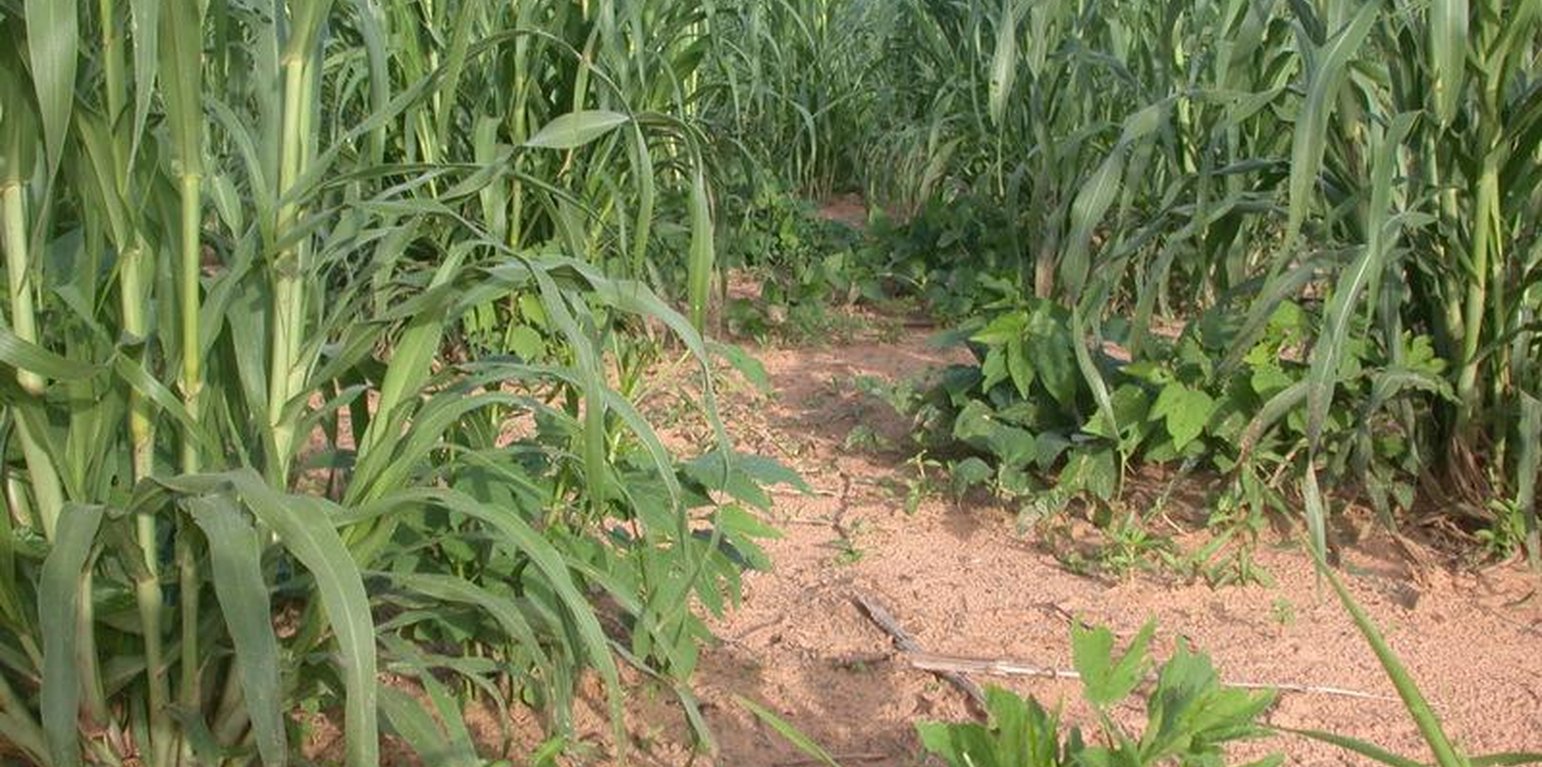
Rotational Fertilization
(ไนเจอร์)
คำอธิบาย
Rotational fertilization is an integrated crop-livestock management measure practiced by the agropastoralist Peulh.
At intervals of 2-3 years the Peulh agropastoralists relocate with their livestock to a new area previously used for crop cultivation - where they install their temporary dwellings and improve soil fertility by applying farmyard manure and other organic materials.
The rotation of temporary habitation areas leads to successive fertilization of the land. Livestock (cattle or small ruminants) are corralled or tethered in the rehabilitation area over-night. They feed on crop residues and emerging grasses after harvesting of the crops. Dung dropped within the coral area is collected and then distributed on the fields. The main criterion for site selection is the level of land degradation. The size of the area occupied is maximum 500 m2, and depends on family size, herd size and on the quantitative and qualitative objectives of soil fertilization of the land owner.
In the years after settlement (after families move to a new location) the treated area is used for crop cultivation, and crop rotation/intercropping are practiced (e.g. millet/ legumes) for increased and diversified production, improved pest control and fertility management.
The effectiveness of this technology has led to field-fertilization contracts between agro-pastoralists and sedentary farmers. The farmers offer post-harvest grazing rights to the agropastoralists who in turn fertilize the land and benefit from the access to the important weekly markets in the area where they can sell milk. In this case the agropastoralist families and their livestock split up after the rainy season: a part assures fertilization of the own land, the other part is in charge of fertilizing foreign land (during 3-4 months) before returning home.
สถานที่
สถานที่: Tillabéry Region, Niger, Damari, Kollo District, ไนเจอร์
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี:
ตำแหน่งทางภูมิศาสตร์ของสถานที่ที่ถูกเลือ
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
In a permanently protected area?:
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: มากกว่า 50 ปี (แบบดั้งเดิม)
ประเภทของการแนะนำ
-
ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
-
เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
-
ในช่วงการทดลองหรือการทำวิจัย
-
ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
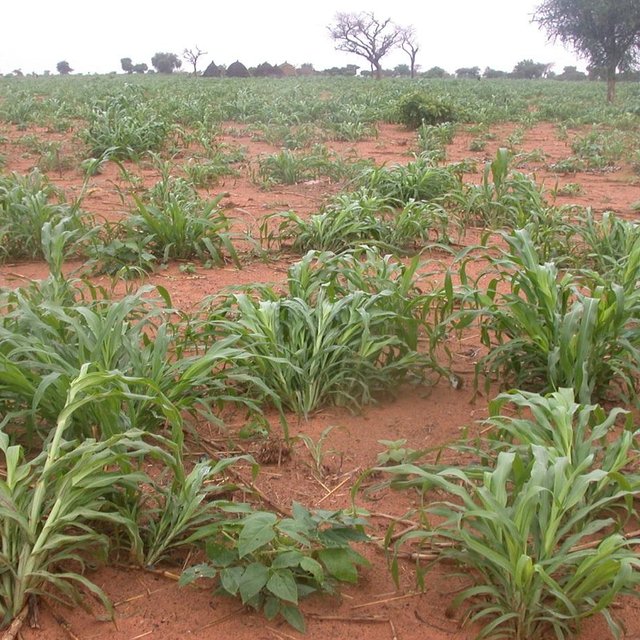

Millet growing on fertilized fields (Adamou Kalilou)
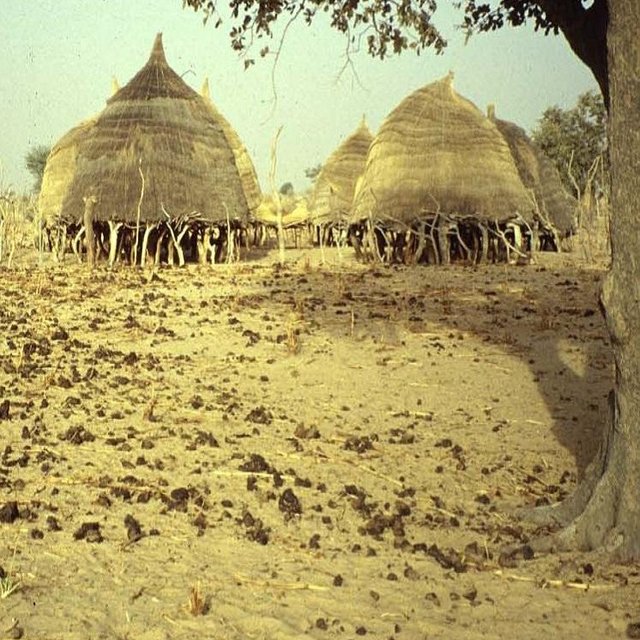

Dung dropped by animals feeding on crop residues; sheltered corrals in the background. (Pierre Hiernaux)
จุดประสงค์หลัก
-
ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
-
ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
-
อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
-
ป้องกันพื้นที่ลุ่มน้ำ/บริเวณท้ายน้ำ โดยร่วมกับเทคโนโลยีอื่นๆ
-
รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
-
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
-
ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
-
ชะลอการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลกและผลกระทบ
-
สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
-
สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านสังคมที่เป็นประโยชน์
การใช้ที่ดิน
-
พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว: cereals - millet, legumes and pulses - peas
-
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
- กึ่งโนแมนดิซึ่มหรือแพสโตแรลลิซึ่ม (Semi-nomadism/pastoralism)
การใช้น้ำ
-
จากน้ำฝน
-
น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
-
การชลประทานแบบเต็มรูปแบบ
ความมุ่งหมายที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
-
ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
-
ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
-
ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
-
ปรับตัวกับสภาพความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
-
ไม่สามารถใช้ได้
ที่อยู่ของการเสื่อมโทรม
-
การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ - Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
-
การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม - Et (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบน
-
การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี - Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)
กลุ่ม SLM
-
การจัดการปลูกพืชร่วมกับปศุสัตว์
-
การจัดการความอุดมสมบรูณ์ของดินแบบผสมผสาน
มาตรการ SLM
-
มาตรการจัดการพืช - A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
-
มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ - M1: การเปลี่ยนรูปแบบของการใช้ประโยชน์ที่ดิน
แบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค
การจัดตั้งและการบำรุงรักษา: กิจกรรม ปัจจัยและค่าใช้จ่าย
การคำนวนต้นทุนและค่าใช้จ่าย
- ค่าใช้จ่ายถูกคำนวน
- สกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย n.a.
- อัตราแลกเปลี่ยน (ไปเป็นดอลลาร์สหรัฐ) คือ 1 ดอลลาร์สหรัฐ = ไม่มีคำตอบ
- ค่าจ้างเฉลี่ยในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวันคือ 1.5
ปัจจัยที่สำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
Establishment of housing infrastructure is done collectively, involving dozens of community members within less than a week. Construction material is taken from the woodlands; many parts are re-used after moving. While expenses are expressed in US$, in reality costs are in kind (mutual help) or not paid for (free lumber). Maintenance activities include: maintenance and re-building of dwellings. Costs for crop cultivation (US$ 335-535 annually) are not included.
กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
-
Identification of site where level of land degradation is high (ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่: None)
-
Level and clean the land (ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่: None)
-
Layout/disposition of infrastructure (dwellings, barns, corral, poles, poultry habitat) according (ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่: None)
-
Establishment of infrastructure (ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่: None)
ปัจจัยและค่าใช้จ่ายของการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า |
หน่วย |
ปริมาณ |
ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (n.a.) |
ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (n.a.) |
%ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|
แรงงาน
|
| All the Labour |
persons/day |
100.0 |
1.5 |
150.0 |
100.0 |
|
วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง
|
| Lumber and straw for hut |
ha |
1.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี |
250.0 |
|
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD |
250.0 |
|
กิจกรรมสำหรับการบำรุงรักษา
-
On land being treated: on-going fertilisation by applying farmyard manure and any kind of organic material accruing from daily human activities to the soil during 2-3 years (ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่: during 2-3 years)
-
Maintenance/ re-location of huts to improve fertilization of land (after rainy season). (ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่: None)
-
On previously treated land: Land preparation (ploughing, e.g. cowpea). (ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่: None)
-
Cultivation of millet and legumes ('niébé') as intercrop or in the form of crop rotation. (ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่: None)
ปัจจัยและค่าใช้จ่ายของการบำรุงรักษา
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า |
หน่วย |
ปริมาณ |
ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (n.a.) |
ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (n.a.) |
%ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|
แรงงาน
|
| On-going fertilisation |
persons/day |
10.0 |
1.5 |
15.0 |
100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี |
15.0 |
|
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD |
15.0 |
|
สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติ
ปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี
-
< 250 ม.ม.
-
251-500 ม.ม.
-
501-750 ม.ม.
-
751-1,000 ม.ม.
-
1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
-
1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
-
2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
-
3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
-
> 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
-
ชื้น
-
กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
-
กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
-
แห้งแล้ง
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเรื่องภูมิอากาศ
Thermal climate class: tropics
ความชัน
-
ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
-
ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
-
ปานกลาง (6-10%)
-
เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
-
เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
-
ชัน (31-60%)
-
ชันมาก (>60%)
ภูมิลักษณ์
-
ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
-
สันเขา
-
ไหล่เขา
-
ไหล่เนินเขา
-
ตีนเนิน
-
หุบเขา
ความสูง
-
0-100 เมตร
-
101-500 เมตร
-
501-1,000 เมตร
-
1,001-1,500 เมตร
-
1,501-2,000 เมตร
-
2,001-2,500 เมตร
-
2,501-3,000 เมตร
-
3,001-4,000 เมตร
-
> 4,000 เมตร
เทคโนโลยีถูกประยุกต์ใช้ใน
-
บริเวณสันเขา (convex situations)
-
บริเวณแอ่งบนที่ราบ (concave situations)
-
ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
ความลึกของดิน
-
ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
-
ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
-
ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
-
ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
-
ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน)
-
หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
-
ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
-
ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
เนื้อดิน (> 20 ซม. ต่ำกว่าพื้นผิว)
-
หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
-
ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
-
ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
สารอินทรียวัตถุในดิน
-
สูง (>3%)
-
ปานกลาง (1-3%)
-
ต่ำ (<1%)
น้ำบาดาล
-
ที่ผิวดิน
-
<5 เมตร
-
5-50 เมตร
-
> 50 เมตร
ระดับน้ำบาดาลที่ผิวดิน
-
เกินพอ
-
ดี
-
ปานกลาง
-
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ยังไม่ได้รับการบำบัด)
-
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
-
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
-
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
-
ใช้ประโยชน์ไม่ได้
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่?
การเกิดน้ำท่วม
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่
ลักษณะเฉพาะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่ประยุกต์ใช้เทคโนโลยี
เป้าหมายทางการตลาด
-
เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
-
mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
-
ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้จากภายนอกฟาร์ม
-
< 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
-
10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
-
> 50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ
-
ยากจนมาก
-
จน
-
พอมีพอกิน
-
รวย
-
รวยมาก
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล
-
งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
-
การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
-
การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน
-
อยู่กับที่
-
กึ่งเร่ร่อน
-
เร่ร่อน
เป็นรายบุคคลหรือกลุ่ม
-
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
-
กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
-
สหกรณ์
-
ลูกจ้าง (บริษัท รัฐบาล)
อายุ
-
เด็ก
-
ผู้เยาว์
-
วัยกลางคน
-
ผู้สูงอายุ
พื้นที่ที่ใช้ต่อครัวเรือน
-
< 0.5 เฮกตาร์
-
0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
-
1-2 เฮกตาร์
-
2-5 เฮกตาร์
-
5-15 เฮกตาร์
-
15-50 เฮกตาร์
-
50-100 เฮกตาร์
-
100-500 เฮกตาร์
-
500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
-
1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
-
>10,000 เฮกตาร์
ขนาด
-
ขนาดเล็ก
-
ขนาดกลาง
-
ขนาดใหญ่
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน
-
รัฐ
-
บริษัท
-
เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
-
กลุ่ม
-
รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
-
รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน
-
เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
-
เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
-
เช่า
-
รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
-
เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
-
เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
-
เช่า
-
รายบุคคล
เข้าถึงการบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
ผลกระทบ
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมและวัฒนธรรม
โอกาสทางวัฒนธรรม (ด้านจิตวิญญาณ ทางศาสนา ด้านสุนทรียภาพ)
สถาบันของชุมชน
Through mutual aid in technology implementation
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่าย
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น
ด้านลบอย่างมาก
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว
ด้านลบอย่างมาก
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษา
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น
ด้านลบอย่างมาก
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว
ด้านลบอย่างมาก
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
การเปลี่ยนแปลงของสภาพภูมิอากาศ
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
อุณหภูมิประจำปี เพิ่มขึ้น
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
การน้อมเอาความรู้และการปรับใช้
เปอร์เซ็นต์ของผู้ใช้ที่ดินในพื้นที่ที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
-
ครั้งเดียวหรือเป็นการทดลอง
-
1-10%
-
11-50%
-
> 50%
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใดๆ?
-
0-10%
-
11-50%
-
51-90%
-
91-100%
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเร็วๆ นี้เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่?
สภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงอันไหน?
-
การเปลี่ยนแปลงแบบค่อยเป็นค่อยไปและสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ
-
การเปลี่ยนแปลงของตลาด
-
การมีแรงงานไว้ให้ใช้ (เนื่องจากการอพยพย้ายถิ่นฐาน)
บทสรุปหรือบทเรียนที่ได้รับ
จุดแข็ง: มุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
จุดแข็ง: ทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรคนอื่นๆ
จุดด้อย/ข้อเสีย/ความเสี่ยง: มุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดินแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร
จุดด้อย/ข้อเสีย/ความเสี่ยง: ทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรคนอื่นๆแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร
-
Growing costs and decreasing availability of timber and poles for establishment of infrastructure
re-introduce traditional techniques of long-term conservation of housing materials.
-
High labour input for implementation
reinforce community structures for mutual help.
-
Area treated by the technology is too small regarding the area in need of treatment (degraded land)
reinforce the solidarity between communities to increase the treated area.
-
Negative effect on the woodland (brousse tigrée): cutting for building materials, clearing for cultivation
identify new ecological materials for house construction; tree plantation.
-
Marginalization of families with low activity potential
reinforce mutual help systems to support poor / small families.
การอ้างอิง
ผู้ตรวจสอบ
-
Alexandra Gavilano
-
David Streiff
-
Deborah Niggli
วันที่จัดทำเอกสาร: 8 พฤศจิกายน 2010
การอัพเดทล่าสุด: 12 มิถุนายน 2019
วิทยากร
-
Soumaila Abdoulaye - ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM
คำอธิบายฉบับเต็มในฐานข้อมูล WOCAT
การจัดทำเอกสารถูกทำโดย
องค์กร
โครงการ
- Book project: SLM in Practice - Guidelines and Best Practices for Sub-Saharan Africa (SLM in Practice)
การอ้งอิงหลัก
-
Caroline Dandois Dutordoir (2006): Impact de pratiques de gestion de la fertilité sur les rendements en mil dans le Fakara (Niger), Université catholique de Louvain, 2006:
-
Bationo, A., Ntare, B. R. 2000 : Rotation and nitrogen fertilizer effects on pearl millet, cowpea and groundnut yield and soil chemical properties in a sandy soil in the semiarid tropics, West Africa. Journal of Agricultural Science, 134, p. 277-284.: Journal of Agricultural Science, 134, p. 277-284.
-
Ministère du développement agricole (2005): recueil des fiches techniques en gestion des ressources naturelles et de productions agro-sylvo-pastorales.:













