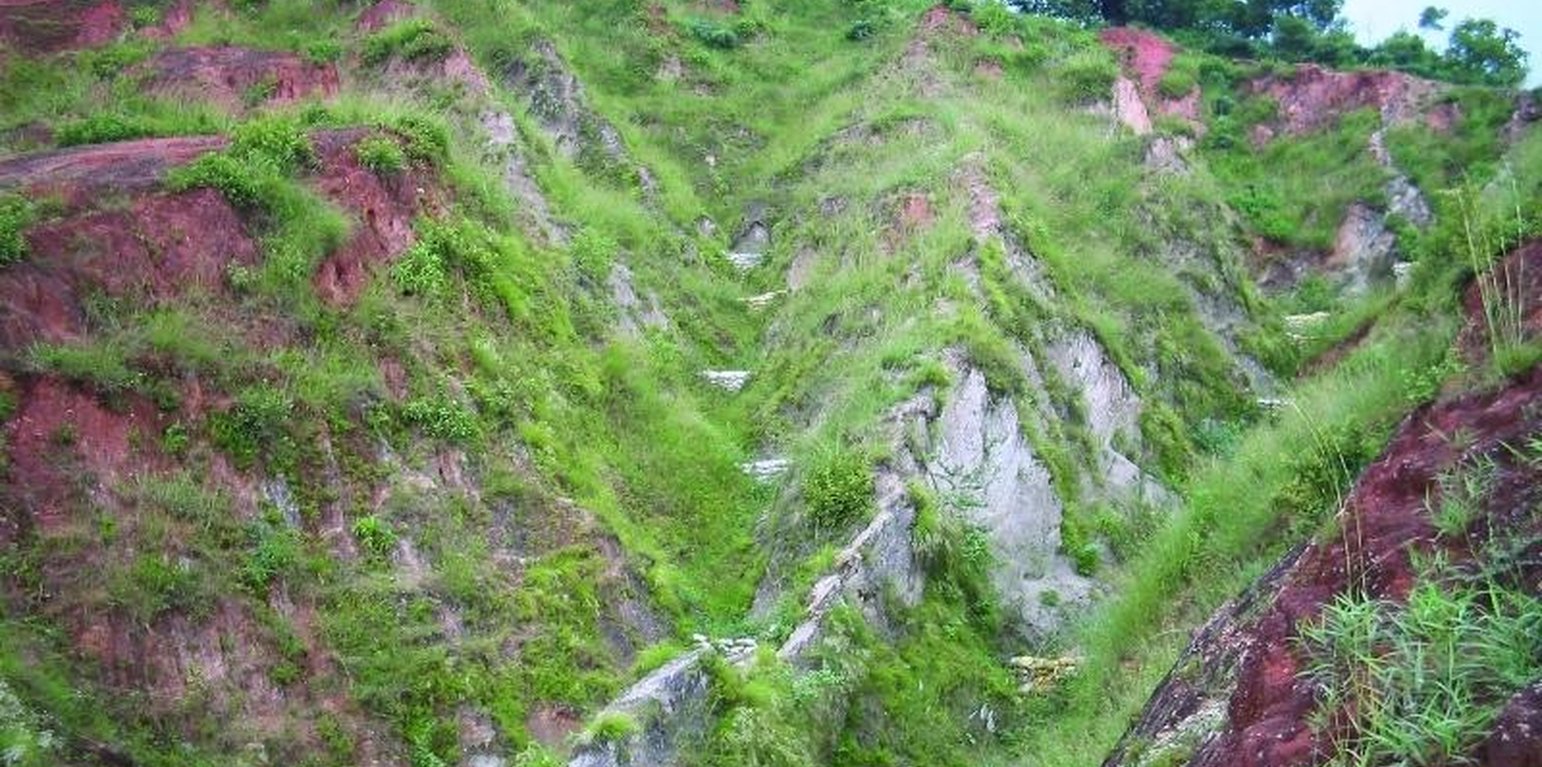
Gully plugging using check dams
(เนปาล)
Galchhi niyantran - Nepali
คำอธิบาย
Small dam structures constructed across erosion gullies
Check dams are small low structures built across a gully or a channel to prevent them from deepening further. These small dams reduce the speed of water flow and minimise the erosive power of runoff. They also promote the deposition of eroded materials to further stabilise the gullies.
Two gullies adjacent to a degraded area of communal grazing land were controlled by constructing check dams and with vegetative measures including planting bamboo. The main purpose was to control the further development of the gullies, which were affecting the adjacent grazing land and blocking a downstream irrigation channel. The site is community land used by the 40 households (240 people) of Dhotra village in the intensively used Jhikhu Khola watershed. Irrigated cropland lies downstream from the site, whilst the site itself is bordered by grazing land, degraded sal-dominated forest, and rainfed forward-sloping terraces.
The check dams were made of old cement bags filed with soil and were 1m high with 0.5m deep foundations. The check dams were spaced so that a line joining the top of two adjacent dams had about a 3% slope gradient. Twenty-four check dams were built in the two gullies using a total of 2400 filled cement bags. Forty clumps of bamboo were planted between the dams for stabilisation.
All that is needed to maintain this technology is to inspect the condition of the check dams occasionally, especially before and after the monsoon. Displaced bags should be replaced and the water courses cleared of branches and big stones. Further planting should be carried out if needed.
The case study area has a distinct dry season from November to May and a wet monsoon period from June to October. Annual rainfall is around 1200 mm. The site has red soils that are highly weathered and, if not properly managed, are very susceptible to erosion.
สถานที่
สถานที่: Kavre Palanchok/ Dhotra village, Jhikhu Khola watershed, เนปาล
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี:
ตำแหน่งทางภูมิศาสตร์ของสถานที่ที่ถูกเลือ
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ (0.006 km²)
In a permanently protected area?:
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: 10-50 ปี
ประเภทของการแนะนำ
-
ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
-
เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
-
ในช่วงการทดลองหรือการทำวิจัย
-
ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
จุดประสงค์หลัก
-
ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
-
ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
-
อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
-
ป้องกันพื้นที่ลุ่มน้ำ/บริเวณท้ายน้ำ โดยร่วมกับเทคโนโลยีอื่นๆ
-
รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
-
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
-
ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
-
ชะลอการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลกและผลกระทบ
-
สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
-
สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านสังคมที่เป็นประโยชน์
-
reduce land loss
การใช้ที่ดิน
-
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
- การทำฟาร์มปศุสัตว์ (Ranching)
การใช้น้ำ
-
จากน้ำฝน
-
น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
-
การชลประทานแบบเต็มรูปแบบ
ความมุ่งหมายที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
-
ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
-
ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
-
ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
-
ปรับตัวกับสภาพความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
-
ไม่สามารถใช้ได้
ที่อยู่ของการเสื่อมโทรม
-
การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ - Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ, Wo (Offsite degradation): ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่
กลุ่ม SLM
-
การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
-
มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
มาตรการ SLM
-
มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช - V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
-
มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง - S5: เขื่อน ชั้นดินที่แน่นแข็งบ่อน้ำ
แบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค
Schematic drawing of two gullies with 24 check dams and bamboo planted below the check dams for stabilisation
Location: Dhotra. Khabre
Date: 22.6.06
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, increase of infiltration
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 40
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 4 m
Trees/ shrubs species: Bamboo
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 25.00%
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): 4 m
Construction material (earth): soil resulting from digging activities from the adjacent grassland was used to fill cement bags for
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 25%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
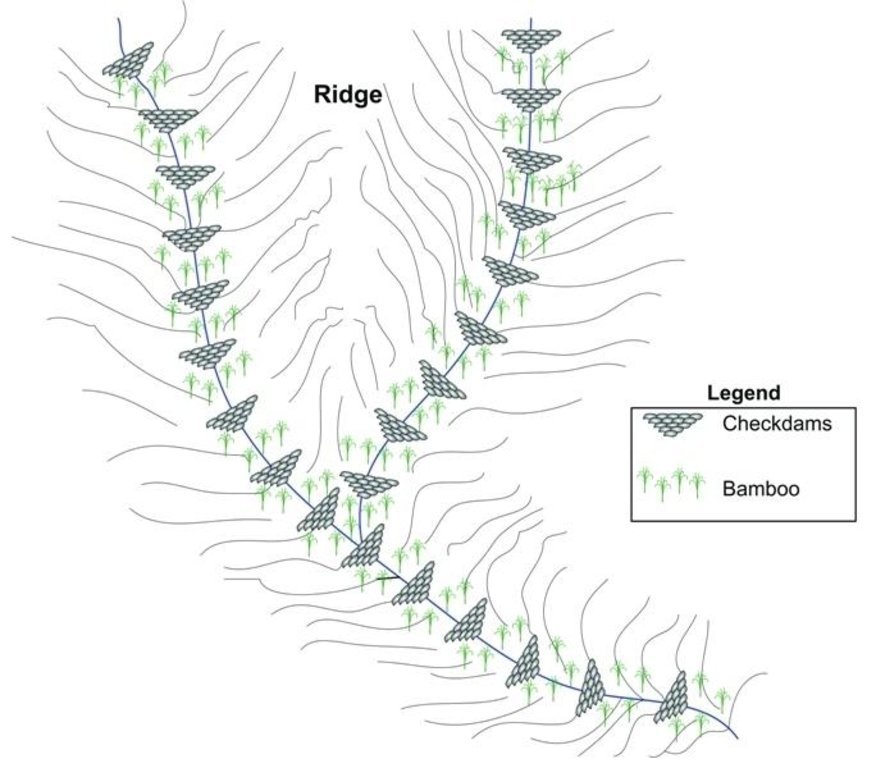
Author: I. Providoli, A.K.Thaku ICIMOD
การจัดตั้งและการบำรุงรักษา: กิจกรรม ปัจจัยและค่าใช้จ่าย
การคำนวนต้นทุนและค่าใช้จ่าย
- ค่าใช้จ่ายถูกคำนวน
- สกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย Nepali Rupee
- อัตราแลกเปลี่ยน (ไปเป็นดอลลาร์สหรัฐ) คือ 1 ดอลลาร์สหรัฐ = 73.0 Nepali Rupee
- ค่าจ้างเฉลี่ยในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวันคือ 2.00
ปัจจัยที่สำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
n.a.
กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
-
Plantating of bamboo plants (clumps) below the check dams (ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่: before onset of monsoon (June))
-
Placing filled cement bags across gullies to form checkdams (ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่: before onset of monsoon (June))
-
Filling cement bag with soil (ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่: before onset of monsoon (June))
-
Digging trenches for dam foundations (ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่: before onset of monsoon (June))
ปัจจัยและค่าใช้จ่ายของการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า |
หน่วย |
ปริมาณ |
ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (Nepali Rupee) |
ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (Nepali Rupee) |
%ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|
แรงงาน
|
| Building dams and planting bamboo |
Persons/day |
18.0 |
2.0 |
36.0 |
100.0 |
|
วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง
|
| Cement bags |
ha |
1.0 |
73.0 |
73.0 |
|
|
อื่น ๆ
|
| Lunch, tea for farmers |
ha |
1.0 |
16.0 |
16.0 |
|
| Transportation |
ha |
1.0 |
14.0 |
14.0 |
|
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี |
139.0 |
|
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD |
1.9 |
|
กิจกรรมสำหรับการบำรุงรักษา
-
Maintaining gullies: repair or replace damaged check dams, plant (ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่: before onset of monsoon (June))
-
Ensuring good drainage for bamboo (ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่: before onset of monsoon (June))
-
Maintaining gullies: repair or replace damaged check dams,plant more grassesor trees if needed (ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่: before onset of monsoon (June)/once a year)
สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติ
ปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี
-
< 250 ม.ม.
-
251-500 ม.ม.
-
501-750 ม.ม.
-
751-1,000 ม.ม.
-
1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
-
1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
-
2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
-
3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
-
> 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
-
ชื้น
-
กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
-
กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
-
แห้งแล้ง
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเรื่องภูมิอากาศ
Thermal climate class: subtropics
ความชัน
-
ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
-
ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
-
ปานกลาง (6-10%)
-
เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
-
เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
-
ชัน (31-60%)
-
ชันมาก (>60%)
ภูมิลักษณ์
-
ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
-
สันเขา
-
ไหล่เขา
-
ไหล่เนินเขา
-
ตีนเนิน
-
หุบเขา
ความสูง
-
0-100 เมตร
-
101-500 เมตร
-
501-1,000 เมตร
-
1,001-1,500 เมตร
-
1,501-2,000 เมตร
-
2,001-2,500 เมตร
-
2,501-3,000 เมตร
-
3,001-4,000 เมตร
-
> 4,000 เมตร
เทคโนโลยีถูกประยุกต์ใช้ใน
-
บริเวณสันเขา (convex situations)
-
บริเวณแอ่งบนที่ราบ (concave situations)
-
ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
ความลึกของดิน
-
ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
-
ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
-
ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
-
ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
-
ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน)
-
หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
-
ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
-
ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
เนื้อดิน (> 20 ซม. ต่ำกว่าพื้นผิว)
-
หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
-
ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
-
ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
สารอินทรียวัตถุในดิน
-
สูง (>3%)
-
ปานกลาง (1-3%)
-
ต่ำ (<1%)
น้ำบาดาล
-
ที่ผิวดิน
-
<5 เมตร
-
5-50 เมตร
-
> 50 เมตร
ระดับน้ำบาดาลที่ผิวดิน
-
เกินพอ
-
ดี
-
ปานกลาง
-
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ยังไม่ได้รับการบำบัด)
-
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
-
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
-
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
-
ใช้ประโยชน์ไม่ได้
Water quality refers to:
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่?
การเกิดน้ำท่วม
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่
ลักษณะเฉพาะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่ประยุกต์ใช้เทคโนโลยี
เป้าหมายทางการตลาด
-
เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
-
mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
-
ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้จากภายนอกฟาร์ม
-
< 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
-
10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
-
> 50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ
-
ยากจนมาก
-
จน
-
พอมีพอกิน
-
รวย
-
รวยมาก
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล
-
งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
-
การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
-
การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน
-
อยู่กับที่
-
กึ่งเร่ร่อน
-
เร่ร่อน
เป็นรายบุคคลหรือกลุ่ม
-
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
-
กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
-
สหกรณ์
-
ลูกจ้าง (บริษัท รัฐบาล)
อายุ
-
เด็ก
-
ผู้เยาว์
-
วัยกลางคน
-
ผู้สูงอายุ
พื้นที่ที่ใช้ต่อครัวเรือน
-
< 0.5 เฮกตาร์
-
0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
-
1-2 เฮกตาร์
-
2-5 เฮกตาร์
-
5-15 เฮกตาร์
-
15-50 เฮกตาร์
-
50-100 เฮกตาร์
-
100-500 เฮกตาร์
-
500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
-
1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
-
>10,000 เฮกตาร์
ขนาด
-
ขนาดเล็ก
-
ขนาดกลาง
-
ขนาดใหญ่
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน
-
รัฐ
-
บริษัท
-
เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
-
กลุ่ม
-
รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
-
รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน
-
เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
-
เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
-
เช่า
-
รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
-
เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
-
เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
-
เช่า
-
รายบุคคล
เข้าถึงการบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
ผลกระทบ
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมและวัฒนธรรม
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
At the beginning a few people opposed the activities.
ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่าย
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น
ด้านลบอย่างมาก
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว
ด้านลบอย่างมาก
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษา
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น
ด้านลบอย่างมาก
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว
ด้านลบอย่างมาก
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
การเปลี่ยนแปลงของสภาพภูมิอากาศ
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
อุณหภูมิประจำปี เพิ่มขึ้น
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
การน้อมเอาความรู้และการปรับใช้
เปอร์เซ็นต์ของผู้ใช้ที่ดินในพื้นที่ที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
-
ครั้งเดียวหรือเป็นการทดลอง
-
1-10%
-
11-50%
-
> 50%
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใดๆ?
-
0-10%
-
11-50%
-
51-90%
-
91-100%
จำนวนหลังคาเรือนหรือขนาดพื้นที่รวมทั้งหมด
40 households in an area of 0.006 sq km
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเร็วๆ นี้เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่?
สภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงอันไหน?
-
การเปลี่ยนแปลงแบบค่อยเป็นค่อยไปและสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ
-
การเปลี่ยนแปลงของตลาด
-
การมีแรงงานไว้ให้ใช้ (เนื่องจากการอพยพย้ายถิ่นฐาน)
บทสรุปหรือบทเรียนที่ได้รับ
จุดแข็ง: มุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
-
Reduced soil erosion, rill erosion, and top soil loss
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular maintenance of the structure and grasses is required
-
The technology is easy to maintain.
How can they be sustained / enhanced? As above
จุดแข็ง: ทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรคนอื่นๆ
-
It's a low cost technology , easy to apply, little knowledge needed.
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular maintenance of the structure and grasses is required
-
The effect of the technology can be seen easily.
How can they be sustained / enhanced? As above
จุดด้อย/ข้อเสีย/ความเสี่ยง: มุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดินแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร
จุดด้อย/ข้อเสีย/ความเสี่ยง: ทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรคนอื่นๆแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร
การอ้างอิง
ผู้ตรวจสอบ
-
David Streiff
-
Alexandra Gavilano
วันที่จัดทำเอกสาร: 6 มิถุนายน 2011
การอัพเดทล่าสุด: 3 มิถุนายน 2019
วิทยากร
-
Nicole Guedel - ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM
-
Madhav Dhakal - ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM
-
Isabelle Providoli - ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM
คำอธิบายฉบับเต็มในฐานข้อมูล WOCAT
การจัดทำเอกสารถูกทำโดย
องค์กร
- ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - เนปาล
โครงการ
- People and Resource Dynamics Project, Nepal (PARDYP)
การอ้งอิงหลัก
-
Nakarmi, G. (2000) Soil Erosion Dynamics in the Middle Mountains of Nepal, a report submitted to PARDYP, ICIMOD, Kathmandu: ICIMOD
-
Schreier, H.; Brown, S.; Shah, P. B.; Shrestha, B.; Merz, J. (2002) Jhikhu Khola Watershed – Nepal, CD ROM. Vancouver: Institute for Resources and Environment, University of British Columbia.: ICIMOD
-
Shrestha, B. (2004) Progress Report PARDYP- Nepal. Paper presented at the PARDYP Access Mid Year Meeting, 19-22 July 2004, ICIMOD, Kathmandu: ICIMOD









