Drought-resistant crops [Швейцария]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Seraina Lerf
- Редакторы: Tatenda Lemann, Maria Eliza Turek, Joana Eichenberger
- Рецензенты: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_6272 - Швейцария
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Технологии
Ответственный (-ые) специалист (-ы)
землепользователь:
Brunner Stefan
Brunner Eichhof
Швейцария
Название проекта, содействовавшего документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Швейцария1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование данных, собранных ВОКАТ
Составитель и ответственный(-ые) специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.4 Декларация по устойчивости описываемой Технологии
Вызывает ли описанная здесь Технология проблемы деградации земель настолько, что ее нельзя назвать природосберегающей?
Нет
2. Описание Технологии УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Технологии
Определение Технологии:
In response to changing environmental conditions, it can be valuable to adopt new plant varieties that offer benefits such as drought tolerance. The technology described covers one such response in Switzerland.
2.2 Подробное описание Технологии
Описание:
In response to changing environmental conditions, it can be valuable to adopt new plant varieties that offer benefits such as drought tolerance. The key is the improved adaptation of the crops to heat and drought. These adaptations are based on plant physiological and morphological characteristics that confer increased drought tolerance, as well as phenology, which can also affect the plants' water requirements. The goal is to reduce production losses and promote a regional, plant-based food system in Switzerland. To introduce and maintain drought-resistant crops requires specific activities and inputs, such as selecting suitable seeds and ensuring long-term profitable cultivation. This technology is applied to cropland in Switzerland, especially in the Swiss Plateau, where climate change is causing increasingly warmer and drier summers, as well as more intense precipitation in the winter months. These climatic changes favour the cultivation of crops that can better cope with drought periods, allowing for the replacement of crops that require irrigation in the same growing areas.
The main purpose is to adapt agricultural production to the effects of climate change while simultaneously reducing the emissions caused by farming. By cultivating drought-resistant crops, the risk of production losses during drought periods can be minimized, and a transformation towards more diverse, plant-based, and regional food production systems can be promoted. A major advantage of this technology lies in the adaptability of the selected crops to climate change. Since they are better adapted to tolerating drought periods, no additional irrigation is needed: this saves labour and other resources. Moreover, growing drought tolerant crops enables the production of regional, plant-based, and protein-rich foods (especially legumes) that are appreciated by certain consumer groups and can be better marketed.
However, there are also challenges and disadvantages that are not yet appreciated by land users. The lack of knowledge about non-traditional crops in Switzerland is a significant problem. Both theoretical knowledge and practical experience in cultivation are lacking, leading to high risk for farmers who must experiment with cultivation. Additionally, despite climate scenarios predicting drier summers, there is still the risk of cool and wet summers with increased precipitation. Besides the biophysical challenges, there are also socio-economic obstacles, as the demand from wholesalers is often focused on traditional crops, and niche crops like millet are commonly not popular.
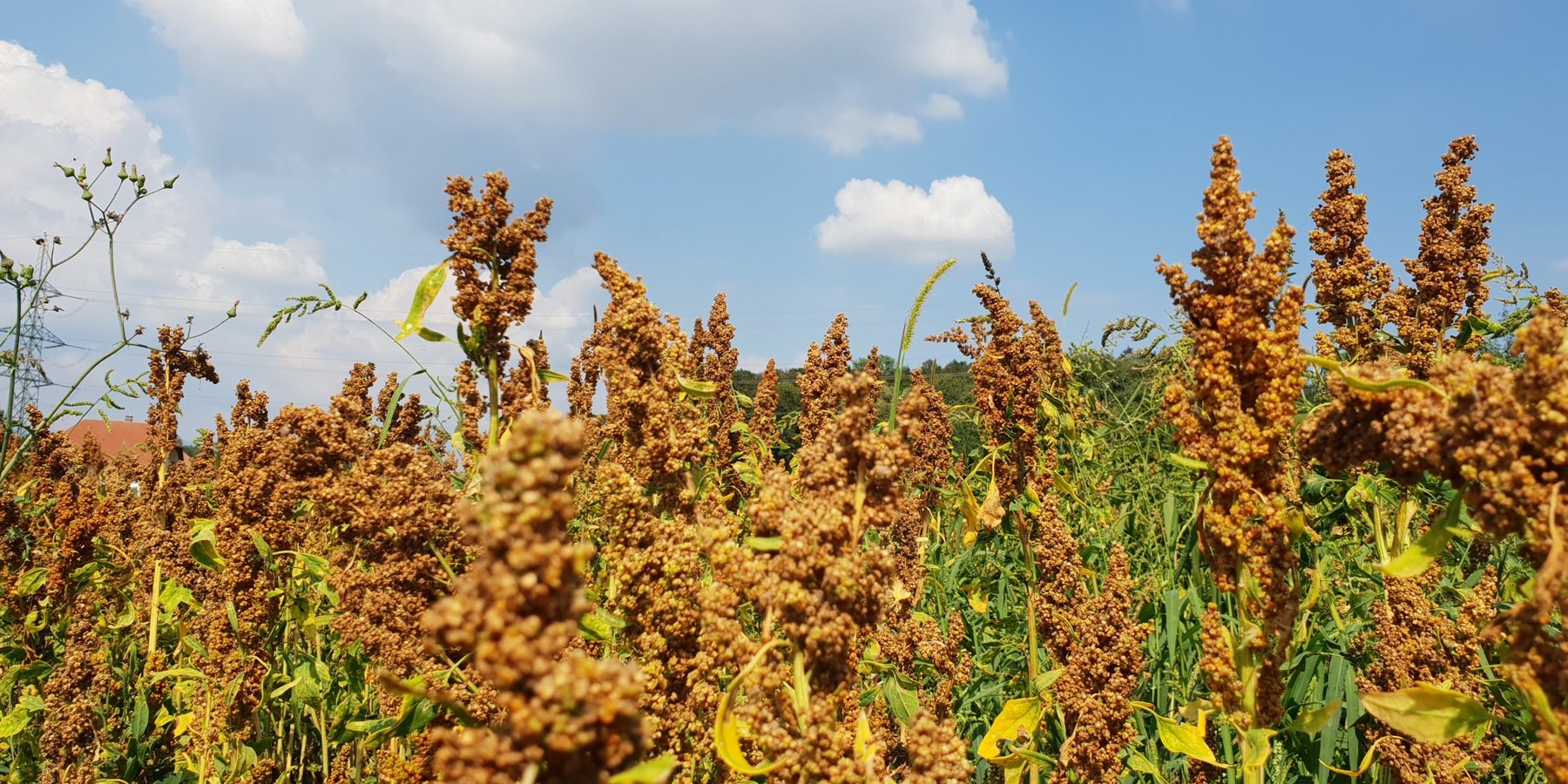
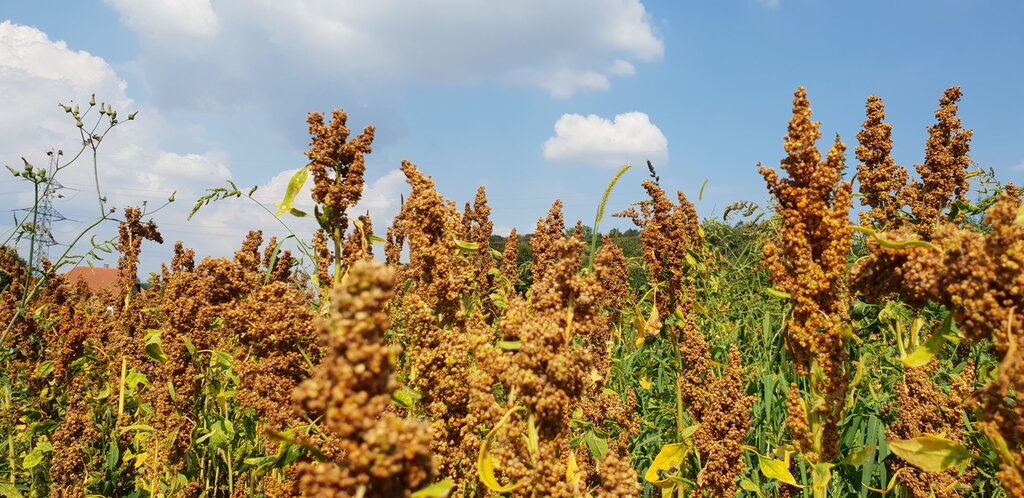
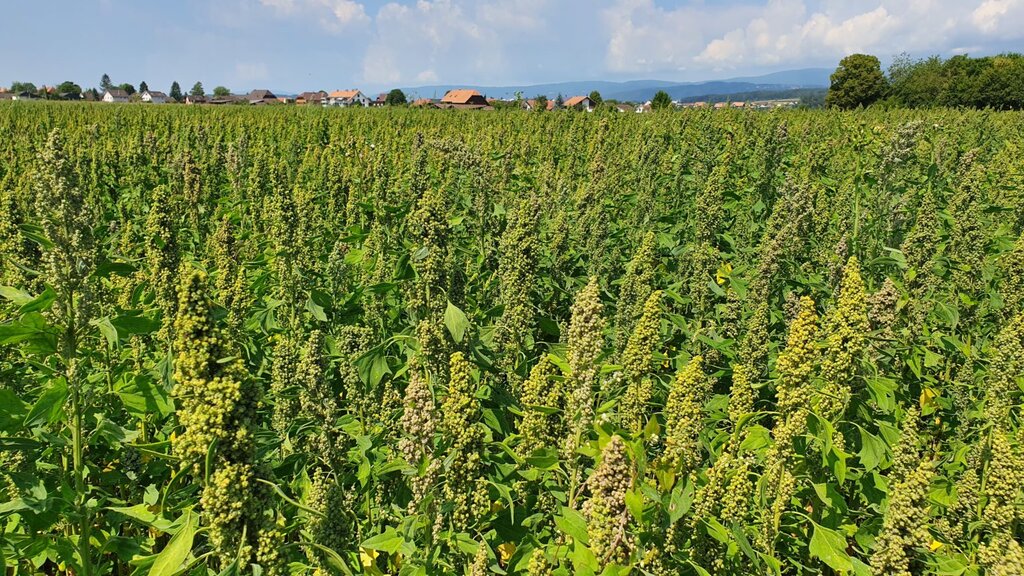
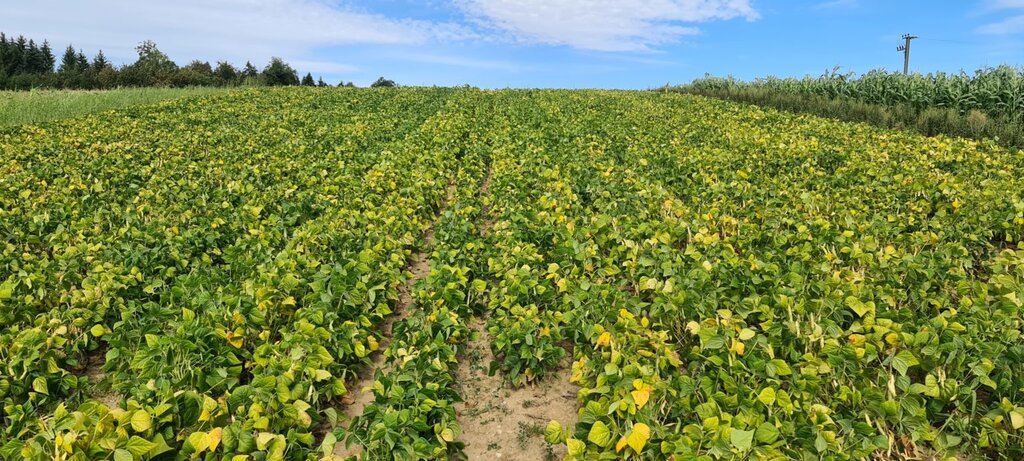
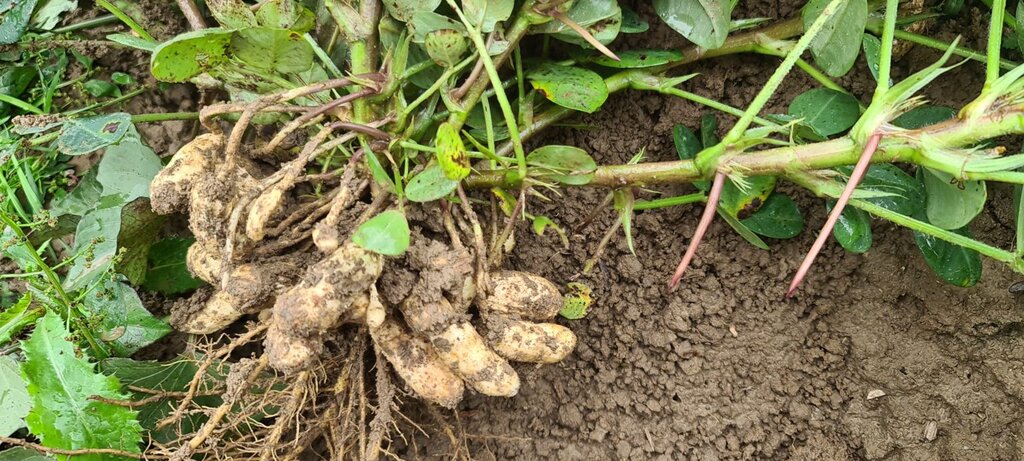
This documentation focuses on an example of an innovative farmer in Spins, Switzerland. Stefan Brunner has been testing a wide variety of drought-resistant legumes such as lentils, lupins and black runner beans on his Eichhof farm since 2017. In addition to the large-scale cultivation of these drought-resistant crops, he also cultivates quinoa, peanuts, chia, sorghum, millet and rice in a demonstration plot. Stefan Brunner simultaneously attaches great importance to sustainable cultivation methods which include surface tillage and mulching.
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Технологию
Комментарии к фотографиям:
All pictures were taken on the agricultural land of Stefan Brunner in Spins near Aarberg. The pictures of the quinoa field, the bean cultivation and the peanut harvest were taken from the website of the Brunner family's Eichhof farm:
2.5 Страна/ регион/ места, где применяется Технология, информация о которых собрана в данной Анкете
Страна:
Швейцария
Административная единица (Район/Область):
western midlands of switzerland
Более точная привязка места:
western midlands of switzerland (Broye catchment area), example farm in the canton of berne in Spins (near Aarberg)
Охарактеризуйте пространственное распространение Технологии :
- равномерно-однородное применение на определенной площади
Если точная область неизвестна, укажите приблизительную площадь:
- 0,1-1 км2
Технология применяется на ООПТ?
Нет
Пояснения:
The regions in which the technology is used are located in the agricultural zone of Switzerland
Map
×2.6 Сколько лет применяется данная Технология
Год начала реализации:
2017
2.7 Внедрение Технологии
Укажите, как именно Технология УЗП была внедрена:
- как инновация (инициатива) землепользователей
3. Классификация Технологии УЗП
3.1 Основные цели и задачи реализации Технологии
- повышение производства
- снижение или предотвращение деградации земель, восстановление нарушенных земель
- адаптация к изменению климата / экстремальным погодным явлениям и их последствиям
- создание благоприятных экономических условий
3.2 Текущий(-ие) тип(-ы) землепользования на территории, где применяется Технология
Комбинированное землепользование в пределах одной и той же земельной единицы:
Нет

Пахотные угодья и плантации
- Однолетние культуры
Ежегодный урожай - Уточните культуры:
- зерновые культуры - кукуруза
- зерновые культуры - киноа или амарант
- зерновые культуры - сорго
- зерновые культуры - пшеница (озимая)
- кормовые культуры - травы
- legumes and pulses - lentils
Число урожаев за год:
- 2
Поясните:
The number of growing seasons depends on the crops grown. With a crop rotation of 6 years, winter cereals, winter lentils/winter legumes and lupins are grown overlapping after three years of permanent grassland (grass production). Brunner also uses green manure between the different crops and therefore has around 2 growing seasons per year
Применяются ли посевы в междурядьях?
Нет
Применяется ли севооборот?
Да
Если да, укажите:
6 years crop rotation:
3 years grass
Winter cereals
Winter lentil (winter legumes)
Lupin

Пастбищные угодья
Интенсивный выпас/ выращивание кормов:
- Стойловое содержание/ нулевой выпас
3.3 Изменилось ли использование земель в связи с внедрением Технологии?
Изменилось ли использование земель в связи с внедрением Технологии?
- Нет (см. пункт 3.4)
Комбинированное землепользование в пределах одной и той же земельной единицы:
Нет
3.4 Водоснабжение
Обеспеченность водой участков, где реализуется Технология :
- полное орошение
Пояснения:
Stefan Brunner is able to irrigate all his fields in Spins near Aarberg. He owes this to the nearby location of the "Alte Aare" river, which gives him the privilege of having sufficient water available even during the summer.
3.5 Категория УЗП, к которой относится Технология
- улучшение сортов растений/ пород животных
3.6 Мероприятия УЗП, выполняемые в рамках Технологии

Агрономические мероприятия
- A5: Семенное хозяйство, селекция, применение улучшенных сортов
3.7 Основные проблемы деградации земель, на решение которых направлена Технология

водная эрозия почв
- ВЭп: поверхностная эрозия/смыв верхних почвенных горизонтов

ухудшение физических свойств почв
- Фу: уплотнение

биологическая деградация
- Бр: сокращение растительного покрова
Пояснения:
Brunner sees soil degradation as an unavoidable consequence of all agricultural tillage. However, this can vary greatly depending on the type of tillage. Brunner does not see a direct improvement in soil degradation through the cultivation of drought-resistant plants. However, in combination with soil-conserving forms of cultivation. Brunner attaches particular importance to shallow tillage (maximum depth of 5 cm). Accordingly, crops that can be sown at this depth are suitable. Brunner strives for permanent rooting of the soil and prefers crops that can be sown in the fall so that the soil is rooted over the winter or can handle green manure. These measures (shallow cultivation and root penetration) keep the soil looser. The roots form flow paths, which increases the water storage capacity of the soil. The shallow tillage with small machines, which Brunner uses for his drought resistent crops, also reduces the physical pressure on the soil compaction.
3.8 Предотвращение и снижение деградации земель, или восстановление нарушенных земель
Укажите цель Технологии по отношению к деградации земель :
- предотвращение деградации земель
4. Технические характеристики, мероприятия по практической реализации, вложения и стоимость
4.1 Технический рисунок, иллюстрирующий Технологию
Спецификация (пояснения к техническому рисунку):
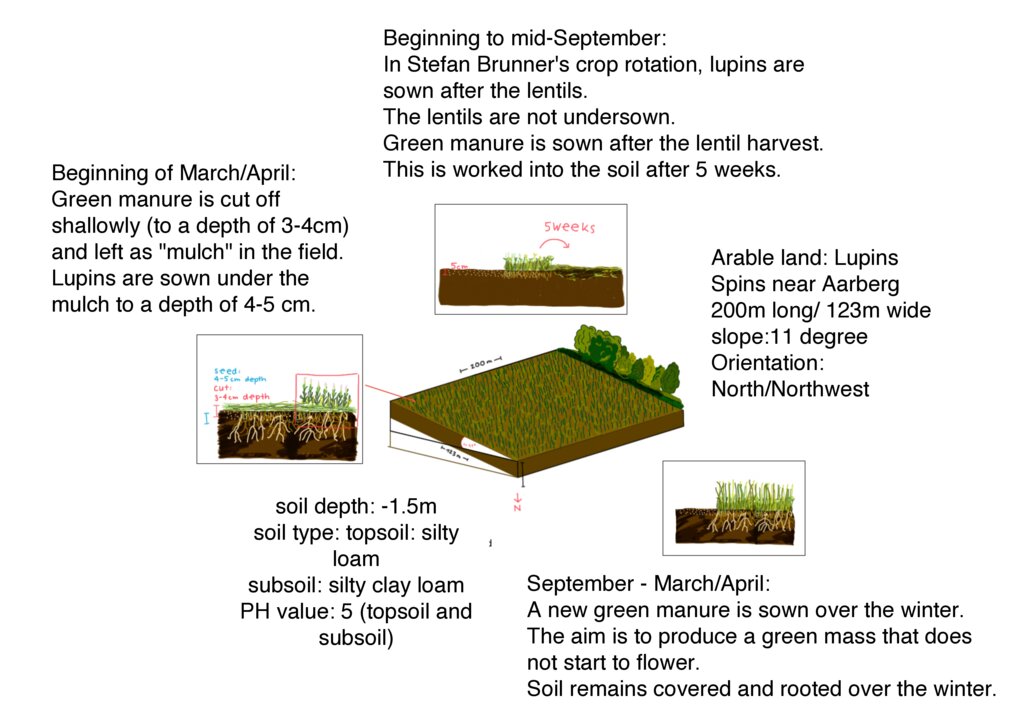
The depicted technical drawing shows the farmland of Stefan Brunner, where lupins were sown in the spring of 2024. This field is representative of all the arable land, totaling 14 hectares of crop rotation areas managed by Brunner. The cultivation areas are situated at an altitude of 487 meters above sea level on flat or slightly sloping terrain on a hill range in the Bernese Mittelland. The depicted field is 200 meters long and 100 meters wide, with a slope of approximately 11° and an orientation towards the north/northwest. The soil is classified as silty loam based on the finger roll test, with the subsoil containing more clay compared to the topsoil. The pH value is 5, which is in the slightly acidic range.
The fields in Spins are located near the river "Alte Aare." Due to the proximity to the water, the farmer has the privilege of having irrigation available for all his fields. Since the implementation of large-scale cultivation of drought-resistant crops in 2017, Brunner has been growing a variety of crops on his land. According to Brunner, the following crops that he cultivates can cope well with drought: lentils, lupins, sorghum, corn, peanuts, millet, and cabbage. In combination with the method of surface rotting and mulching, the soil is protected against drying out and erosion and can retain moisture for longer. The cultivation of various crops can be combined with this farming method, leading to better drought resistance.The graphic illustrates the cultivation of lupins using a green manure cultivation method.
Автор:
Seraina Lerf
Дата:
21/06/2024
4.2 Общая информация по необходимым вложениям и стоимости
Уточните, как рассчитывались затраты и вложения:
- на площадь, где применяется Технология
Укажите размер и единицу площади:
18 ha
Укажите денежные единицы, использованные для подсчета затрат:
- Доллары США
4.5 Поддержание/ текущее обслуживание
| Деятельность | Сроки/ повторяемость проведения | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | tillage: and sowing | (once per cultivation period) |
| 2. | maintenance: weeding (recurring work step, but less labor-intensive than tillage) | (Recurring work throughout the year) |
| 3. | harvesting: threshing | (once a year for grain legumes) |
| 4. | Threshing the previous crop. Before the lupins, lentils were grown in Stefan Brunner's crop rotation. | summer (july-september) |
| 5. | If there is no undersowing (as with the lentils), the soil must be tilled. This is very shallow, i.e. no more than 5 cm deep. | summer (july-september) |
| 6. | A varied green manure is sown in the cultivated soil. The aim of this is to keep the soil rooted and to incorporate nutrients into the soil | summer (july-september) |
| 7. | After 6-7 weeks, the green manure is worked back into the soil. When the plants are still young, they have the highest nutrient input before they extract the nutrients from the soil again if they continue to grow. As a result, the nutrients are mineral-bound in the soil, i.e. stored so that they are available to the plants. | autumn (early/mid-September) |
| 8. | Another green manure is sown, which produces a lot of mass but freezes off in winter before it starts to flower. The aim is to keep the soil covered and rooted throughout the winter. | autumn |
| 9. | In spring, the soil is again worked shallowly. This means a maximum depth of 3-4 cm. The winter green manure is "planed". This means cutting it to a depth of 3-4 cm and leaving the plant material on the ground. | spring |
| 10. | The lupins are sown under the plant material to a depth of 4-5 cm, so that the soil remains moist and the plant material protects the soil from drying out. | spring (beginning of March/April) |
Пояснения:
The first three information does not refer to a specific crop, but describes general maintenance activities that Brunner takes into account when cultivating his crops.
Stefan Brunner's crop rotation also includes 3 years of grassland. This cultivation reduces the workload, as no maintenance work has to be taken into account in addition to the harvest.
The activities 4-10 described relate to the cultivation of lupins. This crop was cultivated at the time of documentation in spring 2024.
4.6 Стоимость поддержания/ текущего обслуживания ( в год)
Если Вы не можете указать расходы в приведенной выше таблице постатейно, дайте оценку общих затрат на поддержание Технологии:
22575,0
Пояснения:
The costs of cultivating drought-resistant plants cannot be precisely quantified. Based on the interview results, it is therefore not possible to make any general statements about the costs of cultivation.
Nevertheless, in order to be able to make a rough estimate of the input costs required to implement the technology (Example based on the cultivation of lupins), information from REFLEX 2024 (AGRIDEA's business database) and FiBL (Research Institute of Organic Agriculture) was used. According to REFLEX 2024, the target price for lupins in 2023 and 2024 is 144Fr./dt. A FiBL leaflet also states a requirement of 130-170kg seed/ha (blue lupins).
According to the results collected, the documented farm uses a disk coulter seed drill with a row spacing of 12.5 cm, sows approx. 3-4 cm deep and requires 200 kg/ha of seed.
With a field size of the documented farm of approx. 2 ha, the costs for the required lupin seed amount to CHF 576 according to the data from REFLEX 2024.
Then there are the labor costs and the machines. Depending on which machines are required and whether the required machines are already available or whether a new investment or rental would be necessary.
The estimate only refers to the seed required. Additional recurring costs include maintenance/ rental costs for machinery and labour. Unfortunately, it is not possible to provide more precise information on this. It depends on the machines and labor costs used.
However, according to the interview results with a farmer who grows drought-resistant crops, there are no significant additional costs if the drought-resistant crops can be grown with the same machinery as for conventional crops.
4.7 Наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат
Опишите наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат:
The greatest difficulty in terms of costs lies in the lack of knowledge in the cultivation of these crops. The fact that very little scientific and practical knowledge and experience is available means that farmers take a greater risk in cultivating these crops. If cultivation is not carried out correctly and the farmer suffers production losses as a result, he bears the consequences. This is why they have to look for inventive solutions.
5. Природные и социально-экономические условия
5.1 Климат
Среднегодовое количество осадков
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1000 мм
- 1001-1500 мм
- 1501-2000 мм
- 2001-3000 мм
- 3001-4000 мм
- > 4000 мм
Укажите среднегодовое количество осадков (если известно), мм:
865,00
Укажите название соответствующей метеостанции:
Payerne
Агроклиматическая зона
- Умеренно-влажная
average maximum temperature 14.2°C, average minimum temperature 5.1°C
5.2 Рельеф
Склоны (преобладающие):
- пологие (0-2%)
- покатые (3-5%)
- покато-крутые (6-10%)
- крутые (11-15%)
- очень крутые (16-30%)
- чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
- обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа:
- плато/ равнины
- гребни хребтов/холмов
- склоны гор
- склоны холмов
- подножья
- днища долин
Зона высотной поясности:
- 0-100 м над уровнем моря
- 101-500 м н.у.м.
- 501-1000 м н.у.м.
- 1001-1500 м н.у.м.
- 1501-2000 м н.у.м.
- 2001-2500 м н.у.м.
- 2501-3000 м н.у.м.
- 3001-4000 м н.у.м.
- > 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
Укажите, приурочено ли применение Технологии к специфическим условиям:
- не имеет значения
5.3 Почвы
Средняя мощность почв:
- поверхностные (0-20 см)
- неглубокие (21-50 см)
- умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
- глубокие (81-120 см)
- очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта):
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
Гранулометрический состав (на глубине более 20 см):
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем горизонте:
- среднее (1-3%)
5.4 Доступность и качество воды
Уровень грунтовых вод:
5-50 м
Доступность поверхностных вод:
хорошая
Качество воды (без обработки):
исключительно для сельскохозяйственного использования (орошение)
Качество воды относится к:
поверхностные воды
Является ли солёность воды проблемой?
Нет
Происходят ли периодические затопления территории?
Да
Регулярность:
эпизодически
Комментарии и дополнительная информация по качеству и количеству воды:
The increasing threat of heavy rainfall events due to climate change enhances the threat of flooding.
5.5 Биоразнообразие
Видовое разнообразие:
- низкое
Разнообразие местообитаний:
- низкое
Комментарии и дополнительная информация по биоразнообразию:
Both are in between low and medium, but rather low
5.6 Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Осёдлый или кочевой:
- Осёдлый
Рыночная ориентация производства:
- товарное/ рыночное хозяйство
Доходы из других источников:
- < 10% всех доходов
Относительный уровень достатка:
- средний
Индивидуальное или коллективное хозяйство:
- частное/ домовладение
Уровень механизации:
- механизировано/ есть автотранспорт
Пол:
- женщины
- мужчины
Возраст землепользователей:
- средний возраст
5.7 Средняя площадь земель, используемых землепользователями с применением Технологии
- < 0,5 га
- 0,5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1000 га
- 1000-10000 га
- > 10000 га
Считается ли это мелким, средним или крупным хозяйством (по местным масштабам)?
- крупное
Пояснения:
The Swiss average of agricultural area per farm is 20.9 ha. In the Broye region, it is 31.65 ha
5.8 Собственность на землю, права на земле- и водопользование
Землевладелец:
- индивидуальная, оформленная в собственность
Право землепользования:
- аренда
- индивидуальное
Право водопользования:
- общинное (контролируемое)
5.9 Доступ к базовым услугам и инфраструктуре
медицинское обслуживание:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
образование:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
технические консультации:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
занятость (вне хозяйства):
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
рынки:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
электроснабжение:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
транспорт и дорожная сеть:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
водоснабжение и канализация:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
финансовые услуги:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
6. Воздействия и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Технологии УЗП в пределах территории ее применения
Социально-экономическое воздействие
Продуктивность
риск потери продуктивности
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Production losses during periods of drought can be minimised
разнообразие продукции
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Product diversity can be increased by growing alternative drought-resistant crops
управление землями
Комментарий/ пояснения:
By improving the soil's ability to cope with weather extremes (drought/heavy rainfall), land management in cultivation is simplified through greater flexibility.
Доступность и качество воды
доступность питьевой воды
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Gentle tillage without the use of pesticides in the cultivation of drought-resistant crops (good groundwater quality)
потребность в оросительной воде
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Drought-resistant crops require less irrigation. In addition, the tillage method (surface rotting) also prevents the soil from drying out.
Доходы и затраты
сельскохозяйственные издержки
доходы хозяйства
Комментарий/ пояснения:
more diverse market thanks to greater product diversity in the cultivation of alternative crops
разнообразие источников дохода
Комментарий/ пояснения:
more diverse market thanks to greater product diversity in the cultivation of alternative crops
объем работ
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Gentle soil cultivation with minimal use of machinery (and application of surface rotting) requires more labour, even if the cultivation of drought-resistant crops does not mean additional work compared to conventional crops
Экологическое воздействие
Водный цикл/ поверхностный сток
количество воды
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Less water required for irrigation
качество воды
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Avoiding the use of pesticides leads to improved water and soil quality
Harvesting/collection of water
сбор воды/ водоудержание
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The improved water absorption capacity of the soil (through soil cultivation methods) can lead to improved groundwater recharge
поверхностный сток
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Surface runoff can be minimised by improving the water absorption capacity of the soil (permanent root penetration).
водный дренаж
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Due to the improved water absorption capacity of the soil (through soil cultivation methods), less excess water is formed
уровень грунтовых/ подземных вод
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The improved water absorption capacity of the soil can lead to improved groundwater recharge
испарение
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Permanent ground cover can reduce soil drying out
Почвы
влажность почв
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The permanent ground cover reduces drying out and the permanent root penetration leads to improved water absorption capacity of the soil. This can improve the soil water balance.
почвенный покров
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The ground should be permanently covered. The permanent ground cover reduces drying out.
утрата почв
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The permanent covering and rooting of the soil prevents surface run-off. This can prevent soil loss.
аккумуляция почвенного материала (намыв, эоловая, и др.)
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Green manuring can ensure an improved hummus structure.
образование корки на поверхности почв/ запечатывание
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The permanent ground cover reduces dehydration and the permanent root penetration leads to improved water absorption capacity of the soil. This prevents soil sealing.
уплотнение почв
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The soil should remain permanently rooted and covered and be worked with as few and light machines as possible. This minimises soil compaction.
круговорот/ восполнение питательных веществ
Комментарий/ пояснения:
By applying green manure, the soil can be enriched with nutrients (nutrient cycle of the soil).
почвенное / подземное органическое вещество/ углерод
Биоразнообразие: растительность, животный мир
разнообразие флоры
Комментарий/ пояснения:
greater plant diversity in the cultivation of alternative crops
Климат и снижение риска стихийных бедствий
влияние засух
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Due to the improved ability of plants to cope with drought. to deal with drought. In combination with good water storage capacity of the soil, the effects of drought on the harvest can be minimised.
Укажите оценку внешних воздействий (измерений):
Information in this chapter on practical experience in the cultivation of drought-resistant crops is based on interview results from Stefan Brunner. He cultivates drought-resistant crops in combination with surface cultivation and mulching. As a result the effects of the two technologies cannot be considered entirely separately.
6.2 Влияние Технологии за пределами территории ее применения
доступность воды
Комментарий/ пояснения:
In the analysed area (Spins near Aarberg) there is a permanent possibility to irrigate the fields due to the water availability of the nearby river Aare
надежность и постоянство водотоков
Комментарий/ пояснения:
In the analysed area (Spins near Aarberg) there is a permanent possibility to irrigate the fields due to the water availability of the nearby river Aare
загрязнение подземных/ речных вод
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The use of herbicides and fungicides was avoided in the cultivation of drought-resistant crops, thus preventing contamination
буферная/ фильтрационная способность
Комментарий/ пояснения:
improved water absorption capacity (through soil cultivation methods) of the soil
Stability of production
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Due to the improved adaptability to climatic conditions, production remains more stable
Укажите оценку внешних воздействий (измерений) :
Information in this chapter based on the state of knowledge from the research of Dr. Annelie Holzkämper
6.3 Подверженность и чувствительность Технологии УЗП к постепенным изменениям климата и экстремальным погодным явлениям/ стихийным бедствиям, связанным с изменением климата (в понимании землепользователей)
Постепенное изменение климата
Постепенное изменение климата
| Сезон | увеличение или уменьшение | Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| среднегодовые температуры | увеличилось | умеренно | |
| сезонные температуры | лето | увеличилось | умеренно |
| сезонное количество осадков | лето | снизилось | хорошо |
Экстремальные явления, связанные с изменением климата (стихийные бедствия)
Стихийные бедствия климатического характера
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| сильная жара | умеренно |
| экстремально холодная погода | не известно |
| экстремальные зимние условия | не известно |
| засухи | хорошо |
Биологические стихийные бедствия
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| эпидемии | не известно |
Пояснения:
Information in this chapter based on the state of knowledge from the research of Dr. rer. nat. Annelie Holzkämper
6.4 Анализ эффективности затрат
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с текущими расходами по поддержанию технологии (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
отрицательно
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Пояснения:
The more equipment has to be used in cultivation, the more expensive the maintenance costs become. As Brunner is able to cultivate drought-resistant crops such as lupins and lentils with the existing equipment, he did not incur any additional costs. Even if a new machine for gentle soil cultivation in the cultivation of drought-resistant crops, such as a “planer”, had to be purchased, a plow could be sold in return. As long as the same mechanization can be used as Brunner was already using for conventional crops, the costs remain the same. As a result, Brunner's cost-benefit ratio was assessed as positive, even in the short term.
In the long term (over a period of 10 years), Brunner also sees an increased positive cost/benefit ratio. Consistently good soil cultivation regenerates the soil so well that it is able to absorb much more water. The amount of work required to implement this form of cultivation increases in the short term. However, the improved soil conditions in connection with the cultivation of drought-resistant crops have a positive effect on the workload and yield in the long term, as the crops on healthy soil are more flexible in the face of extreme weather conditions such as increasingly frequent droughts. Brunner also emphasizes that, from his perspective, it is worth incurring higher start-up costs for careful cultivation in order to generate long-term benefits.
The start-up costs are often relatively high, but the long-term benefits are all the more valuable. Start-up capital is therefore essential to be able to generate long-term benefits.
6.5 Внедрение Технологии
- отдельные случаи/ эксперимент
Среди применяющих Технологию землепользователей, какова доля лиц, применяющих её по собственной инициативе, т.е. без какого-либо материального стимулирования со стороны?
- 0-10%
Пояснения:
Information based on the experience of Stefan Brunner (Spins)
6.6 Адаптация
Была ли Технология УЗП изменена в недавнее время с целью адаптации к меняющимся условиям среды?
Да
другое (поясните):
breeding
Укажите, что именно изменилось в Технологии (дизайн, используемые материалы или виды растений/животных и т.д.):
Continuous adaptation in the context of breeding
6.7 Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности Технологии
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
| No Irrigation Needed: These crops do not require irrigation, thus saving water and reducing labor. |
| Promotion of Soil Health: The cultivation of these crops is beneficial for the soil, as as the tillage is shallow and legumes do not require additional nutrient inputs through fertilization. |
| Benefits in Direct Marketing: These crops are niche products produced in limited quantities in Switzerland. Conscious consumers who value regional food products appreciate these items and understand the higher costs due to the high labor requirements. |
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
| Reduced Irrigation Needs: If the crops can tolerate more drought, less irrigation is needed. |
| Minimized Economic Risk: Drought tolerance reduces the risk of crop failure during dry periods. |
| Crop Rotation Benefits: Better adaptation through diverse crop cultivation. |
6.8 Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски Технологии и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению землепользователей | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| High Labour Requirements: initial labour requirements are significantly higher due to limited knowledge and practical experience in cultivation, but with time this reduces - as less and less work is required on healthy and nutrient rich soils. | More practical knowledge should be gathered by encouraging more farmers to cultivate these crops and facilitating knowledge exchange. |
| Lack of Mechanization: Available market machines are not suited for the desired cultivation methods. | Alternative machines are needed, which are smaller and lighter and only minimally till the soil. New approaches and inventions in machinery are required. |
| The wholesale market is not particularly interested in domestically produced alternative foods. Wholesalers are profit-oriented and primarily offer what is consumed in Switzerland. | A reorientation of dietary habits is necessary. Millet, for example, is ideally suited to the climatic conditions in the Seeland region. Increased consumption could lead to more extensive cultivation. |
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Lack of knowledge: limited knowledge and practical experience in cultivation | More research should be carried out in this area and practical experience in cultivation should be gained through practical implementation. Inovative farmers are in demand. |
| Weather Variability: There is no guarantee that heavy rains won't occur, potentially ruining the harvest. | The extent to which crops are affected by severe weather events depends on when they occur. Severe weather events have an impact on every crop, but of course you don't know when they will occur. A useful strategy is therefore to build a highly diverse production system at farm and landscape level. |
| Practical and Socioeconomic Challenges: Market preferences and practical issues, such as livestock not favoring sorghum feed, can be obstacles. | No answer given. |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/ источники информации
- опросы землепользователей
On June 10, 2024, an interview was conducted with farmer Stefan Brunner on his farm in Spins near Aarberg. Additionally, the cultivated area was inspected
- опросы специалистов/экспертов по УЗП
On June 20, 2024, an interview was conducted with PD Dr. Annelie Holzkämper.
Когда были собраны данные (на местах)?
10/06/2024
Пояснения:
Inspection of the cultivation aera
7.2 Ссылки на опубликованные материалы
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Heinz, Malve et al. (2023): How to find alternative crops for climate-resilient regional food production, in: Agricultural Systems, Bd. 213, S. 103793, doi:10.1016/j.agsy.2023.103793.
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Wuyts, Nathalie et al. (2023): Klimaresilienter Ackerbau 2035, Agrarforschung Schweiz, doi:10.34776/afs13-135.
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Heinz, Malve. (2021): Prospects of cultivating alternative crops in a changing climate in Switzerland, Master’s Thesis, University of Bern.
7.3 Ссылки на соответствующую онлайн-информацию
Название/ описание:
Internet platform of the Eichhof of the Brunner family from Spins near Aarberg
Адрес в сети Интернет:
https://www.brunnereichhof.ch
7.4 Общие комментарии
The information used to complete this documentation is mainly based on the experience reports of Stefan Brunner from an interview on June 10, 2024
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки
Нет ссылок
Модули
Нет модулей