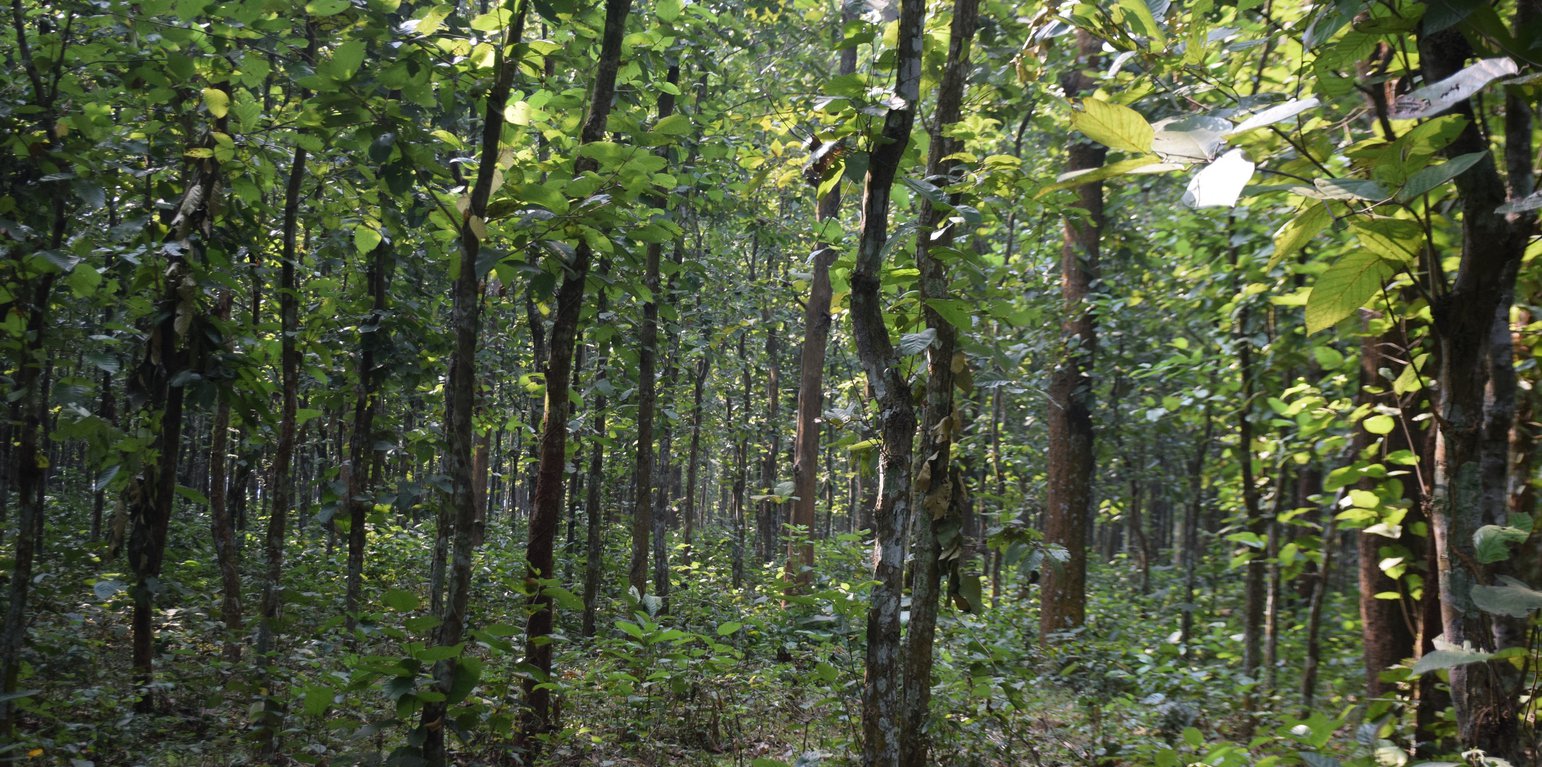




Sal forests have a fairly wide and interrupted distribution in the drier central and northern parts of the country. These tropical moist deciduous forests are popularly known as Sal forest as the predominant species is Sal (Shorea robusta). The importance of Sal forests lies in the fact that these are the only natural forest resources of the central and northern parts of Bangladesh where the majority of the country’s population lives. Historically, the agrarian rural people around the forests have been heavily dependent on Sal forests for their livelihood. Until the beginning of the 20th century, Sal forests existed as a large continuous belt with rich biological resources but increasing pressure from population growth has been placed on them ever since. Most of the Sal forests have either become degraded in quality or reduces by conversion to agricultural land.
The Forest Department introduced coppice management with natural regeneration in Sal forest that have a rotation of 20-30 years to regain the forest structure and biomass. Coppicing is a traditional method of forest management, which exploits the capacity of tree species to put out new shoots from their stump or roots if cut down. Due to the fact that shoots perform better than seedlings, because they obtain water, nutrients and carbohydrates from a well-developed root system of the parent tree, they are more resilient to human disturbances that affect tree growth and survival. As new growth emerges after a number of years, the coppiced tree is harvested, and the cycle begins again. Therefore, coppicing is considered an efficient mechanism by which trees regain above-ground biomass immediately after disturbance.
The Gazipur Sal forest is located in lowland plain areas of the central parts of Bangladesh. The average temperature in Gazipur is 25.8 °C and the annual rainfall is 2036 mm. The area is densely populated with a population density of 2,505 per square km. The dominant land use is still agriculture, but industrialization rate is higher in the area as it is only 25km away from capital Dhaka. The Sal forest area is managed by Bangladesh Forest division. Co-management approach is introduced in some buffer areas for the coppice management of Shorea robusta with a profit-sharing ratio of 65:25 between forest department and community beneficiaries. The rest of 10% money allocated for further tree farming activities.
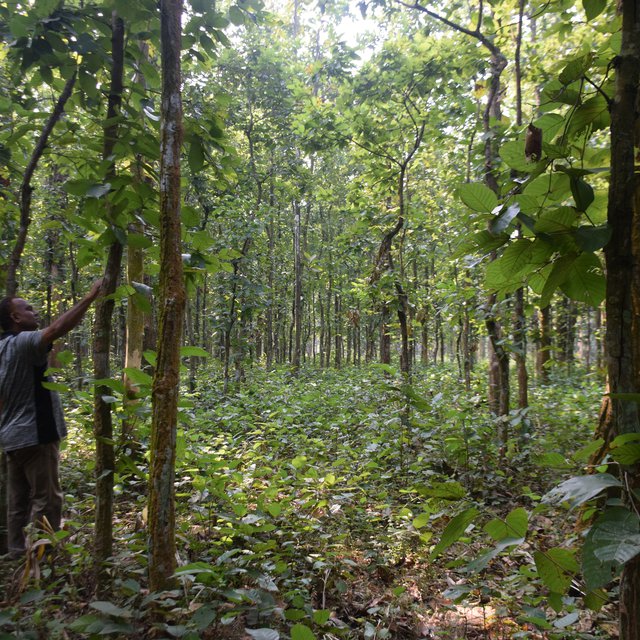
No new planting of Sal seedlings is necessary for this practice. In the first year a relatively poor-quality Sal stand of Gazipur site were selected where coppice regeneration took place from stumps. Then, the multiple shoots regenerated from the stump were singled to three best shoots per stump and the rest were harvested. These three shoots were maintained in the following years and new shoots were removed if there were any. In addition, regular weeding was needed to maintain the technology. Local community people engaged to the maintenance and surveillance activities through co-management modalities and they will get their profit share after harvesting of the mature stand.
Where the density of Sal stumps is between 200-400 stems/ha, coppice management potentially protects and promotes the growth of new Sal seedling and other natural species in open areas. The native species regeneration under coppice management helps protect biodiversity value in a cost-effective manner. Coppice Sal Forests have the capacity to regenerate a rich variety of Non-Timber Forest Products (NTFPs). The major NTFPs collected by the co-management beneficiaries include fuelwood, dry leaves for fuel, and medicinal plants. Apart from this, they also collect mushroom, tuber crops, wild fruits, cane, honey and resin from coppice forests. As the area is under permanently protected area the beneficiaries cannot harvest any timber from the stand.
As the artificial regeneration of Sal is difficult, the sustainable forest management can be ensured through coppice management of Sal. In Gazipur, the depleted Sal forest are now slowly regaining its health and habitats for wildlife are improving as well. These forests, which historically were seen as timber sources, are now managed for multiple products through coppice management. The forest now supports alternate income for community people and also playing important role for ecological balance of this region.
สถานที่: Gazipur, Dhaka division, บังกลาเทศ
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี: 2-10 แห่ง
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ (approx. 10-100 ตร.กม.)
In a permanently protected area?: ใช่
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: 10-50 ปี
ประเภทของการแนะนำ








| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (BDT) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (BDT) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Site preparation (prepare plantation site map with GPS, jungle cutting, debris collection) | person-days | 5.0 | 500.0 | 2500.0 | 100.0 |
| Thinning (removal of unwanted shoots from stumps) | person-days | 12.0 | 500.0 | 6000.0 | 100.0 |
| Application of fertilizer | person-days | 5.0 | 500.0 | 2500.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Spade, saw, bucket, knife, etc. | lump sum | 1.0 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | |||||
| Compost fertilizer | kg | 2000.0 | 4.0 | 8000.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 21'000.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 250.0 | ||||
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (BDT) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (BDT) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| 1st year weeding | person-days | 12.0 | 500.0 | 6000.0 | 100.0 |
| 2nd year weeding | person-days | 12.0 | 500.0 | 6000.0 | 100.0 |
| 3rd year weeding | person-days | 8.0 | 500.0 | 4000.0 | 100.0 |
| 4th year weeding | person-days | 4.0 | 500.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Spade, saw, bucket, knife, etc. | Lump-sum | 1.0 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 20'000.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 238.1 | ||||
Some agroforestry products also derived from the practice of local communities
re-establishment of Sal forest through coppice management with involving local community allowed them to collect NTFP from the forest
Ecotourism has benn promoted in the area
Through co-management of Sal forest the local community institutions strengthened
The scattered degraded forest is now managed in a sustainable manner
Conflict on forest land use has been reduced due to co-management
the extreme poor people who were depended on forest now are member of the co-management group under the profit sharing approach
groundwater aquifer recharges due to presence of forest canopy cover