Conservation agriculture for maize-legume systems with velvet bean as a dense cover crop [Кения]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Kennedy Were
- Редактор: –
- Рецензенты: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Tatenda Lemann
Kilimo hifadhi
technologies_5775 - Кения
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Технологии
Специалист по УЗП:
Специалист по УЗП:
Специалист по УЗП:
Специалист по УЗП:
Название проекта, содействовавшего документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
GEF-UNEP-AGRA-KALRO SLM ProjectНазвание проекта, содействовавшего документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Carbon Benefits Project (CBP)Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Kenya Agricultural and Livestock Research Organization (KALRO) - Кения1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование данных, собранных ВОКАТ
Составитель и ответственный(-ые) специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.4 Декларация по устойчивости описываемой Технологии
Вызывает ли описанная здесь Технология проблемы деградации земель настолько, что ее нельзя назвать природосберегающей?
Нет
2. Описание Технологии УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Технологии
Определение Технологии:
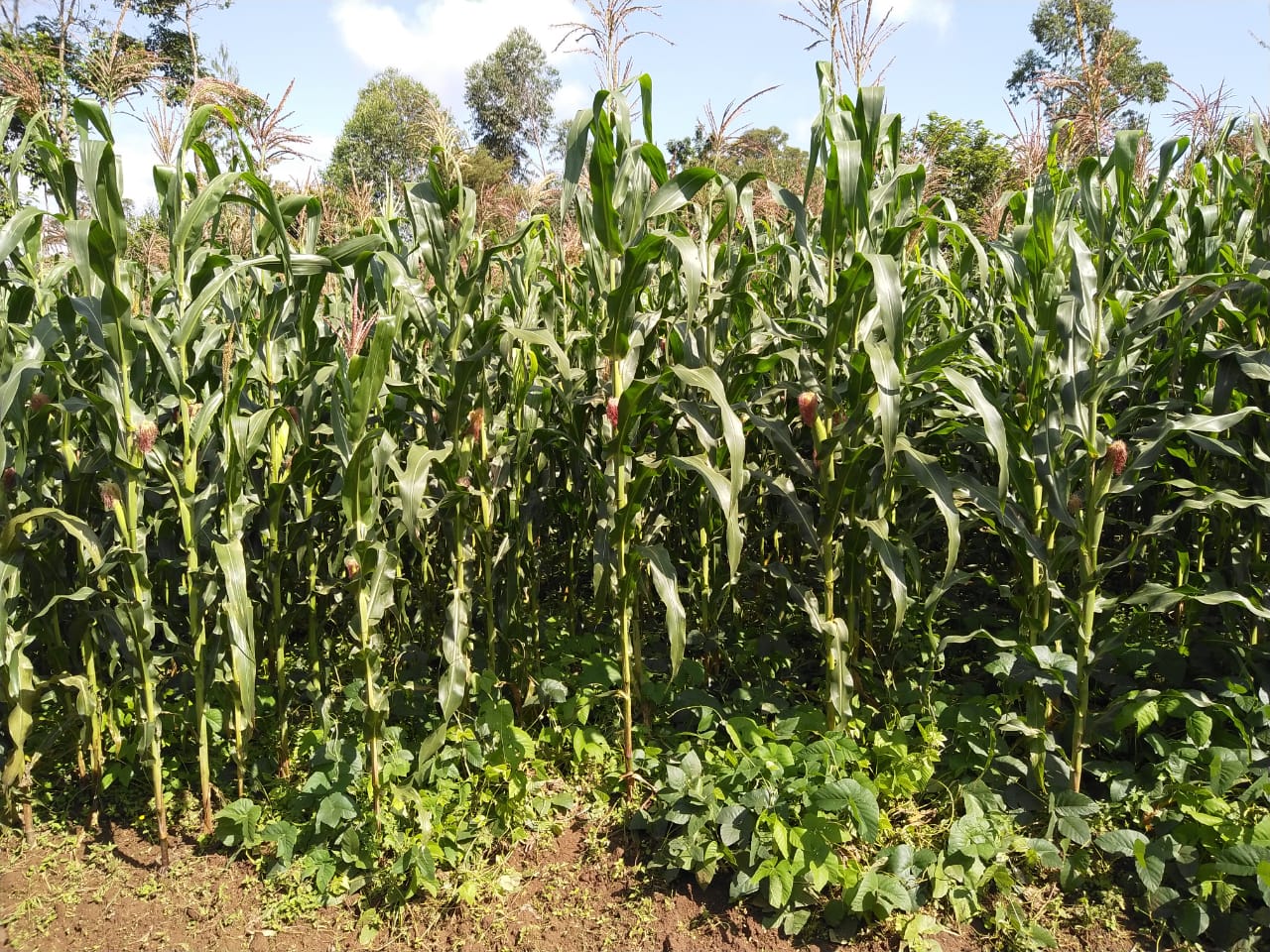
Conservation agriculture for maize-legume systems with velvet bean (Mucuna pruriens) as a dense cover crop is being promoted in western Kenya to address the challenges of land degradation, low crop yields, low incomes, high production costs and climate change.
2.2 Подробное описание Технологии
Описание:
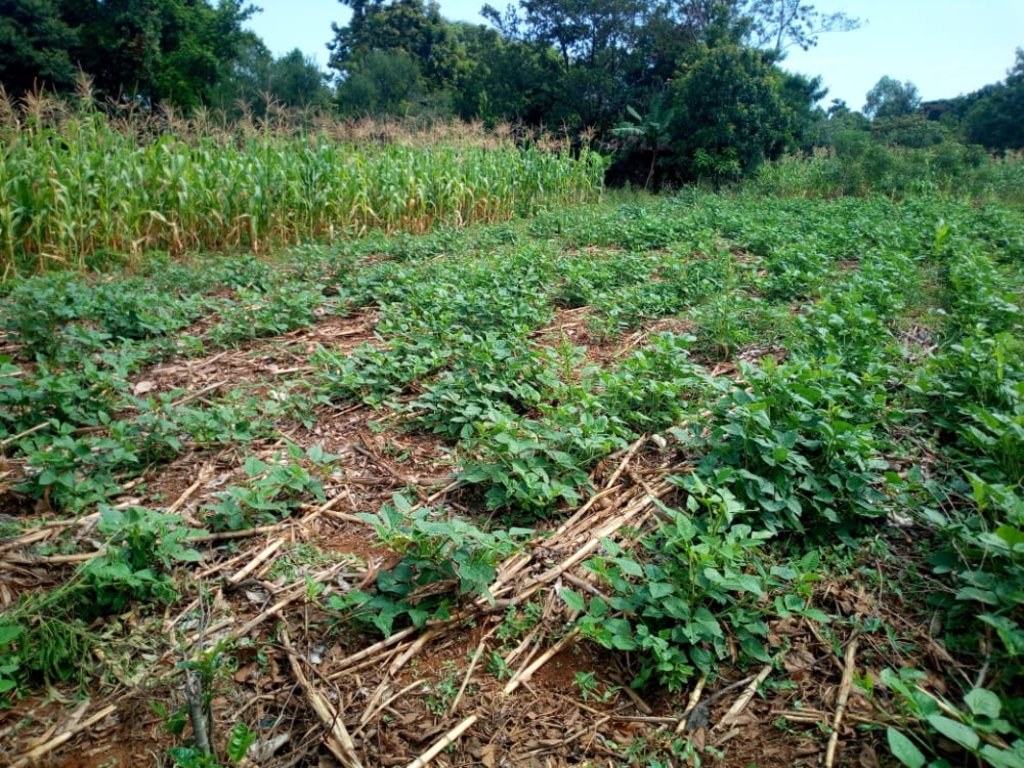
Agriculture in western Kenya suffers from low productivity due to the degraded landscape. The soils are predominantly acidic and low in fertility, with the yields of food staples, such as maize and common bean averaging 1 ton/ ha and 5 tons/ ha, respectively. Consequently, the smallholder farmers have encroached into the adjacent Kakamega and Nandi forests in their quest for supplementary agro-ecosystem services and farm incomes. Degradation of the agro-resource base is underpinned by unsustainable practices carried out under conventional farming; for example, continuous cultivation with low nutrient inputs, mono-cropping, removal of crop residues and full tillage. Some of these practices enhance climate change by intensifying the emissions of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. Therefore, widespread adoption of conservation agriculture (CA) technology is being promoted to reduce the adverse impacts of conventional farming and enhance sustainable land management, environmental protection, and climate change mitigation and adaptation in 10 micro-catchments located within a 5-km radius from the edge of Kakamega and Nandi forests. The CA technology is characterized by the principles of minimum mechanical soil disturbance, maintenance of at least 30 percent permanent organic soil cover, diversified cropping through intercropping and crop rotations, and weed control. These principles have been adapted to the local conditions and needs.
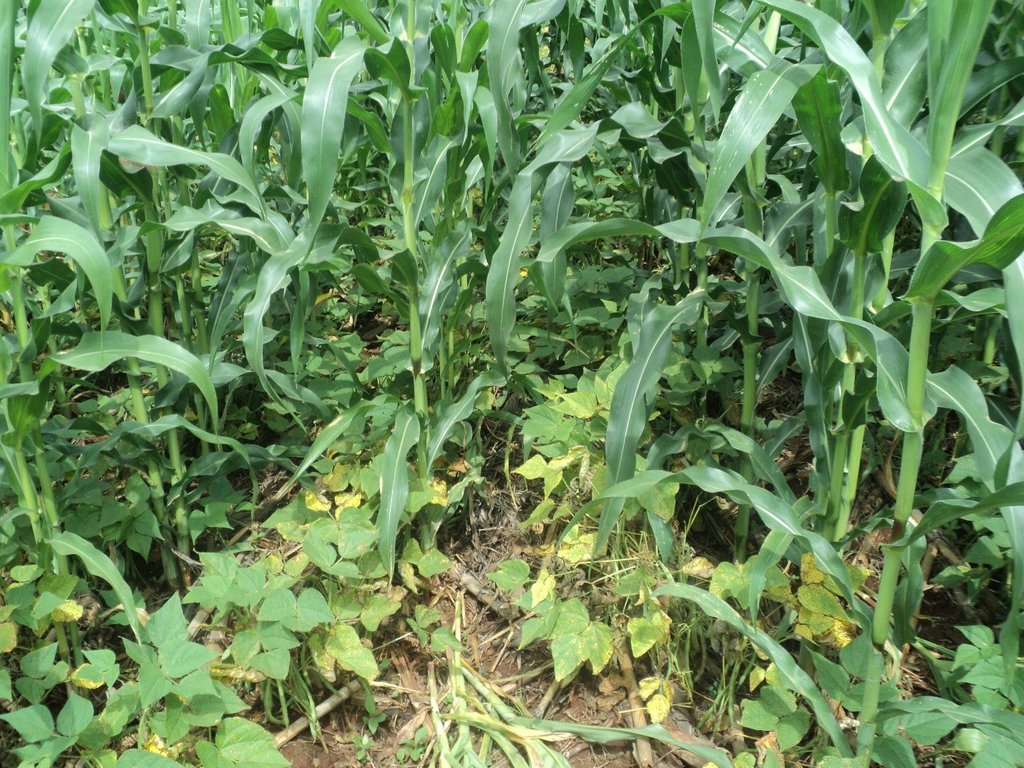
The establishment of CA technology begins with land preparation. That is, the existing weeds and previous crop residues in the field are either slashed, or controlled through the application of appropriate herbicides. All the residues are retained on soil surface as opposed to burning, or removal in the conventional system. Land preparation is followed by planting, where the jab planter is used for precise placement of seeds and fertilizers in un-ploughed field, or within the established planting hills and rip lines to minimize soil tillage. This contrasts with conventional farming practice where a plough, or a hand hoe is used to till the entire field and establish the planting holes for placing seeds and fertilizers. A combination of cereal (maize – Zea mays L.) and legumes (common bean – Phaseolus vulgaris L., soybean - Glycine max, velvet bean – Mucuna pruriens and cowpea – Vigna unguiculata) are either intercropped, or rotated in the field each season to optimize the use of the available soil resources, including water, nutrients, and micro-organisms. The main cereal-legume association involves the establishment of Mucuna pruriens under maize as a dense cover crop. In this cropping system, Mucuna pruriens seeds are sown within a spacing of 1 m × 0.5 m where they grow and spread to completely cover the soil surface. As the cover crop grows, the leaves fall and decompose on the ground, enriching the soil’s nutrients, organic matter and fertility. The maize - Mucuna pruriens mix is rotated with either sole common bean, soybean and cowpea crop, or an intercrop of maize with any of the legumes. Weeding is carried out using either selective herbicides, or weed scrapers. When designing the intercropping and rotation plans, crop families (N-fixing vs. non-fixing), root depths (shallow vs. deep roots), and susceptibility to diseases, pests and weeds are all considered.
Generally, CA technologies have multiple benefits for farmers and the environment. In the context of the Kakamega-Nandi forest landscape, the CA plots with Mucuna pruriens as a dense cover crop have shown improved soil organic matter, soil structure and nutrient status. It is expected that this will reduce the use of fertilizers over time. Most farmers have also reported that reduced tillage and direct placement of inputs (seeds and fertilizers) save them time, money, fuel, labour and inputs. Aside from saving resources, reduced tillage will ultimately enhance soil living organisms and mitigate atmospheric CO2 emissions through the decrease in fuel consumption and soil disturbance. Moreover, farmers have observed that the maize established with Mucuna pruriens as a cover crop remains green and healthy for long during mid-season dry spells compared to those under mono-culture, or light mulch. This implies that the CA technology also increases water infiltration and soil water content; thus, acting as insurance against drought. The increase in water infiltration and soil moisture occurs because the dense Mucuna pruriens cover crop not only regulates the soil surface temperatures and evaporation, but also reduces surface runoff and exposure to wind erosion. In addition, farmers have witnessed the suppression of weeds, such as Striga hermonthica (witchweed) in plots under dense cover crop and diversified cropping. Besides, diversified cropping through rotations has reduced the incidences of insect pests and diseases, as well as the risk of crop failure during extreme weather conditions and pest infestations. Specifically, farmers have noticed that the CA plots under maize - Mucuna pruriens intercrop are less affected by the fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) compared to those under mono-culture. They have also noted that, in seasons of excessive rainfall, the maize intercropped with the common bean is usually harvested even when the common bean fails. Most importantly, these CA benefits have boosted maize yields by over 50 percent, meaning more food and income, and fewer forest encroachments.
Proper adoption of the CA technology by land users within the Kakamega-Nandi forest landscape is being hampered by several factors. Firstly, crop residues are inadequate due to competing uses, such as animal feed and fuel. At times, livestock is even allowed to graze on the stubble field, contravening the CA principles. Besides, some farmers have not fully embraced crop diversification and still grow maize throughout the seasons without rotation with other drought-tolerant cereals, such as sorghum and millet. Conventional ploughing is also quite entrenched. Further, some farmers still do not prefer Mucuna pruriens as a cover crop because of insufficient knowledge on the utilization of its inedible yields. Lastly, some farmers are finding it hard to access CA inputs and tools, such as the jab planters, weed scrapers, herbicides and seeds of Mucuna pruriens owing to either high prices, or shortages.
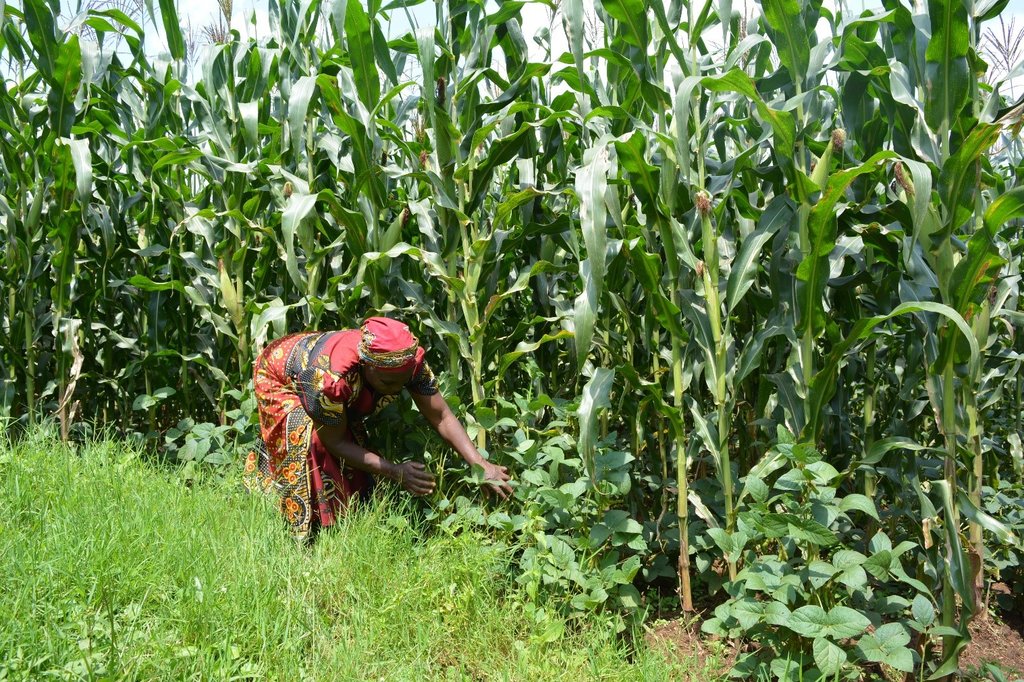
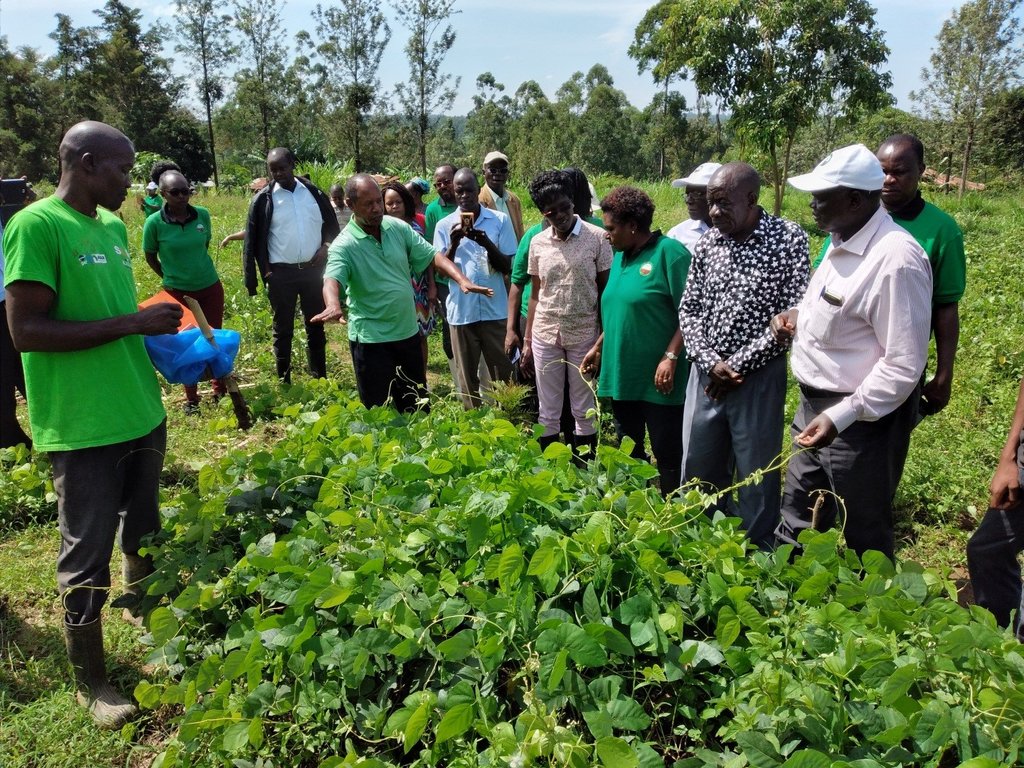
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Технологию
2.4 Видеоматериалы, иллюстрирующие Технологию
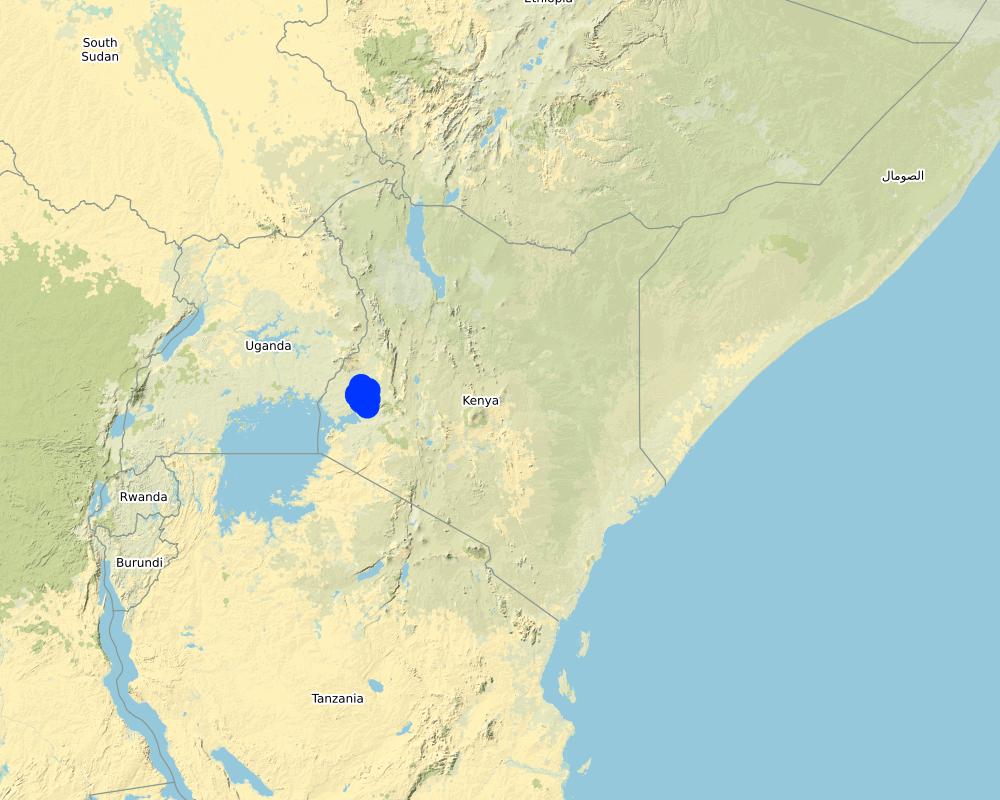
2.5 Страна/ регион/ места, где применяется Технология, информация о которых собрана в данной Анкете
Страна:
Кения
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Western region
Более точная привязка места:
Kakamega-Nandi forest landscape
Охарактеризуйте пространственное распространение Технологии :
- примененяется точечно/ на небольших участках
Технология применяется на ООПТ?
Нет
Map
×2.6 Сколько лет применяется данная Технология
Год начала реализации:
2019
2.7 Внедрение Технологии
Укажите, как именно Технология УЗП была внедрена:
- в качестве научного/ полевого эксперимента
- через проекты/ внешнее вмешательство
Пояснения (тип проекта и т.д.):
Projects and research focusing mainly on advancing land degradation neutrality and agricultural productivity in the area
3. Классификация Технологии УЗП
3.1 Основные цели и задачи реализации Технологии
- повышение производства
- снижение или предотвращение деградации земель, восстановление нарушенных земель
- сохранение/ повышение биоразнообразия
- смягчение последствий изменения климата
- создание благоприятных экономических условий
3.2 Текущий(-ие) тип(-ы) землепользования на территории, где применяется Технология
Комбинированное землепользование в пределах одной и той же земельной единицы:
Да
Укажите сочетания типов землепользования (посевы / пастбища / деревья):
- Агро-пастбищное хозяйство ( включая растениеводство-животноводство)

Пахотные угодья и плантации
- Однолетние культуры
Ежегодный урожай - Уточните культуры:
- зерновые культуры - кукуруза
- бобовые - бобы
- бобовые - зеленый горошек
- бобовые - соя
Годовая система земледелия:
Кукуруза / сорго / просо, смешанные с бобовым
Число урожаев за год:
- 2
Поясните:
Long rain season (March to May) and short rain season (October to December)
Применяются ли посевы в междурядьях?
Да
Если да, укажите, какие посевы применяются:
Maize and legumes (i.e., common bean, soybean and velvet bean – Mucuna pruriens)
Применяется ли севооборот?
Да
Если да, укажите:
Maize and legumes (i.e., common bean, soybean and velvet bean – Mucuna pruriens)

Пастбищные угодья
Интенсивный выпас/ выращивание кормов:
- Стойловое содержание/ нулевой выпас
- Улучшенные пастбища
Вид животных:
- cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
Используется ли комплексное земледельческо-животноводческое хозяйство?
Да
Если да, укажите:
Manure is used for fertilization and crop residues are used as cattle feed
Продукты и услуги:
- manure as fertilizer/ energy production
- мясо
- молоко
- кожа / шкуры
- транспорт / тяга
3.3 Изменилось ли использование земель в связи с внедрением Технологии?
Изменилось ли использование земель в связи с внедрением Технологии?
- Да (Пожалуйста, заполните нижеприведенные вопросы относительно использования земель до внедрения Технологии)
Комбинированное землепользование в пределах одной и той же земельной единицы:
Да
Укажите сочетания типов землепользования (посевы / пастбища / деревья):
- Агро-пастбищное хозяйство ( включая растениеводство-животноводство)

Пахотные угодья и плантации
- Однолетние культуры
Ежегодный урожай - Уточните культуры:
- зерновые культуры - кукуруза
Годовая система земледелия:
Пожнивные посевы кукурузы / сорго / проса
Применяются ли посевы в междурядьях?
Нет
Применяется ли севооборот?
Нет

Пастбищные угодья
Интенсивный выпас/ выращивание кормов:
- Стойловое содержание/ нулевой выпас
Вид животных:
- cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
Используется ли комплексное земледельческо-животноводческое хозяйство?
Да
Если да, укажите:
Manure is used for fertilization and crop residues are used as cattle feed
Продукты и услуги:
- manure as fertilizer/ energy production
- мясо
- молоко
- кожа / шкуры
- транспорт / тяга
3.4 Водоснабжение
Обеспеченность водой участков, где реализуется Технология :
- богарные земли
3.5 Категория УЗП, к которой относится Технология
- Улучшение почвенного/ растительного покрова
- Минимальная обработка почв
- Комплексное управление почвенным плодородием
3.6 Мероприятия УЗП, выполняемые в рамках Технологии

Агрономические мероприятия
- A1: Растительный/ почвенный покров
- A2: Органическое вещество/ почвенное плодородие
- A3: Поверхностная обработка почв
- A6: Управление остатками
А3: Дифференцируйте системы обработки почв:
A 3.2: Reduced tillage (> 30% soil cover)
A6: Указать способ утилизации остатков:
A 6.4: сохранено
3.7 Основные проблемы деградации земель, на решение которых направлена Технология

водная эрозия почв
- ВЭп: поверхностная эрозия/смыв верхних почвенных горизонтов

ветровая эрозия почв
- Эп: утрата плодородного слоя почвы

ухудшение химических свойств почв
- Хп: Снижение плодородия и уменьшение содержания органического вещества (вызванное не эрозией, а другими причинами)

ухудшение физических свойств почв
- Фу: уплотнение

биологическая деградация
- Бф: утрата биологической составляющей почв

деградация водных ресурсов
- Ва: почвенная засуха
3.8 Предотвращение и снижение деградации земель, или восстановление нарушенных земель
Укажите цель Технологии по отношению к деградации земель :
- снижение деградации земель
4. Технические характеристики, мероприятия по практической реализации, вложения и стоимость
4.1 Технический рисунок, иллюстрирующий Технологию
Спецификация (пояснения к техническому рисунку):
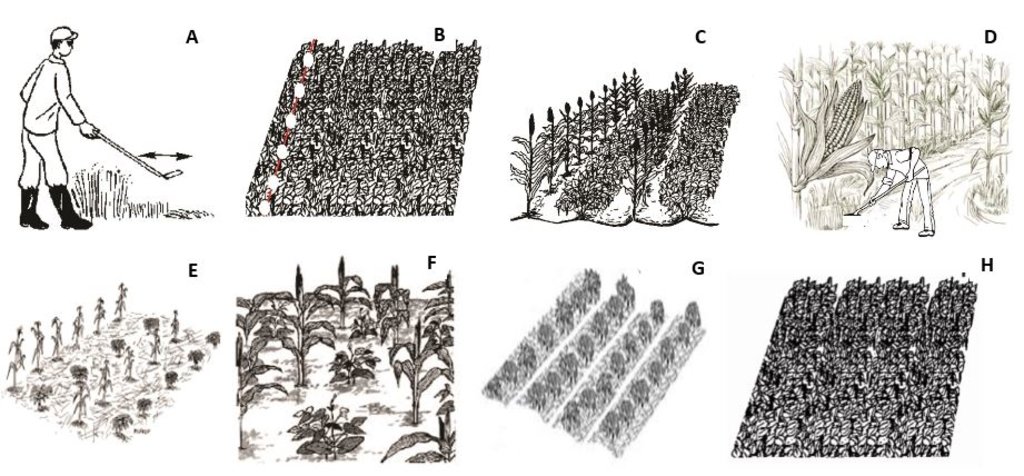
The first technical drawing shows a typical farm under CA with various principles:
A - Clearance of weeds and previous crop residues through slashing in preparation for planting in season 1 (long rains). The residues are retained on the plot.
B - In a plot under total soil cover with Mucuna pruriens, maize seed and fertilizer are placed at the precise planting hills, denoted by the white circles along the red line, using a jab planter to minimize soil tillage.
C - Maize crop establishes under the dense cover of Mucuna pruriens.
D - Weeding of the maize crop is done using a weed scraper.
E & F - In season 2 (short rains), after harvesting maize in the previous maize – Mucuna cropping system and cutting down the residues, either a row intercropping system with alternate rows of maize and soybean (E), or maize and common bean (F) under maize straw mulch is established.
G & H - Alternatively, in season 2 (short rains), either sole common bean (cowpea, or soybean) production under maize straw mulch (G), or total soil cover with Mucuna pruriens (H) is established in the plot.
Автор:
Sam Koile, Kennedy Were & George Ayaga
Дата:
31/05/2020
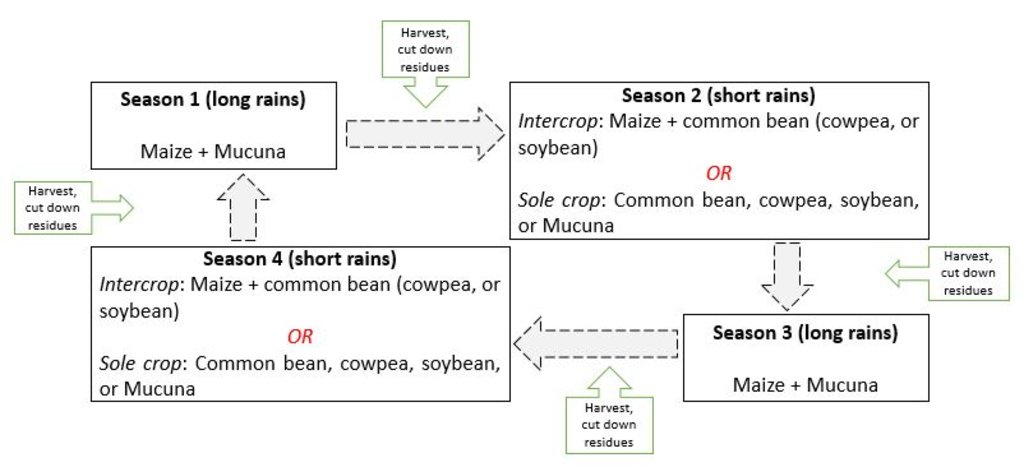
Спецификация (пояснения к техническому рисунку):
The second technical drawing is an illustration of a four season (2-year) rotation of maize, legumes and cover crop
Автор:
Kennedy Were, Sam Koile & George Ayaga
Дата:
15/07/2020
4.2 Общая информация по необходимым вложениям и стоимости
Уточните, как рассчитывались затраты и вложения:
- на площадь, где применяется Технология
Укажите размер и единицу площади:
1 ha
Если вы используете местные системы измерения, укажите коэффициент пересчета на один гектар (например, 1 га = 2,47 акров): 1 га =:
2.47 acres
другая/ национальная валюта (название):
KES
Если это необходимо, укажите обменный курс от доллара США к местной валюте (например, 1 доллар США = 79,9 бразильского реала): 1 доллар США =:
107,08
Укажите среднюю дневную заработную плату наемных работников:
300
4.3 Мероприятия, необходимые для начала реализации
| Деятельность | Время (сессия) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchase of CA tools - jab planter, knapsack sprayer, protection gear, slasher, weed scraper, and gunny bag) | Initial stage |
4.4 Вложения и затраты, необходимые для начала реализации
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оборудование | Jab planter | Piece | 2,0 | 1500,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Knapsack sprayer | Piece | 2,0 | 2500,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Protection gear | Piece | 2,0 | 1000,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Weed scraper | Piece | 2,0 | 500,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Slasher | Piece | 2,0 | 500,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Gunny bag | Piece | 50,0 | 50,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| Общая стоимость запуска Технологии | 14500,0 | |||||
| Общие затраты на создание Технологии в долларах США | 135,41 | |||||
4.5 Поддержание/ текущее обслуживание
| Деятельность | Сроки/ повторяемость проведения | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation - Slashing | Initial stage |
| 2. | Preparing the planting hills and rip lines | Initial stage |
| 3. | Planting - placing seeds and fertilizer using jab planter | Initial stage |
| 4. | Herbicide application | Initial and growing stages |
| 5. | Pesticide application | Growing stage |
| 6. | Fertilizer application (top-dressing) | Growing stage |
| 7. | Harvesting, drying and shelling | Final stage |
4.6 Стоимость поддержания/ текущего обслуживания ( в год)
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Land preparation - slashing and herbicide application | Man day | 4,0 | 300,0 | 1200,0 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Planting - preparing the planting hills and placing seeds and fertilizer | Man day | 38,0 | 300,0 | 11400,0 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Top-dressing and pesticide application | Man day | 8,0 | 300,0 | 2400,0 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Harvesting, shelling and drying | Man day | 30,0 | 300,0 | 9000,0 | 100,0 |
| Посадочный материал | Maize seed | Kg | 20,0 | 250,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Посадочный материал | Legume seed | Kg | 8,0 | 250,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Planting fertilizer | Kg | 125,0 | 60,0 | 7500,0 | 100,0 |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Top-dressing fertilizer | Kg | 125,0 | 50,0 | 6250,0 | 100,0 |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Pesticide | Litre | 2,0 | 1250,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Herbicide | Litre | 5,0 | 875,0 | 4375,0 | 100,0 |
| Другие | Transport | Km | 5,0 | 1500,0 | 7500,0 | 100,0 |
| Общая стоимость поддержания Технологии | 59125,0 | |||||
| Общие затраты на поддержание Технологии в долларах США | 552,16 | |||||
4.7 Наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат
Опишите наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат:
1. Prevailing market prices of the inputs, equipment and labour.
5. Природные и социально-экономические условия
5.1 Климат
Среднегодовое количество осадков
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1000 мм
- 1001-1500 мм
- 1501-2000 мм
- 2001-3000 мм
- 3001-4000 мм
- > 4000 мм
Пояснения/ комментарии по осадкам:
Rainfall is bi-modal with the long rain season starting from March to May, and the short rains from October to December.
Агроклиматическая зона
- влажная
- Умеренно-влажная
mean annual temperature varies from 18 to 29° C
5.2 Рельеф
Склоны (преобладающие):
- пологие (0-2%)
- покатые (3-5%)
- покато-крутые (6-10%)
- крутые (11-15%)
- очень крутые (16-30%)
- чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
- обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа:
- плато/ равнины
- гребни хребтов/холмов
- склоны гор
- склоны холмов
- подножья
- днища долин
Зона высотной поясности:
- 0-100 м над уровнем моря
- 101-500 м н.у.м.
- 501-1000 м н.у.м.
- 1001-1500 м н.у.м.
- 1501-2000 м н.у.м.
- 2001-2500 м н.у.м.
- 2501-3000 м н.у.м.
- 3001-4000 м н.у.м.
- > 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
Укажите, приурочено ли применение Технологии к специфическим условиям:
- не имеет значения
5.3 Почвы
Средняя мощность почв:
- поверхностные (0-20 см)
- неглубокие (21-50 см)
- умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
- глубокие (81-120 см)
- очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта):
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
- тонкодисперсный/ тяжёлый (глинистый)
Гранулометрический состав (на глубине более 20 см):
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
- тонкодисперсный/ тяжёлый (глинистый)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем горизонте:
- среднее (1-3%)
- низкое (< 1%)
5.4 Доступность и качество воды
Уровень грунтовых вод:
5-50 м
Доступность поверхностных вод:
средняя
Качество воды (без обработки):
питьевая вода плохого качества (необходима обработка)
Качество воды относится к:
одновременно грунтовые и поверхностные воды
Является ли солёность воды проблемой?
Нет
Происходят ли периодические затопления территории?
Нет
5.5 Биоразнообразие
Видовое разнообразие:
- средняя
Разнообразие местообитаний:
- средняя
5.6 Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Осёдлый или кочевой:
- Осёдлый
Рыночная ориентация производства:
- натуральное хозяйство (самообеспечение)
- смешанный (натуральный / коммерческий)
Доходы из других источников:
- < 10% всех доходов
- 10-50% всех доходов
Относительный уровень достатка:
- плохой
- средний
Индивидуальное или коллективное хозяйство:
- частное/ домовладение
Уровень механизации:
- ручной труд
- тягловая сила
Пол:
- женщины
- мужчины
Возраст землепользователей:
- средний возраст
- пожилой
5.7 Средняя площадь земель, используемых землепользователями с применением Технологии
- < 0,5 га
- 0,5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1000 га
- 1000-10000 га
- > 10000 га
Считается ли это мелким, средним или крупным хозяйством (по местным масштабам)?
- мелкое
5.8 Собственность на землю, права на земле- и водопользование
Землевладелец:
- индивидуальная, не оформленная в собственность
- индивидуальная, оформленная в собственность
Право землепользования:
- индивидуальное
Право водопользования:
- общинное (контролируемое)
- индивидуальное
Права на землепользование основаны на традиционной правовой системе?
Да
5.9 Доступ к базовым услугам и инфраструктуре
медицинское обслуживание:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
образование:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
технические консультации:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
занятость (вне хозяйства):
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
рынки:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
электроснабжение:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
транспорт и дорожная сеть:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
водоснабжение и канализация:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
финансовые услуги:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
6. Воздействия и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Технологии УЗП в пределах территории ее применения
Социально-экономическое воздействие
Продуктивность
производство сельскозяйственных культур
Количество до применения УЗП :
24 bags/ ha
Количество после применения УЗП:
43 bags/ ha
Комментарий/ пояснения:
This can be attributed to the multiple benefits of the CA technology, such as improved soil organic matter content and nutrient status. Note: A standard bag weighs 90 kgs.
качество урожая
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The multiple benefits of the CA technology, such as improved soil conditions and alleviation of pests and diseases, not only increased crop production (yields), but also the quality of the crops.
производство кормов
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Increased crop production also means increased fodder production because the crop residues are partly used as animal feed
качество кормов
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Increased crop quality also implies increased fodder quality because the crop residues are partly used as animal feed
риск потери продуктивности
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Specifically,
- the maize established with Mucuna pruriens as a cover crop have remained green and healthy for long during mid-season dry spells. The CA technology increases water infiltration and soil moisture because the dense cover crop not only regulates the soil surface temperatures and evaporation, but also reduces surface runoff
- the CA plots under maize - Mucuna pruriens inter-crop have been less affected by the fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda).
- in seasons of excessive rainfall, the maize intercropped with the common bean has been harvested even when the common bean fails.
разнообразие продукции
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Farmers not only grow maize, but also mix or rotate it with common bean, soybean and cowpea
управление землями
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Operations such as precise and direct placement of inputs and minimum tillage have simplified land management
Доходы и затраты
сельскохозяйственные издержки
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Expenses on inputs, such as herbicides and fertilizers increased marginally, because the conventional farming practice had been characterized by low inputs; however, with improved soil organic matter, soil structure and nutrient status, as well as reduced incidences of pest, diseases and weeds, it is expected that the use of these inputs will diminish over time
доходы хозяйства
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Increased crop production means, more surplus and incomes
разнообразие источников дохода
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Diversified cropping enables the farmers to get income from maize, common bean, soybean and cowpea production
объем работ
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Reduced tillage has subsequently decreased the farmers' workload because they no longer have to plough the entire field
Социальное и культурное воздействие
продовольственная безопасность/ самообеспечение
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Increased crop production means more food and less hungry periods. The legumes also provide a good source of protein to the farmers' households
местное самоуправление
Комментарий/ пояснения:
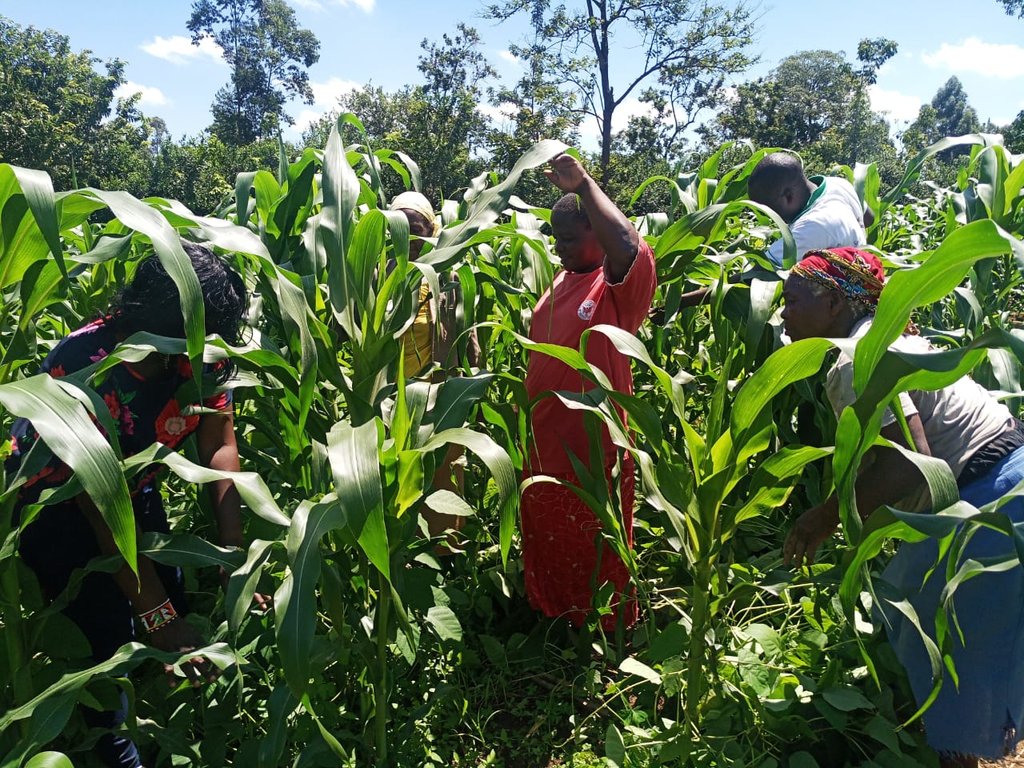
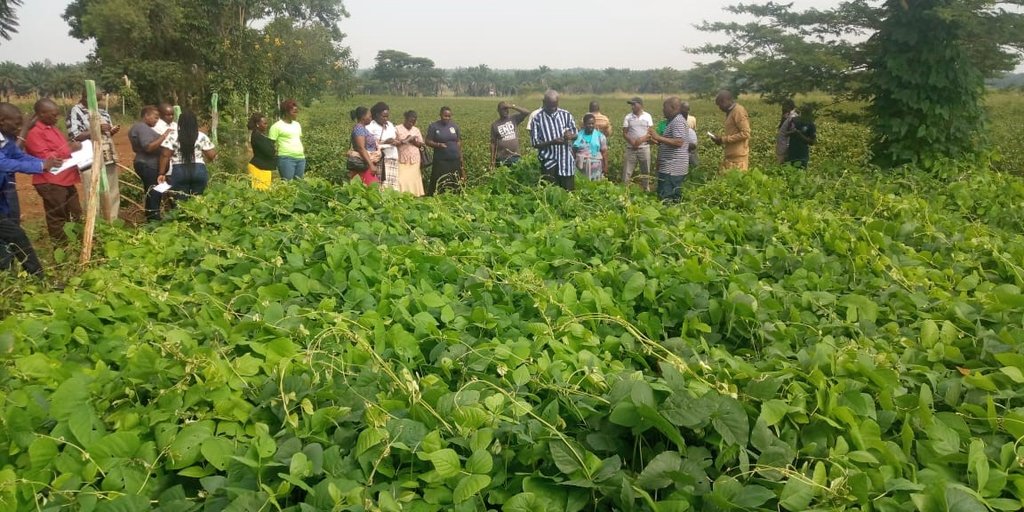
The common interest groups have been greatly involved in the selection of the CA technologies. The strengthening of the community institutions has been done for sustainability and to allow sensitization of the technology to the wider population in the landscape. Some of thaccess by the communities. e promotion approaches have been on-farm demonstrations and training of trainers (ToTs), which have involved and empowered different farmer groups within the communities. Seed producers have also been trained to multiply seeds of specific crops, such as Mucuna pruriens for ease of access
знания в области УЗП/ деградации земель
Комментарий/ пояснения:
On-farm demonstrations of the CA technology and the training of trainers (ToTs) have empowered different stakeholders within the communities with sufficient SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Экологическое воздействие
Водный цикл/ поверхностный сток
поверхностный сток
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The dense Mucuna pruriens cover crop reduces surface runoff
уровень грунтовых/ подземных вод
Комментарий/ пояснения:
There has been increase in water infiltration and soil water content because the dense Mucuna pruriens cover crop not only regulates the soil surface temperatures and evaporation, but also reduces surface runoff. This recharges the aquifer
испарение
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The dense Mucuna pruriens cover crop regulates both the soil surface temperatures and evaporation
Почвы
влажность почв
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The increase in soil water content occurs because the dense Mucuna pruriens cover crop not only regulates the soil surface temperatures and evaporation, but also reduces surface runoff
почвенный покров
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The dense Mucuna pruriens completely covers the soil surface, and is left on the ground even after the harvesting of maize
утрата почв
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The dense Mucuna pruriens cover crop reduces surface runoff and exposure to wind erosion
аккумуляция почвенного материала (намыв, эоловая, и др.)
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Accumulation of soil organic carbon has occurred because the dense cover crop has a higher net primary productivity and sheds more leaves on the ground, resulting in more inputs of detritus to the soil. Similarly, retention of the large amount of crop residues especially those obtained from the leguminous crops has increased the inputs of carbon and nitrogen to the soil.
образование корки на поверхности почв/ запечатывание
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The cover crop, minimum tillage and crop residues have protected the soil from the impact of raindrops, improved the surface soil structure and aggregate stability by increasing the organic matter content in the soil and stimulated soil biological activity, making the soil resistant to crusting
уплотнение почв
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Reduced tillage or zero tillage has minimized farm land activities, e.g, ploughing which often result in compaction of soil. Incorporation of deep rooted crops with shallow rooted crops has also helped to break the various soil layers, thus hindering compaction. In addition, accumulation of soil organic carbon has improved soil biological activities that help to reduce soil compaction, through continuous burrowing.
круговорот/ восполнение питательных веществ
Комментарий/ пояснения:
As the dense cover crop grows, the leaves fall and decompose on the ground, enriching the soils with nitrogen and organic matter
почвенное / подземное органическое вещество/ углерод
Комментарий/ пояснения:
As the dense cover crop grows, the leaves fall and decompose on the ground, with organic matter additions.
Биоразнообразие: растительность, животный мир
биомасса/ содержание углерода в надземной биомассе
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The dense cover crop has higher net primary productivity/ above-ground biomass C, which is left when the maize crop is harvested.
разнообразие флоры
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Farmers grow a mix of crops under the diverse cropping principle, which has increased plant diversity
инвазивные чужеродные виды
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Farmers have witnessed the suppression of weeds, such as Striga hermonthica (witchweed) in plots under dense cover crop and diversified cropping.
полезные виды
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Reduced tillage and accumulation of soil organic carbon have increased beneficial soil living organisms, such as the earthworms.
борьба с вредителями/ болезнями
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Diversified cropping through rotations has reduced the incidences of insect pests and diseases through disruption of pest and disease cycles. Specifically, farmers have noticed that the CA plots under maize - Mucuna pruriens intercrop are less affected by the fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda)
Климат и снижение риска стихийных бедствий
влияние засух
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The maize established with Mucuna pruriens as a cover crop has remained green and healthy for long during mid-season dry spells. This implies that the CA technology also increases water infiltration and soil water content; thus, acting as insurance against drought.
выбросы углекислого газа и парниковых газов
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Reduced tillage mitigates atmospheric carbon dioxide emissions through the decrease in fossil fuel consumption and soil disturbance. Crop residues are also retained in the field and not burnt; hence, reducing emission of carbon.
6.2 Влияние Технологии за пределами территории ее применения
воздействие парниковых газов
6.3 Подверженность и чувствительность Технологии УЗП к постепенным изменениям климата и экстремальным погодным явлениям/ стихийным бедствиям, связанным с изменением климата (в понимании землепользователей)
Постепенное изменение климата
Постепенное изменение климата
| Сезон | увеличение или уменьшение | Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| среднегодовые температуры | увеличилось | хорошо | |
| среднегодовое количество осадков | увеличилось | хорошо |
Экстремальные явления, связанные с изменением климата (стихийные бедствия)
Стихийные бедствия климатического характера
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| засухи | хорошо |
Биологические стихийные бедствия
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| эпидемии | хорошо |
| нашествия насекомых/ поражения червями | хорошо |
6.4 Анализ эффективности затрат
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с первоначальными вложениями (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
слабо позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с текущими расходами по поддержанию технологии (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
слабо позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Пояснения:
For example, it is expected that the associated improvement in soil organic matter, soil structure and nutrient status will reduce the use of fertilizers in the long term.
6.5 Внедрение Технологии
- 1-10%
Среди применяющих Технологию землепользователей, какова доля лиц, применяющих её по собственной инициативе, т.е. без какого-либо материального стимулирования со стороны?
- 51-90%
6.6 Адаптация
Была ли Технология УЗП изменена в недавнее время с целью адаптации к меняющимся условиям среды?
Нет
6.7 Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности Технологии
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
| Maize established with Mucuna pruriens as a dense cover crop is not adversely affected by the fall army worm (Spodoptera frugiperda) |
| Reduced tillage saves time, money and energy, while the direct placement of inputs (seeds and fertilizers) minimizes wastage. The saved resources can be used to engage in other income-generating activities |
| Maize established with Mucuna pruriens as a dense cover crop remains green and healthy for long during mid-season dry spells |
| Weeds, such as Striga hermonthica (witchweed) are suppressed in plots under dense cover crop and diversified cropping (rotations and inter-crops) |
| In seasons of excessive rainfall, the maize intercropped with the common bean is usually harvested even when the common bean fails |
| The CA technology has boosted maize yields, meaning more food and income, and reduced cost of feeding the family |
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
| The CA plots with Mucuna pruriens as a dense cover crop have improved soil organic matter, soil structure and nutrient status |
| Reduced tillage has enhanced soil living organisms, such as earthworms and decreased fuel consumption and soil disturbance; hence, mitigating atmospheric carbon dioxide emissions and storing carbon in soils |
| The CA technology has increased water infiltration and soil water content (moisture); thus, acting as insurance against drought |
| Diversified cropping through rotations has reduced the incidences of insect pests and diseases, as well as the risk of crop failure during extreme weather conditions and pest infestations |
6.8 Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски Технологии и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению землепользователей | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| The Mucuna pruriens used as a dense cover crop intertwines on maize crop, which might increase manual labour | Promote other erect cover crops like the lablab bean (Dolichos lablab), Desmodium and Canavalia that will have less effect on the cereal crop established |
| The yields of Mucuna pruriens used as a dense cover crop are not edible |
- Extension agents and Trainer of Trainees (ToTs) to equip farmers with knowledge on the options available for utilizing Mucuna pruriens yields other than being a cover crop - Promote other erect cover crops like the lablab bean (Dolichos lablab), Desmodium and Canavalia |
| Residue retention reduces the availability of fodder and fuel materials | Adopt an agro-forestry system with tree species that can provide alternative source of fodder and fuel |
| The critical CA inputs and implements, such as the jab planters, weed scrapers, herbicides and Mucuna seeds are hard to access |
- Incentivize and train the local fabricators to fabricate affordable CA tools - Subsidize CA inputs, such as fertilizer and herbicides - Facilitate access to credit - Train more seed producers to multiply the seeds of Mucuna pruriens |
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Agro-ecosystem contamination through use of herbicides and inorganic fertilizers | Use the right doses of herbicides and fertilizers |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/ источники информации
- выезды на места, полевые обследования
- опросы землепользователей
- опросы специалистов/экспертов по УЗП
Когда были собраны данные (на местах)?
31/05/2020
7.4 Общие комментарии
Simple and clear.
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки
Нет ссылок
Модули
Нет модулей