Geocoding of Million Fruit Trees for Monitoring and Tracking [Бутан]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Nima Dolma Tamang
- Редактор: Haka Drukpa
- Рецензенты: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Not Applicable (NA)
technologies_6829 - Бутан
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Технологии
Ответственный (-ые) специалист (-ы)
Agriculture Extension Officer:
Penjor Thuji
Geog Renewable Natural Resources (RNR) Center, Agriculture Office, Mewang Gewog, Thimphu Dzongkhag
Бутан
Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric (National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric) - Бутан1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование данных, собранных ВОКАТ
Составитель и ответственный(-ые) специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.4 Декларация по устойчивости описываемой Технологии
Вызывает ли описанная здесь Технология проблемы деградации земель настолько, что ее нельзя назвать природосберегающей?
Нет
Пояснения:
The technology enables remote monitoring of the growth and development of fruit trees ensuring the sustainable use of land and its resources. Further, the technology aids in the success of the Million Fruit Tree Plantation Project reducing the risk of converting cultivable land to fallow.
2. Описание Технологии УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Технологии
Определение Технологии:
Geocoding of fruit trees allows remote monitoring and progress tracking of the growth of seedlings. The Smart App MoDA (Mobile Operation and Data Acquisition) is used in geocoding.
2.2 Подробное описание Технологии
Описание:
Geocoding of the “million fruit trees” initiative has been carried out across Bhutan. Different fruit trees suitable for particular agroecological zones were planted in farmers' fields in twenty districts and each sapling was geocoded.
The main elements of geocoding fruit trees involve assigning unique geographical codes or coordinates to individual trees within an orchard, utilizing technical specifications and equipment such as handheld GPS to accurately determine the location. The potential benefits of this form of geocoding include:
1. Location Mapping: Geocoding allows fruit trees to be accurately located on a map, providing a visual representation of their spatial distribution. This mapping can help identify patterns, clusters, and gaps in tree distribution.
2. Data Integration: Geocoded data can be integrated with geographic information systems (GIS) and other data sources, such as climate data, soil information, and topography. This integration provides a holistic view of the factors influencing fruit tree growth and productivity.
3. Precision: Geocoding provides precise coordinates for each fruit tree, enhancing the accuracy of data collection and analysis. This precision is crucial for making informed decisions regarding tree management and resource allocation.
4. Monitoring and Management: Geocoded fruit tree data enables efficient monitoring of tree health, growth, and potential issues. It facilitates targeted interventions, such as irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, based on the specific needs of individual trees or clusters.
5. Yield Estimation: By combining geocoded data with relevant environmental and growth information, it's possible to estimate the potential fruit yield in specific areas. This information aids in resource planning and harvest predictions.
6. Disease and Pest Management: Geocoded data can help identify patterns of disease or pest infestations. Early detection through geocoded monitoring can enable prompt intervention and prevent the spread of pests or diseases.
7. Biodiversity Analysis: Geocoding allows researchers to study the diversity of fruit tree species in different regions. This analysis can be useful for conservation efforts and understanding the ecological impact of specific tree species.
8. Research and Analysis: Geocoded fruit tree data serves as a valuable resource for scientific research. Researchers can study the effects of climate change, urbanization, and land use changes on fruit tree populations and ecosystems.
9. Decision-Making: Geocoded data assists farmers, agricultural agencies, and policymakers in making informed decisions about land use, tree planting initiatives, and resource allocation for sustainable agriculture.
10. Community Engagement: Geocoded maps of fruit trees can be shared with communities, promoting awareness of local resources, fostering community engagement, and encouraging initiatives like urban orchards or community gardens.
11. Data Visualization: Geocoded data can be visualized using maps and spatial tools, making it easier to interpret and communicate information to various stakeholders.
12. Long-Term Tracking: Geocoded data allows for long-term tracking of changes in fruit tree populations, aiding in the assessment of the success of planting initiatives and the overall health of the environment.
The major activity of the technology is marking the fruit trees with the help of GPS so that these geocoordinates can be useful in tracking down the exact location of the plant. Geocoding is labour-intensive as the field workers need to be physically present in the field while carrying out the activity. Then the data recorded in GPS is transferred to the computer and analyzed using ArcGIS. This information is available to the policymakers and Agriculture officers and is shared with the Extension Agents through which it is disseminated to the land users.
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Технологию
Комментарии к фотографиям:
The Photo does not directly depicts the technology described here.
2.5 Страна/ регион/ места, где применяется Технология, информация о которых собрана в данной Анкете
Страна:
Бутан
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Thimphu Dzongkhag
Более точная привязка места:
Sigay Chiwog, Mewang Gewog
Охарактеризуйте пространственное распространение Технологии :
- примененяется точечно/ на небольших участках
Технология применяется на ООПТ?
Нет
Пояснения:
The geocoding of fruits are in the land users field. Therefore, the area does not fall under any of the protected area or national parks.
Map
×2.6 Сколько лет применяется данная Технология
Год начала реализации:
2022
2.7 Внедрение Технологии
Укажите, как именно Технология УЗП была внедрена:
- через проекты/ внешнее вмешательство
Пояснения (тип проекта и т.д.):
The geocoding of the million fruit trees in the country was initiated as per the directives of His Majesty the 5th King of Bhutan where all the saplings are funded by the Royal Government of Bhutan. Plantation and geocoding were done by the Desuups (Desuup is the highest form of the voluntary act in Bhutan. They wear orange uniforms and are also known as the Guardians of Peace).
3. Классификация Технологии УЗП
3.1 Основные цели и задачи реализации Технологии
- повышение производства
- снижение или предотвращение деградации земель, восстановление нарушенных земель
- сохранение экосистем
- создание благоприятных экономических условий
- создание благоприятных социальных условий
3.2 Текущий(-ие) тип(-ы) землепользования на территории, где применяется Технология
Комбинированное землепользование в пределах одной и той же земельной единицы:
Да
Укажите сочетания типов землепользования (посевы / пастбища / деревья):
- Агролесоводство

Пахотные угодья и плантации
- Однолетние культуры
- Многолетние (недревесные) культуры
Ежегодный урожай - Уточните культуры:
- зерновые культуры - рис (суходольный)
Годовая система земледелия:
Рис на заболоченных территориях - пшеница
- Apple
Число урожаев за год:
- 2
Поясните:
Paddy in summer is followed by winter wheat or vegetables
Применяются ли посевы в междурядьях?
Да
Если да, укажите, какие посевы применяются:
They intercrop vegetables with lugumes.
Применяется ли севооборот?
Да
Если да, укажите:
The land used for paddy cultivation is used for planting vegetables such as potatoes.
3.3 Изменилось ли использование земель в связи с внедрением Технологии?
Изменилось ли использование земель в связи с внедрением Технологии?
- Нет (см. пункт 3.4)
3.4 Водоснабжение
Обеспеченность водой участков, где реализуется Технология :
- сочетание богарных и орошаемых земель
3.5 Категория УЗП, к которой относится Технология
- агролесоводство
- улучшение сортов растений/ пород животных
3.6 Мероприятия УЗП, выполняемые в рамках Технологии

Мероприятия с использованием растительности
- Р1: Древесный и кустарниковый покров
Пояснения:
The technology aids in maintaining land cover by ensuring vegetative coverage of the land in which geocoding enhances easy management and improved health of the fruit trees such as apples, dragon fruit, banana, areca nut, kiwi, avocado and others.
3.7 Основные проблемы деградации земель, на решение которых направлена Технология

водная эрозия почв
- ВЭп: поверхностная эрозия/смыв верхних почвенных горизонтов
- ВЭл: овражная эрозия / оврагообразование

ветровая эрозия почв
- Эп: утрата плодородного слоя почвы

биологическая деградация
- Бр: сокращение растительного покрова
3.8 Предотвращение и снижение деградации земель, или восстановление нарушенных земель
Укажите цель Технологии по отношению к деградации земель :
- предотвращение деградации земель
- снижение деградации земель
Пояснения:
Fruit tree plantations will potentially prevent land degradation in the long term by giving cover and strengthening soil structure by its roots.
4. Технические характеристики, мероприятия по практической реализации, вложения и стоимость
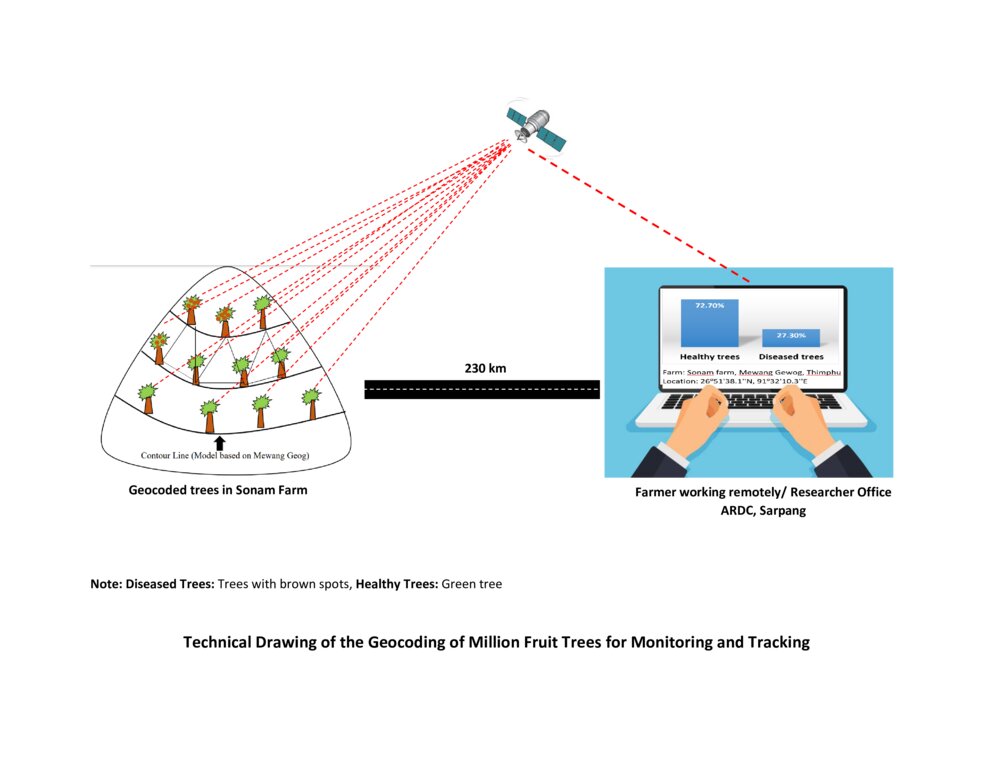
4.1 Технический рисунок, иллюстрирующий Технологию
Спецификация (пояснения к техническому рисунку):
The technical drawing represents the general method of million fruit tree plantation and geocoding done on each tree. It depicts how geocoding enables the researcher or farmer to remotely check the health of the trees using satellite data. ARDC stands for Agriculture Research and Development Center.
Автор:
Nima Dolma Tamang, Singye Dorji, Tshering Gyeltshen
Дата:
07/07/2023
4.2 Общая информация по необходимым вложениям и стоимости
Уточните, как рассчитывались затраты и вложения:
- на технологическую единицу
Укажите единицу:
No of Seedlings
Укажите единицы измерения (если необходимо):
8000 seedlings (Only in Mewang Geog)
другая/ национальная валюта (название):
Ngultrum (Bhutanese Currency)
Если это необходимо, укажите обменный курс от доллара США к местной валюте (например, 1 доллар США = 79,9 бразильского реала): 1 доллар США =:
82,62
Укажите среднюю дневную заработную плату наемных работников:
800
4.3 Мероприятия, необходимые для начала реализации
| Деятельность | Время (сессия) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Meeting between Gewog leaders and land users | NA |
| 2. | Identified a village for planation | NA |
| 3. | Identified households that wanted the seedings and number of seedlings | NA |
| 4. | Site identification | NA |
| 5. | Orchard layout | NA |
| 6. | Pit digging | NA |
| 7. | Plantation | March- April |
| 8. | Basin making | After planation |
| 9. | Geocoding | After one month of orchard establishment |
| 10. | Growth Tracking | After every six months |
Пояснения:
The above information is limited to only Mewang Gewog, Thimphu Dzongkhag.
4.4 Вложения и затраты, необходимые для начала реализации
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Desuup (Guardians of peace) - Volunteers | Person-days | 6,0 | |||
| Оплата труда | Farmers | Person-days | 10,0 | 800,0 | 8000,0 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Shovel | No. | 10,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Оборудование | crow-bar | No. | 5,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Оборудование | Spade | No. | 20,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Оборудование | GPS remote | No | 6,0 | 12000,0 | 72000,0 | |
| Оборудование | Tabs/ mobile phones | No. | 6,0 | 15000,0 | 90000,0 | |
| Посадочный материал | Apple | No. | 3500,0 | 70,0 | 245000,0 | |
| Посадочный материал | Walnut | No. | 1000,0 | 120,0 | 120000,0 | |
| Посадочный материал | Almond | No. | 500,0 | 120,0 | 60000,0 | |
| Посадочный материал | Peach | No. | 1000,0 | 70,0 | 70000,0 | |
| Посадочный материал | Pear | No. | 2000,0 | 70,0 | 140000,0 | |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Manure and fertillizers | Metric Tonnes | 16,0 | 1600,0 | 25600,0 | 100,0 |
| Общая стоимость запуска Технологии | 830600,0 | |||||
| Общие затраты на создание Технологии в долларах США | 10053,26 | |||||
Если землепользователем оплачено менее 100% затрат, укажите, кем покрывались остальные затраты:
Almost all the cost were covered by the Million Fruit Tree Project of Desuung National Service and Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock jointly.
Пояснения:
The total cost calculated is for planting and geocoding. The actual costs borne by land users are very minimal. The only cost the land users have to bear is labour cost and fertilizer cost. The high cost of the project is contributed mainly by seedling cost, GPS remote, tablets and mobile phones which was used during the marking position of fruit trees.
Cost for shovel spade and crowbar is not included as they are available at the farm and are reused.
4.5 Поддержание/ текущее обслуживание
| Деятельность | Сроки/ повторяемость проведения | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | Twice a year |
| 2. | Fertillizer application | Twice a year |
| 3. | Irrigation | Once a week |
| 4. | Replacement of dead plants | After 6 months from plantation |
| 5. | Growth tracking | After every six month |
Пояснения:
The information obtained are through verbal communication with the Agriculture Extension Officer of Mewang Gewog.
4.6 Стоимость поддержания/ текущего обслуживания ( в год)
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Weeding and fertilizer application | Per year | 4,0 | 1600,0 | 6400,0 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Irrigation | Litres | ||||
| Оплата труда | Geocoding | per plant | 8000,0 | |||
| Посадочный материал | Replacement of plants | per plant | 10,0 | 70,0 | 700,0 | |
| Общая стоимость поддержания Технологии | 7100,0 | |||||
| Общие затраты на поддержание Технологии в долларах США | 85,94 | |||||
Пояснения:
The geocoding was done by the Desuung volunteers. so, the exact costs cannot be deduced.
4.7 Наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат
Опишите наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат:
Most important factors affecting the costs are seedling and labour cost.
5. Природные и социально-экономические условия
5.1 Климат
Среднегодовое количество осадков
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1000 мм
- 1001-1500 мм
- 1501-2000 мм
- 2001-3000 мм
- 3001-4000 мм
- > 4000 мм
Укажите среднегодовое количество осадков (если известно), мм:
2076,00
Пояснения/ комментарии по осадкам:
The rainfall data for Mewang Gewog is not available. The provided data is for Thimphu Dzongkhag as Mewang Gewog is under Thimphu Dzongkhag (Gewog is one of the geographic units below Dzongkhag). Thimphu falls under a temperate region and experiences minimal rainfall compared to the other parts of Bhutan. Thimphu had the wettest month in July with 497 mm and experienced the least rainfall in December with 5 mm.
Укажите название соответствующей метеостанции:
National Center for Hydrology and Metoerology, Thimphu.
Агроклиматическая зона
There are six Agro-ecological Zones (AEZ) in Bhutan and the current place of study falls under warm temperate zone which occurs between 1,800 – 2,500 m. Rainfall is low but the temperature is moderately warm in summer with frost in winter.
5.2 Рельеф
Склоны (преобладающие):
- пологие (0-2%)
- покатые (3-5%)
- покато-крутые (6-10%)
- крутые (11-15%)
- очень крутые (16-30%)
- чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
- обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа:
- плато/ равнины
- гребни хребтов/холмов
- склоны гор
- склоны холмов
- подножья
- днища долин
Зона высотной поясности:
- 0-100 м над уровнем моря
- 101-500 м н.у.м.
- 501-1000 м н.у.м.
- 1001-1500 м н.у.м.
- 1501-2000 м н.у.м.
- 2001-2500 м н.у.м.
- 2501-3000 м н.у.м.
- 3001-4000 м н.у.м.
- > 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
Укажите, приурочено ли применение Технологии к специфическим условиям:
- в условиях выпуклого рельефа
Комментарии и дополнительные сведения по условиям рельефа/ топографии :
The area was characterized by a steep valley near the river with minimal slope as the valley widened.
5.3 Почвы
Средняя мощность почв:
- поверхностные (0-20 см)
- неглубокие (21-50 см)
- умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
- глубокие (81-120 см)
- очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта):
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
Гранулометрический состав (на глубине более 20 см):
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем горизонте:
- среднее (1-3%)
5.4 Доступность и качество воды
Доступность поверхностных вод:
средняя
Качество воды (без обработки):
исключительно для сельскохозяйственного использования (орошение)
Качество воды относится к:
поверхностные воды
Является ли солёность воды проблемой?
Нет
Происходят ли периодические затопления территории?
Нет
Комментарии и дополнительная информация по качеству и количеству воды:
The availability of water in Mewang Gewog was a concern since a decade ago. Irrigation water was not enough for every farmers which resulted in delayed paddy plantation.
5.5 Биоразнообразие
Видовое разнообразие:
- низкое
Разнообразие местообитаний:
- средняя
Комментарии и дополнительная информация по биоразнообразию:
The species of flora and fauna diversity cannot be quantified under "high" as per the field observation. The area was surrounded by coniferous forest which generally has low biodiversity.
5.6 Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Осёдлый или кочевой:
- Осёдлый
Рыночная ориентация производства:
- смешанный (натуральный / коммерческий)
Доходы из других источников:
- 10-50% всех доходов
Относительный уровень достатка:
- средний
Индивидуальное или коллективное хозяйство:
- частное/ домовладение
Уровень механизации:
- механизировано/ есть автотранспорт
Пол:
- женщины
Возраст землепользователей:
- средний возраст
Укажите другие важные характеристики землепользователей:
The majority of the land users who were part of the Geocoding of million fruit plantation had already established apple orchards.
5.7 Средняя площадь земель, используемых землепользователями с применением Технологии
- < 0,5 га
- 0,5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1000 га
- 1000-10000 га
- > 10000 га
Считается ли это мелким, средним или крупным хозяйством (по местным масштабам)?
- среднего размера
Пояснения:
An average land holding capacity for Bhutanese household as per the Land Act is 3 acres. The land holding that exceeds 3 acres are categorized in large scale in Bhutanese context.
5.8 Собственность на землю, права на земле- и водопользование
Землевладелец:
- индивидуальная, оформленная в собственность
Право землепользования:
- аренда
- индивидуальное
Право водопользования:
- общинное (контролируемое)
Права на землепользование основаны на традиционной правовой системе?
Да
5.9 Доступ к базовым услугам и инфраструктуре
медицинское обслуживание:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
образование:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
технические консультации:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
занятость (вне хозяйства):
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
рынки:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
электроснабжение:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
транспорт и дорожная сеть:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
водоснабжение и канализация:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
финансовые услуги:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
Internet:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
Пояснения:
The drinking water is insufficient as some households face scarcity of drinking water.
6. Воздействия и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Технологии УЗП в пределах территории ее применения
Социально-экономическое воздействие
Продуктивность
производство сельскозяйственных культур
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The technology aids in the monitoring and improves health and ease management of the already established orchard. Therefore, it indirectly increases crop production.
качество урожая
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Remote or constant monitoring ensures timely management to prevent biotic and abiotic factors deteriorate the crop quality.
производство кормов
качество кормов
риск потери продуктивности
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Geocoding enables land user to determine potential risk so that the land user can use appropriate methods to prevent crop failure.
разнообразие продукции
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The technology is not directly related to the product diversity. However, it provides data on existing fruit tree diversity so that the land user can plan and plant different fruit trees based on the market need which indirectly increases diversity.
площадь, используемая для производства продукции
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Geocoding enables the land user to remotely view the cropped area and the area where the crop failed (could be due to dying of the seedlings/diseased). It enables the land user to narrow their focus on the specific area, learn about the issues causing the crop loss, provide appropriate management, and conduct plantation in that area which indirectly increases production area.
Доступность и качество воды
доступность оросительных вод
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Due to increased production area with no increase in the quantity of irrigation water, water availability is likely to reduce.
потребность в оросительной воде
Комментарий/ пояснения:
There is increased demand for irrigation water for new plantations. However, with the use of technology land users can monitor the water requirement and use efficiently based on the need of the tree whereby the land users can avoid watering the trees that require less water and provide to those that require more water.
Доходы и затраты
сельскохозяйственные издержки
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Minimal increase in expenses on agriculture inputs as planting materials (except manure) were provided to the land users for free of cost.
доходы хозяйства
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Once the fruit trees starts bearing fruits, income is expected to increase.
разнообразие источников дохода
Комментарий/ пояснения:
It adds to farmers sources of income other than vegetable and dairy product sale.
экономическое неравенство
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The technology is expected to reduce economic disparity by providing equal opportunity for the land users to generate income.
объем работ
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Workload for the project implementors or land users are significantly reduced as they need not go to the actual site to determine the progress of the Million Fruit Trees Plantation Project.
Социальное и культурное воздействие
продовольственная безопасность/ самообеспечение
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The technology indirectly aids in the increased production making an individual land user and the nation self-sufficient in fruits.
возможности отдыха и рекреации
Комментарий/ пояснения:
With reduced workload, land users can engage in recreational activities.
знания в области УЗП/ деградации земель
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The technology will enable the project implementors to determine specific knowledge gaps and provide training in that particular field to the land users. Improving knowledge of both project implementors and land users.
положение социально и экономически уязвимых групп населения
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Land users willing to be involved in fruit tree plantation are supported without discrimination of their social status or economic background and geocoding services are provided. This leads to the improved situation of socially and economically disadvantaged groups.
Экологическое воздействие
Водный цикл/ поверхностный сток
количество воды
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The total water quantity remains same. However, the available water per tree or sapling is reduced.
поверхностный сток
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Due to the absorption of water by the roots of the fruit trees, surface run-off is decreased.
испарение
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Evaporation will be decreased due to an increase in the vegetation cover from the plantation of the fruit trees.
Почвы
влажность почв
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Slight increase in the soil moisture in long run due to addition of soil organic matter and monitored irrigation.
почвенный покров
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The technology enhances easy monitoring of the trees and encourages increased soil cover.
утрата почв
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The technology enhances soil cover reducing the soil loss from erosion.
круговорот/ восполнение питательных веществ
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Geocoding enables the land user to have overview of the nutrient content of the production area aiding land users to add nutrient based on the need.
почвенное / подземное органическое вещество/ углерод
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Generally, there will be an increase in the soil organic matter due to an increase in production area and management practice such as the addition of manures by the land user.
Биоразнообразие: растительность, животный мир
Растительный покров
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Increase due to the scheduled irrigation applied to the fruit trees.
биомасса/ содержание углерода в надземной биомассе
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Slight increase due to proper management and care provided to the orchard.
разнообразие фауны
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Animal diversity in the case of pollinators such as bees increases as the fruit trees mature and start flowering.
полезные виды
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Beneficial species such as bees are attracted to the orchards.
борьба с вредителями/ болезнями
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Pest and diseases control improves with the use of remote monitoring facilitated by this technology.
Климат и снижение риска стихийных бедствий
оползни и селевые потоки
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Once the fruit trees establish themselves, landslides can be reduced significantly due to vegetation cover.
выбросы углекислого газа и парниковых газов
Комментарий/ пояснения:
This technology could potentially reduce greenhouse gas as trees utilize carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
скорость ветра
Комментарий/ пояснения:
In the long run, a well-established orchard can act as a windbreak and reduce wind velocity and damage it poses to the property.
микроклимат
Комментарий/ пояснения:
An orchard can act as a micro-climate harbouring many plants and insect species.
6.2 Влияние Технологии за пределами территории ее применения
доступность воды
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Fruit trees require irrigation which reduces the availability of water for other purposes.
воздействие парниковых газов
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Having a land cover with vegetation compared to barren land reduces greenhouse gases.
6.3 Подверженность и чувствительность Технологии УЗП к постепенным изменениям климата и экстремальным погодным явлениям/ стихийным бедствиям, связанным с изменением климата (в понимании землепользователей)
Постепенное изменение климата
Постепенное изменение климата
| Сезон | увеличение или уменьшение | Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| среднегодовые температуры | увеличилось | очень хорошо | |
| сезонные температуры | лето | увеличилось | очень хорошо |
| среднегодовое количество осадков | увеличилось | очень хорошо | |
| сезонное количество осадков | лето | снизилось | очень хорошо |
Экстремальные явления, связанные с изменением климата (стихийные бедствия)
Погодные стихийные бедствия
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| местный град | очень хорошо |
Биологические стихийные бедствия
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| эпидемии | очень хорошо |
Пояснения:
The technology copes very well with gradual climate change because it sends rapid messages to farmers on actions to take (e.g., concerning pests and diseases). In a way it’s a form of early warning systems (EWS).
6.4 Анализ эффективности затрат
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с первоначальными вложениями (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
отрицательно
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с текущими расходами по поддержанию технологии (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
влияние незаметно
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Пояснения:
Although the initial establishment of the orchard is costly considering the labour charge, it is expected to have positive income and impact once the fruit trees start bearing.
6.5 Внедрение Технологии
- > 50%
Если возможно, дайте количественную характеристику (число домохозяйств и/или площадь применения):
Total 8000 fruit trees are planted in the five Chiwogs (third level administrative division under Gewog) under Mewang Gewog.
Среди применяющих Технологию землепользователей, какова доля лиц, применяющих её по собственной инициативе, т.е. без какого-либо материального стимулирования со стороны?
- 0-10%
Пояснения:
Almost all those who adopted the technology are funded by the government.
6.6 Адаптация
Была ли Технология УЗП изменена в недавнее время с целью адаптации к меняющимся условиям среды?
Нет
6.7 Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности Технологии
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
| 1. Precision Mapping: Geocoding allows for accurate mapping and identification of fruit trees. By assigning specific geographic coordinates to each tree, it becomes easier to locate and monitor individual trees or orchards. |
| 2. Efficient Resource Allocation: Geocoding helps optimize resource allocation by providing information on tree density and distribution. Land users can identify areas with high fruit tree concentrations and strategically allocate resources such as labour, water, fertilizers, and pesticides, leading to improved productivity and reduced costs. |
| 3. Data-driven Decision Making: Geocoded data on fruit trees can be analyzed to gain insights into their distribution patterns, growth rates, and health status. This information enables land users, researchers, and policymakers to make informed decisions regarding fruit tree cultivation, pest control, and disease management. |
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
| 1. Conservation and Biodiversity Analysis: Geocoded fruit tree data aids in the conservation and analysis of biodiversity. By mapping the locations of different fruit tree species, experts can assess the distribution and abundance of specific varieties, identify endangered local or traditional landraces varieties, and develop strategies for their preservation. |
| 2. Targeted Marketing and Distribution: Geocoded fruit tree data facilitates targeted marketing and distribution strategies. By understanding the location of fruit trees and their yields, producers can identify potential markets and plan transportation logistics more effectively, minimizing waste and ensuring timely delivery to consumers. |
6.8 Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски Технологии и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению землепользователей | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Geocoding large numbers of fruit trees can be a time-consuming and resource-intensive task, particularly when manual processes are involved. It may require extensive fieldwork and manual data entry, making it impractical or costly for large-scale fruit tree inventories. | |
| Privacy Concerns: Geocoding fruit trees raises privacy concerns, particularly when tree locations are associated with specific individuals or properties. Care must be taken to ensure that privacy is respected and sensitive information is appropriately handled | An updated and secured security-protected website can be used. |
| Lack of knowledge of geocoding by the farmers. | Provide awareness trainings |
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| The higher expense of the geocoding in terms of labour cost for geo-coding | Train land users on geocoding, instead of using trained professionals. |
| Difficult to constantly update information on time. |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/ источники информации
- выезды на места, полевые обследования
The information documented was from the field visit to orchards near the RNR center.
- опросы специалистов/экспертов по УЗП
The information collected are from first-hand interview with the Agriculture Extension Officer who was engaged fully during the implementation of the technology.
Когда были собраны данные (на местах)?
07/07/2023
7.2 Ссылки на опубликованные материалы
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
De-suung National Service (DNS). (n.d.). Million Fruit Trees Plantation
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
https://desuung.org.bt/25978-2/#:~:text=In%20order%20to%20monitor%20the,from%20the%20date%20of%20plantation.
7.3 Ссылки на соответствующую онлайн-информацию
Название/ описание:
Million Fruit Trees Plantation Initiative launched
Адрес в сети Интернет:
http://www.bbs.bt/news/?p=166763
Название/ описание:
Kuensel. (2022). Million Fruit Trees Plantation Initiative launched. Thimphu.
Адрес в сети Интернет:
Website: https://kuenselonline.com/414000-fruit-trees-planted-in-45-days/
Название/ описание:
Geocoding of trees from street addresses and street-level images
Адрес в сети Интернет:
https://www.fs.usda.gov/psw/publications/vandoorn/psw_2020_vandoorn001_laumer.pdf
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки
Нет ссылок
Модули
Нет модулей