Terraces with improved seed and fertilizer application [Афганистан]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Roziya Kirgizbekova
- Редактор: Bettina Wolfgramm
- Рецензент: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Palbandi bo tukhmihoi behbudyofta va kud
technologies_607 - Афганистан
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Технологии
Ответственный (-ые) специалист (-ы)
землепользователь:
Mohammad Azim Habibullah
Natural Resources Management Comittee (NRMC)
Sari Joy Village, Takhar Province
Афганистан
Специалист по УЗП:
Специалист по УЗП:
Researcher:
Название проекта, содействовавшего документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Potential and limitations for improved natural resource management (NRM) in mountain communities in the Rustaq district, Afghanistan (Rustaq NRM Study)Название проекта, содействовавшего документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar, Afghanistan (LIPT)Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Terre des Hommes (Terre des Hommes) - ШвейцарияНазвание организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (DEZA / COSUDE / DDC / SDC) - ШвейцарияНазвание организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - ШвейцарияНазвание организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Bern University of Applied Sciences, School of Agricultural, Forest and Food Sciences (HAFL) - Швейцария1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование данных, собранных ВОКАТ
Когда были собраны данные (на местах)?
17/10/2016
Составитель и ответственный(-ые) специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.4 Декларация по устойчивости описываемой Технологии
Вызывает ли описанная здесь Технология проблемы деградации земель настолько, что ее нельзя назвать природосберегающей?
Нет
Пояснения:
SLM practices documented in the frame of the Rustaq NRM study were established only recently (1-3 years ago). It is too early for a final judgment on the sustainability of these technologies within the human and natural environment of Chokar watershed.
1.5 Ссылка на Анкету (-ы) по Подходам УЗП
2. Описание Технологии УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Технологии
Определение Технологии:
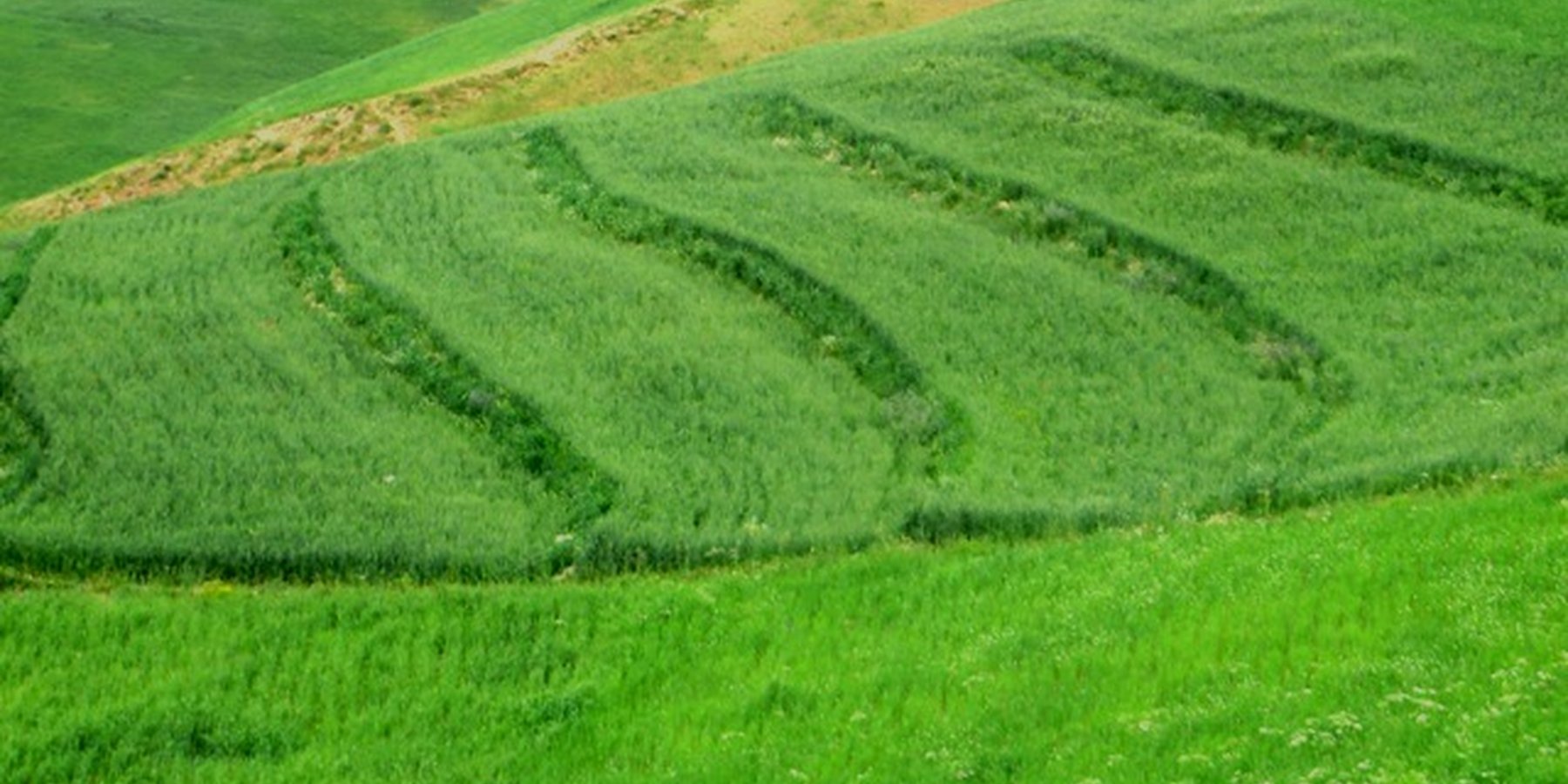
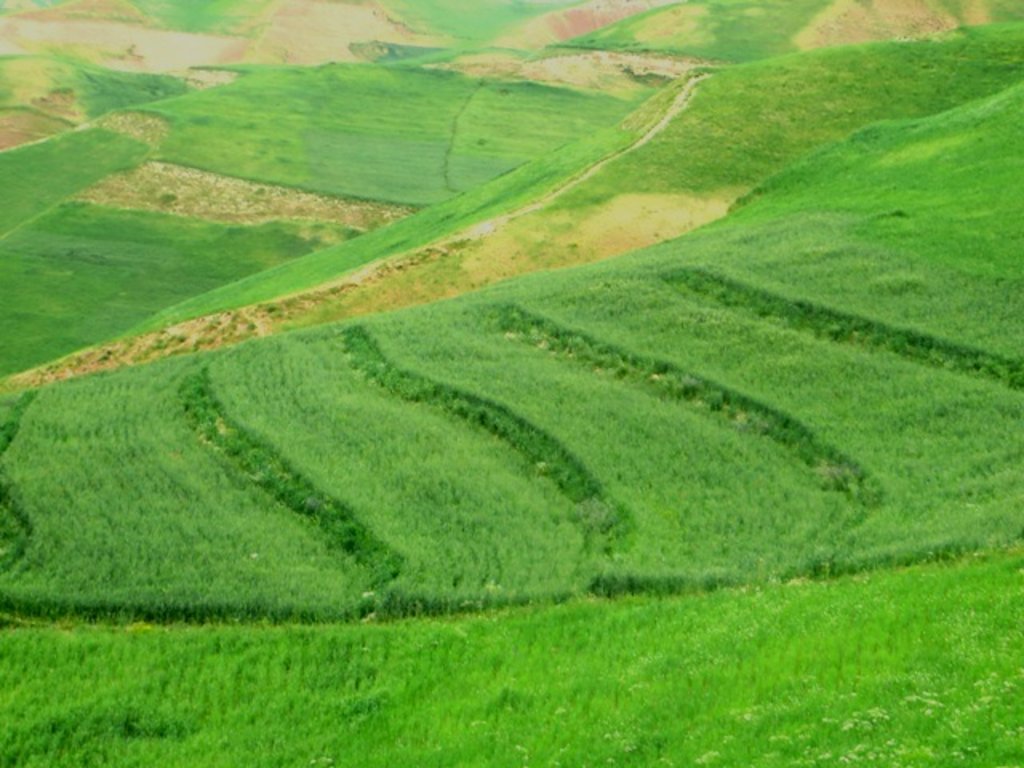
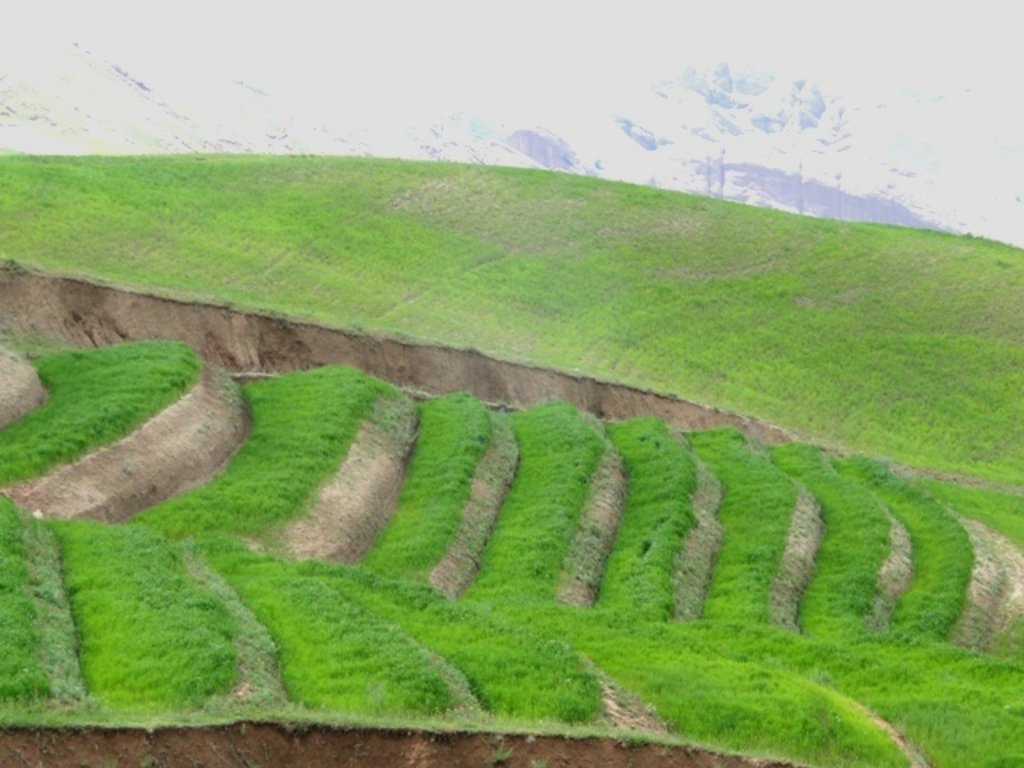
Terraces are established on mountain slopes used mainly for cropping wheat, with the purpose of soil protection from erosion, preserving runoff, sediments and nutrients on-site. Improved seeds and fertilizer are applied on the terraces for increasing crop yield, but also vegetation cover and biomass production, and thus prevent further land degradation.
2.2 Подробное описание Технологии
Описание:
Project supported implementation of terraces with application of improved seeds and fertilizer has taken place in the villages Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai, located in Chokar watershed of Rustaq District in Northern Afghanistan. The Chokar watershed is a mountainous area situated between 600 - 2,500 m above sea level. The climate is semi-arid with harsh and cold weather in winter and hot and dry summers. The annual precipitation in average years is 580mm. Land degradation affects all forms of land use and includes low vegetation cover, heavy top soil erosion from water, and poor soil fertility. Unsustainable agricultural practices, over-exploitation and high pressure on the natural resources are adversely impacting on the socio-economic well-being of local communities as well as contributing to the risk for being adversely affected by drought as well as landslides and flash floods triggered by heavy rainfall.
The data used for the documentation of the technology is based on field research conducted in Chokar watershed, namely in the villages: Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai. These villages represent the upper, the middle and the lower zone of Chokar watershed, respectively. They differ considerably in access to services and infrastructure, but in general are poorly served. The communities depend mainly on land resources for sustaining their livelihoods. In a good year with high yields, wheat-self-sufficiency lasts about 5 months.
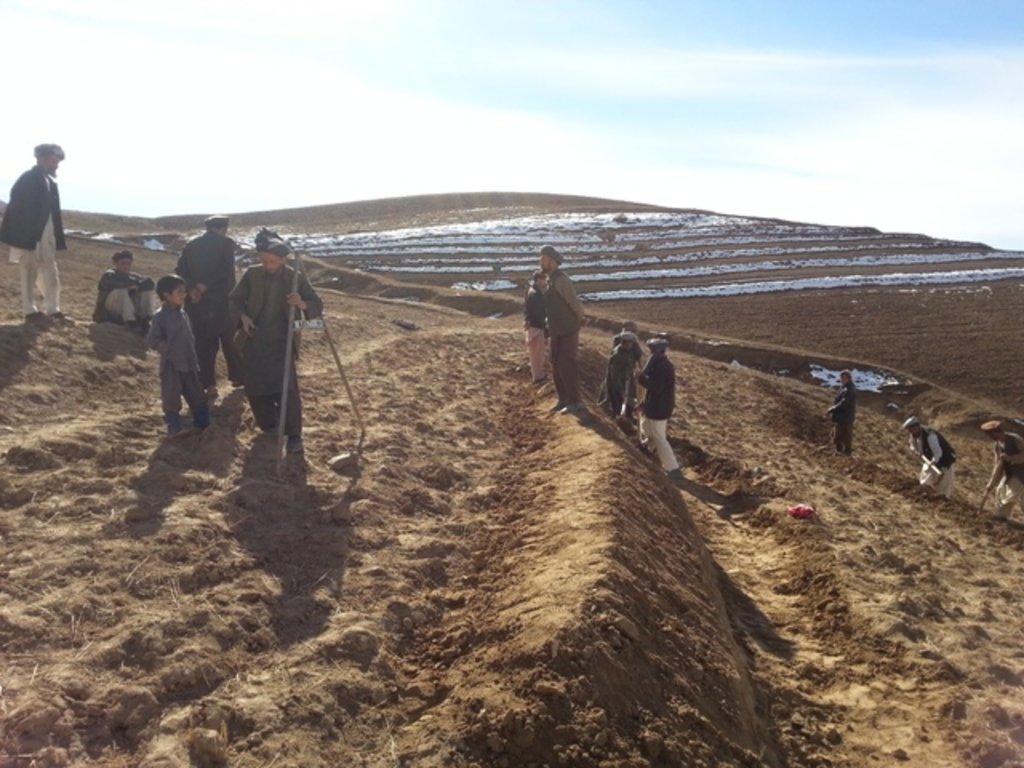
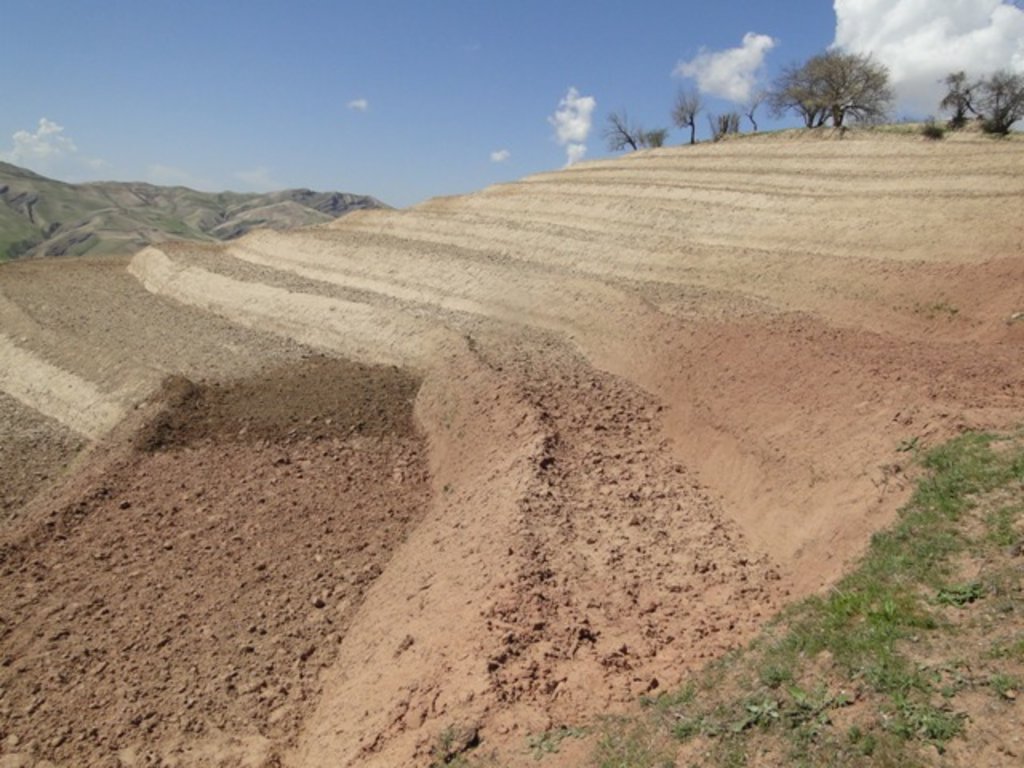
Since 2012 the Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des hommes (Tdh) Switzerland has initiated a range of NRM interventions. The project introduced terraces as sustainable land management practices on private plots, situated on rolling (11-15%) and hilly (16-30%) slopes to protect the land from soil erosion and prevent the loss of water and fertile topsoil, seeds and fertilizers. The average plot size for terrace implementation is 2 Jerib (0.4 hectares) with contour strips of 40m x 4m. The height of the risers is 1m-1,5 m. Terrace benches are built along the contour by moving the soil above the bench downwards. The leveled benches of the terrace are cultivated with wheat. The risers of the terrace are mostly used for growing fodder crops, mostly alfalfa, which also helps to stabilize the terrace. If medicinal herbs (ferula) are included they are cultivated along the bench contours .
Maintenance activities include small repair work on the riser by adding some amount of soil and re-sowing of alfalfa seeds on those spots.
The terraces allow application of improved seeds and fertilizers without them being washed off. The land-users report noticeable increase of wheat yield from the terraced plot with application of improved seeds and fertilizer compared to the non-terraced plot. An average plot of 0.2 ha on non-terraced hilly cropland used to give about 70 kg of wheat (350kg/ha). On terraces the yield has increased/ doubled to 140 kg on the same plot area (700kg/ha). The expectations regarding terraces remain high as over the time the land user hope their land will become more stable and improved soil moisture and fertility will have positive impact on the productivity as well. However, so far no cost-benefit assessment has been conducted allowing attribution of individual measure to the wheat increase.
Many land users are interested in the terrace technology due to a number of environmental and economic benefits expected, however the costs for building the terrace are considered high by an average local land user. They have to rely on external support in order to have sufficient resources for implementation. Women considered an advantage that during the establishment phase, men were paid by the project to work on their own land (or other villagers land) when building the terraces. Thus, there was no need for men to go for seasonal labour migration and they stayed at home.
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Технологию
2.5 Страна/ регион/ места, где применяется Технология, информация о которых собрана в данной Анкете
Страна:
Афганистан
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Takhar Province, Rustaq District
Более точная привязка места:
Chokar Watershed: Sari Joy (upper watershed), Jawaz Khana (middle watershed), Dashti Mirzai (lower watershed)
Пояснения:
This documentation is based on the experiences of SLM impementers from Sari Joy (8 terraced plots), Jawaz Khana, (7 terraced plots), and Dashti Mirzai (11 terraced plots) as compiled during FGDs. The terraces located in Jawaz Khana have not been digitized yet. Additionally insights were gained through interviews in all three villages on farmers experiences and observations of terraced plots, with both SLM implementers (46) and observers (28).
Map
×2.6 Сколько лет применяется данная Технология
Если год начала применения Технологии достоверно неизвестен, дайте примерную оценку:
- менее 10 лет назад (недавняя)
2.7 Внедрение Технологии
Укажите, как именно Технология УЗП была внедрена:
- через проекты/ внешнее вмешательство
Пояснения (тип проекта и т.д.):
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) supported by Swiss Development Cooperation (SDC) from 2012-17
3. Классификация Технологии УЗП
3.1 Основные цели и задачи реализации Технологии
- повышение производства
- снижение или предотвращение деградации земель, восстановление нарушенных земель
3.2 Текущий(-ие) тип(-ы) землепользования на территории, где применяется Технология

Пахотные угодья и плантации
- Однолетние культуры
- Многолетние (недревесные) культуры
Основные сельскохозяйственные культуры (товарные и продовольственные):
Wheat, Alfalfa
Если использование земель изменилось с началом применения Технологии, укажите тип землепользования до применения Технологии:
Before implementation of the Technology, only annual crops were cultivated, with wheat as the main crop. Plots were ploughed along the countours mostly by animal traction. In recent years land users are starting to use tractors for ploughing, , where villages and plots are accessible by machinery.
3.3 Дополнительная информация о землепользовании
Обеспеченность водой участков, где реализуется Технология :
- богарные земли
Число урожаев за год:
- 1
Поясните:
May-July
3.4 Категория УЗП, к которой относится Технология
- мероприятия по влагозадержанию и снижению эрозии почв на склонах
3.5 Распределение Технологии по площади
Охарактеризуйте пространственное распространение Технологии :
- равномерно-однородное применение на определенной площади
Если Технология равномерно применяется на той или иной территории, укажите ее приблизительную общую площадь:
- 0,1-1 км2
3.6 Мероприятия УЗП, выполняемые в рамках Технологии

Агрономические мероприятия
- A2: Органическое вещество/ почвенное плодородие

Мероприятия с использованием растительности
- Р2: Злаковые и многолетние травянистые растения

инженерные мероприятия
- И1: Террасирование
Пояснения:
Agronomic measures: Terraces increase the economic viability of applying improved seeds and (chemical) fertilizer to badly nutrient depleted cropland.
Vegetative measures: Alfalfa is planted on the risers for stabilizing the terraces, and as an important contribution to fodder cropping.
Structural measures: The leveling of countour strips allows to harvest water and sediments.
3.7 Основные проблемы деградации земель, на решение которых направлена Технология

водная эрозия почв
- ВЭп: поверхностная эрозия/смыв верхних почвенных горизонтов
- ВЭл: овражная эрозия / оврагообразование
- ВЭд: косвенное воздействие водной эрозии

ухудшение физических свойств почв
- Фп: запечатывание почв

биологическая деградация
- Бр: сокращение растительного покрова
- Бк: сокращение количества биомассы

деградация водных ресурсов
3.8 Предотвращение и снижение деградации земель, или восстановление нарушенных земель
Укажите цель Технологии по отношению к деградации земель :
- снижение деградации земель
- восстановление/ реабилитация нарушенных земель
4. Технические характеристики, мероприятия по практической реализации, вложения и стоимость
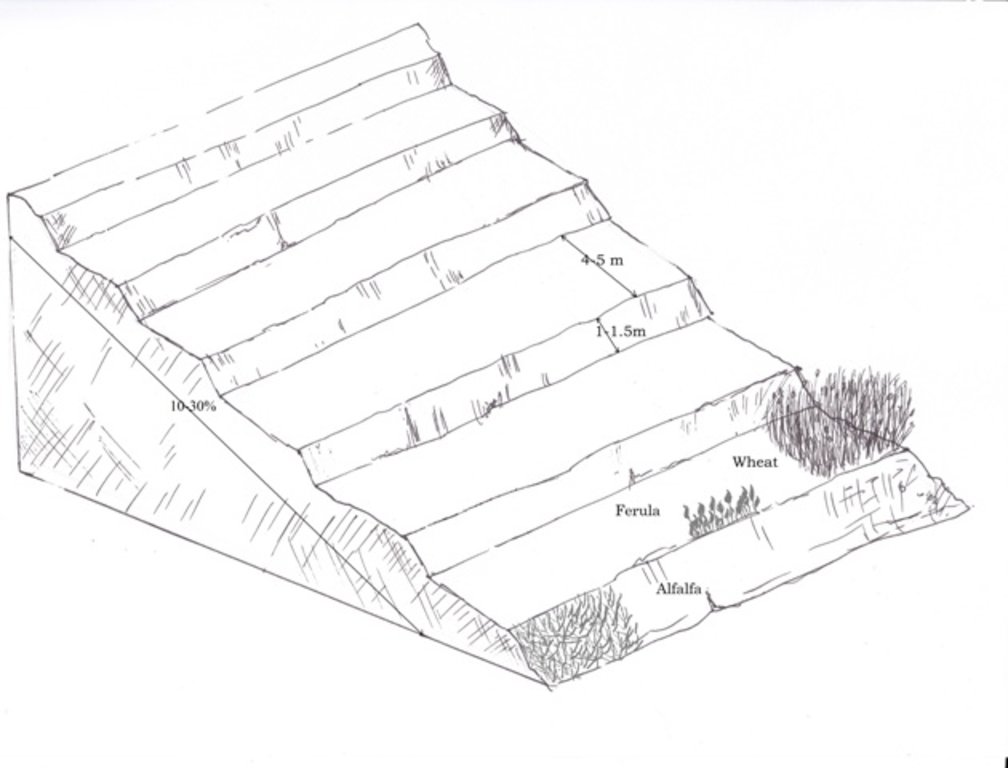
4.1 Технический рисунок, иллюстрирующий Технологию
4.2 Спецификация / пояснения к техническому рисунку
Terraces are established predominantly on a privately owned land in a mountainous landscape with varying steepness of slopes.
The average size of a plot is 2 Jerib, which is equal to 0.4 ha. The design of the terrace depends on the steepness of the slope. Mostly rolling (11-15%) and hilly (16-30%) slopes are used for building terraces.
Using an A-frame, the terrace is designed by dividing the slope into contour strips. Depending on the slope steepness, the terrace bench is around 4m wide and the the height of the risers is 1m-1,5 m. The terrace benches are built along the contour by moving the soil of upper bench to the lower bench. The leveled benches of the terrace are cultivated with wheat. The risers of the terrace are mostly used for growing fodder crops, such as alfalfa, which also helps to stabilize the terrace. If medicinal herbs are included, such as ferula, they are cultivated along the bench contours.
4.3 Общая информация по необходимым вложениям и стоимости
Уточните, как рассчитывались затраты и вложения:
- на площадь, где применяется Технология
Укажите размер и единицу площади:
1 ha
Укажите денежные единицы, использованные для подсчета затрат:
- Доллары США
Укажите обменный курс между долларом США и местной валютой (если уместно): 1 доллар США =:
67,0
Укажите среднюю дневную заработную плату наемных работников:
5.2-5.3 USD
4.4 Мероприятия, необходимые для начала реализации
| Деятельность | Тип мероприятия | Сроки | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selection of the area for establishing a terrace (Men) | Управленческие | Autumn |
| 2. | Designing of the terrace using A-frame, assisted by trained technician/project staff (Men) | Инженерные | End of autumn after rainy days |
| 3. | Leveling the soil with a shovel (Men) | Инженерные | Autumn/Winter |
| 4. | Sowing of alfalfa seeds on the risers (Men/women) | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | After 20 days of sowing wheat |
| 5. | Sowing of wheat seeds on benches (Men/Women) | Агрономические | Winter/Spring |
| 6. | Sowing of ferula along the contours (Men/women) | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | Winter/Spring |
4.5 Вложения и затраты, необходимые для начала реализации
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Designing of the terrace using A-frame | person-day | 10,0 | 9,0 | 90,0 | |
| Оплата труда | Leveling the soil with a shovel | person-day | 150,0 | 5,3 | 795,0 | 51,0 |
| Оплата труда | Sowing of wheat and alfalfa seeds | person-day | 10,0 | 5,3 | 53,0 | 51,0 |
| Оплата труда | Sowing of ferula | person-day | 2,0 | 5,3 | 10,6 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Pick axe | Pcs | 1,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Pitchfork | Pcs | 1,0 | 5,3 | 5,3 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Wheel barrow | Pcs | 1,0 | 38,0 | 38,0 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Shovel | Pcs | 1,0 | 3,8 | 3,8 | |
| Оборудование | Hoe | Pcs | 1,0 | 7,5 | 7,5 | |
| Оборудование | A-Frame | Pcs | 1,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 | |
| Посадочный материал | Wheat seeds | Kg | 140,0 | 0,42 | 58,8 | |
| Посадочный материал | Alfalfa seeds | Kg | 17,5 | 0,42 | 7,35 | 100,0 |
| Посадочный материал | Ferula seeds | Kg | 2,5 | 6,35 | 15,88 | 100,0 |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | DAP | Kg | 125,0 | 0,9 | 112,5 | |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Urea | Kg | 125,0 | 0,45 | 56,25 | |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Herbicide | Liter | 50,0 | 0,25 | 12,5 | |
| Общая стоимость запуска Технологии | 1275,48 | |||||
Если землепользователем оплачено менее 100% затрат, укажите, кем покрывались остальные затраты:
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des Hommes (Tdh)
Пояснения:
Equipment provided by the project was re-used for the implemenation of different SLM practices on different plots. For completness equipment costs are fully accounted for.
Costs calculated for a Technology area of 1ha was only done for the purpose of the WOCAT documentation. In reality SLM plots are on average 0.4 ha or 2 jiribs. Costs were simply multiplied by 2.5. The actual costs for a 1ha plot might be slightly different.
4.6 Поддержание/ текущее обслуживание
| Деятельность | Тип мероприятия | Сроки/ повторяемость проведения | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ploughing the land with animal traction (Men) | Агрономические | Winter/Spring/Annually |
| 2. | Sowing of wheat seeds on benches (Men/Women) | Агрономические | Winter/Spring/Annually |
| 3. | Application of fertilizer (Men/Women) | Агрономические | Fall |
| 4. | Weeding (Women) | Агрономические | Summer |
| 5. | Harvesting wheat (Men and women together) | Агрономические | Summer/Fall |
| 6. | Harvesting alfalfa (Men and women together) | Агрономические | Summer/Fall |
| 7. | Collecting and delivering harvested wheat (Men and women) | Агрономические | Fall |
| 8. | Collecting and delivering harvested alfalfa (Men and women) | Агрономические | Fall |
| 9. | Repairing terrace risers with a shovel (Men) | Инженерные | Winter/Spring/After heavy rain or snow |
| 10. | Sowing alfalfa seeds on the repaired area (Men/Women) | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | Winter/Spring/When required |
4.7 Стоимость поддержания/ текущего обслуживания ( в год)
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Ploughing the land with animal traction | person day | 2,5 | 5,3 | 13,25 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Sowing of wheat seeds on benches | person day | 5,0 | 5,3 | 26,5 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Weeding and Fertilizer application | person day | 5,0 | 5,3 | 26,5 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Harvesting and delivering wheat and alfalfa | person day | 70,0 | 5,3 | 371,0 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Sickle | Pcs | 1,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Посадочный материал | Wheat seeds | Kg | 140,0 | 0,42 | 58,8 | 100,0 |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | DAP | Kg | 125,0 | 0,9 | 112,5 | 100,0 |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Urea | Kg | 125,0 | 0,45 | 56,25 | 100,0 |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Herbicide | Liter | 50,0 | 0,25 | 12,5 | 100,0 |
| Общая стоимость поддержания Технологии | 677,3 | |||||
Если землепользователем оплачено менее 100% затрат, укажите, кем покрывались остальные затраты:
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des Hommes (Tdh)
Пояснения:
Costs calculated for a Technology area of 1ha was only done for the purpose of the WOCAT documentation. In reality SLM plots are on average 0.4 ha or 2 jiribs. Costs were simply multiplied by 2.5. The actual costs for a 1ha plot might be slightly different.
4.8 Наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат
Опишите наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат:
Due to the remoteness of the villages where the Technology has been implemented, all the inputs for establishment, such as agricultural equipment, plant material, fertilizers, etc., are purchased in Rustaq town. The expenses for traveling and delivering the inputs affect the establishment costs.
5. Природные и социально-экономические условия
5.1 Климат
Среднегодовое количество осадков
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1000 мм
- 1001-1500 мм
- 1501-2000 мм
- 2001-3000 мм
- 3001-4000 мм
- > 4000 мм
Укажите среднегодовое количество осадков (если известно), мм:
580,00
Пояснения/ комментарии по осадкам:
Average annual precipitation for the area was calculated with 580 mm, with minimums in dry years (2000 and 2001) of 270 mm and maximums in wet years (2009/2010) of 830 mm. The absolute maximum rainfall was calculated for 1986 with 1024 mm. The data series covers the time from 1979 to 2014.
Укажите название соответствующей метеостанции:
Climate Forecast System Reanalysis (CFSR), http://rda.ucar.edu/pub/cfsr.html
Агроклиматическая зона
- полузасушливая
Specifications: Derived from the publically available dataset on length of growing period (LGP) (Fischer 2009 / IIASA-FAO). Internet link: http://tiles.arcgis.com/tiles/P8Cok4qAP1sTVE59/arcgis/rest/services/Length_of_growing_period/MapServer
5.2 Рельеф
Склоны (преобладающие):
- пологие (0-2%)
- покатые (3-5%)
- покато-крутые (6-10%)
- крутые (11-15%)
- очень крутые (16-30%)
- чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
- обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа:
- плато/ равнины
- гребни хребтов/холмов
- склоны гор
- склоны холмов
- подножья
- днища долин
Зона высотной поясности:
- 0-100 м над уровнем моря
- 101-500 м н.у.м.
- 501-1000 м н.у.м.
- 1001-1500 м н.у.м.
- 1501-2000 м н.у.м.
- 2001-2500 м н.у.м.
- 2501-3000 м н.у.м.
- 3001-4000 м н.у.м.
- > 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
Комментарии и дополнительные сведения по условиям рельефа/ топографии :
The information was derived from two different sources:
- SLM implementers information provided in the Land User Protocol (LUP) during an FGD
- Elevation and slope statistics derived for terraced plots from ASTGTM. ASTGTM is the ASTER Global Digital Elevation Model V002 with a 30 m spatial resolution. More information on ASTGTM is available here: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/node/1079. The data can be downloaded here: https://gdex.cr.usgs.gov/gdex/
5.3 Почвы
Средняя мощность почв:
- поверхностные (0-20 см)
- неглубокие (21-50 см)
- умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
- глубокие (81-120 см)
- очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта):
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
Гранулометрический состав (на глубине более 20 см):
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем горизонте:
- среднее (1-3%)
- низкое (< 1%)
Если возможно, приложите полное описание почв или укажите доступную информацию, например тип почв, рH/ кислотность почв, ёмкость катионного обмена, содержание азота, содержание солей и т.д.
Local land users differentiate between the following soil types where terraces are implemented:
- Light soils: moderately deep; texture of topsoil medium (loamy, silty); low topsoil organic matter
- Dark soils: moderately deep; texture of topsoil medium (loamy, silty); medium topsoil organic matter
5.4 Доступность и качество воды
Доступность поверхностных вод:
средняя
Качество воды (без обработки):
питьевая вода хорошего качества
Является ли солёность воды проблемой?
Нет
Происходят ли периодические затопления территории?
Да
Регулярность:
эпизодически
Комментарии и дополнительная информация по качеству и количеству воды:
Floods occur mainly during the rainy seasons in spring and autumn. Availability of surface water differs for the three study villages Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana, and Dashti Mirzai. Sari Joy has sources and good surface water availability. Jawaz Khana has poor water availability as water has to be fetched from a lower laying stream. Dashti Mirzai has good water availability also from an irrigation channel.
5.5 Биоразнообразие
Видовое разнообразие:
- низкое
Разнообразие местообитаний:
- низкое
5.6 Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Осёдлый или кочевой:
- Осёдлый
Рыночная ориентация производства:
- натуральное хозяйство (самообеспечение)
- смешанное (самообеспечение/ товарное хозяйство
Доходы из других источников:
- 10-50% всех доходов
- > 50% всех доходов
Относительный уровень достатка:
- средний
- обеспеченный
Индивидуальное или коллективное хозяйство:
- частное/ домовладение
Уровень механизации:
- ручной труд
- тягловая сила
Пол:
- женщины
- мужчины
Возраст землепользователей:
- средний возраст
- пожилой
5.7 Средний размер земельных участков, арендуемых или находящихся в собственности землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
- < 0,5 га
- 0,5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1000 га
- 1000-10000 га
- > 10000 га
Считается ли это мелким, средним или крупным хозяйством (по местным масштабам)?
- среднего размера
5.8 Собственность на землю, права на земле- и водопользование
Землевладелец:
- индивидуальная, не оформленная в собственность
Право землепользования:
- индивидуальное
Право водопользования:
- общинное (контролируемое)
Пояснения:
Those who own land and use water for irrigation are obliged to pay for the water. The payment is made both in kind and in cash to the Mirob, the person in charge of distributing water in the community. The amount of the payment varies from village to village.
6. Воздействия и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Технологии УЗП в пределах территории ее применения
Социально-экономическое воздействие
Продуктивность
производство сельскозяйственных культур
Количество до применения УЗП :
350 kg / ha
Количество после применения УЗП:
700 kg / ha
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The integration of measures including agronomic (improved seed and fertilizer) and structural (terraces to control water flow and loss of top soil, including nutrients and seeds) results in an increase of crop yield already in the first year. The effects cannot be attributed to one or the other measure specifically.
производство кормов
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Alfalfa is planted on the risers.
разнообразие продукции
площадь, используемая для производства продукции
Комментарий/ пояснения:
No change in total area for production, as the riser of the terraces are used for fodder production. However, there is some reduction of area available for annual crop production.
Социальное и культурное воздействие
продовольственная безопасность/ самообеспечение
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The yield of the main staple crop (wheat)has been reported to be double on terraced plots with application of improved seed and fertilizer. In addition, fodder crops, such as alfalfa grown on the risers, can be harvested.
знания в области УЗП/ деградации земель
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Technicians in the villages were trained in the use of A-frames. Implementers of terraces voiced that they themselves would not be able to replicated the designing of terraces.
положение социально и экономически уязвимых групп населения
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Female headed households are not included. Technology is implemented on private land, therefore people without land are excluded. However, they have the opportunity to earn income as a hired worker for the SLM implementers.
Экологическое воздействие
Водный цикл/ поверхностный сток
поверхностный сток
Почвы
влажность почв
Комментарий/ пояснения:
in situ water harvesting
утрата почв
Биоразнообразие: растительность, животный мир
Растительный покров
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Both an increase in vegetation cover during the growing season when most erosive rains are observed as well as permenant vegetation cover from perennial alfalfa plants can been observed.
биомасса/ содержание углерода в надземной биомассе
6.2 Влияние Технологии за пределами территории ее применения
подтопление ниже по течению
отложение наносов ниже по течению
буферная/ фильтрационная способность
Коммментарий по оценке влияния:
These comments apply to 6.1 and 6.2:
- Socio-economic impacts: Based on the Land User Protocols: Individual SLM implementers were asked to rate the benefits for their Technology. They were asked to indicate production increase of crops; fodder; animals; wood; non-wood forest products; increase in product diversity; or production area. The most important increase they rated with 3, the second most with 2, others with 1 point. Averages of the points given by all SLM implementers are reflected here.
- Ecological impacts and off-site impacts: Based on the Land User Protocols: Individual SLM implementers were asked to rate the on-site and off-site impacts of the Technology on water; soil; and vegetation. They were asked to indicate the strength of impacts with three, two or one points. Averages of the points given by all implementers are reflected here.
6.3 Подверженность и чувствительность Технологии УЗП к постепенным изменениям климата и экстремальным погодным явлениям/ стихийным бедствиям, связанным с изменением климата (в понимании землепользователей)
Экстремальные явления, связанные с изменением климата (стихийные бедствия)
Погодные стихийные бедствия
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| местные ливневые дожди | очень хорошо |
Стихийные бедствия климатического характера
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| засухи | хорошо |
Пояснения:
Based on the multi-criteria matrix: SLM implementers from three villages were asked to jointly discuss and rate how much the SLM technology reduced the lands vulnerability to drought and local rainstorms. Only vulnerability to the most prevalent climate extremes (drought and local rainstorms) was discussed. SLM technologies were rated as reducing vulnerability poorly , well, or very well. The average points reflected here are from multi-criteria matrices compiled in three villages where the SLM technology had been implemented.
6.4 Анализ эффективности затрат
Пояснения:
Costs: As larger parts of the establishment of the technology were covered by the project, farmers consideration of the total costs are likely underestimated.
Benefits: Two plots were terraced in 2012, and 5 plots in 2013. However, most terraces were implemented in 2014 (11 plots ) and 2015 (8 plots). The Rustaq NRM study was conducted in autumn 2016. 1-2 years of cultivating the terrace system is too short a period for providing evidence on short- and long-term returns.
6.5 Внедрение Технологии
- 1-10%
Если возможно, дайте количественную характеристику (число домохозяйств и/или площадь применения):
10.7 ha has been terraced within the 3 study villages with LIPT project support.
Среди применяющих Технологию землепользователей, какова доля лиц, применяющих её по собственной инициативе, т.е. без какого-либо материального стимулирования со стороны?
- 0-10%
Пояснения:
Based on the Land User Protocol: Individual SLM implementers were asked whether they received support for implementing the Technology. Each indicated the type of support he received from the proposed options: "Full Support 100%, Some Support, No Support 0%". 3 implementers claimed full project support, 22 claimed some support, and 1 implementer claimed no project support.
6.6 Адаптация
Была ли Технология УЗП изменена в недавнее время с целью адаптации к меняющимся условиям среды?
Да
Если да, укажите, по отношению к каким именно изменяющимся условиям среды произведена адаптация?
- изменяющиеся условия рынка
Укажите, что именно изменилось в Технологии (дизайн, используемые материалы или виды растений/животных и т.д.):
Ferula is planted on the terrace in addition to wheat and alfalfa. The resin-like gum from the dried sap extracted from the stem and roots of Ferula is in high demand as a basic product for pharmaceuticals. Ferula can be sold to local merchants, who resell it to India, and is thus intercropped by some farmers on the terraces.
6.7 Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности Технологии
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
| Notable higher crop yields on the plots where improved seeds and fertilizer are applied on newly established terraces. Farmers have high expectations for the years to come and for yields of annual crops (such as wheat) to remain high. |
| Diversity of crops planted on terraces is valued by the land users. For example, cultivating wheat and alfalfa on the terraced plot provides household with the key crop and also fodder for the livestock and thereby contributes to securing food for the family and maintaining better health of their cattle. Additionally, some farmers have started intercropping Ferula, a medical herb and cash crop. |
| Farmers percieve soil quality on terraced plots with fertilizer application to improve. An improvement in soil fertility (which may relate first of all to the effects of fertilizer application) and increased soil moisture have been reported. Single statements also related to effectiveness of applying fertilizer on terraced plots, as here fertilizer is not washed away during rains. |
| Terraced plots are considered less vulnerable to the effects of rainstorms and dry spells, than non-terraced plots on slopes where annual crops are cultivated. |
| Women considered an advantage that during the establishment phase, men were paid by the project to work on their own land when building the terraces. Thus, there was no need for men to go for seasonal labour migration and they stayed at home. At the same time the terracing of the land is seen as an opportunity to improve the land resources on their families plots. An increase in women's workload related to bringing food to the field during establishment was considered to be acceptable, especially compared to the expected increase in yields. |
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
| The application of fertilizer on terraces is expected to show multiple effects: yields from these fertility depleted croplands can be increased. This includes an increase in biomass production, which may be used as green manure on the field or as animal feed or as straw. Further, vegetation cover during the growing period can be increased, which helps to protect the soil from erosive rains. |
| The project paid establishment of terraces on farmers' plots provided 20 days of employment per 2 jerib (0.4 ha) plot for farmers in their home villages. At the same time the terracing is a long-term investment into the land resources. Terracing provides an opportunity to decrease soil degradation and even to rehabilitate degraded lands. Application of improved seeds and fertilizer contribute in the establishment year to increased crop and fodder yields. |
6.8 Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски Технологии и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению землепользователей | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
|
The implementation costs are high and land users state that it is impossible for them to cover establishment costs on their own. |
|
| Farmers expectations partly exceeded the actual yield harvested from the terraces in the first years after the implementation. | |
| Both men and women from households that have implemened terraces state that during the establishment year the household experiences an increased workload, that is not well compatible with other on-going household / farm activities. | |
| The production area for annual crops only is slighty reduced. | So far not all farmers seem to use the production area fully. Intercropping with perennial plants is recommended in order to use the risers of the terraces for fodder production. Some farmers have started intercropping of Ferula as cash crop. |
| Sufficient own land is required. | How does the amount of cropland affect the innovation readiness of a farmer? A better understanding is required on farmers willingness to take a risk for investing in a new SLM technology, and especially terracing, and influencing factors. |
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| The technology requires technical knowledge for implementation and maintenance, which is key for successful adoption, replication and upscaling. The project trained technicians to support land users with the design of terraces. While the project aided implementation of terraces has improved the general knowledge and awareness of the land users on the benefits of SLM practices, most farmers will not be able to design terraces on their own. | |
|
Technically correct design of the terrace presents a challenge and might not be always achieved. Forward sloping terrace benches may lead to channeled runoff and have the risk of rills and gully formation. |
|
| There is an attribution gap regarding the increased wheat yields, especially with regard to individual contribution of the terraces, the application of improved seeds and the fertilizer, and the combined effects (role of terraces in making improved seed and fertilizer application effective). | A cost benefit analysis (CBA) needs to be conducted to determine short- and long-term returns of the SLM technology. On farm trials are necessary for assessing impacts of the different measures (agricultural, vegetative and structural measures) before-and-after, as well as with-without the SLM technology. |
| Terrace maintenance is crucial. If not maintained properly for a longer period of time, the damaged terrace can lead to further land degradation through channeled runoff, sever erosion and possible risks of disaster for the surrounding settlements on the slopes. | |
| The technology is established mainly by better-off households, which own more land than the average SLM implementer. |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/ источники информации
- опросы землепользователей
Focus group discussions (FGD) were organized by the CDE team to collect information from SLM implementers. Total of 26 land users who have implemented terraces participated in the FGDs held in the three villages of Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai.
Interviews were conducted by the HAFL team to collect information from persons representing all the three study villages. Very detailed interviews were conducted with 74 persons interested in terrace implementation, of which 46 persons are from households that already have implemented terraces.
- опросы специалистов/экспертов по УЗП
The technical staff of Tdh LIPT Project in Rustaq, responsible for the implementation of the technology were consulted on a number of occasions during the compilation of this material.
- данные, собранные из отчетов и достоверных документов
Information provided in the reports of Tdh LIPT Project in Rustaq served as an initial source of information during the preparatory phase and also solidifying the description of the technology and area of implementation. Other background papers on Afghanistan were referred to for general information on agriculture and natural resource management in Afghanistan.
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки
Нет ссылок
Модули
Нет модулей