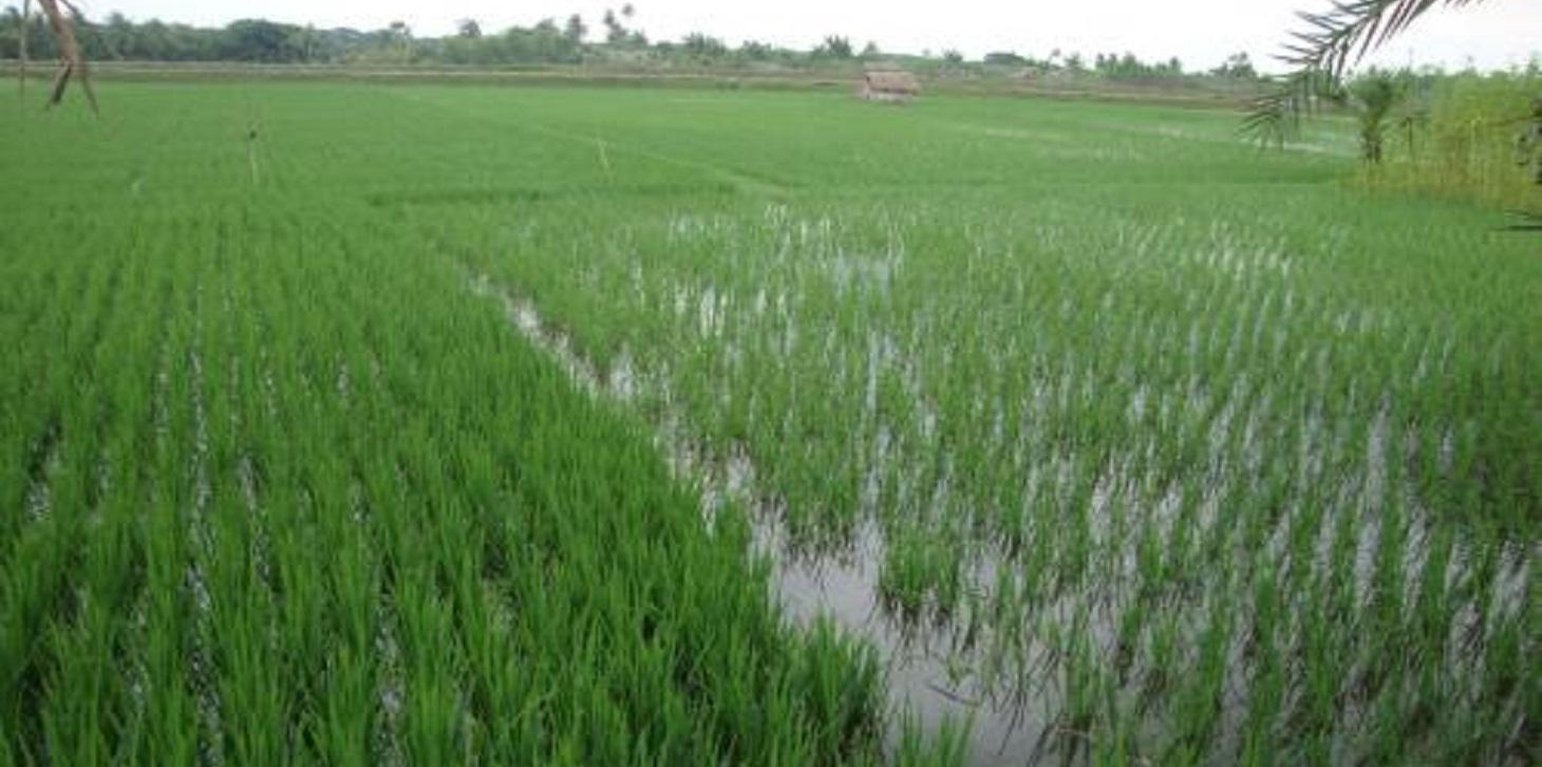




Gher is a local word used for shrimp cultivation plot. The boundaries of these ghers are nowadays raised and maintained to grow vegetables, fruits and also some tree species. In this case the boundary of the plot is raised at least 3 feet with grest width 1 feet plus depending on the height of the boundary (Bund/dyke). Within the gher the land is used for both sweet water prawn (Golda) or saline water prawn (Bagda) with other different types of fishes (locally called Sada Mach) if suitable depending on the salinity of water. Some of the gher lands are used for transplanted Aman with shrimp/fishes.
Farmers dug a ditch along the boundary or in any corner of the field or at the center of the plot to preserve water and fishes during the dry season. In some of the cases the farmers used shallow tube well water to sustain the fishes. In non-to slightly saline areas they used it even for boro (winter rice).
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of this technology is a boundary which is used for various types of crops, including year round vegetables and land for rice and fishes including shrimps.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The boundary is constructed above flood level (2-3 feet), the width is approx. 2-3 feet, the ditches are 2-3 feet deep along the boundary or at the corner or at the center.
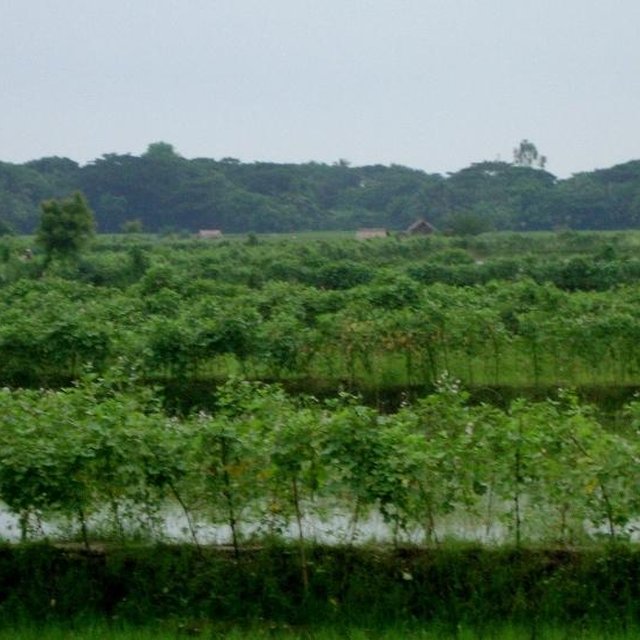
To grow vegetables farmers used nylon nets for creeping supported by the bamboo or Dhaincha or strings.
Top soils kept on top of the bunds to avoid relatively less fertile soil on the bunds.
Main inputs are seeds of vegetables, nets, bamboo, strings, fingerlings of fish etc.
Natural / human environment: The salinity of the soils from the bunds is washed away by rainwater, which facilitates vegetable production: Rain water desolves salt and moves to the bottom of the bund, and soil becomes non-saline or slightly saline where vegetable could be grown.
สถานที่: Khulna, Bangladesh Southern region, บังกลาเทศ
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี:
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ (approx. 1-10 ตร.กม.)
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
ประเภทของการแนะนำ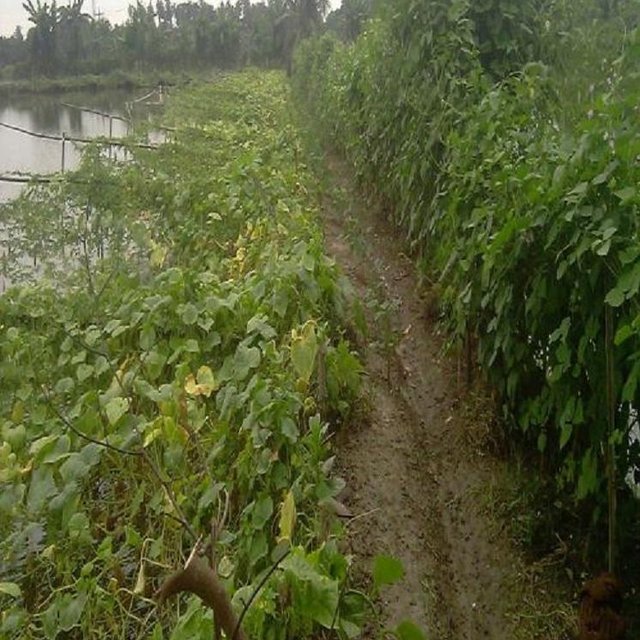







ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค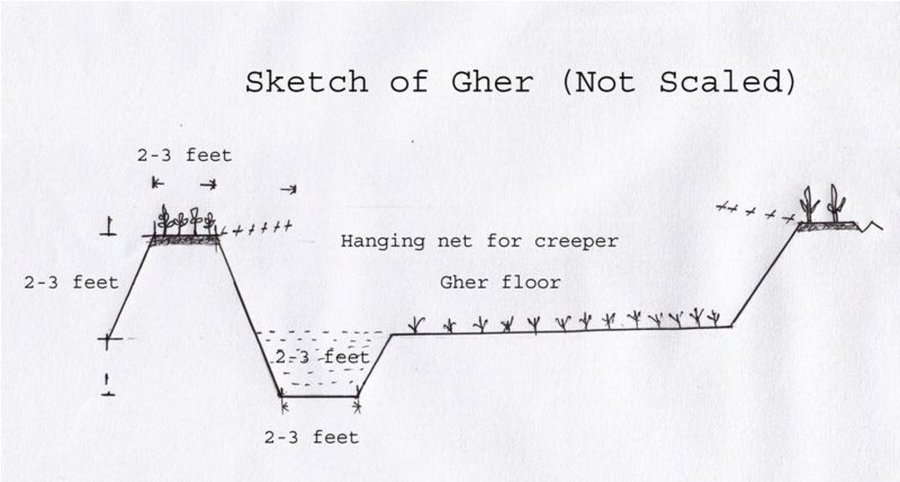
ผู้เขียน Shoaib Jalal
The gher boundary is raised approximately 2-3 feet with a crest of 2-3 feet. A ditch also dug to store water and fish during dry season.
Location: Dumuria. Khulna Date: 03-09-13 Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (It is only land manipulation.) Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Previously farmer did not put the top soil on the top of the bunds. That impedes crop production on bunds.) Main technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), water harvesting / increase water supply, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use, Decrease of soil salinity, Increase of options for growing more crops Agronomic measure: Top soil kept on top Structural measure: Bunds Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1 Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5-1 Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 10-50 Construction material (earth): Bunds are raised by piling earth Change of land use practices / intensity level: Bunds are used for year round cropping |
|||||||||||
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (Taka) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (Taka) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Farmers cut the earth from adjacent lands | ha | 10.0 | 65.0 | 650.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | ha | 2.0 | 300.0 | 600.0 | 100.0 |
| Watch and ward | ha | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Seeds, nets etc | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | |||||
| Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 1'605.0 | ||||
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (Taka) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (Taka) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Transplanting seedlings/seeds | persons/day/ha | 2.0 | 10.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 20.0 | ||||
Desalinized soil of the bund
Cash from vegetables
Conflicts to use water resource
Ghers are ponded and no water can be drained
+ Soil salinity reduced as washed by rainwater -> found in soils of Gher bunds
- Due to ground water abstraction -> found in coastal regions, increasing trend