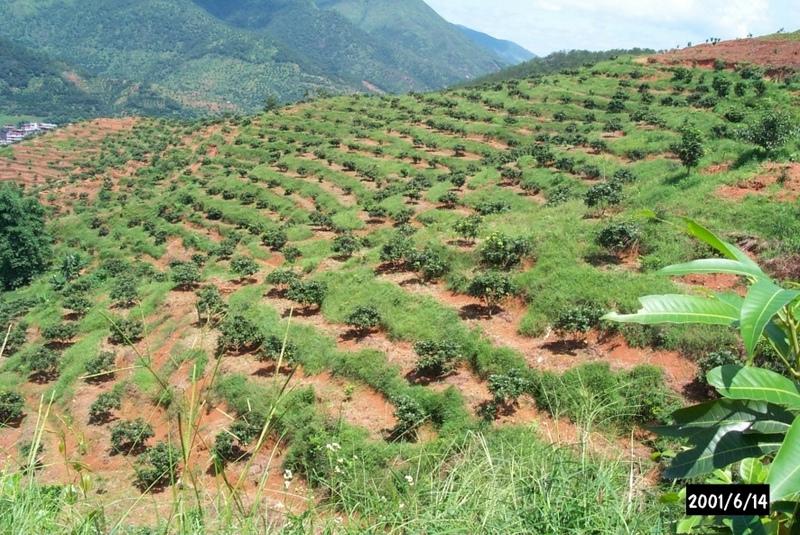
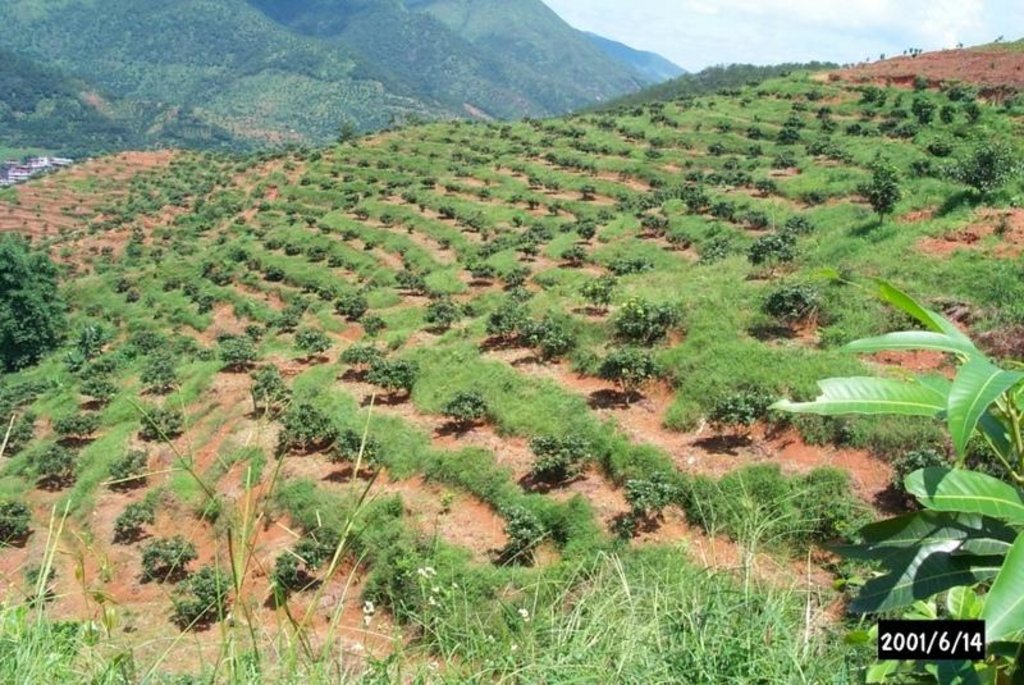
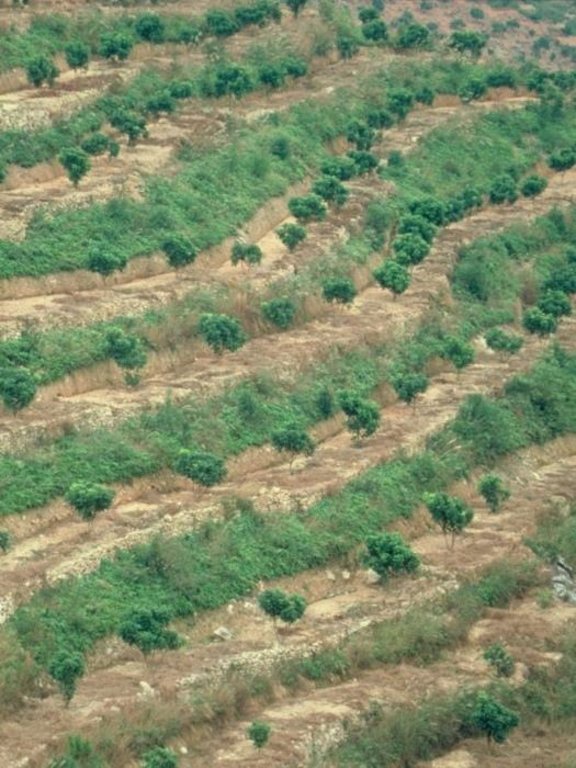
Orchard terraces with bahia grass cover [Китай]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Zhanguo Bai
- Редактор: –
- Рецензенты: David Streiff, Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Bahia grass interplanted in orchard
technologies_1106 - Китай
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Технологии
Ответственный (-ые) специалист (-ы)
Специалист по УЗП:
Liu Zhengming
Soil Conservation Office of Yongchun County
Китай
Специалист по УЗП:
Nie Bijuan
Fujian Soil and Water Conservation Experimental Station
Китай
Специалист по УЗП:
Yang Xuezhen
Fujian Soil and Water Conservation Experimental Station
Китай
Специалист по УЗП:
Название проекта, содействовавшего документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
ISRIC World Soil Information (ISRIC World Soil Information) - НидерландыНазвание организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Soil Conservation Office of Yongchun (SCOY) - КитайНазвание организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Fujian Soil and Water Conservation Office (Fujian Soil and Water Conservation Office) - Китай1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование данных, собранных ВОКАТ
Составитель и ответственный(-ые) специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
2. Описание Технологии УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Технологии
Определение Технологии:
Rehabilitation of degraded hillsides through the establishment of fruit trees on slope-separated orchard terraces, with bahia grass planted as protective groundcover.
2.2 Подробное описание Технологии
Описание:
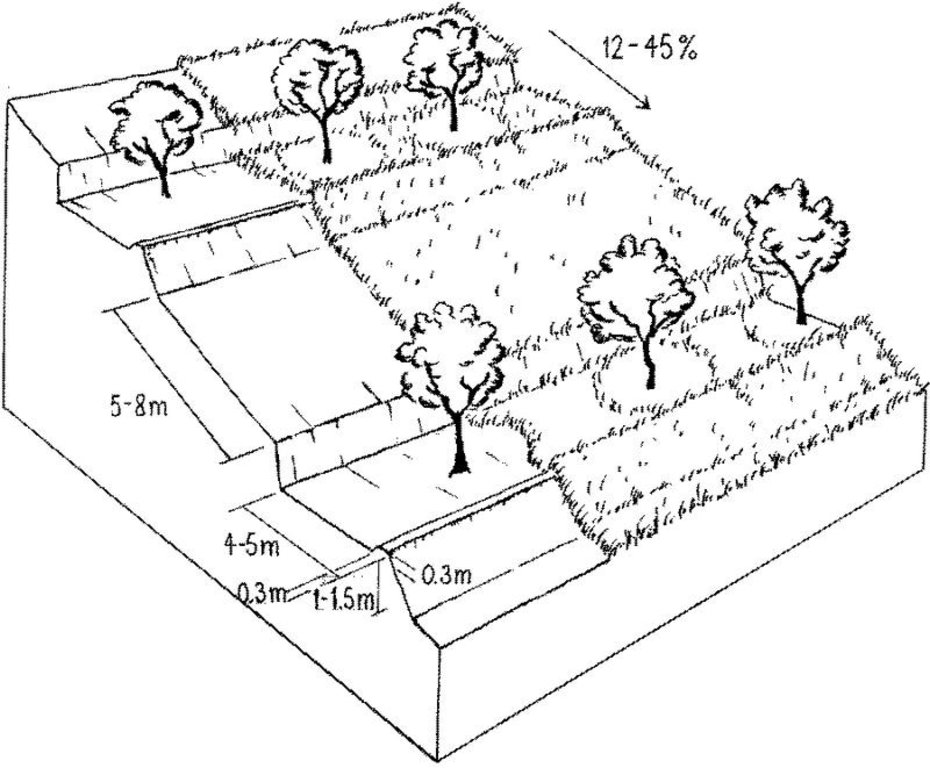
In this case study orchards were established between 1991 and 1992 on degraded and unproductive hillsides (wasteland), with slopes of 12-45%. This was achieved by constructing level beds on the contour, mainly as continuous slope-separated orchard terraces, but in some cases as individual planting platforms. Terrace construction was generally undertaken by hand using hoes and shovels.
Purpose of the Technology: A typical terrace has a 4-5 m wide bed and a 1.0-1.5 m high riser. Commonly, a raised earth lip (0.3 m high) is constructed on the terrace edge to retain rainwater. The terrace riser walls are not protected. Even before terrace construction there was little topsoil and in some places the upper subsoil had been lost to erosion. The establishment of fruit trees (lychee, Litchi chinensis and longan, Dimocarpus longan) therefore required deep planting holes (1 m3), filled with organic matter/manure, into which seedlings were planted. In subsequent years additional large quantities of organic matter/manure were applied in circular trenches to the side of the trees, succeeding trenches being gradually further away as the trees grew. Bahia grass (Paspalum notatum) was planted for SWC purposes as a cover crop, to stabilise terrace risers and to improve soil fertility. It has not been used for fodder in this case. The germination rate of bahia grass seeds is comparatively low; therefore instead of direct seeding, nurseries were established to produce seedlings. The bahia grass seedlings were transplanted onto the terrace risers and beds (leaving a space around each fruit tree) and on the hillside slopes between the terraces. The grass grew and spread quickly, restoring a protective vegetative cover following terrace construction.
Natural / human environment: The primary overall purpose of the technology was to rehabilitate degraded hillsides through the planting of economically valuable fruit trees. Terracing reduces soil erosion while retaining most of the rainwater. The application of organic matter creates improved rooting conditions, while restoring and maintaining soil fertility. The bahia grass further provides protective groundcover preventing splash erosion, increasing surface roughness, and thereby slowing down runoff velocity, while contributing to the restoration of the soil’s biological, chemical and physical properties. Irrigation ditches dug along the terraces help to reduce erosion further. This project was planned by SWC specialists: around 6,000 families were allocated orchard plots and provided with seedlings at a subsidised price.
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Технологию
2.5 Страна/ регион/ места, где применяется Технология, информация о которых собрана в данной Анкете
Страна:
Китай
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Fujian Province
Более точная привязка места:
Yongchun County
Охарактеризуйте пространственное распространение Технологии :
- равномерно-однородное применение на определенной площади
Если технология равномерно занимает территорию, укажите площадь покрытия (в км2):
55,0
Если точная область неизвестна, укажите приблизительную площадь:
- 10-100 км2
Пояснения:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 55 km2.
This is a part of the comprehensive development of Shan Huxi small watershed.
Map
×2.6 Сколько лет применяется данная Технология
Если год начала применения Технологии достоверно неизвестен, дайте примерную оценку:
- менее 10 лет назад (недавняя)
2.7 Внедрение Технологии
Укажите, как именно Технология УЗП была внедрена:
- через проекты/ внешнее вмешательство
Пояснения (тип проекта и т.д.):
The technology comes from the soil conservation theory books and accumulated experiences over years.
3. Классификация Технологии УЗП
3.1 Основные цели и задачи реализации Технологии
- снижение или предотвращение деградации земель, восстановление нарушенных земель
3.2 Текущий(-ие) тип(-ы) землепользования на территории, где применяется Технология
Комбинированное землепользование в пределах одной и той же земельной единицы:
Да
Укажите сочетания типов землепользования (посевы / пастбища / деревья):
- Агролесоводство

Пахотные угодья и плантации
- Однолетние культуры
- Древесные и кустарниковые культуры
Ежегодный урожай - Уточните культуры:
- кормовые культуры - травы
Древесные и кустарниковые культуры - Уточните культуры:
- косточковые плоды (персик, абрикос, вишня, слива и т. д.)
Поясните:
Longest growing period in days: 365Longest growing period from month to month: May - Sep

Леса/ лесистая местность
Продукции и услуги:
- Древесина
- Плоды и орехи
- Природоохранные/ защитные
Пояснения:
Crop: bahia grass
Tree and shrub cropping: lychee, Litchi chinensis and longan, Dimocarpus longan
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Degraded and unproductive hillside slopes (wasteland), with low and declining soil fertility, subject to severe soil erosion
(sheet, rill, gully and mass movement) during periods of heavy and prolonged rainfall.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low fruit yield and little income after consideration of input.
Problems / comments regarding forest use: The farmers\' consciousness of soil conservation are gradually improved and their ability of forest protection are also increased.
Forest products and services: timber, fruits and nuts, nature conservation / protection
Constraints of wasteland (before SWC)
Forest/ woodlands: Also nature conservation / protection
3.4 Водоснабжение
Обеспеченность водой участков, где реализуется Технология :
- сочетание богарных и орошаемых земель
3.5 Категория УЗП, к которой относится Технология
- Улучшение почвенного/ растительного покрова
- hillside stabilizing and restoration
3.6 Мероприятия УЗП, выполняемые в рамках Технологии

Агрономические мероприятия
- А7: Другие

Мероприятия с использованием растительности
- Р5: Другие

инженерные мероприятия
- И1: Террасирование
Пояснения:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, structural measures
Secondary measures: management measures
3.7 Основные проблемы деградации земель, на решение которых направлена Технология

водная эрозия почв
- ВЭп: поверхностная эрозия/смыв верхних почвенных горизонтов
- ВЭл: овражная эрозия / оврагообразование
- ВЭо: гравитационное перемещение горных пород / оползни

ухудшение химических свойств почв
- Хп: Снижение плодородия и уменьшение содержания органического вещества (вызванное не эрозией, а другими причинами)
Пояснения:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wm: mass movements / landslides, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), land tenure (land subdivision)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes), poverty / wealth (lack of captial), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
3.8 Предотвращение и снижение деградации земель, или восстановление нарушенных земель
Укажите цель Технологии по отношению к деградации земель :
- снижение деградации земель
Пояснения:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Технические характеристики, мероприятия по практической реализации, вложения и стоимость
4.1 Технический рисунок, иллюстрирующий Технологию
Спецификация (пояснения к техническому рисунку):
Fruit trees on slope-separated terraces with a spacing of 5-8 metres between (dependent on slope). Terrace risers and beds are protected by the fast spreading bahia grass (right): note a grass-free space is maintained around each tree.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, reduction of slope angle, improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in soil fertility, control of dispersed runoff
Secondary technical functions: increase of surface roughness, increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of soil structure
Agronomic measure: organic matter application
Vegetative measure: aligned trees
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: dispersed grass
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Fruit trees / shrubs species: longan, lychee
Grass species: bahia
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 16.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 12.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 9.00%
Terrace: forward sloping
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1-1.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 4-5
Construction material (earth): Using earth for the construction can reduce investment.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 25%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 20%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 6%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:20
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Other type of management: Changing land use patterns - Mountain and hilly areas closure for recover of the forest and grass.
Автор:
Mats Gurtner
4.2 Общая информация по необходимым вложениям и стоимости
Укажите денежные единицы, использованные для подсчета затрат:
- Доллары США
Укажите среднюю дневную заработную плату наемных работников:
3.00
4.3 Мероприятия, необходимые для начала реализации
| Деятельность | Время (сессия) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 2.On each terrace one line of fruit trees was established. Deep planting | winter of 1991 |
| 2. | 2.Fruit tree seedlings were planted. Spacing between trees was | spring of 1992 |
| 3. | 3.Bahia grass was transplanted onto the terraced hillside | spring of 1992 |
| 4. | Terraces were constructed by hand.Soil was excavated from the upper portion of the terrace and used to build up the lower portion behind the terrace riser wall to create a level platform (bed). Part of the excavated soil was used to build a terrace lip. | winter of 1991 |
| 5. | land preparation for the grass planting | winter of 1991 |
| 6. | hill closure | Nov. 1999 |
4.4 Вложения и затраты, необходимые для начала реализации
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Voluntary and paid | ha | 1,0 | 840,0 | 840,0 | 100,0 |
| Посадочный материал | Bahia transplants | ha | 1,0 | 435,0 | 435,0 | |
| Посадочный материал | Fruit tree seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 350,0 | 350,0 | 60,0 |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 145,0 | 145,0 | 100,0 |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 70,0 | 70,0 | 100,0 |
| Общая стоимость запуска Технологии | 1840,0 | |||||
| Общие затраты на создание Технологии в долларах США | 1840,0 | |||||
Если землепользователем оплачено менее 100% затрат, укажите, кем покрывались остальные затраты:
NA
Пояснения:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.5 Поддержание/ текущее обслуживание
| Деятельность | Сроки/ повторяемость проведения | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 2.Digging trenches by the side of the fruit trees and filling with organic | |
| 2. | prune, fertilize, pest control for the fruit trees of Longan and Litchi | spring, autumn and winter /3 times/year |
| 3. | grass plantation, fertilizaion | spring and summer /3 times/year |
| 4. | Filling any gaps in the bahia grass. | |
| 5. | In the first 1–2 years maintenance also involves replacing any fruit tree | |
| 6. | Weeding around the trees. | |
| 7. | Repairing terraces damaged by storms. | after raining season/4 times/year |
| 8. | regular inspection and management | Jan. 1991 / 6 times/year |
4.6 Стоимость поддержания/ текущего обслуживания ( в год)
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Voluntary and paid | ha | 1,0 | 144,0 | 144,0 | 100,0 |
| Посадочный материал | Bahia transplants | ha | 1,0 | 58,0 | 58,0 | 100,0 |
| Посадочный материал | Fruit tree seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 36,0 | 36,0 | 100,0 |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 84,0 | 84,0 | 100,0 |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | biocides | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 44,0 | 44,0 | 100,0 |
| Общая стоимость поддержания Технологии | 376,0 | |||||
| Общие затраты на поддержание Технологии в долларах США | 376,0 | |||||
Если землепользователем оплачено менее 100% затрат, укажите, кем покрывались остальные затраты:
NA
Пояснения:
Machinery/ tools: hoe, shovel
For establishment: 200 person days for terrace construction, 100 for digging pits and planting trees, 50 for transplanting
bahia grass. For maintenance: 15 person days for terrace maintenance, 40 for digging organic matter trenches, 5 for
bahia grass gap filling. The SWC department produces bahia transplants in nurseries; these are then distributed to the
farmers.
4.7 Наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат
Опишите наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат:
steep slope and lots of civil work.
5. Природные и социально-экономические условия
5.1 Климат
Среднегодовое количество осадков
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1000 мм
- 1001-1500 мм
- 1501-2000 мм
- 2001-3000 мм
- 3001-4000 мм
- > 4000 мм
Агроклиматическая зона
- влажная
5.2 Рельеф
Склоны (преобладающие):
- пологие (0-2%)
- покатые (3-5%)
- покато-крутые (6-10%)
- крутые (11-15%)
- очень крутые (16-30%)
- чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
- обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа:
- плато/ равнины
- гребни хребтов/холмов
- склоны гор
- склоны холмов
- подножья
- днища долин
Зона высотной поясности:
- 0-100 м над уровнем моря
- 101-500 м н.у.м.
- 501-1000 м н.у.м.
- 1001-1500 м н.у.м.
- 1501-2000 м н.у.м.
- 2001-2500 м н.у.м.
- 2501-3000 м н.у.м.
- 3001-4000 м н.у.м.
- > 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
Укажите, приурочено ли применение Технологии к специфическим условиям:
- не имеет значения
5.3 Почвы
Средняя мощность почв:
- поверхностные (0-20 см)
- неглубокие (21-50 см)
- умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
- глубокие (81-120 см)
- очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта):
- грубый крупнозернистый/ лёгкий (песчаный)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем горизонте:
- среднее (1-3%)
- низкое (< 1%)
5.6 Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Рыночная ориентация производства:
- товарное/ рыночное хозяйство
Доходы из других источников:
- 10-50% всех доходов
Относительный уровень достатка:
- средний
- обеспеченный
Уровень механизации:
- ручной труд
- тягловая сила
Укажите другие важные характеристики землепользователей:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land.
40% of the land users are rich and own 35% of the land.
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 45% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: off-farm income is mainly from factory labour
5.7 Средняя площадь земель, используемых землепользователями с применением Технологии
- < 0,5 га
- 0,5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1000 га
- 1000-10000 га
- > 10000 га
5.8 Собственность на землю, права на земле- и водопользование
Землевладелец:
- государственная
Право землепользования:
- аренда
6. Воздействия и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Технологии УЗП в пределах территории ее применения
Социально-экономическое воздействие
Продуктивность
производство сельскозяйственных культур
Доходы и затраты
доходы хозяйства
объем работ
Другое социально-экономическое воздействие
input constraints
Комментарий/ пояснения:
organic matter/manure
Социальное и культурное воздействие
местное самоуправление
институты госуправления
смягчение конфликтов
Экологическое воздействие
Водный цикл/ поверхностный сток
сбор воды/ водоудержание
Комментарий/ пояснения:
rainwater retention
поверхностный сток
Количество до применения УЗП :
70
Количество после применения УЗП:
35
Почвы
влажность почв
почвенный покров
утрата почв
Количество до применения УЗП :
24.3
Количество после применения УЗП:
3
почвенное / подземное органическое вещество/ углерод
Другие экологические последствия
erosion due to raindrop splash
competition between fruit trees and bahia grass
6.2 Влияние Технологии за пределами территории ее применения
надежность и постоянство водотоков
подтопление ниже по течению
отложение наносов ниже по течению
6.4 Анализ эффективности затрат
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с первоначальными вложениями (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
слабо позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
очень позитивное
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с текущими расходами по поддержанию технологии (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
слабо позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
очень позитивное
6.5 Внедрение Технологии
- > 50%
Если возможно, дайте количественную характеристику (число домохозяйств и/или площадь применения):
6593 Households (56 percent of the area)
Среди применяющих Технологию землепользователей, какова доля лиц, применяющих её по собственной инициативе, т.е. без какого-либо материального стимулирования со стороны?
- 11-50%
Пояснения:
88% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
5755 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
12% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
784 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is a slow spontaneous adoption of the technology, based on the fact that bahia grass is remarkably helpful in controlling soil erosion.
6.7 Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности Технологии
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
|
An increase in vegetative cover reduces erosion, improves the ecological environment, increases soil fertility and organic matter content, improves How can they be sustained / enhanced? Control weeds and fertilize well. |
|
The combination of structural and vegetative measures has a quick impact on reducing soil erosion and preventing mass movement on hillside slopes How can they be sustained / enhanced? ncrease the vegetative cover and improve soil properties through the addition of plenty of organic matter/manure. |
|
Improved land management practices bringing back degraded wasteland sites into economic production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Demonstration and extension while also improving the enabling legislative environment. |
| Editors’ comments: In China, large areas of degraded hillsides have been brought back into production by constructing terraces on which fruit trees are planted. In this example the technology has been further improved through planting of bahia grass, as a groundcover, to restore the structure and increase the soil organic matter. On a much smaller scale a case of degraded land conversion is presented from Tajikistan. |
6.8 Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски Технологии и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Orchard development can extend too far up the slope, onto steep mountain sides | Reserve the upper slopes for forest, and restrict orchards to the lower slopes. |
| Potential competition for water and nutrients between the bahia grass | Clean weed (bahia grass included) in the area immediately around the fruit tree. |
| Increase in farm income becomes very positive only after fruit trees start | Consider replacing bahia grass with a more palatable perennial fodder plant to improve farm income in the short term. |
| Low germination rate of bahia seeds | Expand experimental studies (seed treatments, cuttings, taking splits, etc). |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/ источники информации
7.2 Ссылки на опубликованные материалы
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Acceptance Materials of Shan Huxi Small Watershed.. 2001.
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
Soil Conservation Office of Yongchun County
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки
Нет ссылок
Модули
Нет модулей