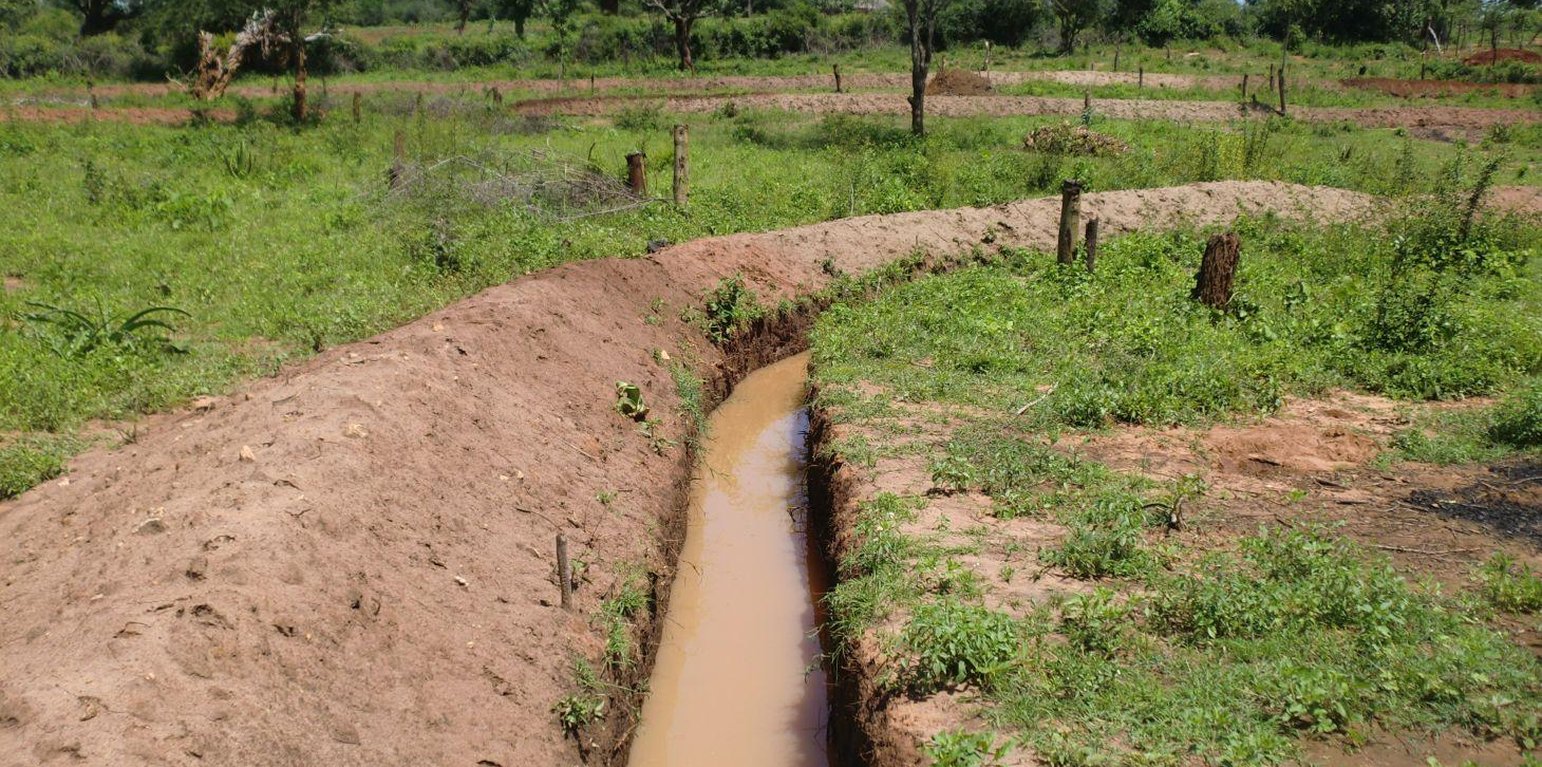




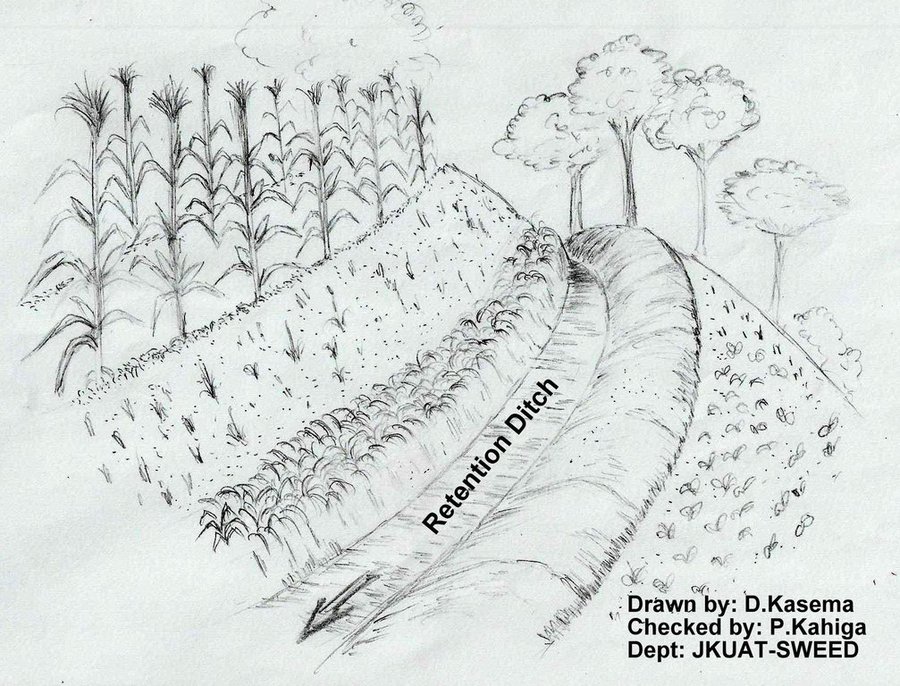
Retention ditches, also called infiltration ditches, are larger ditches designed to catch and retain all incoming runoff for infiltration into the soil. They operate like contour furrows, increasing the supply of water made available to crops planted in and adjacent the ditch, while also reducing soil erosion. However, they handle much more water. Retention ditches are in essence water harvesting and conservation structures
Purpose of the Technology: They are commonly used as an alternative to diversion ditches if there is no places to discharge runoff or if there is a need , as in semi –arid areas , to harvest water , e.g. for bananas.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: When constructing the ditches, the soil is thrown to the lower side to form an embankment that prevents soil from falling back in. This structure can be stabilized further by planting grass on it. On soils with lower infiltration rate, or on slopes, the ends can be left open to allow excess water to drain out.
Natural / human environment: Retention ditches are normally constructed on relatively flat areas with closed ends and wide and deep enough to hold all the runoff expected. They are often found on steep slopes in humid area under small scale farming where there is no opportunity to discharge runoff to a waterway. Retentions ditches can be useful where soils are permeable, deep and stable. However, retention ditches are not recommended for areas with shallow soil, those prone to land slides or where soil salinity is a possibility.
สถานที่: Mbeere, Eastern, เคนยา
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี:
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ (approx. < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์))
In a permanently protected area?:
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: 10-50 ปี
ประเภทของการแนะนำ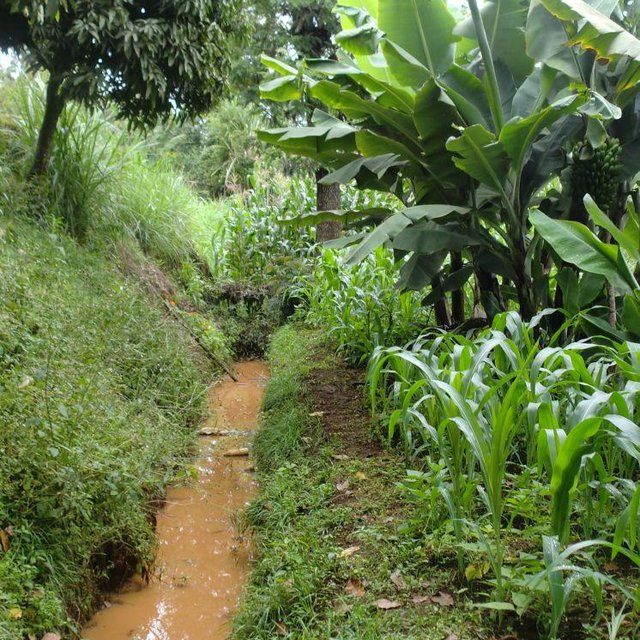



| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (Kshs) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (Kshs) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 80.0 | 80.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Tools | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 130.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 1.3 | ||||
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (Kshs) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (Kshs) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 45.0 | 45.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Tools | ha | 1.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 80.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 0.8 | ||||
waterborne pests