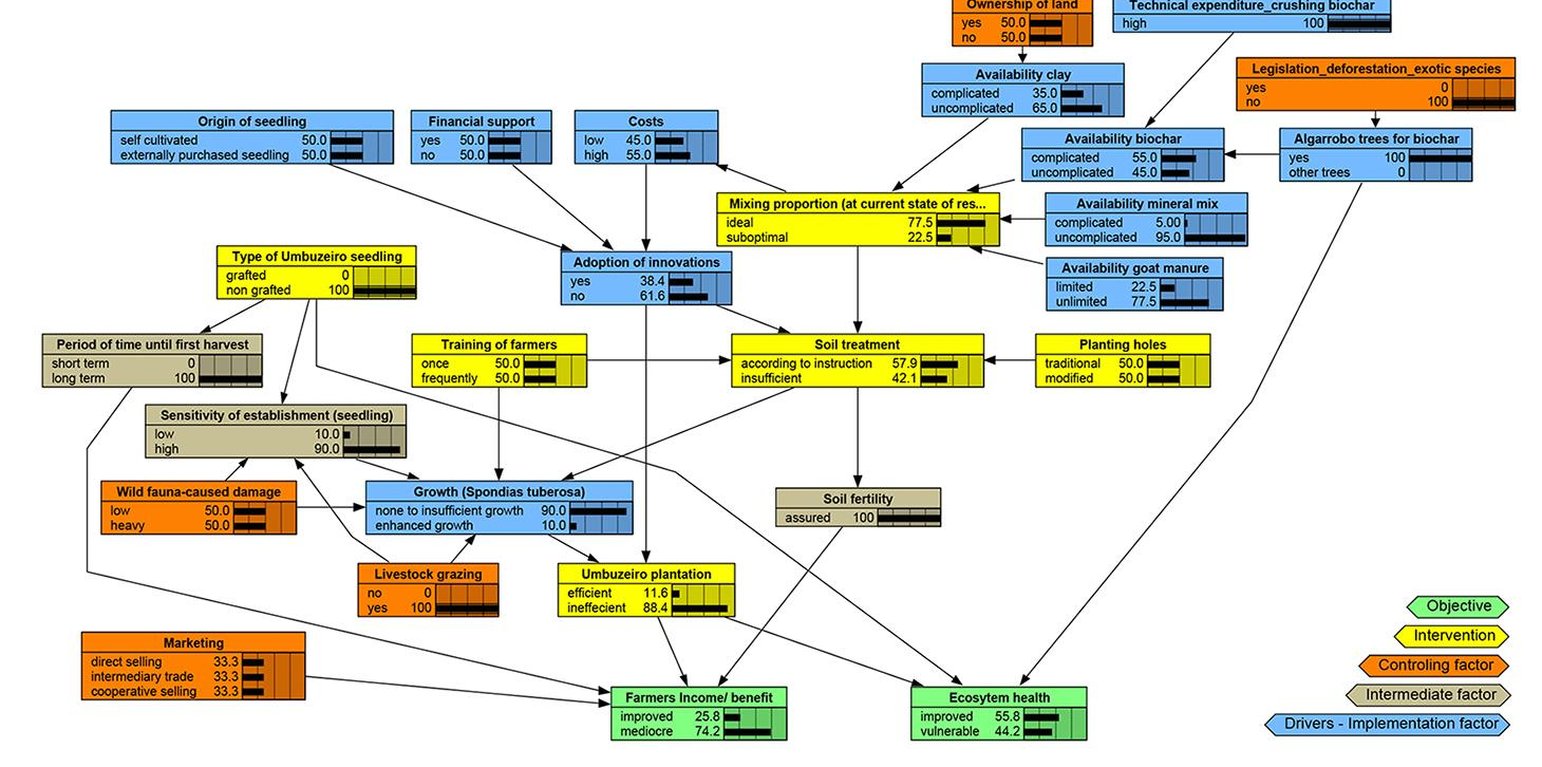



The study focus was on the determinants behind the adoption of innovations developed under a scientific project. The specific innovation analysed was intended to benefit both the environment and local smallholder farmers: namely cultivating a multi-purpose, low-growing, to the prevailing harsh semiarid environment well-adapted tree species (Spondias tuberosa L. – so called umbuzeiro). The assessment method was selected as it allows the combination of qualitative and quantitative data, and can be applied even in data-scarce situations. Moreover, it allows downscaling from a broad overview to small-scale management.
Knowledge is collected from different disciplines to support decision-making through the inter- and transdisciplinary approaches of constellation analysis and Bayesian networks. A Bayesian Network (BN) is a probabilistic graphical model that represents a set of variables (elements, nodes) and their conditional dependencies. There are three input components to a Bayesian Network: (a) a set of elements representing factors relevant to a particular environmental system or problem, (b) the links between these elements, and (c) the conditional probability tables (CPTs) behind each node (element) used to calculate the state of the node. Collected data and ratings are arranged in a hierarchical Bayesian Network model in Netica software (Netica 5.12 - freeware up to 15 nodes).
The creation of a Bayesian Network model is as follows: the objectives and necessary interventions for the innovation process aimed at sustainable management are characterized, with scientists arranging a conceptual diagram, including the mapping of elements. States of the nodes are determined through study of the literature and expert consultation (by scientists, stakeholders and experts on related topics). In a final step, a sensitivity analysis is performed on the Bayesian Network to highlight crucial nodes with the highest influence on objectives in order to derive actions to be recommended.
Stakeholder participation is the core process of designing Bayesian Networks. In pre-consultations stakeholders help identifying major influencing factors and relationships. Assessments are compiled in interview sessions enabling the states of the nodes to be quantified later. In this case study, the stakeholders were farmers, farmer-supporting institutions, and expert in soils, vegetation and crops.
สถานที่: Itaparica Reservoir, Petrolândia, Pernambuco, Brazil, บราซิล
วันที่ริเริ่ม: 2014
ปีที่สิ้นสุด: 2016
ประเภทของแนวทาง
| ผู้มีส่วนได้เสียหรือองค์กรที่นำไปปฏิบัติใช้มีส่วนเกี่ยวข้องกับแนวทางนี้อย่างไร | ระบุผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสีย | อธิบายบทบาทของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสีย |
| ผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น | Farmers of a resettlement community on dryland; Representatives of the indigenous tribe of Pankararu | |
| ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM หรือที่ปรึกษาการเกษตร | Experts in soil and crop sciences; Expert in vegetation and biodiversity science of the Caatinga | |
| รัฐบาลแห่งชาติ (ผู้วางแผน ผู้ทำการตัดสินใจ) | Institute of Agriculture in Pernambuco (IPA); A private company as the hired institution by the National Institute for Colonization and Agrarian Reform - INCRA | |
| Company of plant breeding, seed science |
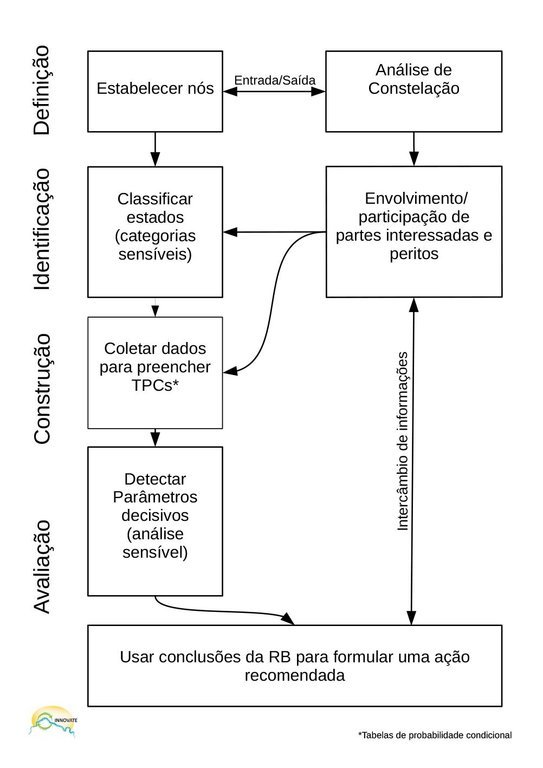
Simplified work flow of Bayesian Network (BN) showing different steps:
Defining: apply or use already applied constellation analysis (see A_BRA003en) for information and visualization of node setting for the BN model and for stakeholder identification.
Identifying: clarify objectives, implementation factors, interventions, intermediates and controlling factors. Give every node a state, e.g. date, temperature range, amount of precipitation, or a classification: high / low…
Building: Collect data to fill the conditional probability tables (CPTs) behind every node. Prepare questionnaires, ask experts and conduct a literature search. Avoid too much states and no more than four nodes indicating the next node. Finish the model by entering all data in a programme (e.g. Netica).
Evaluating: Compare different scenarios by changing the state of inputs (e.g. from low to high). Show a baseline (without changes), a most improved and least improved scenario to justify recommendations. Finally, hand over recommended actions to stakeholders.
การตัดสินใจถูกทำโดย
การตัดสินใจถูกตัดสินอยู่บนพื้นฐานของ
Detecting decisive factors for an ideal scenario of implementation being adopted by land users. For the participants it was interesting to participate in preparing a joint view of their action space - this is generally known in its parts though not with its major interconnections and complexity. Participants especially acknowledged this value added for them.
Research on the situation of local action and governance was a major driver for the workshops. University project members prepared and held the workshops, while also did extended interpretation and integration of results across a number of different workshops.
The different scenarios of the BN tested highlight the good probability of adoption, which then can support sustainable land management.
The approach was conducted especially for smallscale farmers without sophisticated irrigation tecniques and as well for the indigenous tribe Pankararu.
The BN model offers alternative sources for soil additives in case land use rights are hindering availability.
Not inmediately but a long-term influence is possible.
The different scenarios of the BN tested highlight the good probability of adoption, which can then benefit the livelihoods of adopters.
Lessons learnt (especially on most favorable soil additive mixture) improve effectiveness of potential Umbuzeiro cultivation. Stakeholder pool of BN-creation comprises business networking opportunities for land users.