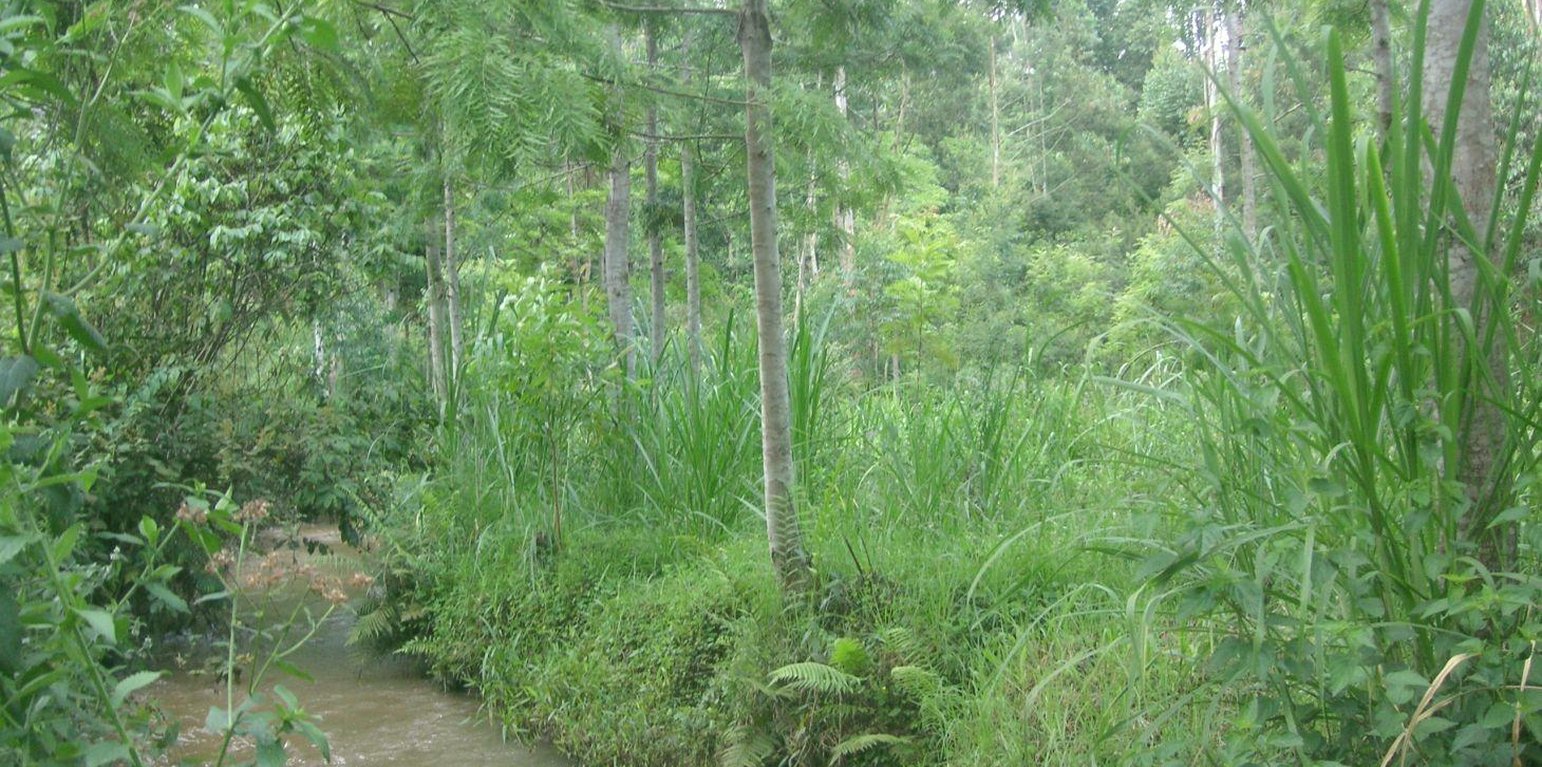




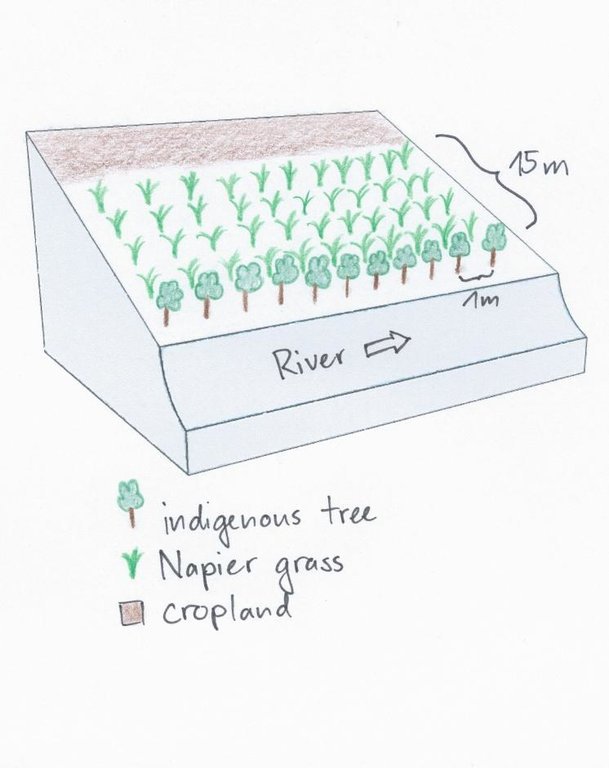
On the southeastern slopes of Mt. Kenya, the circumstances are ideal for agricultural activities, the rains are plenty and normally reliable. The plot owner started realizing a problem of riverbank degradation 17 years ago. But still he continued the traditional way of agriculture, planting beans and maize. Since his plot is on the slip-off slope only few metres above the river level, it experienced regular floods in case of heavy rainfalls, destroying the plants and leading to crop failures. Conventional plants like maize and beans do not resist such an excess of water. To fight the land loss and the bad harvest, the farmer introduced indigenous trees along the river and Napier fighting the riverbank degradation. Behind that, several rows of the flood resistant Napier grass were planted to still use the area in a productive way.
Purpose of the Technology: Above all, the goal of this technology is to get a high grass production. As a side effect results a quite good protection of the riparian area. The vegetation prevents rainwater from running directly from the fields into the water. Therefore, the chemicals from the field get stuck in the riparian soils and don't pollute the river. In the same way the infiltration in the riparian enlarges the total infiltration since the water would go to the river directly. Especially the raw surface of the riparian allows more infiltration and interception storage of water. This surplus of stored water is able to provide river water for a longer period, when rains are humble for a longer period. In case of floods, the increased infiltration potential can cut the peak flow and thus prevent damages. The grass yield is used as a fodder for the cows.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Before planting the indigenous trees, water guzzlers like eucalyptus trees were cut down. Indigenous seedlings were planted right along the river at a distance of 1 m. Behind the tree row, Napier grass is planted and harvested twice a year. The cutting and harvesting of the grass is done regularly such that animals can be provided with fodder every day. As soon as the trees are big enough, they function as a source of fire wood, they can be pruned every 5 months.
Natural / human environment: The studied plot is situated between the tea and the coffee zone at an elevation of 1663 m.a.s.l. This small-scale farm does not produce tea nor coffee, there is mainly subsistence agricultural production and some few products are sold on the market. Rainfall is reliable and ensures a regular production.
สถานที่: Embu, Kenya/Eastern Province, เคนยา
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี:
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ (0.00075 km²)
In a permanently protected area?:
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: 10-50 ปี
ประเภทของการแนะนำ







| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (USD) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (USD) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Chopping bad trees | Persons/day | 2.5 | 3.2 | 8.0 | 100.0 |
| Tree planting | Persons/day | 5.0 | 3.6 | 18.0 | 100.0 |
| Planting of Napier grass | Persons/day | 2.0 | 2.75 | 5.5 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | |||||
| Seedling | Pieces | 70.0 | 0.114285 | 8.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 39.5 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 39.5 | ||||
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (USD) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (USD) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Adding manure | Persons/day | 0.2 | 2.25 | 0.45 | 100.0 |
| Harvest of Napier | Persons/day | 2.0 | 3.3333 | 6.67 | 100.0 |
| Prunning | Persons/day | 2.0 | 3.25 | 6.5 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 13.62 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 13.62 | ||||