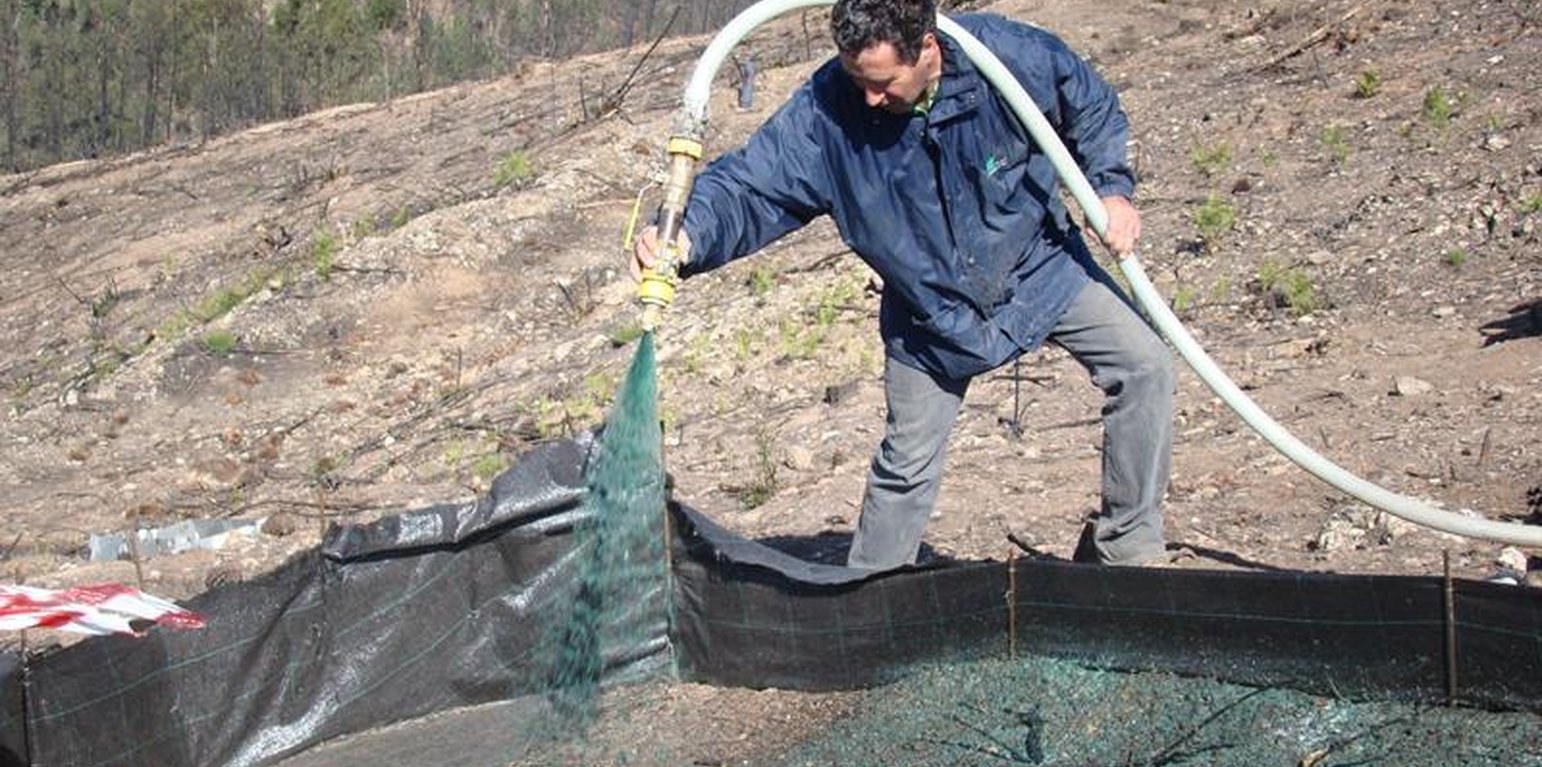




The research team of the University of Aveiro in collaboration with the fire Brigade and a private company applied the hydromulch in a burnt pine area burnt at moderate fire severity. Hydromulch was spreaded manually from a jet hose over a group of erosion plots, and both runoff and erosion were compared to an untreated group of plots.
The hydromulch was applied at a ratio of 3.5 Mg ha-1 providing an initial ground cover of 80%, and was found to reduce post-fire runoff in 70% and soil erosion in 83%.
Purpose of the Technology: Hydromulch has been particularly useful on steep slopes and strongly modified areas such as quarries, construction sites, and cut and fill slopes along roads (Robichaud et al., 2010). The hydromulch is a complex mixture which contain basically water and wood or paper fibers. Additionally it can contain seeds, surfactants, seed-growing biostimulants, nutrients and a green colorant. It is intended that each component affected some of the pieces of the post-fire runoff erosion process.
The high effectiveness in runoff reduction could be related to the effect of the wood fibers, because it increases the surface water storage capacity, but also due to the effect of the surfactants, a wetting agent that reduces SWR and increases soil infiltration. Ideally, post-fire hydromulching must be carried out immediately after the fire, over bare, unprotected and steep burnt areas. It is intended for places in which burnt severity was moderate to high and where there are very important values at risk, such as water reservoirs, populations, industries, human and wild life.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The hydromulch is applied once, immediately after the wildfire, aerially, from a tractor or also manually by using a jet hose operated by a person on foot. It basically consisted of a mixture of water, wood fibers and seeds. The seed composition should include autoctonous plant species, in order to avoid alien species into the burnt area and increase the germination success. Besides the composition, the application technique can influence the hydromulch effectiveness. Rough (2007) and Robichaud et al. (2010) reported that the hydromulch sprayed from vehicles was intercepted by the standing trees, and they recommended special caution when applying the mixture in areas with a high density of dead trees and from long distances. Aerial hydromulch can be a better and less expensive option, but Hubbert et al. (2012) checked that the intended application rates of 50% and 100% hydromulch cover resulted in only 20–26% and 56%.
Natural / human environment: The natural forest in central Portugal has been substituted by pine and eucalypt trees that are typically planted as monocultures for wood and paper pulp production. The landscape reflects a long history of intense land management, with a mosaic of (semi-) natural and man-made agricultural and afforested lands. In recent years, however, wildfires have increased dramatically in frequency and extent, and have been associated to soil fertility losses, and consequently to socio-economic losses.
สถานที่: Gois-Colmeal, Portugal, โปรตุเกส
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี:
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ (approx. < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์))
In a permanently protected area?:
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: 10-50 ปี
ประเภทของการแนะนำ




| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (euros) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (euros) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 128.2 | 128.2 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 128.2 | 128.2 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | |||||
| Hydromulch | ha | 1.0 | 3205.0 | 3205.0 | 100.0 |
| Others | ha | 1.0 | 128.2 | 128.2 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 3'589.6 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 4'602.05 | ||||
Livelihoods and human well-being (eg education, health) are not changed by the use of Hydromulching.
If hydromulching is with seeds, it can introduce invasive species