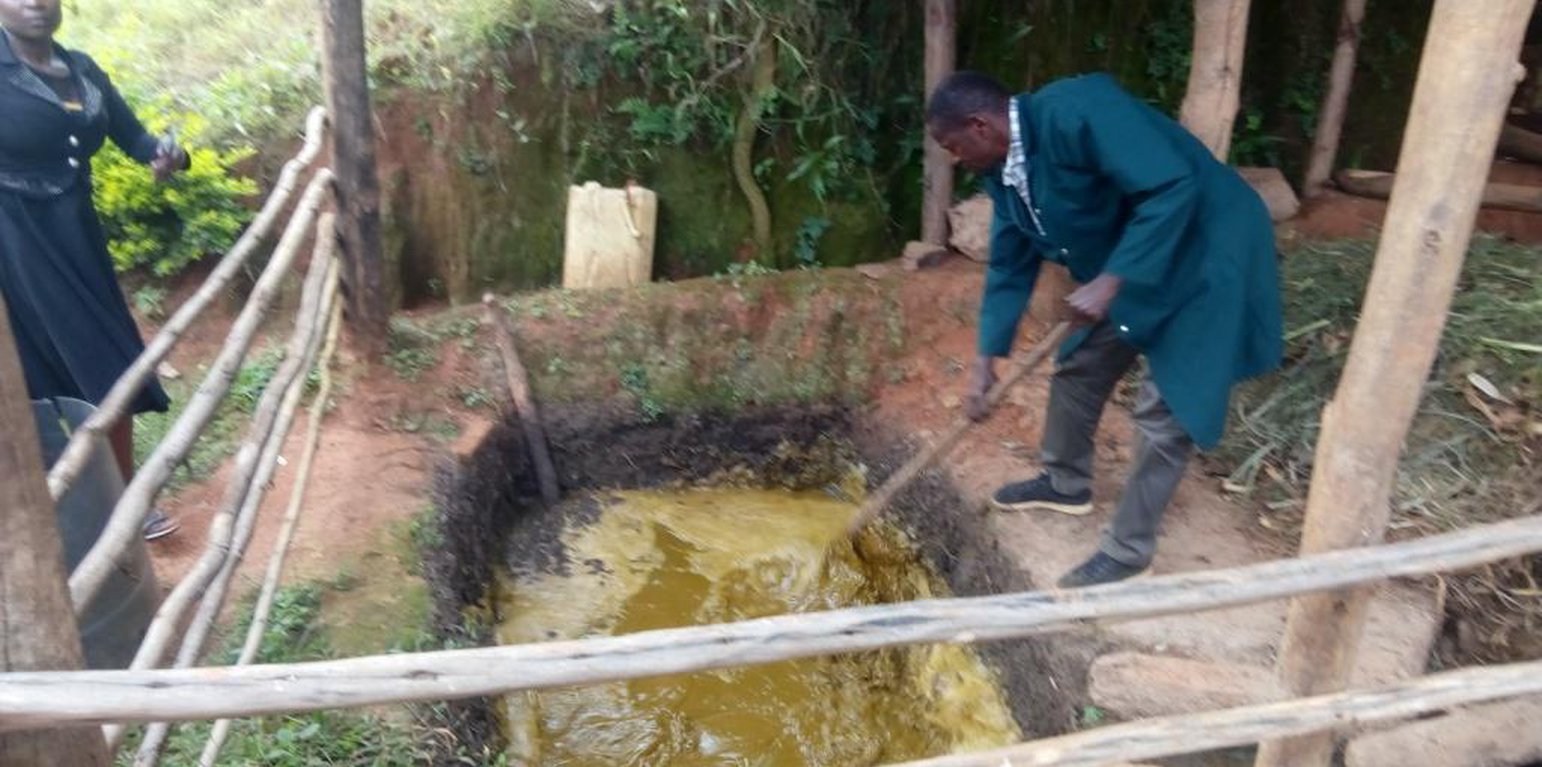




The Kraal (livestock zero grazing shed) was initially designed with a waste management system to hold cow dug in a reservoir for 1 to 2 months before being used in a 2-acre garden as manure. However, the farmer faced challenges transporting and distributing manure to the garden which was tedious and time wasting.
The dung from 4 cows is first mixed with water at a ratio of 1 (dung): 3 (water) as it drains into the reservoir producing approximately 1,500 litres of liquid manure monthly. Therefore, a pipe outlet was devised at the base of the cow dung reservoir to transport the waste 50m down-slope into 3 other reservoirs (each 2×1×1m, l×w×h) evenly distributed within the garden. These reservoirs store the liquid manure until the farmer wishes to fertilize the garden.
The garden preparation starts with clearing the weeds and then excavating small trenches that direct the flow of the liquid manure to any direction of interest in the garden. At different points along the flow in the trenches, the farmer opens tributaries leading to pits dug at least 0.75 m away from the banana plantains of interest. The pits made are normally approximately of 12.5 litres capacity. The trenches, tributaries and pits are then covered with soil after a day. This integrated fertilizer-irrigation system can only be possible on farms established on a gently sloping terrain. To set up the system one must have an animal house or any other source of animal dung uphill. The source must be able to provide enough dung to sustain the gardens established downhill.
Alternatively, the system can also be set up with a biogas plant replacing the cow dung reservoir to produce biogas for domestic energy supply and the slurry being used as manure. In case of such modification, the biogas should be set up at a slightly elevated position to give the liquid digestate a gravity force to flow to the garden. A foundation is excavated and a mixing chamber (50 litres capacity) constructed at some distance away from the farm house as well as 3 reservoirs to store the digestate (of a capacity at least 400 litres each) sited in the garden. An outlet pipe is fixed at the bottom of the mixing chamber through which the slurry can be channelled into the garden after the fermentation process producing biogas has stopped.
The construction process of the system without the biogas plant cost the farmer labour worth USD $ 13.44, construction materials were USD $ 251.04 and equipment USD $ 32.25. According to the farmer, the system is averagely expensive in the short run but profitable in the long run.
The system eases waste management and reduces costs of labour. The farmer, over the last 3 seasons realized improvement in the number of banana bunches harvested from averagely 50 to 60 bunches per month. The bunch weight also increased from 8-15Kg to 10-25Kg on average which is important for food security and livelihood.
The impacts of drought on the plantation have reduced compared to the time before adopting the technology. The farmer recommends upscaling since it is easy to manage, it improves productivity and is environment friendly. The major challenge is lack of enough cow dung supply from the kraal and scarcity of water in the dry season. A rainwater harvest system may be constructed to collect and provide water for diluting the cowdung.
สถานที่: Rwentuha T/C , Kitwe, Wester Uganda, Bushenyi, ยูกันดา
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี: พื้นที่เดี่ยว
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ (approx. < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์))
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: 2016
ประเภทของการแนะนำ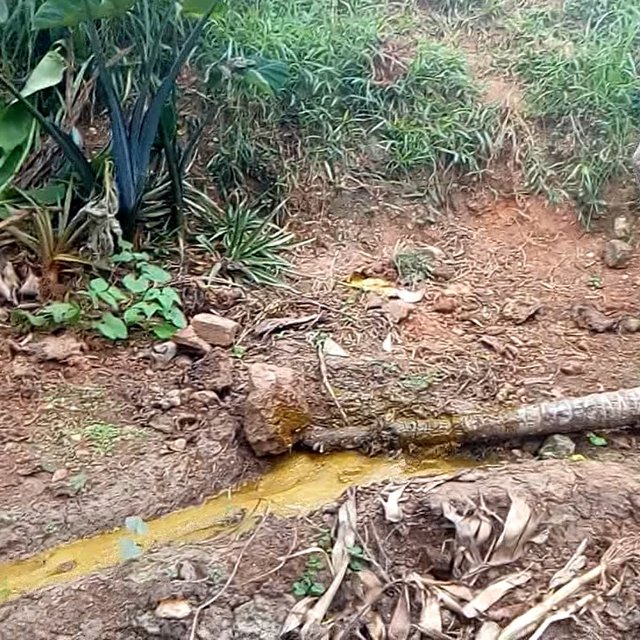






| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (Uganda shillings) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (Uganda shillings) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Labour | Man day | 3.0 | 17000.0 | 51000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Hoe hire | pieces | 2.0 | 5000.0 | 10000.0 | 100.0 |
| Panga | pieces | 1.0 | 9999.0 | 9999.0 | 100.0 |
| Hammer | pieces | 1.0 | 50000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| Wheel barrow hire | pieces | 1.0 | 50000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | |||||
| Cement | 60kg bags | 13.0 | 29000.0 | 377000.0 | 100.0 |
| Sand | 1 tonne trips | 2.0 | 70000.0 | 140000.0 | 100.0 |
| Bricks | 1 tonne trip | 1.0 | 270000.0 | 270000.0 | 100.0 |
| Doom pipe | Meters | 2.0 | 15000.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 987'999.0 | ||||
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (Uganda shillings) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (Uganda shillings) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Labour to clean the cow shed and the reservoir and drain it | Man day | 1.0 | 17000.0 | 17000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour to excavate temporary drains | Man per month | 2.0 | 150000.0 | 300000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Spade | piece | 1.0 | 50000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| Hoe | piece | 1.0 | 50000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 417'000.0 | ||||
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 50 bunches
หลังจาก SLM: 70bunches
The hygiene at the cattle kraal has improved
Increase soil moisture and manure
Less labor required to handle wastes from the cattle
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 3 workers
หลังจาก SLM: 1 worker
Increased production of banana bunches per unit area monthly
No need for casual labor to fetch manure with baskets
Manure from dug is well distributed in the garden
Irrigation through the liquid slurry
Waste from the cattle is well managed and utilized for manure