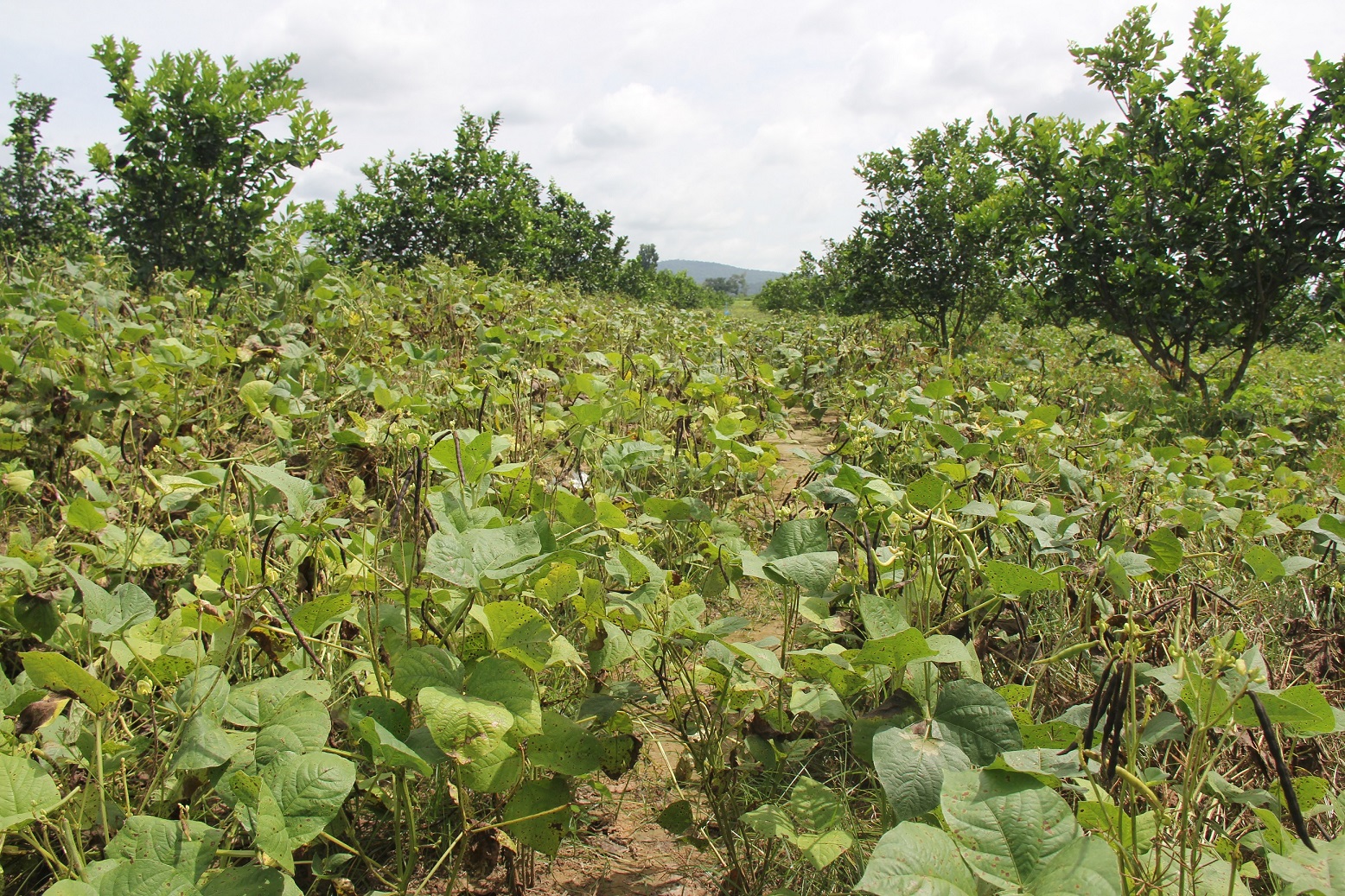
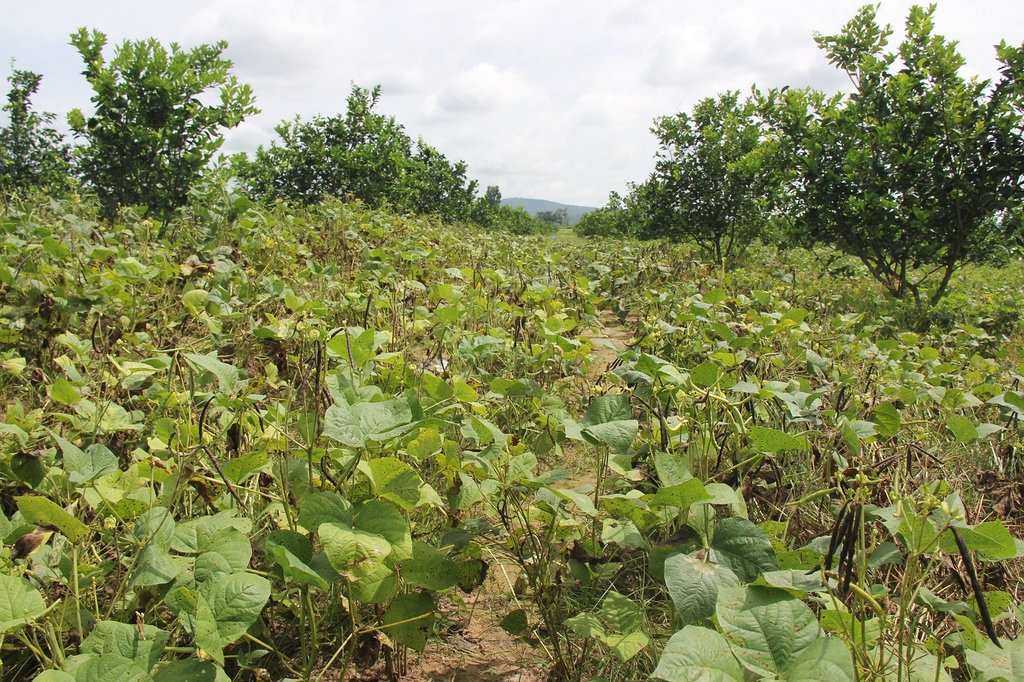
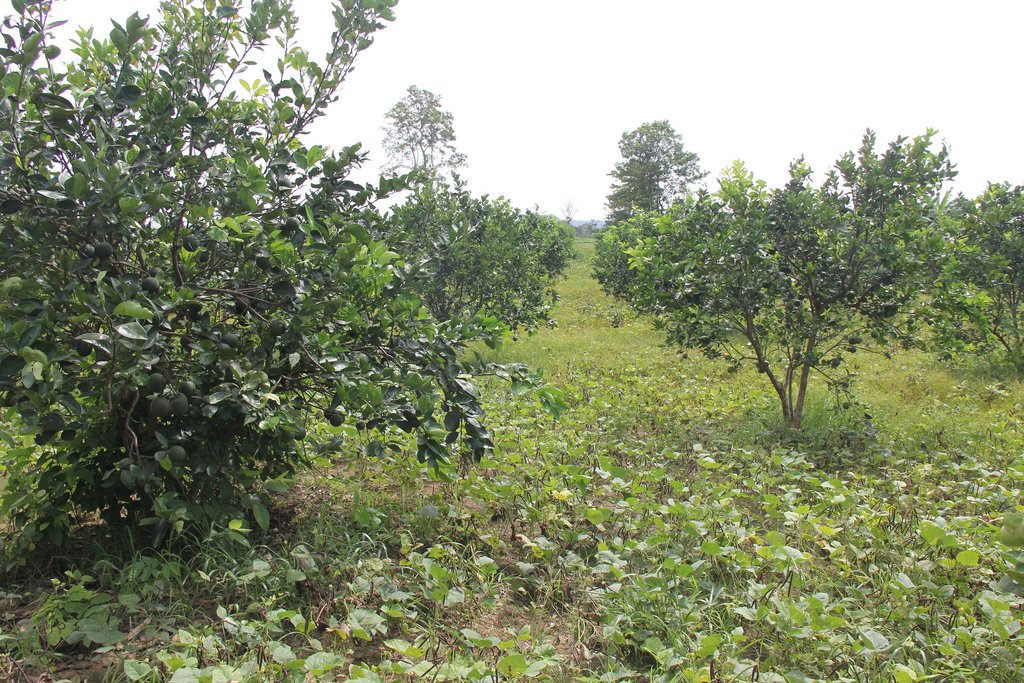
Intercropping of orange trees with mungbean in mountainous areas [Камбоджа]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Navin Chea
- Редакторы: Sophea Tim, Sok Pheak
- Рецензенты: Nimul CHUN, SO Than, Ursula Gaemperli
Intercropping
technologies_3146 - Камбоджа
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Технологии
Ответственный (-ые) специалист (-ы)
землепользователь:
Chea Sarith
(+855) 97 5734083
N/A
Land User
Ongkrong Village, Samrong Commune, Phnum Kravanh District, Pursat Province.
Камбоджа
Acting Chief of District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Phnum Kravanh:
Doung Phanny
(+855) 97 44 222 78 / (+855) 12 17 89 577
N/A
District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Phnum Kravanh.
Prey Khlong Village, Rokat Commune, Phnum Kravanh District, Pursat Province.
Камбоджа
Chief Office of Agricultural Extension at Provincial Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Pursat:
Chief of District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries , Bakan:
Agronomic Official at District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries , Kandieng:
Seng Kompheak
(+855) 96 43 52 665
N/A
District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries , Kandieng
Kandieng village, Kamdieng Commune, Kandieng District, Pursat province
Камбоджа
Название проекта, содействовавшего документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Royal University of Agriculture (RUA) - Камбоджа1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование данных, собранных ВОКАТ
Когда были собраны данные (на местах)?
04/07/2017
Составитель и ответственный(-ые) специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.4 Декларация по устойчивости описываемой Технологии
Вызывает ли описанная здесь Технология проблемы деградации земель настолько, что ее нельзя назвать природосберегающей?
Нет
2. Описание Технологии УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Технологии
Определение Технологии:
Intercropping of mungbean between orange trees improves soil fertility and generates income before the orange trees bear fruit.
2.2 Подробное описание Технологии
Описание:
Agroforestry is a farming practice that can involve growing of a mixture of woody perennials like trees, shrubs, palms, bamboos, etc. with crops and/or animals, on the same land-management units. Agroforestry systems play an important role in ecological and economical interactions between the different land use components (Lundgren and Raintree, 1982). It represents an interface between agriculture and forestry, and encompasses mixed land-use practices. Agroforestry systems are composed of three attributes:
1. Productivity (improved tree products, yields of associated crops, reduction of cropping system inputs, and increased labor use efficiency);
2. Sustainability (beneficial effects of woody perennials);
3. Adoptability (MoE/Adaptation Fund/UNEP, 2016).
In Cambodia, mungbean grows throughout the whole year almost, depending on the moisture factor. Mungbean is short maturity crop which can be grown both in sloping upland and in lowland areas. In upland areas farmers usually plant their second crop in August and harvest it in October. Mungbean is a crop that can be grown on many soil types, but grows best on alluvial, sandy, and volcanic soils which well drained containing high levels of nutrients (incl. N, P, K, Ca, Mg) and organic matter (MAFF, 2005). Mungbean crop duration depends on the variety, with short-term, medium-term and long-term being harvested between 60-65 days, 65-75 days, and 75-80 days, respectively.
Mungbean residues can make an active contribution to improvement of soil quality through nitrogen fixation and subsequent incorporation of this nitrogen into the soil after root and nodule degeneration by Rhizobium bacteria. The incorporation of the organic root material also improves the soil structure (MAFF, 2005, Chadha, 2010, IRRI-CIMMYT Alliance, 2009). The taproot of the mungbean can penetrate the soil to a depth of 50-60 centimeters. Sometimes, some land users grow mungbean as a green manure crop specifically to improve soil quality (Tauch Ung, 2010).
Mr. Chea Sarith is one example of land user who practices intercropping of orange trees with mungbean since 2013. The main purpose is to improve soil fertility, to prevent soil erosion, and to generate income before the orange trees provide fruit. In addition, it eases the weed control. After the harvest the farmer leaves the plant residues on the soil to provide organic matter. With the objective not to harm the roots of the orange trees, he avoids tilling the soil. In general, mungbean grows twice a season depending on the rainfall distribution and soil moisture.
The average yield of direct seeded mungbean as an intercrop between orange trees is about 1,200 kg/ha (harvested 3 times per crop). If mungbean is grown as a single crop the yield is usually ranges from 1,300 to 1,400 kg/ha. The market price for mungbean grain is usually about 4,500 to 5,000 Riel/kg.
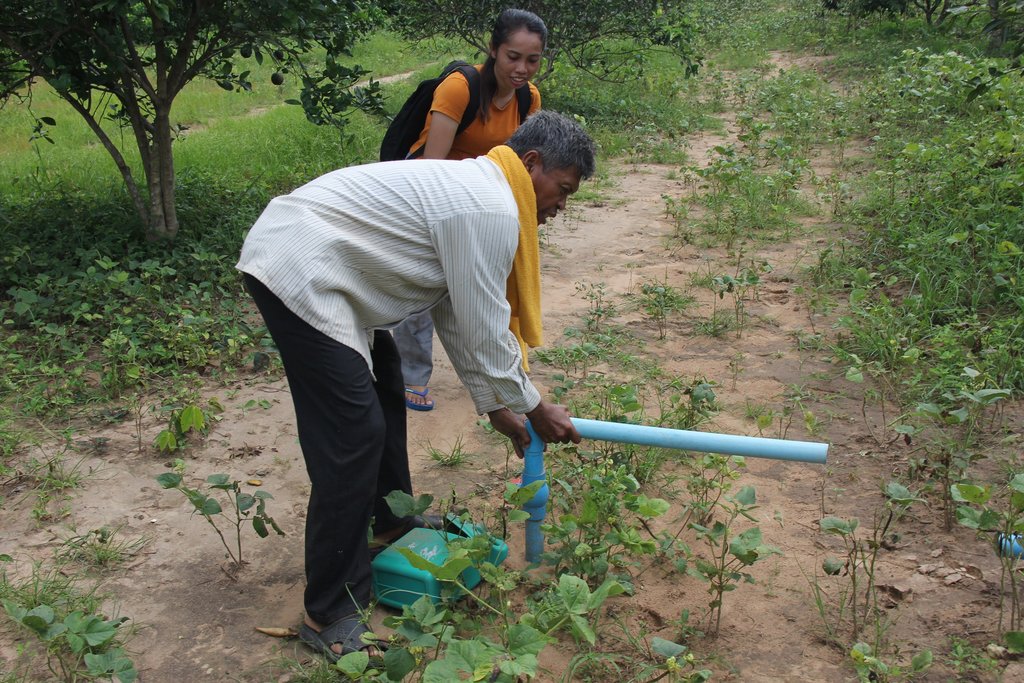
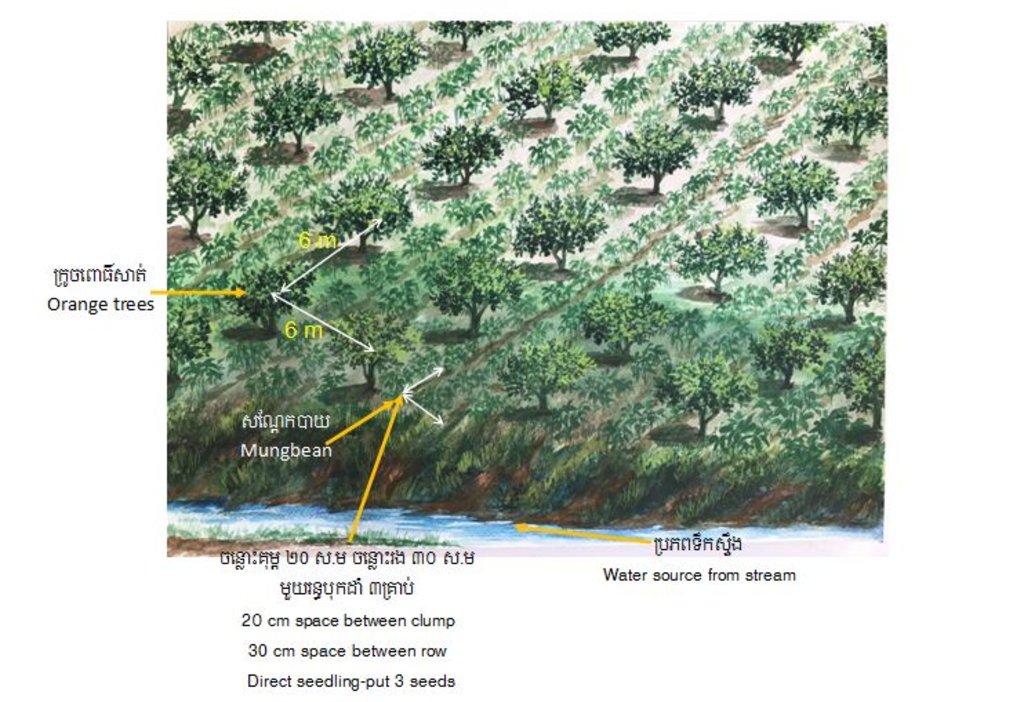
Before planting orange trees the soil requires two turns of ploughing. After first ploughing the soil should dry during 1-2 months, before it can be ploughed again by a wheel harrow. Orange trees then are planted in rows into pits of 1 m x 1 m, with a depth of 70-80 cm. The spacing between the trees, as well as between the rows is usually 6 meters. Before planting, the orange tree seedlings (bought from outside) are usually kept at the farm site for 15 to 20 days, which to allow them to adapt to the conditions of the growing environment. The farmer installed a water pipe in the underground to irrigate the fruit orchard. The nearby stream serves as water source. After the tree plantation, mungbean is sown by direct seeding on the remaining bare soil. This is done by putting 3 to 4 seeds into the seed holes (3 to 4 cm sowing depth at a plant spacing of 20 cm and a row spacing of 30 cm. After harvest the residues of the mungbean plants are squashed by machine and left to rot on the soil surface until is the next mungbean cycle starts by direct seeding.
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Технологию
2.5 Страна/ регион/ места, где применяется Технология, информация о которых собрана в данной Анкете
Страна:
Камбоджа
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Ongkrong Village, Samrong Commune, Phnum Kravanh District, Pursat Province.
Более точная привязка места:
Phnum Kravanh of Cambodia.
Map
×2.6 Сколько лет применяется данная Технология
Год начала реализации:
2013
2.7 Внедрение Технологии
Укажите, как именно Технология УЗП была внедрена:
- как инновация (инициатива) землепользователей
- в качестве научного/ полевого эксперимента
Пояснения (тип проекта и т.д.):
Through farmers experience, investigation on cropping and natural fertilizer application.
3. Классификация Технологии УЗП
3.1 Основные цели и задачи реализации Технологии
- повышение производства
- снижение или предотвращение деградации земель, восстановление нарушенных земель
- создание благоприятных экономических условий
3.2 Текущий(-ие) тип(-ы) землепользования на территории, где применяется Технология

Смешанное землепользование (пашня/ пастбища/ лес), включая агролесоводство
- Агролесоводство
Основные виды продукции/ услуг:
Orange and mungbean.
Если использование земель изменилось с началом применения Технологии, укажите тип землепользования до применения Технологии:
Degraded forest, soil from termite mound.
3.3 Дополнительная информация о землепользовании
Обеспеченность водой участков, где реализуется Технология :
- сочетание богарных и орошаемых земель
Пояснения:
There is a stream near the farm for supply the water for orange trees.
Число урожаев за год:
- 1
Поясните:
Orange trees belong to the long lifespan crop which provide fruit at the age of 4 years. The lifespan of getting fruits is approximately 20 years. Then in general, the farmer cuts the trees down and grow it again. However, it depends on the yield it provides. Mungbean can be harvested within two months and half and can be harvested 3 times per crop cycle.
3.4 Категория УЗП, к которой относится Технология
- агролесоводство
- Улучшение почвенного/ растительного покрова
3.5 Распределение Технологии по площади
Охарактеризуйте пространственное распространение Технологии :
- равномерно-однородное применение на определенной площади
Если Технология равномерно применяется на той или иной территории, укажите ее приблизительную общую площадь:
- < 0,1 км2 (10 га)
3.6 Мероприятия УЗП, выполняемые в рамках Технологии

Агрономические мероприятия
- A1: Растительный/ почвенный покров
- A3: Поверхностная обработка почв

инженерные мероприятия
- И7: Водосборное/ водопроводное/ оборудование для орошения
3.7 Основные проблемы деградации земель, на решение которых направлена Технология

ветровая эрозия почв
- Эп: утрата плодородного слоя почвы

ухудшение химических свойств почв
- Хп: Снижение плодородия и уменьшение содержания органического вещества (вызванное не эрозией, а другими причинами)

ухудшение физических свойств почв
- Фу: уплотнение

биологическая деградация
- Бр: сокращение растительного покрова
- Бф: утрата биологической составляющей почв
3.8 Предотвращение и снижение деградации земель, или восстановление нарушенных земель
Укажите цель Технологии по отношению к деградации земель :
- предотвращение деградации земель
- восстановление/ реабилитация нарушенных земель
Пояснения:
The former degraded forest soil was rehabilitated by the rotten residues of the mungbean, the deep penetration of its taproots, and by the nitrogen fixation through the symbiotic association of nitrogen fixing bacteria in the nodular roots of the mungbean. Thus, the soil structure and the soil fertility were improved little by little.
4. Технические характеристики, мероприятия по практической реализации, вложения и стоимость
4.1 Технический рисунок, иллюстрирующий Технологию
4.2 Спецификация / пояснения к техническому рисунку
The area of implementing this technology is 4 hectares with 1096 orange trees. The pit of planting orange trees is 1m x 1m, with a depth of 70-80 cm. The spacing between trees and between rows is usually 6 meters to get enough sunlight. The mungbean is planted by direct seedling by inserting 3 to 4 seeds per hole (the hole is 3-4 cm in depth). The spacing between the holes is 20 cm and the row spacing is 30 cm. The farmer of this farm also installed an irrigation system by setting up a pipe under the ground.
4.3 Общая информация по необходимым вложениям и стоимости
Уточните, как рассчитывались затраты и вложения:
- на площадь, где применяется Технология
Укажите размер и единицу площади:
4 hectares
другая/ национальная валюта (название):
KHR (Riel)
Укажите обменный курс между долларом США и местной валютой (если уместно): 1 доллар США =:
4000,0
Укажите среднюю дневную заработную плату наемных работников:
20000
4.4 Мероприятия, необходимые для начала реализации
| Деятельность | Тип мероприятия | Сроки | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clear degraded forest | Инженерные | January |
| 2. | Clear the termite mound to flatten the area | Инженерные | Dry season |
| 3. | Drying the soil by sunlight | Агрономические | Dry season |
| 4. | Buy orange trees and adapt them to the condition of the area | Агрономические | Dry season |
| 5. | Planting orange trees | Агрономические | August |
4.5 Вложения и затраты, необходимые для начала реализации
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Clear the degraded forest soil | Person-day | 80,0 | 2000,0 | 160000,0 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Collect the residue of forest and then burn | Person-day | 60,0 | 20000,0 | 1200000,0 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Clear 40 termite mounds in 4 hectares | Person-day | 48,0 | 20000,0 | 960000,0 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Hire labor to carry the soil of termite mound to put in the hole of orange tree for planting | Person-day | 180,0 | 20000,0 | 3600000,0 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Grass cutting marchine | piece | 2,0 | 1200000,0 | 2400000,0 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Two wheel tractor | piece | 1,0 | 12000000,0 | 12000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Посадочный материал | Orange seedlings | seedling | 1026,0 | 6000,0 | 6156000,0 | 100,0 |
| Строительные материалы | Pumping machine | piece | 1,0 | 1200000,0 | 1200000,0 | 100,0 |
| Строительные материалы | Irrigation system such as big tube, small tube etc | set | 1,0 | 8000000,0 | 8000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Другие | Planting orange trees | Person-day | 51,0 | 20000,0 | 1020000,0 | 100,0 |
| Другие | Pesticide sprayer machine | piece | 3,0 | 600000,0 | 1800000,0 | 100,0 |
| Другие | Spraying pesticide hand pump sprayer | piece | 1,0 | 280000,0 | 280000,0 | 100,0 |
| Общая стоимость запуска Технологии | 38776000,0 | |||||
4.6 Поддержание/ текущее обслуживание
| Деятельность | Тип мероприятия | Сроки/ повторяемость проведения | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Watering during dry season in the first year of planting orange trees | Агрономические | Two times per day during dry season |
| 2. | Spraying pesticides when there is present of insects on orange trees | Агрономические | Spray once time per season |
| 3. | Pruning some branches of orange trees | Агрономические | When the orange trees 2 years (One year cut some branches once time) |
| 4. | Apply organic fertilizer for the orange trees | Агрономические | When the orange trees are 4 years |
| 5. | Spray against weeds | Агрономические | Spray once time per half month. |
| 6. | Spray pesticides on mungbean plants | Агрономические | When mungbean flowering |
| 7. | Direct seeding of mungbean | Агрономические | August |
4.7 Стоимость поддержания/ текущего обслуживания ( в год)
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Watering the orange trees | Person-day | 11,0 | 20000,0 | 220000,0 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Pruning some branches of orange trees | Person-day | 100,0 | 20000,0 | 2000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Hire labor to spray pesticides | Person-day | 8,0 | 20000,0 | 160000,0 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Hire labor to harvest mungbean when mature | Person-day | 120,0 | 20000,0 | 2400000,0 | 100,0 |
| Посадочный материал | Mungbean seed (1 hectare need 25 kg of mungbean) seeds) | hectare | 4,0 | 312500,0 | 1250000,0 | 100,0 |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Pesticides for orange trees | bottle | 4,0 | 40000,0 | 160000,0 | 100,0 |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Chemicals for improving of stem of mungbean | package | 60,0 | 1500,0 | 90000,0 | 100,0 |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Pesticide to kill worms on mungbean | bottle | 2,0 | 40000,0 | 80000,0 | 100,0 |
| Другие | Direct seeding of mungbean | Person-day | 56,0 | 20000,0 | 1120000,0 | 100,0 |
| Общая стоимость поддержания Технологии | 7480000,0 | |||||
Пояснения:
The maintenance costs then depend on the age of orange trees. The cost calculation of maintenance of orange trees is for year period, but the the recurrent costs for mungbean cultivation is calculated only for one crop cycle (two months and half).
4.8 Наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат
Опишите наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат:
The establishment of an orange tree orachard requires a lot of money.
5. Природные и социально-экономические условия
5.1 Климат
Среднегодовое количество осадков
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1000 мм
- 1001-1500 мм
- 1501-2000 мм
- 2001-3000 мм
- 3001-4000 мм
- > 4000 мм
Укажите среднегодовое количество осадков (если известно), мм:
1225,70
Пояснения/ комментарии по осадкам:
In 2015 the annual rainfall is 1225.7 mm, in 2014 is 1128.1 and in 2013 is 1316 mm.
Укажите название соответствующей метеостанции:
Ministry of water resources and meteorology, 2015
Агроклиматическая зона
- Умеренно-влажная
5.2 Рельеф
Склоны (преобладающие):
- пологие (0-2%)
- покатые (3-5%)
- покато-крутые (6-10%)
- крутые (11-15%)
- очень крутые (16-30%)
- чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
- обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа:
- плато/ равнины
- гребни хребтов/холмов
- склоны гор
- склоны холмов
- подножья
- днища долин
Зона высотной поясности:
- 0-100 м над уровнем моря
- 101-500 м н.у.м.
- 501-1000 м н.у.м.
- 1001-1500 м н.у.м.
- 1501-2000 м н.у.м.
- 2001-2500 м н.у.м.
- 2501-3000 м н.у.м.
- 3001-4000 м н.у.м.
- > 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
Укажите, приурочено ли применение Технологии к специфическим условиям:
- не имеет значения
Комментарии и дополнительные сведения по условиям рельефа/ топографии :
On Phnum Kravanh mountain area.
5.3 Почвы
Средняя мощность почв:
- поверхностные (0-20 см)
- неглубокие (21-50 см)
- умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
- глубокие (81-120 см)
- очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта):
- грубый крупнозернистый/ лёгкий (песчаный)
Гранулометрический состав (на глубине более 20 см):
- грубый крупнозернистый/ лёгкий (песчаный)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем горизонте:
- среднее (1-3%)
Если возможно, приложите полное описание почв или укажите доступную информацию, например тип почв, рH/ кислотность почв, ёмкость катионного обмена, содержание азота, содержание солей и т.д.
PH=6
5.4 Доступность и качество воды
Уровень грунтовых вод:
5-50 м
Доступность поверхностных вод:
хорошая
Качество воды (без обработки):
питьевая вода хорошего качества
Является ли солёность воды проблемой?
Нет
Происходят ли периодические затопления территории?
Нет
5.5 Биоразнообразие
Видовое разнообразие:
- средняя
Разнообразие местообитаний:
- средняя
5.6 Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Осёдлый или кочевой:
- Осёдлый
Рыночная ориентация производства:
- товарное/ рыночное хозяйство
Доходы из других источников:
- < 10% всех доходов
Относительный уровень достатка:
- средний
Индивидуальное или коллективное хозяйство:
- частное/ домовладение
Уровень механизации:
- ручной труд
- механизировано/ есть автотранспорт
Пол:
- мужчины
Возраст землепользователей:
- средний возраст
5.7 Средний размер земельных участков, арендуемых или находящихся в собственности землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
- < 0,5 га
- 0,5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1000 га
- 1000-10000 га
- > 10000 га
Считается ли это мелким, средним или крупным хозяйством (по местным масштабам)?
- среднего размера
Пояснения:
The total crop land is 15 hectares.
5.8 Собственность на землю, права на земле- и водопользование
Землевладелец:
- индивидуальная, оформленная в собственность
Право землепользования:
- индивидуальное
Право водопользования:
- неограниченное (неконтролируемое)
Пояснения:
There is free access of water stream nearby. He never has water usage conflict.
5.9 Доступ к базовым услугам и инфраструктуре
медицинское обслуживание:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
образование:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
технические консультации:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
занятость (вне хозяйства):
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
рынки:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
электроснабжение:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
транспорт и дорожная сеть:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
водоснабжение и канализация:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
финансовые услуги:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
6. Воздействия и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Технологии УЗП в пределах территории ее применения
Социально-экономическое воздействие
Продуктивность
производство сельскозяйственных культур
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The soil fertility was improved, so that the crop production increased steadily. In addition, the farmer now doesn't grow only orange trees, but he also grows mungbean.
качество урожая
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The residues of mungbean contain many nutrients, which is suitable for getting good crop quality.
риск потери продуктивности
Комментарий/ пояснения:
As the farmer plants more than one crop on the plot now, it reduces the production failure. This means that farmer get income from mungbeans before the orange trees provide fruits. The better weed control also reduces insects, which could be harmful to the crop.
разнообразие продукции
Комментарий/ пояснения:
There are mungbean and orange trees, now.
Доходы и затраты
сельскохозяйственные издержки
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Reduced chemical fertilizers on orange trees and mungbean, because after harvesting mungbean residues are kept on the soil which is very good green manure for soil.
доходы хозяйства
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The farm income increases considerably due the intercropping system, as both mungbean and orange trees provide yield. In addition, mungbeans provide yield two times per year. Last but not least , mungbean play a key role as green manure which reduces the input of chemical fertilizers and therefore cost.
объем работ
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The mungbean and orange tree cultivation does not consume much of labor force because he doesn't have to spend a lot of time for weeding (as instead of weed mungbeans cover the soil now). On the other hand, the farmer mentioned that the orange plantation is time consuming at the beginning, when the orange trees has to be planted. As well the mungbean need more time at the moment when the plot has to be prepared for first direct seedling. But the technology as a whole entails not a lot of maintenance workload as he uses machinery such as pesticide sprayer machine and mungbean squash machine to facilitate the labor.
Социальное и культурное воздействие
продовольственная безопасность/ самообеспечение
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The diversification of the crops (oranges and mungbean) has considerably raised the income and therefore strongly prevent food insecurity situations.
состояние здоровья
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The reduction of chemical fertilizer and pesticides provides safer products that improves the health situation. In addition, mungbean and orange fruit deliver many nutrition benefits to human health.
местное самоуправление
Комментарий/ пояснения:
He has joined the orange trees community to sell the orange fruits. Many researches are convinced of his success and the tastiness of his oranges; as for example researchers from the District Office of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Phnum Kravanh, Provincial Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Pursat etc.”
знания в области УЗП/ деградации земель
Комментарий/ пояснения:
By doing the farmer learned that degraded soil can be rehabilitated by the mean of mungbean residues acting as green manure. And from the moment the soil is rehabilitated he can see that this green manure prevents soil degradation at high degree.
Экологическое воздействие
Почвы
влажность почв
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Mungbean and orange trees keep the soil moisture, prevent the evaporation to the atmosphere.
почвенный покров
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Orange trees and mainly the mungbean intercrop cover the soil almost entirely all year around.
уплотнение почв
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The residue of mungbean reduce soil compact by improving the soil structure through providing organic matter to the soil. The increased amount of soil organisms make the sol less compact.
почвенное / подземное органическое вещество/ углерод
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The residues of mungbean left on the soil after harvesting are transformed to organic matter by the process of decay and therefore contribute essentially to increased soil organic matter.
Биоразнообразие: растительность, животный мир
Растительный покров
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Orange trees and mungbeans are the vegetation cover to avoid bare land, so the sunlight will not come directly to the the soil.
разнообразие флоры
Комментарий/ пояснения:
There is more than one crop (orange trees and mungbean).
полезные виды
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Now, the soil is somewhat richer in termites, ants, earthworms, crickets ect.
разнообразие местообитаний
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Orange trees and mungbean cultivation promote soil organisms in the habitat.
6.3 Подверженность и чувствительность Технологии УЗП к постепенным изменениям климата и экстремальным погодным явлениям/ стихийным бедствиям, связанным с изменением климата (в понимании землепользователей)
Постепенное изменение климата
Постепенное изменение климата
| Сезон | Тип изменения климата/ экстремального явления | Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| среднегодовые температуры | увеличилось | хорошо | |
| сезонные температуры | сезон дождей/ влажный сезон | увеличилось | умеренно |
| сезонные температуры | сухой сезон | увеличилось | хорошо |
| среднегодовое количество осадков | увеличилось | умеренно | |
| сезонное количество осадков | сезон дождей/ влажный сезон | увеличилось | умеренно |
Пояснения:
Change in rainfall. If there is too much rain, the soil will be saturated and the root will be spoiled what reduces the yield of mungbean.
6.4 Анализ эффективности затрат
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с первоначальными вложениями (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с текущими расходами по поддержанию технологии (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
очень позитивное
Пояснения:
When the orange trees grow bigger, it will provide very high income.
6.5 Внедрение Технологии
- 1-10%
Среди применяющих Технологию землепользователей, какова доля лиц, применяющих её по собственной инициативе, т.е. без какого-либо материального стимулирования со стороны?
- 90-100%
6.6 Адаптация
Была ли Технология УЗП изменена в недавнее время с целью адаптации к меняющимся условиям среды?
Нет
6.7 Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности Технологии
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
| Get income from the mungbean before orange trees provide fruit as a potential source of income. |
| The residues from the mungbean plants help to improve soil fertility. |
| The potential market of orange tree fruits is good, with traders buying directly from producers at the farm. |
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
| Residues of mungbean improve soil fertility, reduce soil degradation and help rehabilitate the degraded land. |
| In the initial 3 to 4 years of growth of orange trees it is important to grow short term crops like mungbean to provide an income source. |
6.8 Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски Технологии и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению землепользователей | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Orange trees require a lot of water. | Grow near a water source such as a stream or river, or dig ponds to hold water. Land users need to consider a potential water source. |
| When the soils become saturated due to excessive rain, the mungbean plant roots can degenerate and result in low grain yields and low grain price (due to poor grain quality). | There is little that farmers can do to improve the performance of the mung bean crop in conditions of soil moisture saturation. |
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| As the orange trees grow bigger there is reduced opportunity for intercropping with mungbean. | Grow intercrops that do not require much sunlight, such as ginger or galanga |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/ источники информации
- выезды на места, полевые обследования
One place
- опросы землепользователей
one person.
- опросы специалистов/экспертов по УЗП
4 persons
- данные, собранные из отчетов и достоверных документов
7.2 Ссылки на опубликованные материалы
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Chadha, M. L. (2010). Short Duration Mungbean : A New Success in South Asia.
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
N/A
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
MoE/Adaptation Fund/UNEP. (2016). Forest Restoration and Rehabilitation “ Enhancing Climate Change Resilience of Rural Communities Living in Protected Areas in Cambodia .”
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
Ministry of Environment(MoE). Free of charge.
7.3 Ссылки на материалы, доступные онлайн
Название/ описание:
MAFF. (2005). Mung bean.
Адрес в сети Интернет:
Retrieved November 12, 2017, from http://www.maff.gov.kh/agri-tech/56-ដំណាំឧស្សាហកម្ម/ការដាំដុះសណ្តែក/1519-ដំណាំសណ្តែកបាយ.html
Название/ описание:
Tauch Ung. (2010). Overiew of mung bean.
Адрес в сети Интернет:
Retrieved November 12, 2017, from https://drive.google.com/file/d/0BwhP4tVirBPsOTM3OWFiMzktZTdmNi00NjMyLTg1NjktMzFhYzhmMzUyMjVl/view?hl=en
Название/ описание:
IRRI‐CIMMYT Alliance. (2009).The importance of legumes in cereal cropping systems.
Адрес в сети Интернет:
Retrieved November 12, 2017, from http://www.knowledgebank.irri.org/images/pdfs/the_importance_of_legumes_in_cereal_cropping_systems.pdf
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки
Нет ссылок
Модули
Нет модулей