Conversion of conventional monoculture farmland into a food forest [Израиль]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Tom Cohen
- Редактор: –
- Рецензенты: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Bethlehem of Galilee Food Forest
technologies_7674 - Израиль
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Технологии
Специалист по УЗП:
Brook Anna
University of Haifa
Израиль
землепользователь:
Bethlehem of Galilee Food Forest
Израиль
Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
University of Haifa (uhaifa)1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование данных, собранных ВОКАТ
Составитель и ответственный(-ые) специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.4 Декларация по устойчивости описываемой Технологии
Вызывает ли описанная здесь Технология проблемы деградации земель настолько, что ее нельзя назвать природосберегающей?
Нет
Пояснения:
This intervention is explicitly designed to reverse and restore previously degraded soils (monoculture exhaustion, fertility decline, low biodiversity).
2. Описание Технологии УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Технологии
Определение Технологии:
Converting conventional monoculture farmland into a food forest-based agroforestry system restores soil health, increases vegetation cover, enhances biodiversity while diversifying production. The intervention improves soil organic matter and ecological resilience through multi-storey planting, reduced soil disturbance, and nature-based land management.
2.2 Подробное описание Технологии
Описание:
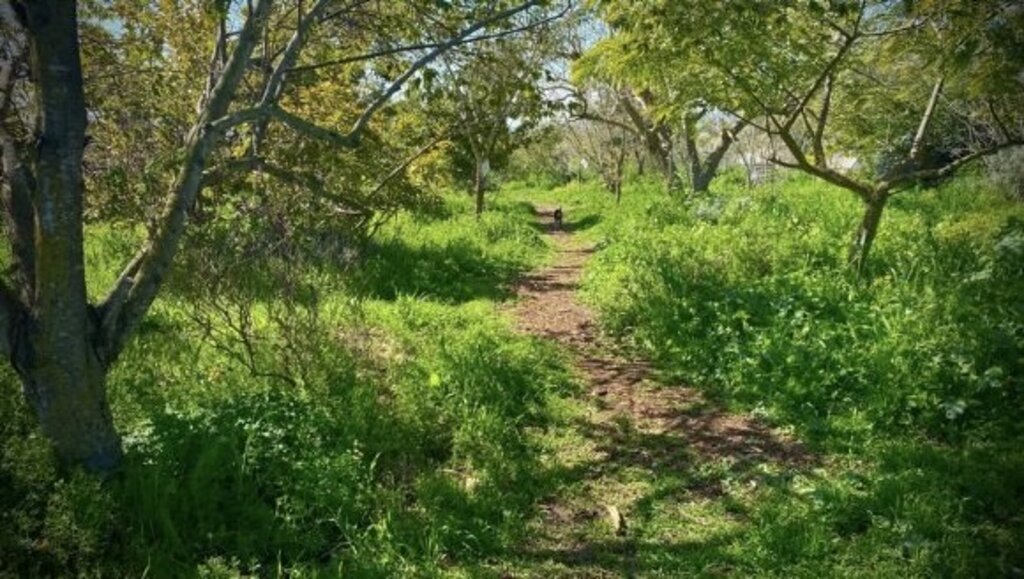
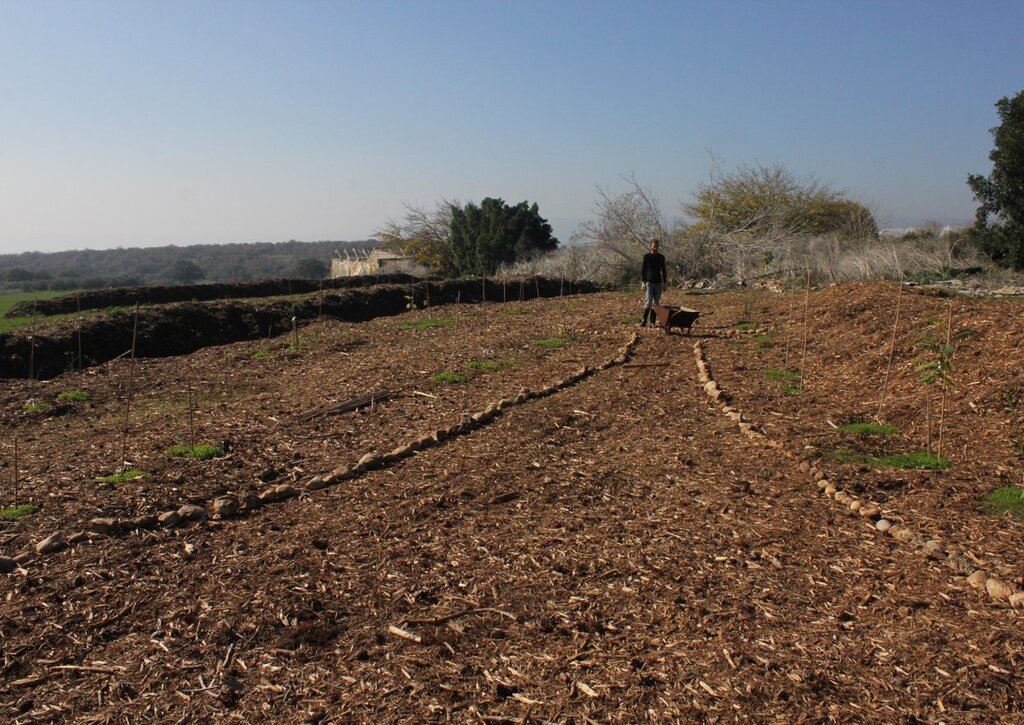
The development of a “food forest” was in response to visible soil degradation caused by years of wheat-based monoculture in Bethlehem of Galilee. The previous land use consisted of annual wheat production, tractor-powered deep ploughing, and routine use of herbicides and pesticides. Over time, these practices depleted soil organic matter, reduced microbial activity, and increased vulnerability to erosion, compaction, and moisture loss. The current food forest, covering approximately 1.5 acres (0.6 hectare), represents a transformative shift from this intensive, extractive system toward a sustainable, perennial, multi-strata agroforestry model.
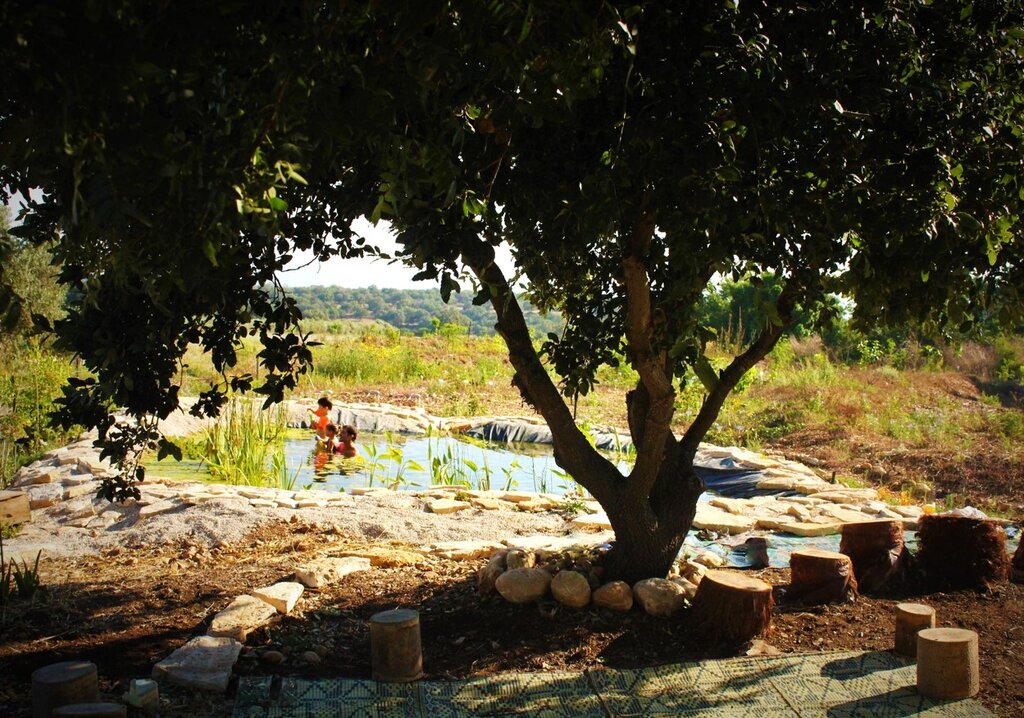
The primary purpose of this site is research and education. It is not intended to be a commercial enterprise, but to demonstrate principles and practices of sustainable land management. The income generated is not from crops but from research grants, workshops and community activities.
The site has been under continuous restoration for approximately eight years, during which it has gradually developed into a multi-layered food forest. The upper canopy includes species such as ficus, tipa, mulberry, pecan, plane trees, and nitrogen-fixing “ice-cream bean” (Inga edulis), which together generate shade, biomass, and structural diversity. The productive mid-storey contains fruit-bearing species including lemon, plum, pomegranate, avocado, and additional deciduous trees. Beneath these layers, aromatic shrubs such as lavender and rosemary provide perennial cover, habitat complexity, and year-round biomass production. A dedicated lower layer supports seasonal vegetables: carrots, radishes, turnips, lettuces and other greens, interplanted within tree alleys and cultivated using organic methods.
Production follows a diversified model typical of food forests. Tree crops currently yield modest but consistent quantities of lemons, plums, mulberries, pomegranates, and herbs, primarily for consumption by visitors, volunteers, and workers on site rather than large-scale commercial sale. The adjoining vegetable-growing area produces additional crops for small-scale marketing, providing a modest revenue stream while maintaining ecological integrity. As the system is still maturing, productive output is expected to increase over the coming years.
The project is privately managed by a couple in their thirties, who own and oversee all aspects of the site. Labour requirements were most intensive during the establishment phase of planting, mulching, earth-shaping, and infrastructure setup. As the food forest enters a more stable successional stage, labour demands have gradually decreased, with current activities centred on pruning, biomass recycling, vegetable cultivation, and occasional enrichment planting. No chemical inputs are applied at any stage.
Irrigation was originally supported by a drip system installed to establish young trees and early perennial layers. Today, irrigation needs have significantly decreased due to higher soil organic matter, increased shade, and improved microclimate regulation. Drip irrigation is now used only minimally and mainly within the annual vegetable plots, while most perennial components rely primarily on natural rainfall.
Overall, this food forest demonstrates a replicable nature-based solution for Mediterranean environments, showcasing how degraded wheat monoculture fields can be restored into resilient, biodiverse, and ecologically functional agroforestry systems. The long-term transition highlights substantial gains in soil health, water retention, and landscape diversity, while supporting small-scale production and community-oriented engagement.
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Технологию
2.5 Страна/ регион/ места, где применяется Технология, информация о которых собрана в данной Анкете
Страна:
Израиль
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Galilee
Более точная привязка места:
Bethlehem of Galilee
Охарактеризуйте пространственное распространение Технологии :
- равномерно-однородное применение на определенной площади
Если технология равномерно занимает территорию, укажите площадь покрытия (в км2):
0,01
Если точная область неизвестна, укажите приблизительную площадь:
- < 0,1 км2 (10 га)
Технология применяется на ООПТ?
Нет
Map
×2.6 Сколько лет применяется данная Технология
Год начала реализации:
2017
Если год начала применения Технологии достоверно неизвестен, дайте примерную оценку:
- менее 10 лет назад (недавняя)
2.7 Внедрение Технологии
Укажите, как именно Технология УЗП была внедрена:
- как инновация (инициатива) землепользователей
- в качестве научного/ полевого эксперимента
- через проекты/ внешнее вмешательство
Пояснения (тип проекта и т.д.):
The landowners developed the site as part of a holistic environmental vision and continue to refine it through ongoing learning, experimentation, and renewal. They actively initiate collaborations with research institutions in Israel and abroad to support long-term monitoring of the site and to advance the food-forest practice within a scientific and evidence-based framework.
3. Классификация Технологии УЗП
3.1 Основные цели и задачи реализации Технологии
- снижение или предотвращение деградации земель, восстановление нарушенных земель
- сохранение экосистем
- сохранение/ повышение биоразнообразия
- адаптация к изменению климата / экстремальным погодным явлениям и их последствиям
- создание благоприятных социальных условий
3.2 Текущий(-ие) тип(-ы) землепользования на территории, где применяется Технология
Комбинированное землепользование в пределах одной и той же земельной единицы:
Да
Укажите сочетания типов землепользования (посевы / пастбища / деревья):
- Агролесоводство

Пахотные угодья и плантации
- Однолетние культуры
- Древесные и кустарниковые культуры
Ежегодный урожай - Уточните культуры:
- бобовые - зеленый горошек
- лекарственные/ ароматические / пестицидные растения и травы
- овощи - листовые овощи (салаты, капуста, шпинат, другие)
- овощи - корнеплоды (морковь, лук, свекла, другие)
Древесные и кустарниковые культуры - Уточните культуры:
- авокадо
- цитрусовые
- инжир
- семечковые плоды (яблоки, груши, айва и т. д.)
- косточковые плоды (персик, абрикос, вишня, слива и т. д.)
- орехи (Бразильский орех, фисташки, грецкие орехи, миндаль и т. д.)
Число урожаев за год:
- 3
Поясните:
Up to three for the fastest growing crops
Применяются ли посевы в междурядьях?
Да
Если да, укажите, какие посевы применяются:
The whole farm forest embodies intercropping throughout its multi-strata structure
Применяется ли севооборот?
Да
Если да, укажите:
Various annual crops as described above - and an adaptive succession strategy

Леса/ лесистая местность
- Лесопосадки, облесение
Лесопосадки. облесение: Укажите происхождение и состав видов:
- Смешанные культуры
Тип лесонасаждений, облесение:
- плантация умеренного континентального леса
- Ficus, Tipu (Tipuana tipu), Plane tree (Platanus spp.), Sissoo (Dalbergia sissoo), Ice-cream bean
Являются ли указанные выше деревья лиственными или вечнозелеными?
- смешанные лиственные / вечнозеленые
Продукции и услуги:
- Плоды и орехи
- Другие продукты леса
- Природоохранные/ защитные
- Рекреация/ туризм
3.3 Изменилось ли использование земель в связи с внедрением Технологии?
Изменилось ли использование земель в связи с внедрением Технологии?
- Да (Пожалуйста, заполните нижеприведенные вопросы относительно использования земель до внедрения Технологии)
Комбинированное землепользование в пределах одной и той же земельной единицы:
Нет

Пахотные угодья и плантации
- Однолетние культуры
Ежегодный урожай - Уточните культуры:
- зерновые культуры - пшеница (яровая)
Годовая система земледелия:
Пшеница или аналогичный севооборот сенокос / пастбища
Применяются ли посевы в междурядьях?
Нет
Применяется ли севооборот?
Да
Если да, укажите:
Occasionally (see above)
3.4 Водоснабжение
Обеспеченность водой участков, где реализуется Технология :
- сочетание богарных и орошаемых земель
Пояснения:
Irrigation was originally supported by a drip system installed to establish young trees and early perennial layers. Today, irrigation needs have significantly decreased due to higher soil organic matter, increased shade, and improved microclimate regulation. Drip irrigation is now used only minimally and mainly within the annual vegetable plots, while most perennial components rely primarily on natural rainfall.
3.5 Категория УЗП, к которой относится Технология
- агролесоводство
- Улучшение почвенного/ растительного покрова
- Минимальная обработка почв
3.6 Мероприятия УЗП, выполняемые в рамках Технологии

Мероприятия с использованием растительности
- Р1: Древесный и кустарниковый покров
- Р2: Злаковые и многолетние травянистые растения

управленческие мероприятия
- У1: Смена типа землепользования
- У2: Изменение формы/ интенсивности хозяйствования
- У5: Регулирование/ изменение видового состава
3.7 Основные проблемы деградации земель, на решение которых направлена Технология

водная эрозия почв
- ВЭп: поверхностная эрозия/смыв верхних почвенных горизонтов

ухудшение химических свойств почв
- Хп: Снижение плодородия и уменьшение содержания органического вещества (вызванное не эрозией, а другими причинами)
- Хс: засоление/ подщелачивание

ухудшение физических свойств почв
- Фу: уплотнение
- Фп: запечатывание почв
- Фп: сработка органических горизонтов почв, оседание поверхности

биологическая деградация
- Бр: сокращение растительного покрова
- Бм: утрата местообитаний
- Бк: сокращение количества биомассы
- Бв: потеря природного разнообразия
Пояснения:
For this pilot, the technology primarily addresses soil degradation (chemical + physical + biological) that resulted from long-term monoculture and herbicide-based management.
3.8 Предотвращение и снижение деградации земель, или восстановление нарушенных земель
Укажите цель Технологии по отношению к деградации земель :
- снижение деградации земель
- восстановление/ реабилитация нарушенных земель
4. Технические характеристики, мероприятия по практической реализации, вложения и стоимость
4.1 Технический рисунок, иллюстрирующий Технологию
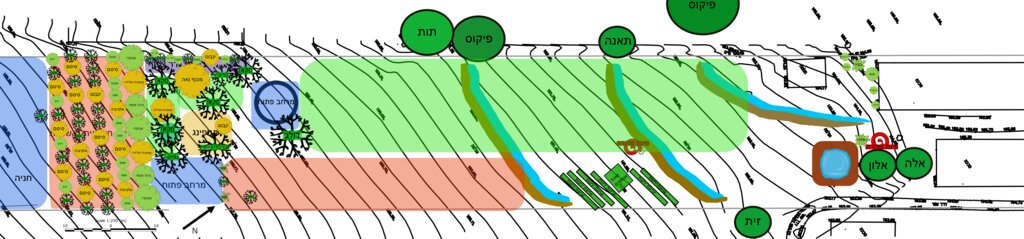
Спецификация (пояснения к техническому рисунку):
The general site plan (above) illustrates the full spatial organization of the food forest, structured into clearly defined functional zones that together create a balanced ecological and productive landscape (Note: original plan reproduced with captions in Hebrew). The outer perimeter consists of a protective tree belt designed to provide wind buffering, habitat continuity, and microclimate regulation. Inside this perimeter lies a series of densely planted clusters of mixed-species trees and support plants, forming the core forested zones of the design. These clusters contain a combination of canopy species, fruit trees, nitrogen-fixing support species, and understory elements arranged to promote ecological interactions and long-term resilience. Several open areas are intentionally integrated throughout the site, providing space for circulation, light penetration, future expansion, and community activities. The plan also includes a designated agricultural strip for annual vegetable production, strategically placed to benefit from the moderated microclimate created by the surrounding tree layers. Additional functional elements such as a compost area, shaded seating or gathering points, and access paths appear throughout the design, supporting both maintenance and educational use. Overall, the plan demonstrates a holistic integration of productive, ecological, and social spaces, emphasizing diversity, spatial layering, and regenerative land-use principles.
Автор:
Nitzan Betzer
Дата:
01/06/2017
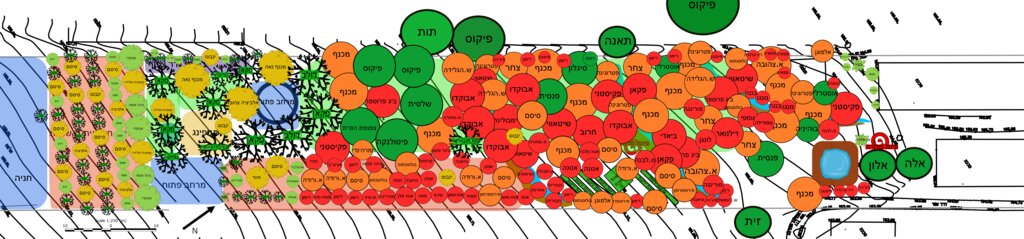
Спецификация (пояснения к техническому рисунку):
The planting plan (below) illustrates the full structural design of the food forest, showing a diverse mixture of perennial species arranged according to ecological function and spatial layout (Note: original plan reproduced with captions in Hebrew). Each color on the map represents a different botanical or functional category. The green circles indicate the major canopy and shade-providing trees that form the upper layer of the system. The red circles mark the fruit-bearing species distributed across the plot, including pomegranate, avocado, fig, loquat, mango, mulberry and others, representing the primary productive component of the mid-storey. The orange circles correspond to nitrogen-fixing trees and shrubs, strategically positioned to enrich soil fertility and support surrounding species through natural nutrient cycling. The yellow circles mark ornamental or habitat-supporting species that enhance biodiversity, microclimate regulation and ecological resilience. Together, these categories create a multi-layered mosaic in which canopy, fruit, support species and habitat elements interweave across the site. The design also includes designated open areas, compost space, perimeter rows and an agricultural strip for annual vegetables, demonstrating an intentional balance between ecological restoration, food production and functional zoning.
Автор:
Nitzan Betzer
Дата:
01/06/2017
4.2 Общая информация по необходимым вложениям и стоимости
Уточните, как рассчитывались затраты и вложения:
- на площадь, где применяется Технология
Укажите размер и единицу площади:
1.5 acres
Если вы используете местные системы измерения, укажите коэффициент пересчета на один гектар (например, 1 га = 2,47 акров): 1 га =:
1 acre = 0.4 hectares
Укажите денежные единицы, использованные для подсчета затрат:
- Доллары США
Укажите среднюю дневную заработную плату наемных работников:
158.2
4.3 Мероприятия, необходимые для начала реализации
| Деятельность | Время (сессия) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Initial site assessment and mapping of soil condition and exposure | Late winter / early spring |
| 2. | Discontinuation of tillage and herbicide applications | Immediately prior to establishment |
| 3. | Soil preparation without deep tillage (light loosening, mulching base layer) | Early spring |
| 4. | Planting of trees in primary layout (skeleton layer) | Spring |
| 5. | Planting of shrubs and understory companion species | Late spring / early summer |
| 6. | Installation of organic mulch cover to protect soil and retain moisture | After planting (early summer) |
| 7. | Enrichment planting / filling gaps with additional groundcover species | Late summer / following spring |
| 8. | Protection of young trees/shrubs if needed (guards, shading, temporary watering) | First growing season |
| 9. | Establishment of biomass cycling (chop-and-drop, composting on-site) | After vegetation takes root |
| 10. | Transition into maintenance phase (reduced intervention, natural succession) | Once canopy begins forming |
4.4 Вложения и затраты, необходимые для начала реализации
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Manual labour | Person-days | 139,0 | 158,2 | 21989,8 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Tools and maintenance equipment | 1,0 | 5000,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 | |
| Оборудование | Tractor (for construction) | 1,0 | 7200,0 | 7200,0 | 100,0 | |
| Посадочный материал | Seedlings, cuttings, and seeds | 1,0 | 14000,0 | 14000,0 | 100,0 | |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Compost | 1,0 | 10500,0 | 10500,0 | 100,0 | |
| Строительные материалы | Irrigation system | 1,0 | 14500,0 | 14500,0 | 100,0 | |
| Строительные материалы | Pruned biomass mulch | 1,0 | 6500,0 | 6500,0 | 100,0 | |
| Общая стоимость запуска Технологии | 79689,8 | |||||
| Общие затраты на создание Технологии в долларах США | 79689,8 | |||||
Если землепользователем оплачено менее 100% затрат, укажите, кем покрывались остальные затраты:
Land user bore all costs: but note the primary purpose of this site is research and education. It is not intended to be a commercial enterprise, but to demonstrate principles and practices of sustainable land management. The income generated is not from crops but from research grants, workshops and community activities.
Пояснения:
No chemical fertilizers or pesticides are used; fertilization is based solely on compost
4.5 Поддержание/ текущее обслуживание
| Деятельность | Сроки/ повторяемость проведения | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mulching with organic biomass (leaf litter, pruning residues, woodchips, etc.) | 2–3 times per year, mainly after rainy season and mid-summer |
| 2. | Selective pruning of trees and shrubs to maintain structure and light balance | Annually / as needed (late winter or autumn) |
| 3. | Enrichment planting and succession planting of understorey species | Seasonally, as ecosystem matures or gaps appear |
| 4. | Weeding by ecological suppression (groundcover strengthening) rather than removal | Continuous, low-intensity maintenance |
| 5. | Soil moisture conservation (biomass renewal / occasional supportive watering in drought years) | Seasonally during dry periods (as needed) |
| 6. | Monitoring soil condition and vegetation health | Ongoing, at least once per season |
| 7. | Replacement of failed or weak young plants | Annually during early growth seasons |
| 8. | Maintenance of biodiversity guilds / companion planting structure | Continuous, adaptive to natural succession |
4.6 Стоимость поддержания/ текущего обслуживания ( в год)
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Manual labour | Person-days | 110,0 | 158,2 | 17402,0 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Equipment renewal and maintenance | 1,0 | 5000,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 | |
| Посадочный материал | Cuttings and seeds | 1,0 | 4000,0 | 4000,0 | 100,0 | |
| Другие | Water bills | 1,0 | 5500,0 | 5500,0 | 100,0 | |
| Другие | Products selling kits | 1,0 | 2000,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 | |
| Общая стоимость поддержания Технологии | 33902,0 | |||||
| Общие затраты на поддержание Технологии в долларах США | 33902,0 | |||||
Пояснения:
The establishment costs refer to the initial food forest area of approximately 1.5 acres, while the annual maintenance costs refer to the forest in its current state, covering about 3 acres. Land user bore all costs: but note that the primary purpose of this site is research and education. It is not intended to be a commercial enterprise, but to demonstrate principles and practices of sustainable land management. The income generated is not from crops but from research grants, workshops and community activities.
4.7 Наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат
Опишите наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат:
The most significant cost factor, both during establishment and ongoing maintenance, is labour. All work is carried out manually using hand tools, and apart from the initial establishment phase, no heavy machinery is used
5. Природные и социально-экономические условия
5.1 Климат
Среднегодовое количество осадков
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1000 мм
- 1001-1500 мм
- 1501-2000 мм
- 2001-3000 мм
- 3001-4000 мм
- > 4000 мм
Укажите название соответствующей метеостанции:
The climatic information for the food forest site was obtained from two sources: official data provided by the Israel Meteorological Service (IMS) and on-site measurements collected through a dedicated rain gauge installed as part of the research infrastructure. Together, these sources provide accurate local rainfall and climate monitoring for the plot.
Агроклиматическая зона
- Умеренно-влажная
5.2 Рельеф
Склоны (преобладающие):
- пологие (0-2%)
- покатые (3-5%)
- покато-крутые (6-10%)
- крутые (11-15%)
- очень крутые (16-30%)
- чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
- обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа:
- плато/ равнины
- гребни хребтов/холмов
- склоны гор
- склоны холмов
- подножья
- днища долин
Зона высотной поясности:
- 0-100 м над уровнем моря
- 101-500 м н.у.м.
- 501-1000 м н.у.м.
- 1001-1500 м н.у.м.
- 1501-2000 м н.у.м.
- 2001-2500 м н.у.м.
- 2501-3000 м н.у.м.
- 3001-4000 м н.у.м.
- > 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
Укажите, приурочено ли применение Технологии к специфическим условиям:
- не имеет значения
5.3 Почвы
Средняя мощность почв:
- поверхностные (0-20 см)
- неглубокие (21-50 см)
- умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
- глубокие (81-120 см)
- очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта):
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
Гранулометрический состав (на глубине более 20 см):
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем горизонте:
- низкое (< 1%)
5.4 Доступность и качество воды
Уровень грунтовых вод:
5-50 м
Доступность поверхностных вод:
недостаточны/ отсутствуют
Качество воды (без обработки):
исключительно для сельскохозяйственного использования (орошение)
Качество воды относится к:
одновременно грунтовые и поверхностные воды
Является ли солёность воды проблемой?
Нет
Происходят ли периодические затопления территории?
Нет
5.5 Биоразнообразие
Видовое разнообразие:
- низкое
Разнообразие местообитаний:
- низкое
Комментарии и дополнительная информация по биоразнообразию:
Both species diversity and habitat diversity have transformed due to the establishment of the food forest, and are now both high. This is a very agrobiodiverse system.
5.6 Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Осёдлый или кочевой:
- Осёдлый
Рыночная ориентация производства:
- натуральное хозяйство (самообеспечение)
Доходы из других источников:
- > 50% всех доходов
Относительный уровень достатка:
- средний
Индивидуальное или коллективное хозяйство:
- частное/ домовладение
Уровень механизации:
- ручной труд
Пол:
- женщины
- мужчины
Возраст землепользователей:
- средний возраст
5.7 Средняя площадь земель, используемых землепользователями с применением Технологии
- < 0,5 га
- 0,5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1000 га
- 1000-10000 га
- > 10000 га
Считается ли это мелким, средним или крупным хозяйством (по местным масштабам)?
- мелкое
Пояснения:
The land user manages approximately 2–5 hectares in total, of which a portion is undergoing transition into a food forest system; this is considered small-scale in the local agricultural context
5.8 Собственность на землю, права на земле- и водопользование
Землевладелец:
- индивидуальная, оформленная в собственность
Право землепользования:
- индивидуальное
Право водопользования:
- индивидуальное
Права на землепользование основаны на традиционной правовой системе?
Нет
5.9 Доступ к базовым услугам и инфраструктуре
медицинское обслуживание:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
образование:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
технические консультации:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
занятость (вне хозяйства):
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
рынки:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
электроснабжение:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
транспорт и дорожная сеть:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
водоснабжение и канализация:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
финансовые услуги:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
6. Воздействия и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Технологии УЗП в пределах территории ее применения
Социально-экономическое воздействие
Доходы и затраты
сельскохозяйственные издержки
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Agricultural input expenses are very limited in this system. Since the site operates as a food forest rather than a conventional agricultural plot, nearly no external inputs are purchased. The management relies on ecological processes, on-site biomass, mulching, and manual care. Inputs are therefore minimal and do not reflect commercial-scale agricultural expenditure.
разнообразие источников дохода
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The plot was originally managed as a monoculture field that depended economically on agricultural production. Today, the food forest operates on a completely different model: its income is derived primarily from research activities, educational programs, workshops, and community engagement. Economic sustainability is no longer based on agricultural yield, as crop production is not the financial foundation of the site anymore.
Социальное и культурное воздействие
культурные возможности
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The food forest contributes significantly to cultural opportunities in the area. It serves as a community-oriented space that hosts educational events, workshops, volunteer activities, and gatherings focused on sustainability and ecological awareness. The site fosters cultural exchange, strengthens community cohesion, and provides a shared environment for learning, creativity, and connection to nature.
местное самоуправление
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Note: The food forest strengthens community institutions by collaborating with local educational programs, volunteer groups, and research initiatives. It provides a stable platform for schools, community organizations, and environmental groups to conduct activities, thereby reinforcing their role in community life and expanding their capacity for outreach and engagement.
знания в области УЗП/ деградации земель
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The food forest contributes to improved SLM and land-degradation knowledge by serving as a living demonstration site where restoration practices can be observed, tested, and monitored over time. It provides real-world evidence on soil recovery, biodiversity enhancement, and regenerative management, supporting both scientific research and practical learning for land users, students, and professionals.
Экологическое воздействие
Водный цикл/ поверхностный сток
поверхностный сток
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The food forest reduces surface runoff through continuous vegetative cover, increased soil organic matter, and improved infiltration. The multi-layered perennial structure slows water movement, stabilizes the soil, and enhances water absorption, thereby decreasing erosion risk and minimizing overland flow during rainfall events.
испарение
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The food forest reduces soil surface evaporation through dense vegetative cover, shading from the multi-layered canopy, and increased soil organic matter. Mulching and groundcover plants further protect the soil surface, lowering temperatures at ground level and limiting direct exposure to sun and wind, which significantly decreases soil surface evaporative water loss.
Почвы
влажность почв
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The food forest increases soil moisture by improving infiltration, enhancing organic matter content, and maintaining continuous groundcover. The multi-layered canopy moderates temperature and reduces evaporation, while mulch and living groundcovers retain water in the upper soil layers. Together, these features create a cooler, moister soil environment that supports long-term ecological function.
почвенный покров
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The food forest improves ground cover through the establishment of multi-layered perennial vegetation, including trees, shrubs, and living groundcovers. Mulch application and natural leaf litter further protect the soil surface, ensuring year-round coverage that reduces erosion, enhances soil health, and supports ecological stability.
образование корки на поверхности почв/ запечатывание
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The food forest reduces soil crusting and surface sealing by increasing organic matter, maintaining continuous vegetative cover, and enhancing biological activity in the upper soil layers. Leaf litter, mulch, and root penetration prevent the formation of hard surface layers, while improved soil structure allows better infiltration and aeration, minimizing the risk of crust development.
круговорот/ восполнение питательных веществ
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The food forest enhances nutrient cycling and soil nutrient recharge through continuous biomass production, leaf litter accumulation, and root turnover. Nitrogen-fixing species, mulch, and on-site organic matter decomposition replenish soil nutrients naturally, while diverse plant strata promote active microbial communities that accelerate nutrient transformation and availability.
почвенное / подземное органическое вещество/ углерод
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The food forest increases soil organic matter and below-ground carbon through continuous inputs of leaf litter, root biomass, and decomposing mulch. The perennial, multi-layered vegetation system supports sustained carbon incorporation into the soil, while reduced disturbance and enhanced microbial activity further promote long-term carbon storage and soil organic matter accumulation.
Биоразнообразие: растительность, животный мир
Растительный покров
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The food forest substantially increases vegetation cover by establishing multiple perennial layers - canopy trees, mid-storey species, shrubs, and groundcovers - that provide continuous, year-round biomass. This expanded plant cover protects the soil, supports ecological processes, and creates a more resilient and biodiverse landscape compared to the former monoculture field.
биомасса/ содержание углерода в надземной биомассе
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The food forest increases above-ground biomass and carbon storage through the establishment of diverse perennial vegetation, including canopy trees, fruit species, shrubs, and herbaceous layers. As these plants grow, they accumulate significant living biomass, sequester carbon, and contribute to long-term ecological stability through continuous organic matter production and structural complexity.
разнообразие флоры
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The food forest greatly increases plant diversity by integrating a wide range of tree species, fruit trees, nitrogen-fixing plants, shrubs, herbs, and groundcovers. This multi-strata design replaces the former single-crop system with a complex, species-rich community that enhances ecological resilience, supports wildlife, and promotes functional biodiversity across the site.
разнообразие местообитаний
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The food forest increases habitat diversity by creating a multi-layered structure that supports varied ecological niches. The combination of canopy trees, understory species, shrubs, groundcovers, open areas, and water features provides habitats for a wide range of insects, birds, and small wildlife. This structural and functional diversity replaces the uniform habitat of the former monoculture and greatly enhances overall ecosystem complexity.
Климат и снижение риска стихийных бедствий
выбросы углекислого газа и парниковых газов
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The food forest helps reduce carbon and greenhouse gas emissions by minimizing external inputs, eliminating chemical fertilizers, and avoiding soil disturbance that would otherwise release stored carbon. The perennial vegetation continuously sequesters carbon in both biomass and soil, while the system’s low-energy, regenerative management reduces emissions associated with conventional agricultural practices.
Укажите оценку внешних воздействий (измерений):
The assessment of on-site impacts combines both social-cultural learning processes and quantitative biophysical measurements. On the social, cultural, and economic side, the site hosts workshops, guided learning sessions, and community activities designed to understand the meaning, role, and value of the food forest for local stakeholders. These engagements provide qualitative insights into cultural benefits, community strengthening, and the educational function of the place. For the more tangible biophysical parameters – soil health, vegetation condition, biodiversity, and ecological recovery – the monitoring relies on analytical laboratory tests and systematic long-term sampling. Soil samples collected at different stages of the establishment process were analyzed for organic matter, nutrients, structure, and biological activity, providing a clear picture of soil improvement over time. In addition, the site is monitored through remote-sensing-based indicators developed in collaboration with the University of Haifa, which track temporal changes in vegetation cover, biomass, soil moisture proxies, and overall ecological function. Together, these qualitative and quantitative assessments offer a comprehensive understanding of the site’s development, documenting both the ecological restoration underway and the parallel social and educational impacts generated by the food forest.
6.2 Влияние Технологии за пределами территории ее применения
воздействие парниковых газов
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Using IPCC Tier-1 methods (2006 Guidelines with the 2019 Refinement), we estimate annual removals from (i) mineral soil organic carbon (SOC) gains after conversion from tilled wheat to multistrata agroforestry, and (ii) incremental woody biomass growth. Mediterranean evidence suggests SOC increases on managed woody systems of ~0.2–1.0 t C ha⁻¹ yr⁻¹, while biomass increments in multistrata/silvo-arable agroforestry typically add ~0.8–2.5 t C ha⁻¹ yr⁻¹ in the establishment decades; together this yields ~1.0–3.5 t C ha⁻¹ yr⁻¹, i.e., ≈ 3.7–13 tCO₂e ha⁻¹ yr⁻¹ (3.67 conversion). For reporting we adopt the conservative lower bound until our paired soil cores (baseline vs. years 2/5/8) and tree allometry—supported by Sentinel-2 time-series—finish quantifying site-specific change. Sources: IPCC 2006/2019 AFOLU guidance; AR6 WGIII (AFOLU); Mediterranean meta-analyses of SOC/biomass in woody systems and agroforestry.
Укажите оценку внешних воздействий (измерений) :
Off-site impacts were assessed through a combination of qualitative and quantitative indicators that capture how the food-forest system influences the surrounding landscape and community beyond the plot boundaries. Hydrological effects were inferred from reduced surface runoff and improved infiltration within the site, which collectively lower downstream sedimentation and erosion risks; these implications were evaluated using rainfall records, soil-moisture trends, and comparison of runoff behavior between the restored area and adjacent conventionally managed fields. Vegetation development and canopy expansion – monitored through Sentinel-2 time-series and UAV imagery – provide additional evidence of landscape-scale improvements such as enhanced microclimatic buffering and habitat connectivity. Social and cultural off-site impacts were evaluated through participation in workshops, educational programs, and community events, which extend ecological knowledge and stewardship beyond the site itself. Together, these measurements and observations offer a coherent picture of how the food forest contributes to broader environmental and community benefits outside its physical boundaries.
6.3 Подверженность и чувствительность Технологии УЗП к постепенным изменениям климата и экстремальным погодным явлениям/ стихийным бедствиям, связанным с изменением климата (в понимании землепользователей)
Постепенное изменение климата
Постепенное изменение климата
| Сезон | увеличение или уменьшение | Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| среднегодовые температуры | увеличилось | умеренно | |
| среднегодовое количество осадков | снизилось | хорошо |
Экстремальные явления, связанные с изменением климата (стихийные бедствия)
Погодные стихийные бедствия
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| местные ливневые дожди | умеренно |
Стихийные бедствия климатического характера
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| сильная жара | хорошо |
| засухи | хорошо |
6.4 Анализ эффективности затрат
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с первоначальными вложениями (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
слабо отрицательное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с текущими расходами по поддержанию технологии (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
влияние незаметно
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Пояснения:
The slightly negative short-term balance does not reflect external subsidies but rather the intentional design and purpose of the site. The food forest is not a commercial enterprise and was never intended to generate profit from agricultural production. Its primary function is research, education, and community engagement, and therefore its revenues come from workshops, collaborations, and research grants rather than crop sales. The short-term financial deficit simply reflects the fact that the landowners invest in a long-term ecological and educational project whose value is measured in environmental and social outcomes rather than immediate economic returns. It should not be interpreted as dependence on agricultural subsidies or market-based support.
6.5 Внедрение Технологии
- отдельные случаи/ эксперимент
Если возможно, дайте количественную характеристику (число домохозяйств и/или площадь применения):
One household: 1.5 acres
Среди применяющих Технологию землепользователей, какова доля лиц, применяющих её по собственной инициативе, т.е. без какого-либо материального стимулирования со стороны?
- 0-10%
6.6 Адаптация
Была ли Технология УЗП изменена в недавнее время с целью адаптации к меняющимся условиям среды?
Да
Если да, укажите, по отношению к каким именно изменяющимся условиям среды произведена адаптация?
- изменения климата/ экстремальные погодные явления
Укажите, что именно изменилось в Технологии (дизайн, используемые материалы или виды растений/животных и т.д.):
The design and composition of the food forest are continuously adapted as the system matures and as new insights emerge from ongoing learning by the landowners and collaborating researchers. Species selection, spatial arrangement, and management practices have been refined over time in response to observed ecological dynamics - such as canopy development, soil improvement, microclimatic changes, and species performance. Additional trees, shrubs, and groundcovers have been introduced to enhance diversity, strengthen ecological functions, and address emerging needs such as shade regulation, soil enrichment, or habitat creation. This adaptive approach reflects the core principle of the technology: the food forest is a living system that evolves through observation, experimentation, and evidence-based adjustments informed by both practical experience and scientific collaboration.
6.7 Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности Технологии
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
| Restores soil fertility and structure without relying on chemicals and reduces weed pressure naturally through permanent groundcover |
| Improves moisture retention and reduces drought stress over time and supports biodiversity and creates a healthier farm ecosystem |
| Transformational: turns degraded land into a productive long-term asset |
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
| Demonstrates a replicable nature-based solution for restoring degraded agricultural soils in Mediterranean climates |
| Increases soil organic matter and biological activity, improving long-term soil function and carbon sequestration |
| Serves as a living demonstration site with high educational and upscaling potential for regenerative farming in the region |
6.8 Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски Технологии и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению землепользователей | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Slow establishment phase before benefits become visible | Patience + phased planting; choose fast-growing pioneer species to accelerate canopy formation |
| Requires knowledge and ecological management skills | Ongoing guidance from experts / capacity building / training |
| Young plants vulnerable to drought during first summers | Supplemental irrigation in the first years and thicker mulching to reduce evaporation |
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Long ecological recovery timeline before system reaches full functionality | Use succession planning and pioneer/perennial nurse species to accelerate canopy closure and soil regeneration |
| Success depends on appropriate species selection for local microclimate and soil | Improve site-specific design using adaptive planting trials, monitoring, and locally adapted cultivars |
| Knowledge-intensive management compared to conventional systems | Provide technical training, extension support, and farmer-to-farmer learning |
| Restoration outcomes may vary with drought years and extreme heat events | Increase biomass cover, soil shading, and water retention strategies in early establishment years |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/ источники информации
- выезды на места, полевые обследования
Field visits and surveys were conducted once every season on-site with the primary land user (one key informant), supplemented by technical assessments from the research team
- опросы землепользователей
One-on-one interviews were conducted with the primary land user (one key informant) at least once a year, focusing on management decisions, perceived benefits and challenges, and changes observed since the start of the transition
- опросы специалистов/экспертов по УЗП
The expert input was provided by specialists involved in the University of Haifa restoration pilot
- данные, собранные из отчетов и достоверных документов
7.2 Ссылки на опубликованные материалы
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Zbedat, G., & Brook, A. (2025). Land Restoration Effectiveness Assessed by Satellite-Based Remote Sensing Technologies as A New Monitoring Approach. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 48, 149-155.
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
Google Scholar
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
T. A. Cohen, A. Brook and G. Zbedat, "Long-Term Land Restoration Assessment Using Remote Sensing in Mediterranean Ecosystems," 2024 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Agriculture and Forestry (MetroAgriFor), Padua, Italy, 2024, pp. 179-183, doi: 10.1109/MetroAgriFor63043.2024.10948855.
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
Google Scholar
7.3 Ссылки на соответствующую онлайн-информацию
Название/ описание:
React4Med site
Адрес в сети Интернет:
https://react4med.eu
Название/ описание:
Bethlehem of Galilee Food Forest Collection
Адрес в сети Интернет:
https://haifa.primo.exlibrisgroup.com/discovery/collectionDiscovery?vid=972HAI_MAIN:HAU&inst=972HAI_MAIN&collectionId=81263109080002791
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки
Нет ссылок
Модули
Нет модулей