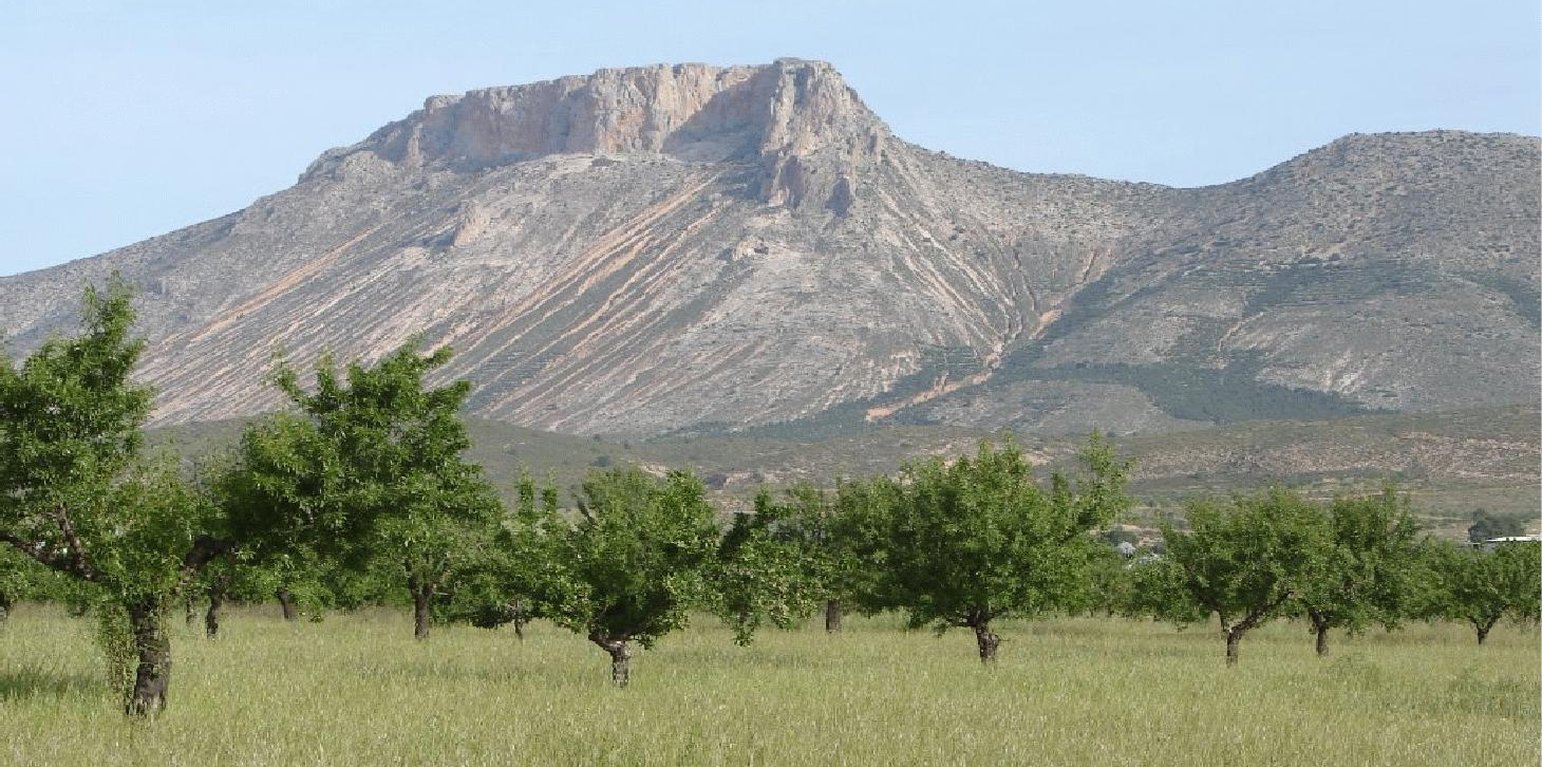




Ecological agriculture is a strictly controlled production system that does not use synthetic chemical products like fertilizers, insecticides or pesticides. Also genetically modified organisms and materials are not used. Green manure or low quantities of organic fertilizers, preferably from dung (sheep, goat, cow, chicken), are used to increase and maintain soil fertility. Green manure is provided by seeding a mixture of leguminous nitrogen-fixing species and cereals in autumn (October) and incorporating this into the soil with tillage in springtime (May). To optimize the fertilizer effect, there is still scientific discussion on the need for mowing the green manure and letting it dry for several days before it is ploughed into the soil. For this system, no ploughing is performed in winter, which reduces fuel use and emission of greenhouse gases. In addition to its fertilising effect, green manure provides a continuous surface cover during winter time protecting the soil from erosion. The products grown under this ecological system command a higher market price than those grown under conventional production schemes.
Purpose of the Technology: The aim of ecological agriculture is to protect biodiversity and the environment and maintain or improve soil fertility and reduce soil, water, and air pollution. Under ecological agriculture and by using green manure, soil cover, soil organic matter, and soil biological activity will increase, which positively affects soil structure, soil fertility and soil water infiltration capacity. This reduces the sensitivity of the soil to surface crusting and it reduces surface runoff and soil erosion by up to 60%. Workload and energy use are up to 50% lower than under conventional agriculture, and benefits may increase around 40% due to higher yields. Moreover, a higher market price of ecologically produced almonds and olives will lead to increased farm income. This better economic return discourages land abandonment of marginal lands with low productivities under conventional farming. Ecological almonds and olives production does not require special establishment activities or investments in specialized equipment.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Infestations by, for example, insects and caterpillars are treated twice yearly by degradable products based on copper salts (Oxicloruro, max 3‰ solution) and mineral oils in winter, or the spores and proteins produced by the bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis or based on natural pyrethrins (from the Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium; max 1.5 l/ha) in springtime. In ecological agriculture, farmers are obliged to take advice and instructions regarding plague control and fertilizer use from technicians specialized in ecological agriculture.
Natural / human environment: Soils mostly have a shallow to medium depth (between 20-60 cm), and slopes are gentle to moderate (between 5 and 15%). The climate is semi-arid with a mean annual rainfall around 300 mm. Droughts, in summer, commonly last for more than 4-5 months. Annual potential evapotranspiration rates larger than 1000 mm are common. The production system is highly mechanised and market-oriented but depends strongly on agricultural subsidies. All cropland is privately owned.
สถานที่: Guadalentin catchment, Murcia, สเปน
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี:
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ (approx. 10-100 ตร.กม.)
In a permanently protected area?:
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
ประเภทของการแนะนำ









| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (EURO) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (EURO) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 37.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 72.0 | 72.0 | 37.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | |||||
| Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 96.0 | 96.0 | 37.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | |||||
| Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 79.0 | 79.0 | 37.0 |
| Biocides | ha | 1.0 | 159.0 | 159.0 | 37.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 431.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 684.13 | ||||
Less fuel use for ploughing but plague control and cow dung can be costly during first years, but after 2-3 years costs are generally lower than under conventional farming because less pesticides are needed. Also use of organic fertilizer is expensive and requires subsidies
Depends on crop yield and market price.
Often farmers feel proud and satisfied of producing in a manner respectfull with the environment.
There is an added value of ecological agriculture for rural tourism activities
Farm income of most ecological farmers has increased due to higher market price, higher yield and subsidies
Only with green manure
Less tractor use
Due to more biological activity
The production process of conventional synthetic fertilizerss and pesticides is an important source of greenhouse gasses. There is also less tractor use.
Under ecological agriculture more carbon is sequestred in the soil than under conventional farming
Green manure potentially leads to competition for water. Therefore it is crucial to plough before competition become simportant in springtime.