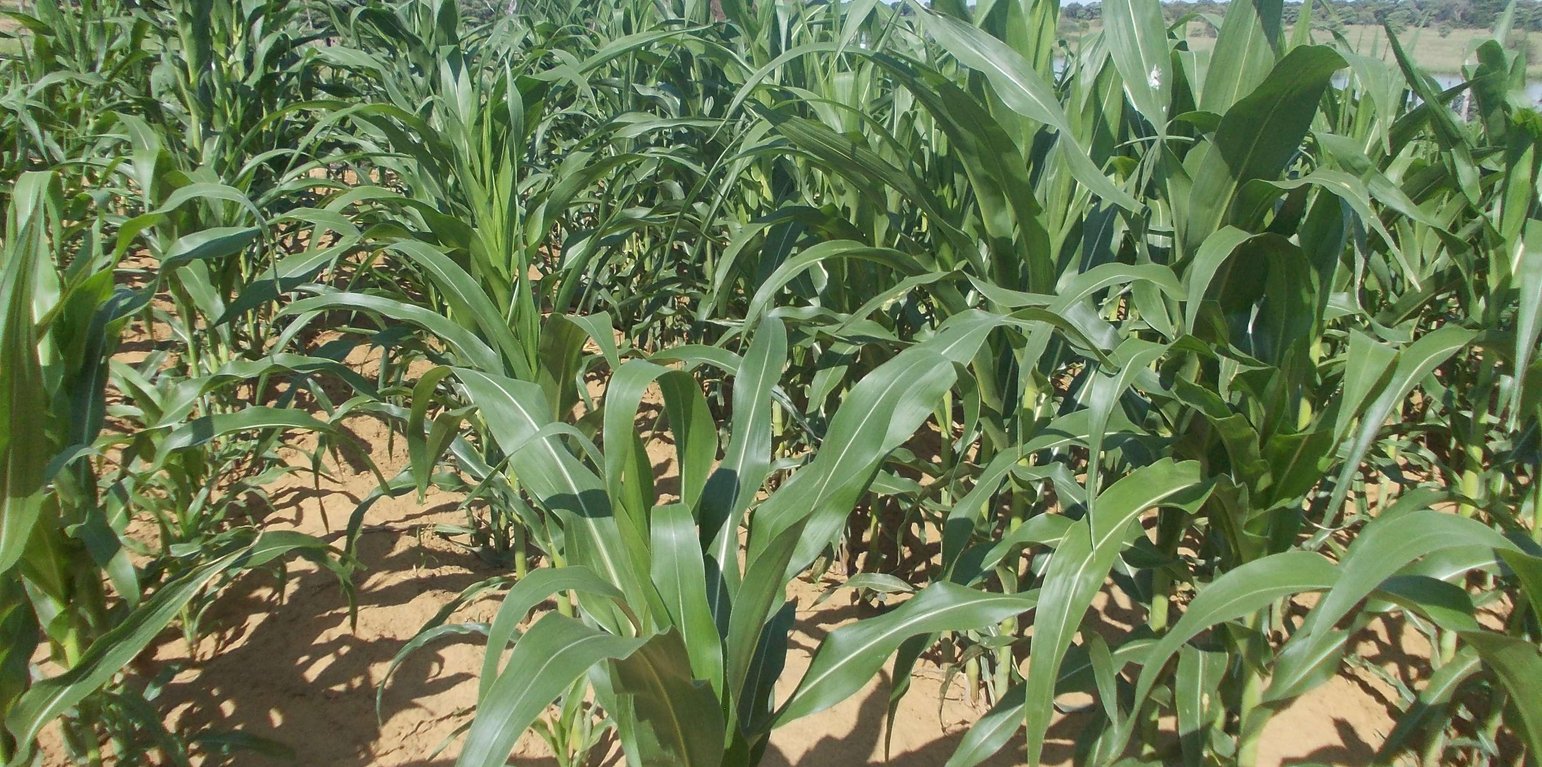




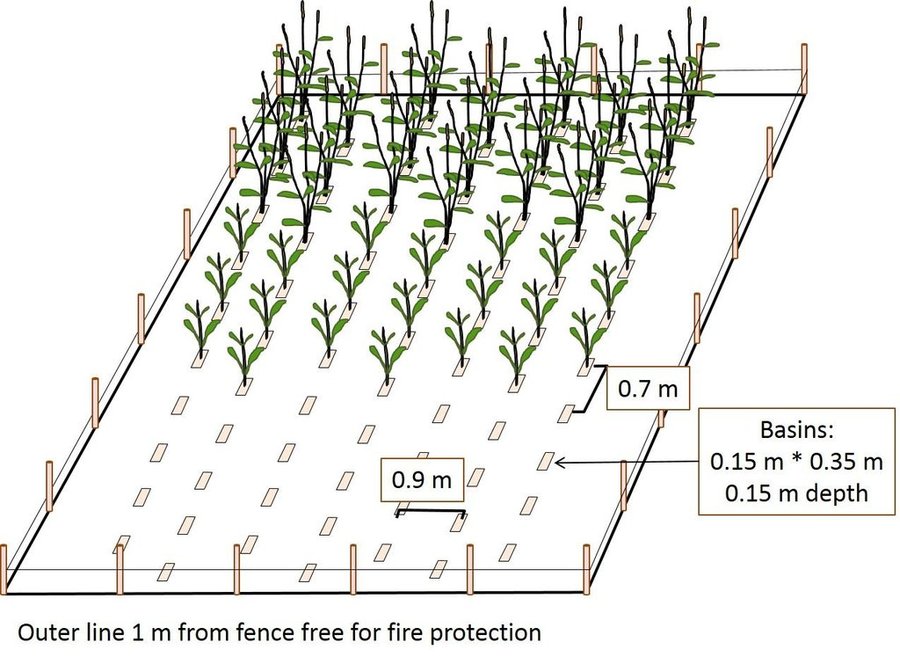
Farmers in north-eastern Namibia practice shifting/semi-permanent subsistence cropping, concentrating on pearl millet cultivation. Here, conservation agriculture (CA) was promoted to sustain and improve production and to reduce conversion of woodland to crops. CA comprises the three principles of minimum soil disturbance, permanent soil cover, and rotation. CA was tested on small plots with volunteers trained by a local NGO. The technology was characterized here by: (i) Early (pre-rains) preparation of the land with two alternative techniques; either: a) basins with a defined spacing opened by a hand hoe, with composted manure added (biochar has also been tested), or b) rip-lines prepared with oxen in lines and with manure application within the rip lines; (ii) Mulching the soil with crop residues, branches or sunnhemp, specially grown for the purpose; (iii) Protection against grazing of crop and mulch by livestock; (iv) Intercropping with vegetables or legumes. (v) Weeding.
CA has been promoted for four seasons, and now trained farmers are transferring their knowledge to others. The technology was promoted to substantially improve the low yields of traditionally practiced agriculture by improving fertility and soil structure as well as better capturing runoff. It was also aimed at avoiding further expansion of croplands into dry woodlands on low fertility arenosols. Eventually it is hoped that the well-being of local subsistence cropping communities will be improved and outmigration reduced.
Knowledge about CA comes from Zambia, where it has been has been practiced successfully for many years by small-scale farmers. A local NGO was engaged by an international project (www.future-okavango.org) which searched for volunteer farmers in the Kavango area. The first CA planting took place in 2011/12. These pioneer farmers were backstopped regularly and the number of farmers trained increased. The NGO monitored crops with contact farmers. 45 more farmers showed interest and were then trained by the contact farmers. Training and backstopping continued until August 2015.
The natural environment is semi-arid. Rainfall is concentrated from November to March. Mean annual precipitation is 570 mm, and mean air temperature is 26.2°C in the hottest month (October) and 16.2°C in the coldest month (July). The landscape forms part of the extended Kalahari basin in central-southern Africa. Deep and extended sands restrict people to living in areas close to surface water. Villages are located along the Okavango on the elevated river terraces – where they produce crops. Here, sedimentation of fine-grained soils, the accumulation of calcium carbonates in the subsoil and the activity of termites have resulted in soils of medium fertility which could potentially ensure yields of 500 kg/ha of millet, if well managed, and assuming good rainfall. Due to the growing population and restricted land availability, cultivation patterns have changed from shifting to semi-permanent and expanded to the adjacent woodlands on the deep Kalahari sands. Here, rapid degradation of soil fertility has caused further expansion and reduced crop yields to very low levels (ca. 150 kg/ha on average). Livestock graze and browse vegetation on the floodplains and in the woodlands. Due to night-time kraaling of livestock, manure is available as fertilizer: thus sustained cropping can be supported. The importance of the woodlands for ecosystem services including timber and firewood, for thatching grass, medicinal plants and biodiversity means they must be conserved and this acts as a reason to support the search for alternative crop production systems such as CA.
สถานที่: Mashare, Kavango East, นามิเบีย
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี:
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ (approx. < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์))
In a permanently protected area?:
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
ประเภทของการแนะนำ






| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (Nam $) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (Nam $) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| labour | ha | 1.0 | 1104.0 | 1104.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | |||||
| Wire for fencing | ha | 1.0 | 224.0 | 224.0 | 100.0 |
| sticks & poles | ha | 1.0 | 1114.0 | 1114.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 2'442.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 157.55 | ||||
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (Nam $) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (Nam $) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| labour | ha | 1.0 | 848.0 | 848.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | |||||
| seeds | ha | 1.0 | 22.0 | 22.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | |||||
| fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 159.0 | 159.0 | 100.0 |
| compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 276.0 | 276.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | |||||
| Wire for fencing | ha | 1.0 | 220.0 | 220.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 1'525.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 98.39 | ||||
not measured but assumed
not measured but assumed
Envy and gossip were observed
Improved and stabilized yields help rural families to adapt to modern lifestyles. However, the long-term contribution of CA to the well-being of the local farmers cannot be foreseen. The establishment of family-owned fenced areas for crop production is likely to have an influence on the social structure of the rural communities.
not measured but assumed
not measured but assumed
not measured but assumed
not measured but assumed
not measured but assumed