can still produce a harvest. Higher crop production improves household food security in proportion to the area of a farm improved with bunds. Under the PASP in Niger, an average of 16% of the area of a farm was improved with stone bunds, resulting in an increase of between 8% and 33% in annual output with no other additional measures.
Экологическое воздействие
Водный цикл/ поверхностный сток
сбор воды/ водоудержание
поверхностный сток
Почвы
влажность почв
почвенный покров
утрата почв
круговорот/ восполнение питательных веществ
Биоразнообразие: растительность, животный мир
разнообразие флоры
Климат и снижение риска стихийных бедствий
скорость ветра
Другие экологические последствия
hazard towards adverse events
6.2 Влияние Технологии за пределами территории ее применения
отложение наносов ниже по течению
отложения, переносимые ветром
ущерб прилегающим полям
6.3 Подверженность и чувствительность Технологии УЗП к постепенным изменениям климата и экстремальным погодным явлениям/ стихийным бедствиям, связанным с изменением климата (в понимании землепользователей)
Постепенное изменение климата
Постепенное изменение климата
| Сезон | Тип изменения климата/ экстремального явления | Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| среднегодовые температуры | увеличилось | хорошо |
Экстремальные явления, связанные с изменением климата (стихийные бедствия)
Погодные стихийные бедствия
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| местные ливневые дожди | плохо |
| местные ураганы | хорошо |
Стихийные бедствия климатического характера
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| засухи | хорошо |
Гидрологические стихийные бедствия
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| регулярные наводнения (выход рек из берегов) | плохо |
Другие воздействия, связанные с изменением климата
Другие воздействия, связанные с изменением климата
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| сокращение вегетационного периода | не известно |
6.4 Анализ эффективности затрат
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с первоначальными вложениями (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
очень позитивное
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с текущими расходами по поддержанию технологии (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
очень позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
очень позитивное
6.5 Внедрение Технологии
Среди применяющих Технологию землепользователей, какова доля лиц, применяющих её по собственной инициативе, т.е. без какого-либо материального стимулирования со стороны?
- 50-90%
Пояснения:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: While in emergency programs erosion control structures are mostly implemented through cash/food for work this is not the case in natural resource programs. As concerns German Development Cooperation, cash/food for work has been used during the 80ies and 90ies to implement stone bunds. Thereafter most programs switched to a voluntary approach where only Tools and transport were provided but all labour has been provided by the beneficiaries without payment.
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The success of this measure and implementation on a wide scale depend to a large extent on whether grants are available to cover the cost of transporting the stones required to the site, good community organisation and the capacity of the community to mobilise the necessary labour, the contribution required from the farmers.
The farmers’ commitment to implementing the measure largely depends on whether they are allowed to choose the sites to be improved in their area. Forcing them to begin the improvement work upstream, as dictated by the traditional watershed development approach, has often proved counterproductive. Most communities prefer to improve individual plots first in order to achieve immediate effects on crop production and leave the treatment of forest/ rangeland areas as a second step.
6.7 Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности Технологии
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
| There is evidence that bunds that have been in place for over 15 years have positive effects on yields. Grain yields increase by more than 40% for millet up to 15 years after the bunds were established, and there is no evidence to suggest that yields decline with time. This can be explained by improved soil structure, which increases infiltration, even after the bunds are completely silted up. |
|
The lifespan of a stone bund is over 20 years. There is a progressive build-up of sediment behind the bunds, resulting in the formation of terraces. Although the capacity of the bunds to retain water declines as the sediment builds up, soil infiltration capacity increases, thanks to improved soil structure, and the slope becomes gentler thanks to the terracing effect. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Farmers can maintain water retention capacity by raising the height of the existing bunds. In some places, farmers take the stones from the original bunds when a ridge of vegetation has been established and use them to form new bunds between the old ones. |
|
The decrease in surface runoff in the treated area reduces the flow of floodwater and the amount of sediment carried by the water downstream, thereby protecting the fertile land in the valley bottoms from siltation and gully erosion. How can they be sustained / enhanced? In order to optimise the positive effects of stone bunds, it is important to ensure that they are constructed closely following the natural contour of the land and in accordance with the established technical standards. |
|
In dry years, while unimproved land produces nothing, land protected by stone bunds can still produce a harvest. How can they be sustained / enhanced? When stone bunds are used in combination with zai planting pits, sorghum yields can increase by 114-124%. When used in conjunction with the application of the right amount of organic fertiliser, sorghum yields can be doubled. |
| Higher crop production improves household food security in proportion to the area of a farm improved with bunds. Under the PASP in Niger, an average of 16% of the area of a farm was improved with stone bunds, resulting in an increase of between 8% and 33% in annual output with no other additional measures. |
6.8 Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски Технологии и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| In wet years, the bunds may cause waterlogging in some parts of the field, which can adversely affect some crops. | If this happens, farmers must open up a gap in the bunds to drain off the water. |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.3 Ссылки на материалы, доступные онлайн
Название/ описание:
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation. A contribution to adaptation and farmers resilience towards climate change in the Sahel. Published by GIZ in 2012.
Адрес в сети Интернет:
http://agriwaterpedia.info/wiki/Main_Page
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки
Нет ссылок
Модули
Нет модулей