Community efforts for improving drinking water quality
(เนปาล)
Piune paani ko gunastar sudhar ka lagi samudayik prayas
คำอธิบาย
Working with communities to demonstrate and disseminate methods for improving drinking water quality using structural and vegetative measures
Aims / objectives: The People and Resource Dynamics in Mountain Watersheds of the Hindu Kush- Himalayas Project (PARDYP) implemented this approach with 30 drinking water user households at Barbot in the Jhikhu Khola watershed, Kavre Palanchok. The aim was to improve water quality and availability from an open spring source through participatory planning and implementation. The approach first identified local concerns and observed the sanitary situation of the catchment area. Meetings were held jointly with men and women users from different caste groups (Brahmin, Chhetri, Newar and Kami) to discuss the problems and issues and to identify viable solutions. The advantages and disadvantages of the various options were discussed, after which users selected the following three measures to improve the drinking water supply: 1) building a brick-cement walled structure around the main local spring, 2) establishing check dams across nearby rills and gullies, and 3) planting grass around the spring box and tree saplings within the catchment area. The aim was to prevent direct flow of surface water into the spring and reduce contamination and turbidity of the source. Understanding and support was gained by demonstrating the technology and running an awareness campaign.
Role of stakeholders: The project helped form a users committee made up of 11 women and 1 man and encouraged them to plant grass and tree seedlings across the entire catchment. The project regularly measured the quality of the water and shared the results with the users. Rules and regulations were developed to ensure equitable access to the spring and its sustainable use and management. A notice board with do’s and don’ts was placed near the spring. The users held monthly meetings and established a revolving fund for maintaining the structures. Spring users followed the rules and regulations by washing, cleaning, and bathing at separate sources. Livestock grazing was stopped in the nearby area and the area was regularly cleaned. Furthermore, users were encouraged to treat water for drinking using simple methods like SODIS and the low cost Safa filter to avoid microbiological contamination. They were made more aware of water quality, sanitation, and health issues.
สถานที่

สถานที่: Kavrepalanchowk district/ Jhikhu Kholawatershed, เนปาล
ตำแหน่งทางภูมิศาสตร์ของสถานที่ที่ถูกเลือ
วันที่ริเริ่ม: n.a.
ปีที่สิ้นสุด: 2005
ประเภทของแนวทาง
-
แบบดั้งเดิม/ แบบพื้นเมิอง
-
เป็นนวัตกรรมท้องถิ่นล่าสุด/ นวัตกรรมใหม่
-
ใช้โครงงานหรือแผนงานเป็นฐาน
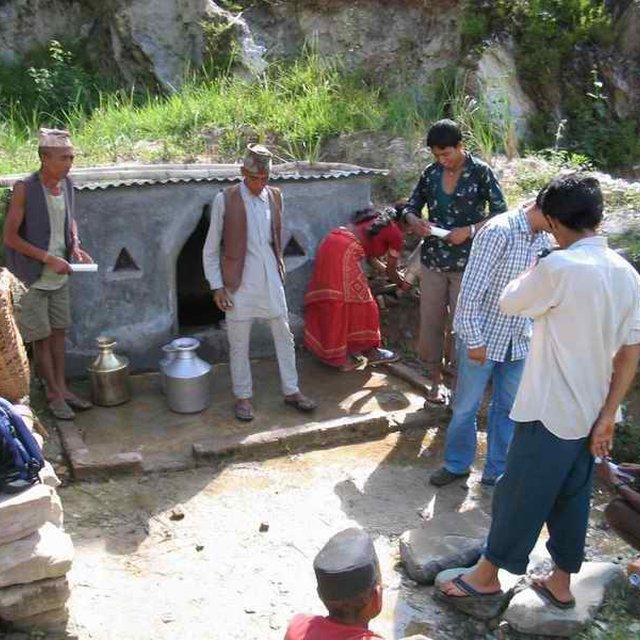

A meeting between project technicians and users to discuss problems and issues related to drinking water and to identify viable solutions. (PARDYP)
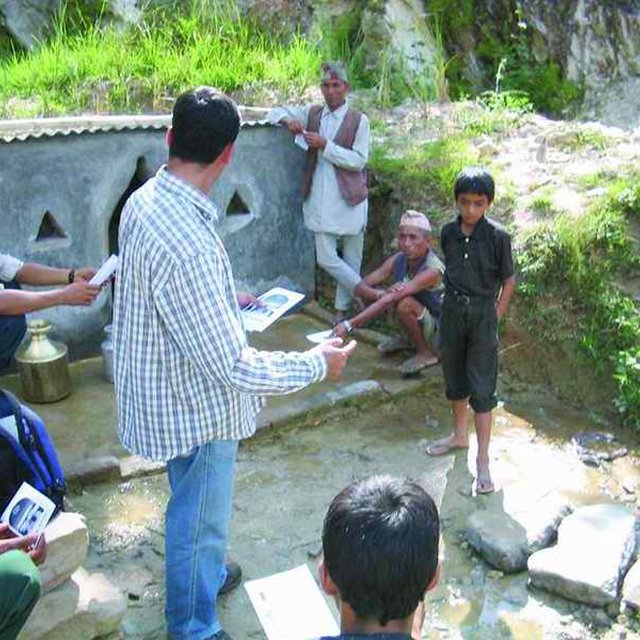

Sharing simple water quality treatment methods like SODIS and the low cost Safa filter with users. (B.S. Dongol)
แนวทางการดำเนินการและบรรยากาศการพัฒนาที่เอื้ออํานวย
เป้าหมายหรือวัตถุประสงค์หลักของแนวทาง
The Approach focused on SLM only
- To explore and demonstrate appropriate water quality improving technologies and methods in a participatory way. - To increase awareness on water quality, water treatment, and health and hygiene. - To share knowledge gained on the water improvement options with farmers and other stakeholders
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Weak institutional collaboration to develop technological options for improving drinking water quality and availability and to raise awareness on health and hygiene and waterborne diseases.
เงื่อนไขที่เอื้ออำนวยต่อการนำเอาเทคโนโลยีภายใต้แนวทางนี้ไปปฏิบัติใช้
-
กรอบแนวทางในการดำเนินการด้านกฎหมาย (การถือครองที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและน้ำ): The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: mostly state owned land and some private land - which helped implementating the technology as there was no conflict.
เงื่อนไขที่เป็นอุปสรรคต่อการนำเอาเทคโนโลยีภายใต้แนวทางนี้ไปปฏิบัติใช้
-
การมีไว้ให้หรือการเข้าถึงแหล่งการเงินและบริการ: For the maintenance of the implemented technology
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Revolving fund collected by users
-
การจัดตั้งระดับองค์กร: Weak institutional collaboration
Treatment through the SLM Approach: User group formed linking local community organisations
-
ความรู้เกี่ยวกับ SLM การเข้าถึงการสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค: Different water treatment methods
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Awareness of structural and vegetative measures; direct water treatment methods including Safa filter, SODIS, chlorination
การมีส่วนร่วมและบทบาทของผู้มีส่วนได้เสีย
ผู้มีส่วนได้เสียที่เกี่ยวข้องในแนวทางนี้และบทบาท
| ผู้มีส่วนได้เสียหรือองค์กรที่นำไปปฏิบัติใช้มีส่วนเกี่ยวข้องกับแนวทางนี้อย่างไร |
ระบุผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสีย |
อธิบายบทบาทของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสีย |
| ผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น |
Land users worked equally divided between men and women |
Improvement of drinking water quality and quantity was the major concern of all spring users. |
| องค์กรพัฒนาเอกชน |
|
|
| รัฐบาลแห่งชาติ (ผู้วางแผน ผู้ทำการตัดสินใจ) |
|
|
| องค์การระหว่างประเทศ |
PARDYP/ICIMOD |
|
เอเจนซี่หลัก
Concept designed by national specialist and implemented jointly with users
การเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่นในช่วงต่าง ๆ ของแนวทาง
ไม่มี
ไม่ลงมือ
จ่ายเงินหรือสนับสนุนจากภายนอก
ปฏิสัมพันธ์
ระดมกำลังด้วยตนเอง
การริเริ่มหรือการจูงใจ
public meetings; meetings organised to identify problems and possible options to overcome them.
การวางแผน
public meetings; organised regularly to identify implementing steps, and role and responsibility of different stakeholders in overcoming problems
การดำเนินการ
responsibility for major steps; the user group responsible for implementation and the project for technical support
การติดตามตรวจสอบหรือการประเมินผล
The quality of the water was measured in each season to monitor the impact of the technology. Detailed progress reports, results, and lessons learned were shared with district level institutions and authorities, water quality reports were shared with spring users at public meetings
Research
Water quality and availability recorded before and after technology implemented. Studies on access to water and confl icts among users
แผนผัง
PARDP project donors and implementing partners-- SDC: Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation IDRC: International Development Research Centre ICIMOD: International Centre for Integrated Mo
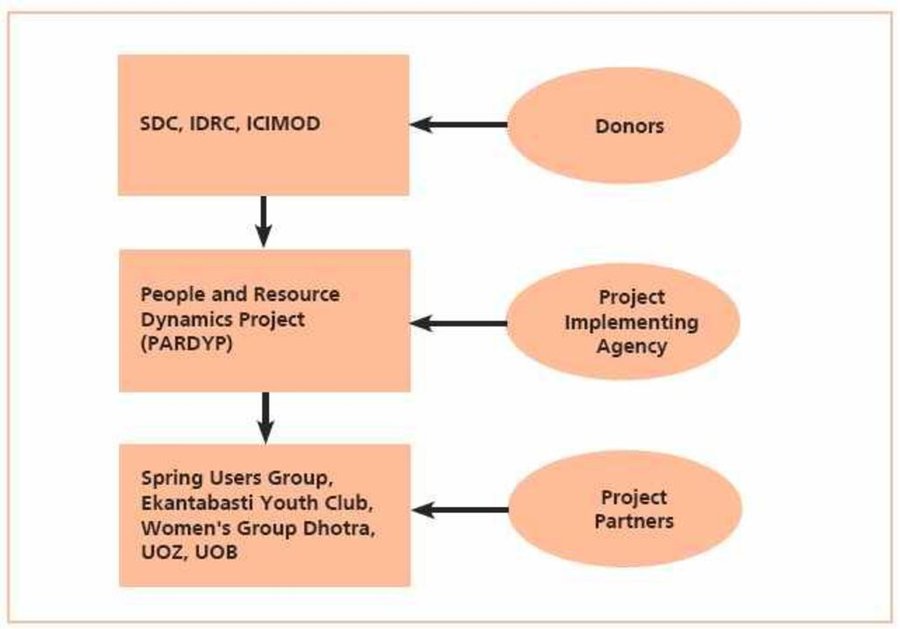
ผู้เขียน Madhav Dhakal
การตัดสินใจในการเลือกใช้เทคโนโลยี SLM
การตัดสินใจถูกทำโดย
-
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินเพียงผู้เดียว ( ริเริ่มด้วยตัวเอง)
-
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินเป็นผู้ตัดสินใจหลัก โดยการสนับสนุนจากผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM
-
ผู้ลงมือปฏิบัติที่เกี่ยวข้องทั้งหมดในฐานะที่เป็นส่วนรวมของแนวทาง
-
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM เป็นผู้ตัดสินใจหลัก ที่ติดตามให้คำปรึกษากับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
-
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM เพียงผู้เดียว
-
นักการเมืองหรือผู้นำ
การตัดสินใจถูกตัดสินอยู่บนพื้นฐานของ
-
การประเมินความรู้ SLM ที่ได้ทำการบันทึกไว้เป็นอย่างดี (การใช้ข้อมูลในการตัดสินใจ)
-
สิ่งที่ค้นพบจากงานวิจัย
-
ประสบการณ์และความคิดเห็นส่วนตัว (ไม่ได้ลงบันทึกไว้)
การสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค การสร้างขีดความสามารถ และการจัดการด้านความรู้
กิจกรรมหรือการบริการต่อจากนี้เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทาง
-
การสร้างขีดความสามารถ / การอบรม
-
การบริการให้คำแนะนำ
-
การเสริมความแข็งแกร่งให้กับสถาบัน (การพัฒนาองค์กร)
-
การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผล
-
การวิจัย
การสร้างสมรรถภาพหรือการอบรม
การจัดอบรมถูกจัดขึ้นสำหรับผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียต่อไปนี้
-
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
-
เจ้าหน้าที่ภาคสนาม / ที่ปรึกษา
รูปแบบของการอบรม
-
กำลังดำเนินการ
-
เกษตรกรกับเกษตรกร
-
ใช้พื้นที่ทำการสาธิต
-
จัดการประชุมสู่สาธารณชน
-
จัดคอร์ส
หัวข้อที่อบรม
Concept of conservation measures, and methods of treating contaminated water using SODIS and safa filter.
การบริการให้คำแนะนำ
การให้คำแนะนำถูกจัดขึ้น
-
ไปเยี่ยมชมสถานที่
-
ที่ศูนย์ถาวร
Name of method used for advisory service: Sharing information on water quality status, and raising awareness among users.; Key elements: catchment conservation, health hygiene, water treatment methods; 1) Advisory service was carried out through: projects own extension structure and agents; Extension staff: specifically hired project employees 2) Target groups for extension: land users; Activities: awareness on health hygiene; catchment conservation activities and water treatment methods were shared during meetings.
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities
การสร้างความแข็งแกร่งให้กับองค์กร
องค์กรถูกทำให้แข็งแกร่งขึ้นหรือจัดตั้งขึ้น
-
ไม่
-
ใช่ เล็กน้อย
-
ใช่ ปานกลาง
-
ใช่ อย่างมาก
อธิบายถึงสถาบัน บทบาทและความรับผิดชอบ สมาชิก เป็นต้น
ประเภทของการให้ความช่วยเหลือสนับสนุน
-
ด้านการเงิน
-
การสร้างขีดความสามารถ / การอบรม
-
อุปกรณ์
รายละเอียดเพิ่มเติม
Training on water quality treatment provided to local club
การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผล
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: land use and degradation, sanitary inspection, history of spring, available resources to trap water
technical aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: seasonal water quality and discharge
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: number of spring users, household water requirements, users' issues
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: participation in conservation activities
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: The project consulted with the local women's cooperative to solve a conflict over water quantity and access to spring source.
การวิจัย
การวิจัยกระทำกับหัวข้อต่อไปนี้
-
สังคมวิทยา
-
เศรษฐศาสตร์หรือการตลาด
-
นิเวศวิทยา
-
เทคโนโลยี
Access to drinking water, conflicts at water fetching times, water quality and quantity measurement, and effectiveness of water treatment methods.
Research was carried out on station
การสนับสนุนด้านการเงินและวัสดุอุปกรณ์
งบประมาณประจำปีสำหรับองค์ประกอบ SLM เป็นจำนวนดอลลาร์สหรัฐ
-
< 2,000
-
2,000-10,000
-
10,000-100,000
-
10,000-100,000
-
> 1,000,000
Precise annual budget: n.a.
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (SDC, IDRC, ICIMOD): 90.0%; local community / land user(s) (users group): 10.0%
การบริการหรือแรงจูงใจต่อจากนี้ได้ถูกจัดให้สำหรับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
-
การสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
-
เงินสนับสนุนสำหรับปัจจัยการผลิต
-
เครดิต
-
แรงจูงใจหรือเครื่องมืออื่น ๆ
แรงงานของผู้ใช้ที่ดินคือ
-
สมัครใจ
-
อาหารสำหรับการทำงาน
-
จ่ายเป็นเงินสด
-
ให้ค่าตอบแทนด้วยการสนับสนุนด้านวัสดุอุปกรณ์อื่น ๆ
เครดิต
-
ข้อกำหนด n.a.
-
ผู้ให้เครดิต n.a.
-
ผู้รับเครดิต n.a.
ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
ผลกระทบของแนวทาง
ไม่ใช่
ใช่ เล็กน้อย
ใช่ ปานกลาง
ใช่ อย่างมาก
ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ที่ดินนำเอาเทคโนโลยี SLMไปใช้และบำรุงรักษาสภาพไว้ได้หรือไม่
To build awareness on SLM and methods of improving drinking water quality. It also helped users to work in a group.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
Similar approaches are being followed in other communities across Nepal.
แรงจูงใจหลักของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเพื่อที่จะนำ SLM ไปปฏิบัติใช้
-
การผลิตที่เพิ่มขึ้น
-
กำไร (ความสามารถ) อัตราส่วนค่าใช้จ่ายต่อผลประโยชน์ที่เพิ่มขึ้น
-
การเสื่อมของที่ดินลดลง
-
ความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติลดลง
-
ภาระงานลดลง
-
การจ่ายเงินหรือการช่วยเหลือ
-
กฎและระเบียบ (ค่าปรับ) หรือการบังคับใช้
-
เกียรติภูมิ แรงกดดันทางสังคม ความเชื่อมแน่นทางสังคม
-
การเข้าร่วมสมทบในขบวนการ โครงการ กลุ่ม เครือข่าย
-
จิตสำนึกด้านสิ่งแวดล้อม
-
ประเพณีและความเชื่อ ศีลธรรม
-
ความรู้และทักษะ SLM ที่เพิ่มพูนขึ้น
-
การปรับปรุงด้านสุทรียภาพ
-
การบรรเทาด้านความขัดแย้ง
ความยั่งยืนของกิจกรรมของแนวทาง
ผู้ใช้ปที่ดินสามารถทำให้สิ่งต่างๆ ที่ได้ปฏิบัติใช้โดยแนวทางนี้ยั่งยืนได้หรือไม่ (โดยไม่มีการสนับสนุนจากภายนอก)?
Users are maintaining the implemented technology and also protecting the other nearby spring sources.
บทสรุปหรือบทเรียนที่ได้รับ
จุดแข็ง: มุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
-
Water users committee formed, revolving fund collected, and rules and regulations developed for the sustainable management of the drinking water system (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Maintain links with local community mobilisation groups for continuous guidance and support for the user group and for the proper use of the revolving fund.)
จุดแข็ง: ทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรคนอื่นๆ
-
Users have become more aware of sanitation issues than before (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Awareness campaigns should be organized regularly covering more villages.)
-
Users have become more aware of 1) the quality of their drinking water, 2) its impact on their health, 3) water quality improvement options, and 4) the importance of soil and water conservation (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Water quality testing campaigns should be continued and technical know how about different water quality treatment methods for improved health shared at regular meetings)
จุดด้อย/ข้อเสีย/ความเสี่ยง: มุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดินแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร
-
Water aviallability is still insufficient during dry period (March -May)
Other available nearrer sources should also be used, catchment protection activities should be continued.
จุดด้อย/ข้อเสีย/ความเสี่ยง: ทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรคนอื่นๆแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร
-
Conflicts are visible during the dry season due to insufficient quantity of water.
Good coordination among the group members should minimise conflicts- the strong and balanced role of users committee is vital for the equitable sharing of benefits.
การอ้างอิง
วันที่จัดทำเอกสาร: 19 มกราคม 2009
การอัพเดทล่าสุด: 9 กรกฎาคม 2017
วิทยากร
-
Madhav Dhakal (mdhakal@icimod.org) - ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM
-
Provodoli Isabelle (himcat@icimod.org) - ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM
คำอธิบายฉบับเต็มในฐานข้อมูล WOCAT
การจัดทำเอกสารถูกทำโดย
องค์กร
- CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์
- ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - เนปาล
โครงการ
การอ้งอิงหลัก
-
ICIMOD (2007) Good Practices in Watershed Management, Lessons Learned in the Mid Hills of Nepal. Kathmandu: ICIMOD: ICIMOD







