Integrated Farming System [Индия]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Srikanta Kumar Parida
- Редактор: –
- Рецензенты: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1085 - Индия
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Технологии
Специалист по УЗП:
Pradhan Gandhi
Индия
Специалист по УЗП:
Pradhan Damodar
Индия
Специалист по УЗП:
Panda R.K
Central Soil & Water Conservation Research & Training Institute
Индия
Специалист по УЗП:
Mohanty B.B
Sarvodaya Samiti
Индия
Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Sarvodaya Samiti - Индия1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование данных, собранных ВОКАТ
Составитель и ответственный(-ые) специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.5 Ссылка на Анкету (ы) по Подходам УЗП (документируется с использованием ВОКАТ)

PARTICIPATORY APPROACH IN IDCWDP, DANIDA [Индия]
Participatory approach for holistic and intigrated development of the defined area on watershed basis involving all level of stake holders.
- Составитель: Srikanta Kumar Parida
2. Описание Технологии УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Технологии
Определение Технологии:
Growing of crops for food, fodder trees and fibre forest in a compact patch.
2.2 Подробное описание Технологии
Описание:
This technology has mainly to be applied on 5 Ha.of private waste land of poor farmers to increase production. This technology focuses on life fencing, planting of trees for both timber and food varieties, land development, water availability and green manuring. Three line bamboo plantation has been done by laying method at all along the boundary line. Agave also planted at boundary line to give additional protection. Then proper compartmentation has been done keeping intact the total area of individual land holders. Here 'V' ditches has been provided accross the slope of total land. Some fruit and fodder, forest trees were planted all along the bunds and inside the field. The density of tree plantation at crop field is less. So as to facilitate crop cultivation. Gullies has also been arrested by construction of gully control structures. One waterhole has been excavated for life saving irrigation. To manage field waste and to get green manure three compost pits also established.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: After several meeting and interaction with village people, this technology has been established. All the land users where technology is applied were fully engaged for every construction work. So as to have a clear understaing of each small intervention. As this technology uses locally available materials, its maintenance by land users become easy.
Natural / human environment: Here Soil & Water Conservation has been given importance, hence more vegetative cover has been noticed in and around technology area. Increase of soil fertility has also been noticed. Complete barren land conveted in to crop land. So the technology has positive impact on the environment undoubtedly.
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Технологию
2.5 Страна/ регион/ места, где применяется Технология, информация о которых собрана в данной Анкете
Страна:
Индия
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Orissa
Более точная привязка места:
Orissa
Охарактеризуйте пространственное распространение Технологии :
- равномерно-однородное применение на определенной площади
Если технология равномерно занимает территорию, укажите площадь покрытия (в км2):
0,05
Если точная область неизвестна, укажите приблизительную площадь:
- < 0,1 км2 (10 га)
Пояснения:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.05 km2.
Map
×2.6 Сколько лет применяется данная Технология
Если год начала применения Технологии достоверно неизвестен, дайте примерную оценку:
- менее 10 лет назад (недавняя)
2.7 Внедрение Технологии
Укажите, как именно Технология УЗП была внедрена:
- через проекты/ внешнее вмешательство
Пояснения (тип проекта и т.д.):
Project SWC Specialist utilizing the earlier experience in the project and other area.
3. Классификация Технологии УЗП
3.1 Основные цели и задачи реализации Технологии
- повышение производства
- снижение или предотвращение деградации земель, восстановление нарушенных земель
3.2 Текущий(-ие) тип(-ы) землепользования на территории, где применяется Технология
Комбинированное землепользование в пределах одной и той же земельной единицы:
Да

Пахотные угодья и плантации
- Многолетние (недревесные) культуры
- Древесные и кустарниковые культуры
Многолетние (недревесные) культуры - Уточните культуры:
- агава / сизаль

Леса/ лесистая местность
- Лесопосадки, облесение
Лесопосадки. облесение: Укажите происхождение и состав видов:
- Монокультуры местных видов деревьев
Вид деревьев:
- Бамбук

Непродуктивные земли
Поясните:
Wastelands, deserts, glaciers, swamps, recreation areas, etc
Пояснения:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Due to slope and lack of vegetation cover, majority top soil were lost and many gullies also formed as a result there was no scope for cultivation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The soil was hard, no fertility, land is slopy. So there was no scope for any kind of cultivation in the same patch of land.
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps: Slope, Soil loss
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct
3.5 Категория УЗП, к которой относится Технология
- мероприятия по влагозадержанию и снижению эрозии почв на склонах
- сбор атмосферных осадков
- Управление орошением (включая водоснабжение и дренаж)
3.6 Мероприятия УЗП, выполняемые в рамках Технологии

инженерные мероприятия
Пояснения:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour, aligned: -graded strips *<sup>3</sup>, aligned: -against wind
3.7 Основные проблемы деградации земель, на решение которых направлена Технология

водная эрозия почв
- ВЭп: поверхностная эрозия/смыв верхних почвенных горизонтов
- ВЭл: овражная эрозия / оврагообразование

ухудшение химических свойств почв
- Хп: Снижение плодородия и уменьшение содержания органического вещества (вызванное не эрозией, а другими причинами)
Пояснения:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes - Coordination of traditional method of agricultural practices like along the slope, use of long term local varieity of seeds etc.), poverty / wealth (lack of captial)
Secondary causes of degradation: education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge), Erosion problem, Common social practices
3.8 Предотвращение и снижение деградации земель, или восстановление нарушенных земель
Укажите цель Технологии по отношению к деградации земель :
- восстановление/ реабилитация нарушенных земель
Пояснения:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Технические характеристики, мероприятия по практической реализации, вложения и стоимость
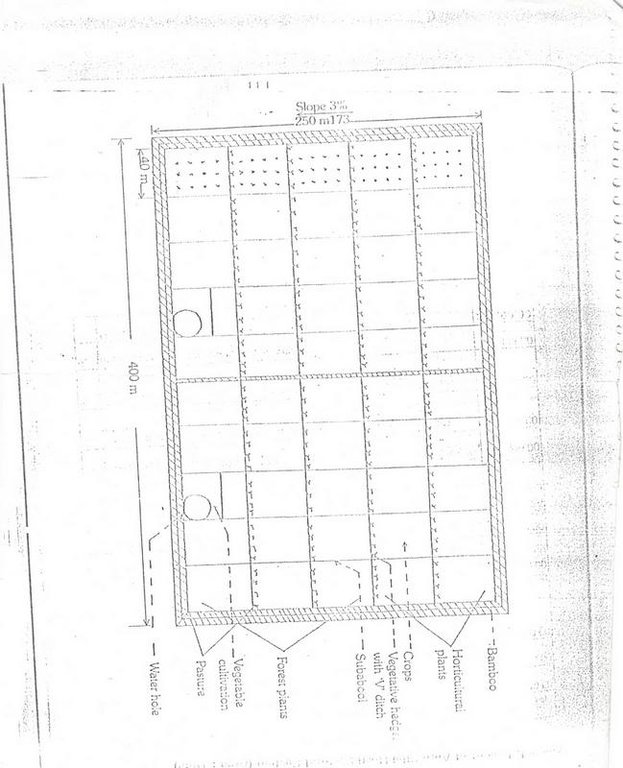
4.1 Технический рисунок, иллюстрирующий Технологию
Спецификация (пояснения к техническому рисунку):
Diagram showing different soil conservation measures
Location: Maliguda. Koraput/Orissa/India
Date: 15/3/2005
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, increase of surface roughness, increase in soil fertility
Agronomic measure: Green Fencing
Material/ species: Bamboo, Agave
Remarks: Two type of Bamboo and Agave provided all round the technology area
Manure / compost / residues
Remarks: 3 compost pits has been established.
Agronomic measure: Tillage with country plough
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 15000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.25
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.25
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Aligned: -graded strips
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs, O : other
Number of plants per (ha): 114
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 9.15
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 9.15
Aligned: -against wind
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 1
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.33
Trees/ shrubs species: Bamboo, Agave (Sisal)
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mango and Cashew
Other species: Teak, S.Glauca, Subabul
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 4.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 2.00%
Wall/ barrier
Spacing between structures (m): 6
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.25
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.7
Structural measure: Pits
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 25
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.9
Structural measure: 'V'Ditch with bund
Vertical interval between structures (m): 20
Spacing between structures (m): 15
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 500
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5
Construction material (earth): Bund constructed with earth
Construction material (other): Barries established with bamboo along the boundary for wind break as well as fence.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 4%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 2%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Автор:
Parida S.K, Koraput,Orissa, In
4.2 Общая информация по необходимым вложениям и стоимости
другая/ национальная валюта (название):
Rupees
Если это необходимо, укажите обменный курс от доллара США к местной валюте (например, 1 доллар США = 79,9 бразильского реала): 1 доллар США =:
0,45
Укажите среднюю дневную заработную плату наемных работников:
0.88
4.3 Мероприятия, необходимые для начала реализации
| Деятельность | Время (сессия) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection of matured bamboo and laying 9" below earth all along boundary in 3 rows | May |
| 2. | Collection of vertiver strips, trees from local nursery | July |
| 3. | Planting grasses, trees | July to Aug |
4.4 Вложения и затраты, необходимые для начала реализации
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 313,0 | 313,0 | |
| Оборудование | Animal traction | ha | 1,0 | 7,72 | 7,72 | |
| Посадочный материал | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 39,22 | 39,22 | |
| Посадочный материал | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 99,0 | 99,0 | |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Biocides | ha | 1,0 | 12,33 | 12,33 | |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 32,0 | 32,0 | |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Others | ha | 1,0 | 193,33 | 193,33 | |
| Строительные материалы | Stone | ha | 1,0 | 13,0 | 13,0 | |
| Строительные материалы | Earth | ha | 1,0 | 55,55 | 55,55 | |
| Строительные материалы | Pitcher | ha | 1,0 | 13,55 | 13,55 | |
| Другие | Compost pit | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | |
| Общая стоимость запуска Технологии | 783,7 | |||||
| Общие затраты на создание Технологии в долларах США | 1741,56 | |||||
Пояснения:
Duration of establishment phase: 48 month(s)
4.5 Поддержание/ текущее обслуживание
| Деятельность | Сроки/ повторяемость проведения | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tillage | Jan to June / Twice |
| 2. | Line showing | July / Once |
| 3. | Weeding | Sept / Once |
| 4. | Fertilizer Application | Sept to Oct / Once |
| 5. | Harvesting | Nov / Once |
| 6. | Manuring, weeding and hoeing | September / |
| 7. | Catchpit, pitcher irrigation | November / |
| 8. | Spraying with plant protection materials | December / |
4.6 Стоимость поддержания/ текущего обслуживания ( в год)
Пояснения:
Convert of degraded fellow private land to a cultivable land on adopting new low cost technology in a 5 Ha. Compact patch. The following benefits -
(1) Slope of the land reduced.
(2) Land protected from severe soil erosion.
(3) Increase the moisture region of the soil.
(4) Soil fertility/ standy increased farmers achieved the minimum common needs (basic) common needy product from the technology i.e food, fuel and fodder etc.
4.7 Наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат
Опишите наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат:
(1) High slope:- Slope reduced Nos. of structure adopted. Labour engagement are expose of sub-surface soil used Nos. of planting materials.
(2) Diference:- The planting materials are not locally available and transported from 20 K.Ms distance (Bamboo, Vertiver, Mango, Cashew)
(3) Comunication was not up to SWC spot during the establishment period.
5. Природные и социально-экономические условия
5.1 Климат
Среднегодовое количество осадков
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1000 мм
- 1001-1500 мм
- 1501-2000 мм
- 2001-3000 мм
- 3001-4000 мм
- > 4000 мм
Агроклиматическая зона
- Умеренно-влажная
Eastern Ghat High Land
5.2 Рельеф
Склоны (преобладающие):
- пологие (0-2%)
- покатые (3-5%)
- покато-крутые (6-10%)
- крутые (11-15%)
- очень крутые (16-30%)
- чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
- обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа:
- плато/ равнины
- гребни хребтов/холмов
- склоны гор
- склоны холмов
- подножья
- днища долин
Зона высотной поясности:
- 0-100 м над уровнем моря
- 101-500 м н.у.м.
- 501-1000 м н.у.м.
- 1001-1500 м н.у.м.
- 1501-2000 м н.у.м.
- 2001-2500 м н.у.м.
- 2501-3000 м н.у.м.
- 3001-4000 м н.у.м.
- > 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
Комментарии и дополнительные сведения по условиям рельефа/ топографии :
Landforms: Hill slopes (ranked 1), ridges (ranked 2) and valley floors (ranked 3)
Slopes on average: Moderate (land Slope having undulated topography)
5.3 Почвы
Средняя мощность почв:
- поверхностные (0-20 см)
- неглубокие (21-50 см)
- умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
- глубокие (81-120 см)
- очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта):
- грубый крупнозернистый/ лёгкий (песчаный)
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем горизонте:
- низкое (< 1%)
Если возможно, приложите полное описание почв или укажите доступную информацию, например тип почв, рH/ кислотность почв, ёмкость катионного обмена, содержание азота, содержание солей и т.д.
Soil texture: Medium (ranked 1, sandy loam to silty clay loam) and coarse/light
Soil fertility: Low (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (loss of top soils due to heavy run off, ranked 1)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium (soil varies from loam to silly clay loam, ranked 2)
Soil water storage capacity: Low
5.6 Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Доходы из других источников:
- 10-50% всех доходов
Относительный уровень достатка:
- плохой
- средний
Укажите другие важные характеристики землепользователей:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
24% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land.
45% of the land users are average wealthy and own 56% of the land (30% of house hold comes in standard wealth.).
31% of the land users are poor and own 14% of the land (70% of house hold comes below average).
Off-farm income specification: Through various training, interaction with specialist, they acquire more knowledge about other small business like Goatery, Poultry, Pisciculture, Beekeeping, Floriculture and also marketing facility and utilizing these knowledge their off-farm income increase.
5.8 Собственность на землю, права на земле- и водопользование
Землевладелец:
- индивидуальная, оформленная в собственность
Право землепользования:
- индивидуальное
6. Воздействия и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Технологии УЗП в пределах территории ее применения
Социально-экономическое воздействие
Продуктивность
производство сельскозяйственных культур
производство кормов
качество кормов
производство древесины
Доходы и затраты
доходы хозяйства
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Finding market and getting better price f or product
экономическое неравенство
Социальное и культурное воздействие
местное самоуправление
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Formation of UG/ SHG
знания в области УЗП/ деградации земель
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Imparting teaching to nearby village people on erosion, loss of top soil and timely aprehension at field
Экологическое воздействие
Водный цикл/ поверхностный сток
поверхностный сток
Количество до применения УЗП :
50
Количество после применения УЗП:
40
водный дренаж
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Safe disposal of water.
Почвы
влажность почв
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Adopting soil conservation activities
почвенный покров
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Practising cropping
утрата почв
Количество до применения УЗП :
46
Количество после применения УЗП:
20
Климат и снижение риска стихийных бедствий
скорость ветра
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Planting of bamboo at boundary
Другие экологические последствия
Soil fertility
Комментарий/ пояснения:
On decomposition of straw
Biodiversity
Seed quality
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Better procurement of good quality of seeds
6.2 Влияние Технологии за пределами территории ее применения
надежность и постоянство водотоков
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Stream flow remains up to February
подтопление ниже по течению
Комментарий/ пояснения:
No flooding seen
6.4 Анализ эффективности затрат
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с первоначальными вложениями (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с текущими расходами по поддержанию технологии (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
6.5 Внедрение Технологии
Если возможно, дайте количественную характеристику (число домохозяйств и/или площадь применения):
26
Пояснения:
6 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
20 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Some land users adopted the technology partially. As the technology has different measures, some took field bunds with local grasses, some did tree plantation. Some are planning to plant bamboo in their plot boundary.
6.7 Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности Технологии
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
| Low cost technology |
|
Early adoptbility by the farmers How can they be sustained / enhanced? Over all it is a best technology with proper management by the farmers |
| Combination of production gain from bamboo and crop, less use of chemical fertilizer as green manure is available localy. |
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
|
Low cost and simple tech nology. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Proper understanding by land user for technology |
| Materials are used for the technology available locally |
|
Due to increase of income migration is reduced How can they be sustained / enhanced? Proper adoption of technology |
|
Reduction of runoff and soil loss and increase of soil fertility and soil moisture regime has been increase How can they be sustained / enhanced? Adopting proper cropping pattern. |
6.8 Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски Технологии и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению землепользователей | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Ownerships of land and additional taxation there on after implementation of technology. | Clear understanding by competant authority ( By revenue people) |
| Fruit trees died | Beneficiaries planted Cashew instead of fruit trees. |
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Clear understanding of the technology. | Regular meeting with local representatives. |
| Availability of materials in the technology area. | Alternative available materials must be used in technology area. |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/ источники информации
7.2 Ссылки на опубликованные материалы
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Watershed Survey Report
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
Director of Soil Conservation, Orissa, Bhubaneswar
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Plan and Estimate
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
-do-
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки

PARTICIPATORY APPROACH IN IDCWDP, DANIDA [Индия]
Participatory approach for holistic and intigrated development of the defined area on watershed basis involving all level of stake holders.
- Составитель: Srikanta Kumar Parida
Модули
Нет модулей