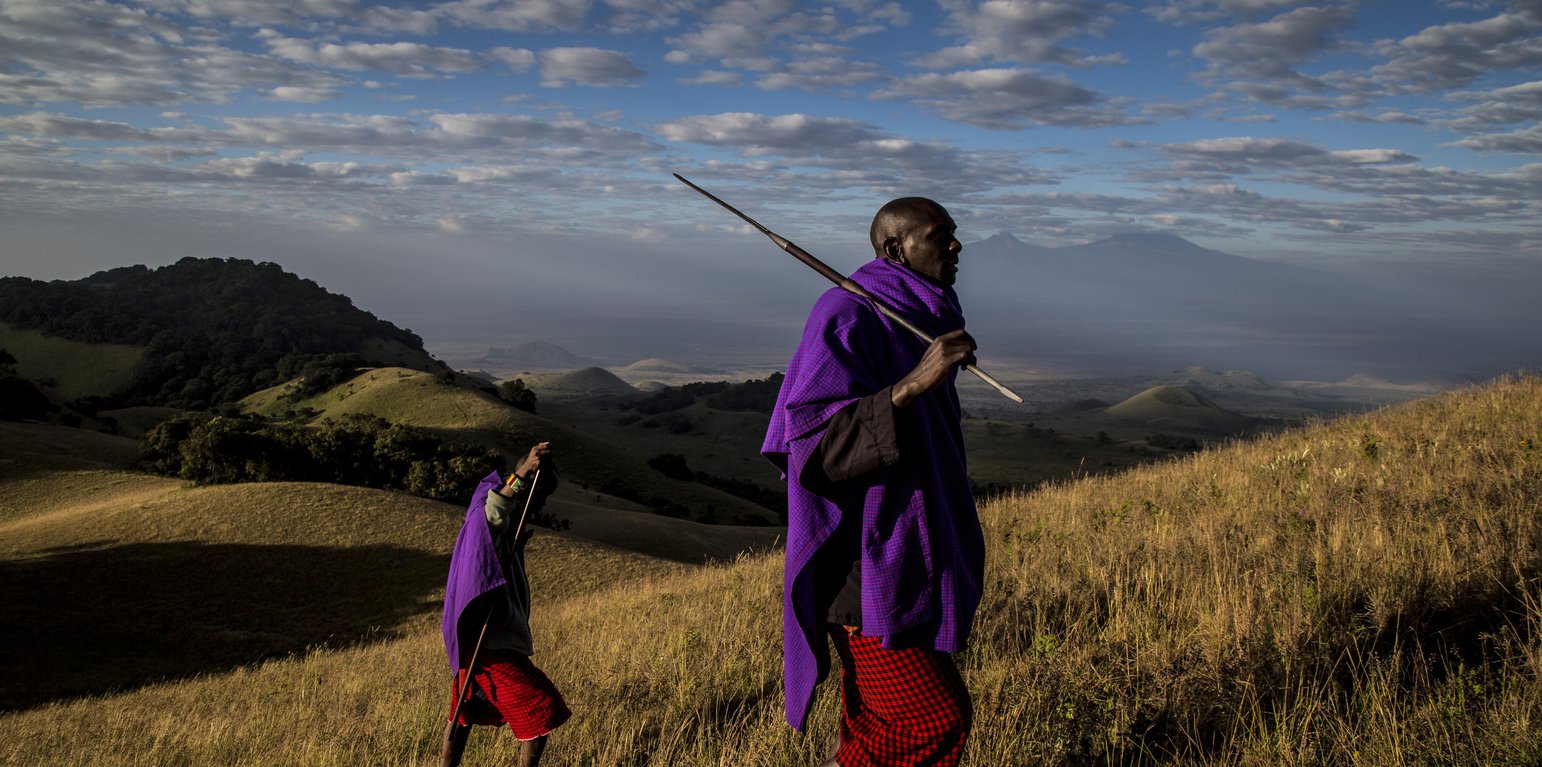




The Chyulu Hills, in southern Kenya, are a volcanic mountain range approximately 100 km long, and form a central pillar of the much larger Tsavo-Amboseli ecosystem which constitutes several national parks, forest reserves and community-owned pastoral land. The emission reduction project established in 2011 under the REDD+ umbrella (Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and forest Degradation) covers 410,000 hectares of both community and public land around the hills. REDD+ offers financial incentives to developing countries to manage and use their forests responsibly. Payments are channelled through the Trust to support land users for quantifiably reducing emissions.
REDD+ creates financial value for the carbon stored in forests by offering incentives for developing countries to reduce emissions from forested lands and invest in low-carbon paths to sustainable development. REDD+ goes beyond simply stopping further deforestation and forest degradation by including sustainable management and enhancement of forest carbon stocks.
This area is home to 140,000 people including Maasai pastoralists to the west, and Kamba farming communities to the east. This land is widely used for livestock production; must of it under communal tenure. Recent pressures, notably increasing populations and changes in land tenure, have led to unsustainable uses of natural resources, threatening the functioning of the ecosystem, through the degradation of the rangeland and over-exploitation of forest resources. This includes cutting of trees for firewood, charcoal, uncontrolled fires, and weakening of traditional grazing management systems.
The Chyulu Hills REDD+ project aims to protect its rangeland and forest landscapes by creating an alternative income opportunity, and improving both livestock and rangeland management, while preventing the emission of over 18 million tons of carbon dioxide over the project’s 30-year lifetime.
This is the first REDD+ project in Kenya that is fully owned and managed by the local community, a vital factor in ensuring sustained impact. Through the project, land users receive financial support per hectare for maintaining or improving carbon stocks above and below ground. Previous REDD+ projects have often been criticised for not properly engaging local communities or addressing their needs.
To achieve this, the Chyulu Hills Conservation Trust (CHCT) was formed in 2015 to act as the project governing body. The Trust represents multiple stakeholders from the community, government, and local NGOs including the Maasai Wilderness Conservation Trust (MMWCT), Big Life Foundation (BLF), and the David Sheldrick Wildlife Trust (DSWT). The government is also represented through the Kenya Wildlife Service (KWS) and Kenya Forest Service (KFS), whose mandates include the Chyulu Hills National Park and the Kibwezi Forest Reserve. The national park is used on an informal basis by the communities for dry season grazing, although access is severely limited by water, and also by disease.
The communities are represented by four Maasai group ranches, who manage the land and its resources. These group ranches are areas of communally titled land. The three NGOs have the technical capacity to advise, provide strategic guidance and assist in implementation of the project activities. They are already involved in helping communities to develop and manage conservation areas, and to improve sustainable use of natural resources.
Proceeds from the sale of Voluntary Emission Reductions (VERs) flow through the CHCT to initiatives/projects which benefit the community and environment. Early in 2017 the first verification was completed, and shortly afterwards the first marketable carbon credits went on sale, providing income to the CHCT for protecting and improving their carbon stock.
To ensure equitable and transparent sharing of proceeds from carbon sales, a revenue allocation model was implemented to fund (i) office and project costs, (ii) discretionary sub-projects, and (iii) to provide strategic investments to counter drivers of deforestation and land degradation.
The proposed investments into the CHCT area to improve rangeland condition comprise several components. The first component is to support grazing management plans to help restore governance over resources, and ensure sustainable use. This should encourage the recovery of perennial grasses, increase grass cover, and create a heterogeneous forage base. The second focus is value addition to beef marketing through collaborative partnerships. This should encourage pastoralists to focus on management of the rangelands to support the production of higher quality cattle. In the long run this will increase revenue generation for livestock farmers, and stimulate the communities to manage their rangeland better.
สถานที่: Chyulu Hills, Kajiado and Makueni, เคนยา
วันที่ริเริ่ม: 2011
ปีที่สิ้นสุด: n.a.
ประเภทของแนวทาง

| ผู้มีส่วนได้เสียหรือองค์กรที่นำไปปฏิบัติใช้มีส่วนเกี่ยวข้องกับแนวทางนี้อย่างไร | ระบุผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสีย | อธิบายบทบาทของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสีย |
| ผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น | Kuku Group Ranch Kuku A Group Ranch Mbirikani Group Ranch Rombo Group Ranch | The communities are the owners of livestock and natural resources. They are nee in the formulation of strategies, in particular grazing management, in their areas. |
| องค์กรพัฒนาเอกชน | Maasai Wilderness Conservation Trust Big Life Foundation David Sheldrick Wildlife Trust | These three NGO oversee the management of natural resources (each has agreements with the respective communities) and provide support for administration of the grants, technical and implementing expertise, and strategy development. They each operate in distinct geographical areas across both community and public land. |
| รัฐบาลแห่งชาติ (ผู้วางแผน ผู้ทำการตัดสินใจ) | Kenya Wildlife Service Kenya Forest Service | These two stakeholders are responsible for the management and project implementation within the officially gazetted protected areas. The Kenya Forest Service is instrumental in the national decision making and policy for the national REDD + programme. |
| องค์การระหว่างประเทศ | Conservation International | Functions as an advisory board member, providing strategic and technical guidance. |
การตัดสินใจถูกทำโดย
การตัดสินใจถูกตัดสินอยู่บนพื้นฐานของ
Research was conducted to establish the potential of the landscape for carbon sequestration for the REDD+ scheme.
The Approach ensures communities are the principle beneficiaries of funding received by the Trust; the technologies implemented are for improved rangeland management.
The Approach monitors rangeland and forest resources, including vegetation, carbon stores and biodiversity, which can then be used by the Trust for evidence based decision making.
The Approach provides technical and strategic expertise to communities to implement technologies at the spatial scale relevant to land management.
The Trust brings together community, government and NGO stakeholders in the landscape to improve coordination under joint work plans.
The Approach generates revenue through the sale of carbon credits, which is allocated to projects through the Trust and the revenue allocation model.
Through the creation of the Chyulu Hills Conservation Trust there is a new institution to build collaboration.
Yes, this approach has provided more employment to the local communities, including transfer of new skills.
The collaborative nature of the project, and the establishment of the Trust allows the community to sustain the approach due to the ongoing support of local NGOs and government. If the CHCT cannot sell Carbon Credits via the REDD+ scheme, then there will be severe limitations on the ability of the project to implement activities.