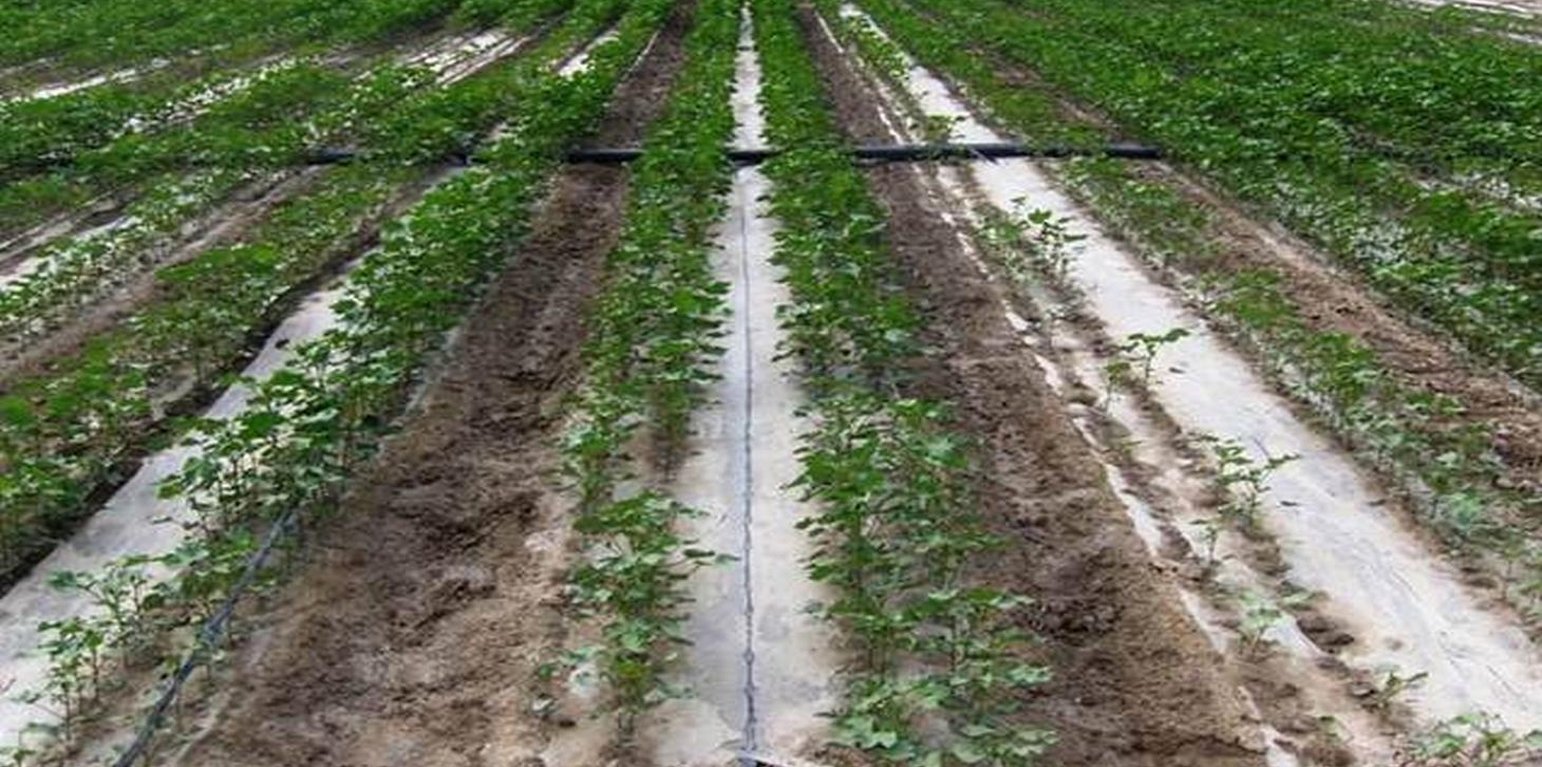




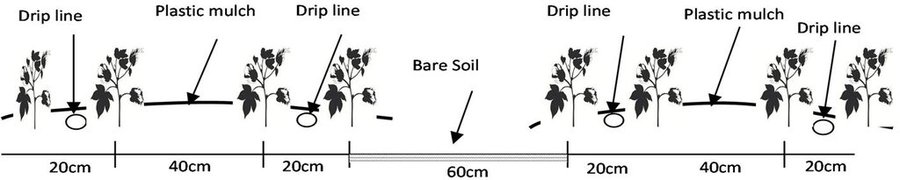
The dry climate and the long hours of sunshine make Xinjiang especially suitable for production of high quality cotton, and as a result some 40% of China’s cotton is grown here. But there are two main problems: shortage of water and salinization of the soil. Farmers who use the traditional flood irrigation method, and don’t have a drainage system, tend to abandon their fields when they become too saline - and then they look for new land to cultivate. A combination of mulching and drip irrigation can be very effective but still needs careful management. Drip irrigation helps to save water for farmers - and for the environment. But it is still very important to install a drainage system to dispose of surplus water in order to reduce the risk of salinization of the soils. Every four cotton rows are covered with transparent polyethylene film and as a result approximately 80% of the ground surface is covered by the plastic mulch. Plastic mulch and drip lines are placed with a specially equipped tractor.
Purpose of the Technology: Low temperatures and dry soil at sowing, in combination with soil salinity, hinder early plant growth. Plastic mulching increases soil temperature, reduces the need for irrigation, and also helps control salinity in the root zone and suppresses weeds, thereby increasing yields by 10–30% (and improving quality also) (Wang, R. et al., 2011). In the first stages after sowing the climate is particularly cold. With plastic mulching the cotton plants can be sown earlier, because the soil will not cool down during the night as much as without plastic mulch.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: For the establishment of the new technology of drip irrigation under plastic mulch, it is simultaneously essential to install a drainage system to avoid raising the groundwater level and causing salinity. For the installation of the drip lines, the transparent plastic film and the seeding, a tractor and a special tool for the installationis needed: one acre can be installed in a day. After the emerging of the cotton plants, holes must be cut in the plastic film so that the cotton plants can emerge. After harvesting, the drip lines and the plastic film must be collected and recycled. If the plastic is left behind it will pollute the soils and injure livestock if they eat it. Furthermore plastic residues in the soil can reduce subsequent yields, as roots are physically inhibited. After the collection of the plastic residues, if there is no adequate drainage system, the field needs to be flooded to flush the salt layer, which has accumulated below the root zone, deeper into the soil. If the field is not flooded the salt will negatively affect the next years’ cotton plantation.
Natural / human environment: Southern Xinjiang is an arid region with 50 to 90 mm per year. Most precipitation occurs between June and August. It is classified as a temperate cold desert climate. For drip irrigation under plastic mulch, it is principally surface water that is used, which is delivered to the field via channels from reservoirs to the fields. The reservoirs are filled in summer with the floods along the Tarim River. The untreated surface water is of poor quality - for agricultural use only. For drip irrigation, the water needs to be treated to avoid blocking the drip outlets. The overall technology is expensive, and only land user groups and communities can afford the machines and the materials.
สถานที่: Tarim River Basin, China / Xinjiang Province, จีน
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี:
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ (approx. > 10,000 ตร.กม.)
In a permanently protected area?:
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: 10-50 ปี
ประเภทของการแนะนำ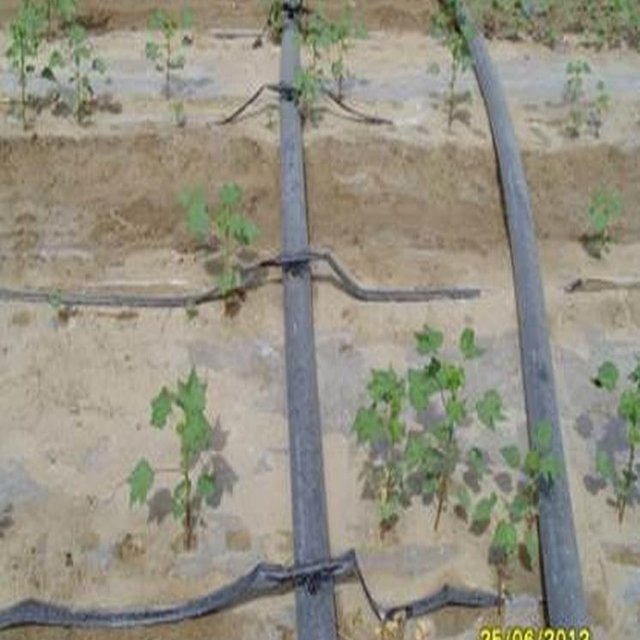






| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (USD) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (USD) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Drip line installation | ha | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Tractor | Piece | 1.0 | 5000.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | |||||
| seeds | kg | 30.0 | 3.0 | 90.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | |||||
| Plastic mulch | 1.0 | 32.0 | 32.0 | 50.0 | |
| Black dripe lines | Set | 1.0 | 380.0 | 380.0 | 50.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 5'510.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 5'510.0 | ||||
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (USD) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (USD) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Collecting mulch | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 98.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | |||||
| Irrigation and flooding water | 1.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 100.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 13.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 13.0 | ||||
15% of more cotton yield