



The technology applies to the specific context of the ‘Char’ land in Bangladesh, characterised as riverine sandy Islands along the Jamuna River. More than 80% of the land in the intervention area can be classified as 'Char' and is inhabited by 60% of the population served by the project. Every year, especially during floods, the rivers deposit huge amount of silt sediment that makes the land fertile. At the same time, river action washes away some portion of the 'Char' which at times can be quite large and has a strong impact on people's lives and livelihoods. Before the intervention, people living on 'Char' land depended on their traditional early warning mechanisms and were frequently surprised by floods that destroyed their crops and put their lives in danger. Due to recurring floods, people didn’t have the means to improve their built environment. The 'Char' land is furthermore characterised by its lack of public infrastructure and remoteness to public services.
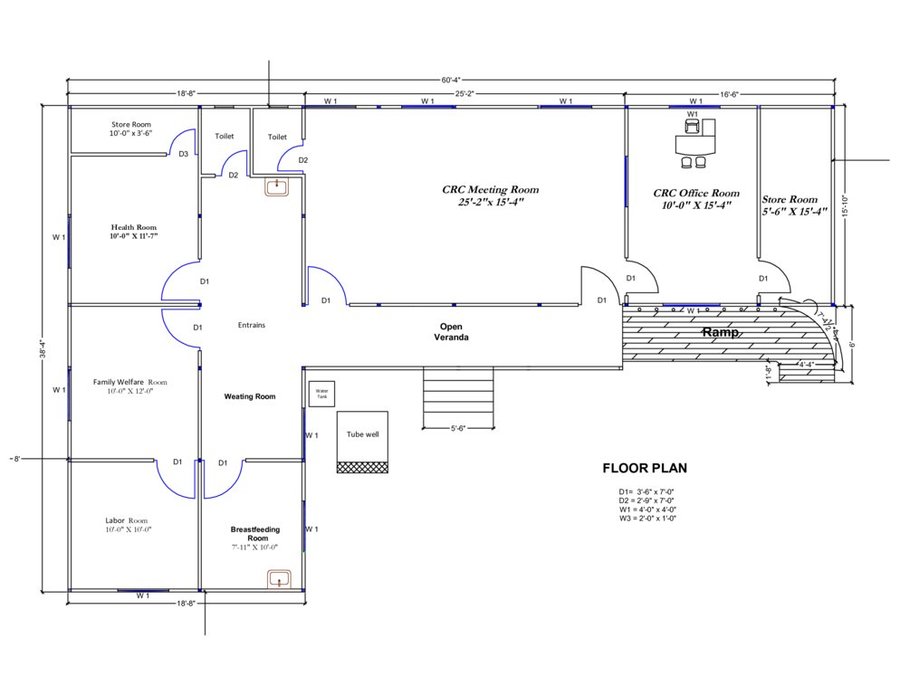
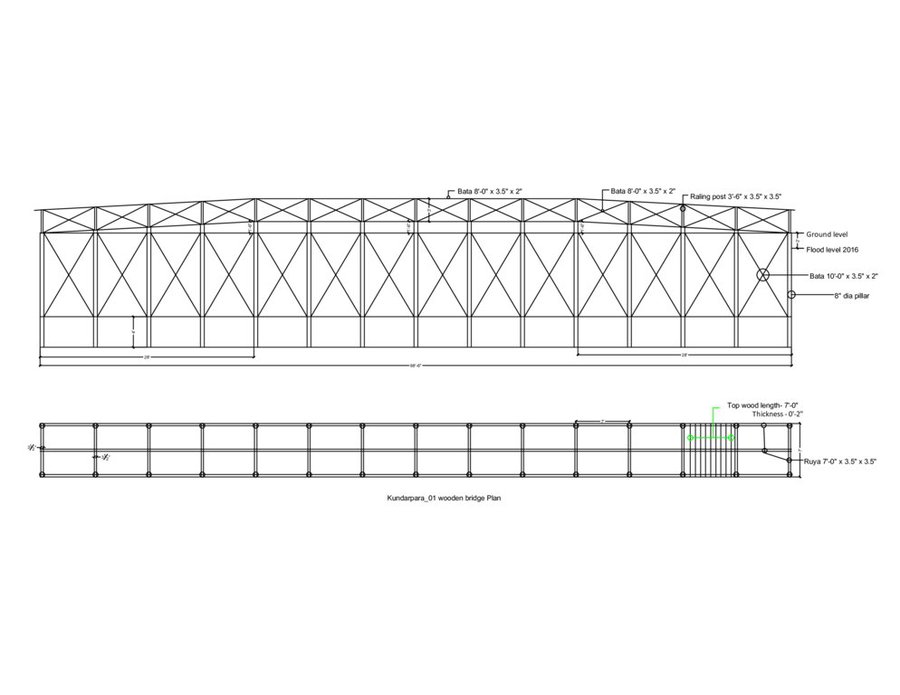
The technology consists of setting up an emergency infrastructure and ensuring community access to these infrastructures during times of floods. It has to be understood in close interrelation with the approach of setting up an early warning system. The emergency infrastructure includes specific flood shelters (for people and animals), flood-proof collective water sources and sanitation systems, transport infrastructure such as foot bridges and elevated rural roads, as well as flood-proof health and school facilities that also serve as emergency shelters during floods. The flood shelters are built on a raised bed of soil and located at sites selected by the communities that are relatively better protected from flood and river erosion within the 'Chars'. The purpose of the technology is to ensure safety of life and protection of assets during times of emergency and also to mitigate sufferings related to floods. The flood shelter is an elevated plane land which is on an average 220 square feet by size and at least five feet high from the existing ground level. The site is selected by the community and should be connected through an elevated road to the nearest community. This arrangement helps people to get easy access during times of floods. The shelter has collective hygienic latrine facilities and safe water sources. People generally dismantle their housing while evacuating and reinstall it on the flood shelter.
The major activities include facilitating the development of community-led risk reduction action plans and their implementation through community participation and engagement of local governance institutions. This includes maintenance of the built infrastructure as the joint responsibility of the community and the local government. Land use, especially sowing and harvesting, is increasingly linked to flood related forecasting measures which has led to significant adaptation in the timing of farming activities. This coupled with the creation and access to emergency infrastructure allows for a relatively safe and healthy living. The adopted technology and approach has led to adapted livelihoods, reduced health costs and increased income. The technology has furthermore led to mainstreaming disaster risk management in policies and approach of local government institutions. Increasingly the local government’s cash and food for work programmes are targeting establishment and/or reinforcement of emergency infrastructure that can cater to larger population. Increased investments are made especially towards flood shelters and improving communication and access to emergency infrastructure. Since the technology is based on local knowledge and has been developed in consultation with the involved communities, it is generally well accepted with a fair degree of ownership and involvement. However, parts of the region are also prone to river erosion and this has a destructive impact on built infrastructures. The technology does not assure any safeguard against this form of uncertain river action.
สถานที่: Kamarjani and Mollar Char Union (i.e. municipality) in Sadar Upazila and Haldia Union in Shaghata Upazila of Gaibandha District, North-Bengal, บังกลาเทศ
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี: > 1,000 แห่ง
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ (approx. 1-10 ตร.กม.)
In a permanently protected area?:
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: 2014; น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
ประเภทของการแนะนำ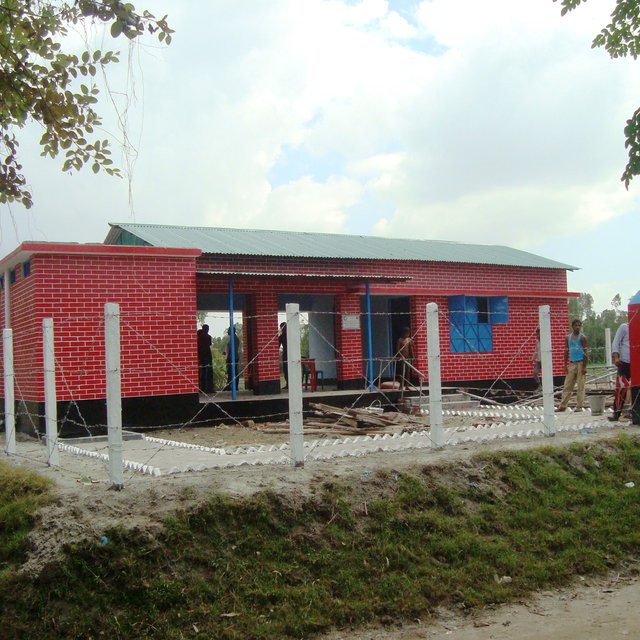







| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (Bangladeshi Taka (BDT)) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (Bangladeshi Taka (BDT)) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Flood shelter: earth work | m3 | 8000.0 | 64.0 | 512000.0 | 10.0 |
| CRC: earth work | m3 | 53.0 | 138.0 | 7314.0 | 10.0 |
| CRC: sand filling | m3 | 302.0 | 99.0 | 29898.0 | 10.0 |
| Raised school compound: earth work | m3 | 1790.0 | 64.0 | 114560.0 | 10.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | |||||
| Flood shelter: grass plantation (turfing) | m2 | 4620.0 | 13.0 | 60060.0 | 10.0 |
| Flood shelter: seedlings | piece | 20.0 | 53.0 | 1060.0 | 10.0 |
| CRC: grass plantation (turfing) | m2 | 3890.0 | 13.0 | 50570.0 | 10.0 |
| CRC: seedlings | piece | 50.0 | 53.0 | 2650.0 | 10.0 |
| Raised school compound: grass plantation (turfing) | m2 | 1390.0 | 13.0 | 18070.0 | 10.0 |
| Raised school compound: seedlings | piece | 40.0 | 53.0 | 2120.0 | 10.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | |||||
| CRC: roof truss | kg | 4375.0 | 100.0 | 437500.0 | |
| CRC: grill and iron work | m2 | 88.0 | 2091.0 | 184008.0 | |
| CRC: gypsum board | m2 | 478.0 | 922.0 | 440716.0 | |
| CRC: RCC work | m3 | 2.9 | 19557.0 | 56715.3 | |
| CRC: deformed bar | kg | 397.0 | 85.0 | 33745.0 | |
| CRC: boundary fencing | m2 | 184.0 | 440.0 | 80960.0 | |
| CRC: brick work | m3 | 44.0 | 5515.0 | 242660.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | |||||
| CRC: electric ware and solar panel | lumpsum | 1.0 | 73000.0 | 73000.0 | |
| CRC: water supply | lumpusm | 1.0 | 66150.0 | 66150.0 | |
| CRC: transportation | lumpsum | 1.0 | 89000.0 | 89000.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 2'502'756.3 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 31'680.46 | ||||
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (Bangladeshi Taka (BDT)) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (Bangladeshi Taka (BDT)) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Earthwork | m3 | 80.0 | 63.0 | 5040.0 | 10.0 |
| Sand bag filling | piece | 50.0 | 15.0 | 750.0 | 10.0 |
| Pipe fitting | piece | 2.0 | 300.0 | 600.0 | 10.0 |
| Mason | lumpsum | 1.0 | 500.0 | 500.0 | 10.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | |||||
| Grass plantation (turfing) | m2 | 85.0 | 13.0 | 1105.0 | 10.0 |
| Seedlings | piece | 15.0 | 53.0 | 795.0 | 10.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | |||||
| Plastic bag | piece | 50.0 | 10.0 | 500.0 | 10.0 |
| PVC pipe | m | 15.0 | 120.0 | 1800.0 | 10.0 |
| Polythene pipe | kg | 5.0 | 160.0 | 800.0 | 10.0 |
| Ciment | bag | 0.5 | 540.0 | 270.0 | 10.0 |
| Sand | ft3 | 5.0 | 18.0 | 90.0 | 10.0 |
| Caping socket | piece | 2.0 | 35.0 | 70.0 | 10.0 |
| Tape etc. | lumpsum | 1.0 | 250.0 | 250.0 | 10.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 12'570.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 159.11 | ||||
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 3600 kg/hectare (maize)
หลังจาก SLM: 11400 kg/hectare (maize)
Crop production has increased thrice due to stability of household which has led to stable use of land in the chars.
จำนวนก่อน SLM: No safe drinking water source was available
หลังจาก SLM: More than 40% water source are safe
Collective water supply systems have groundwater sources and thus no treatment is needed. Further, aspects of availability, easy access and sustainable availability of sufficient water of acceptable quality are well considered. Families can access 10 litres per capita per day (LPCD) during emergencies (which is in line with Sphere standards) and during normal times 40 LPCD is what families can collect from these water sources. All such water sources are within a distance of 50 metres from the settlement as per Bangladesh standards.
จำนวนก่อน SLM: Reliable data not available
หลังจาก SLM: All households have access to safe drinking water as per govt. standard for rural areas
The collective water infrastructure built by the project ensures fulfillment of minimum standards set by the govt for safe drinking water.
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 25% families had farm income
หลังจาก SLM: 95% families have farm income
Cattle and poultries are safe during disaster
The disaster mitigation measures has significantly improved the health situation of the target population.
จำนวนก่อน SLM: Few credit groups in intervention villages
หลังจาก SLM: 30 community based organisatons (i.e. village disaster management committees) and 3 Local Government Committees (Union disaster management committee)
Community based organisations and government mandated institutions have been promoted through project initiatives.
CRC is also being used for UDMC office which is an important committee of union parishad.
จำนวนก่อน SLM: Widespread
หลังจาก SLM: Rare
Conflict sensitive approach has significantly reduced the incidence of conflicts.
จำนวนก่อน SLM: Data not available
หลังจาก SLM: Same
The disaster resilient tube well ensures year round drinking water.
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 95% families were effected from flood
หลังจาก SLM: 47% families are affected from flood
The above figures are from 2016 when Bangladesh experienced one of the worst floods in recent times.