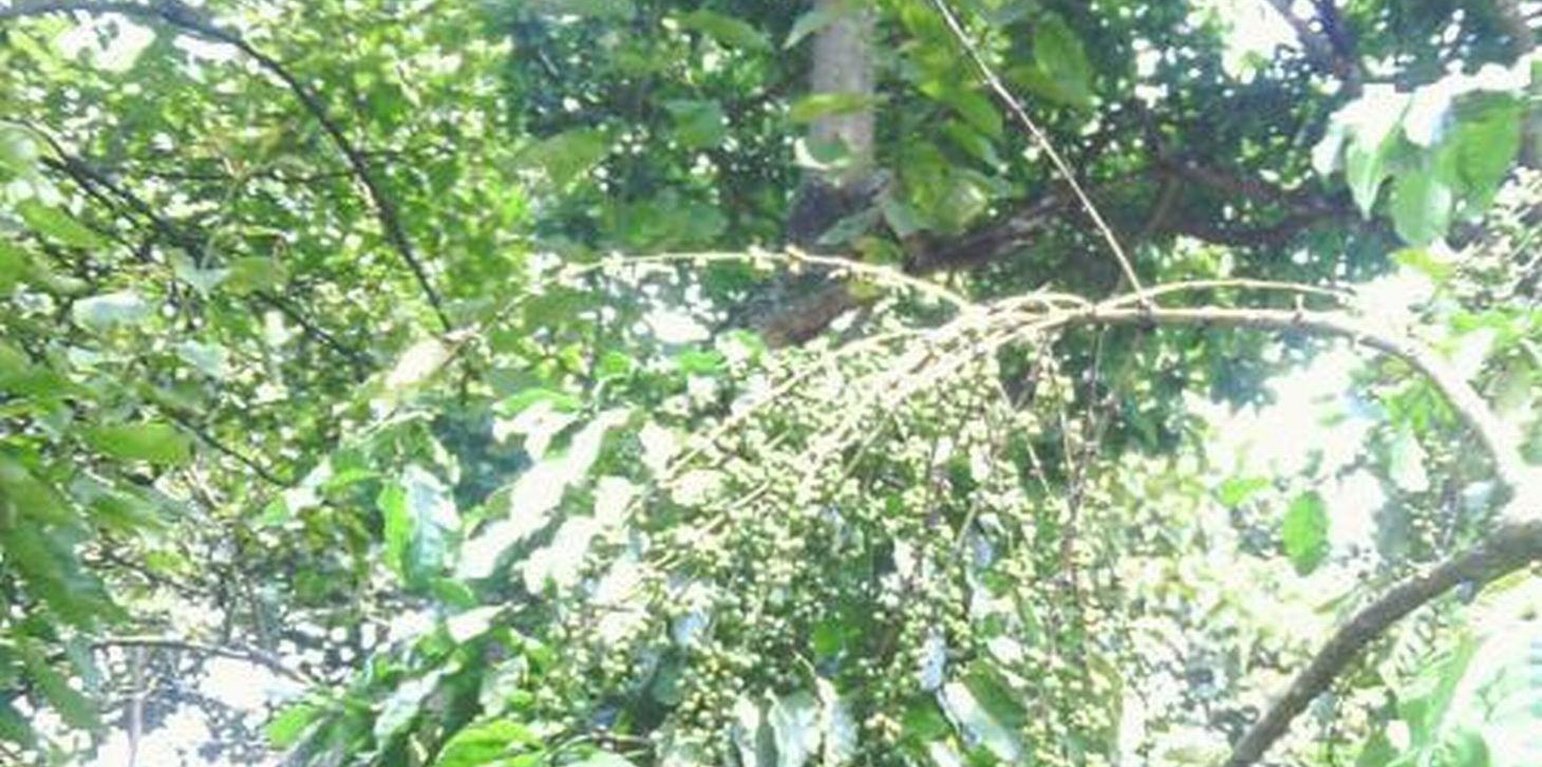




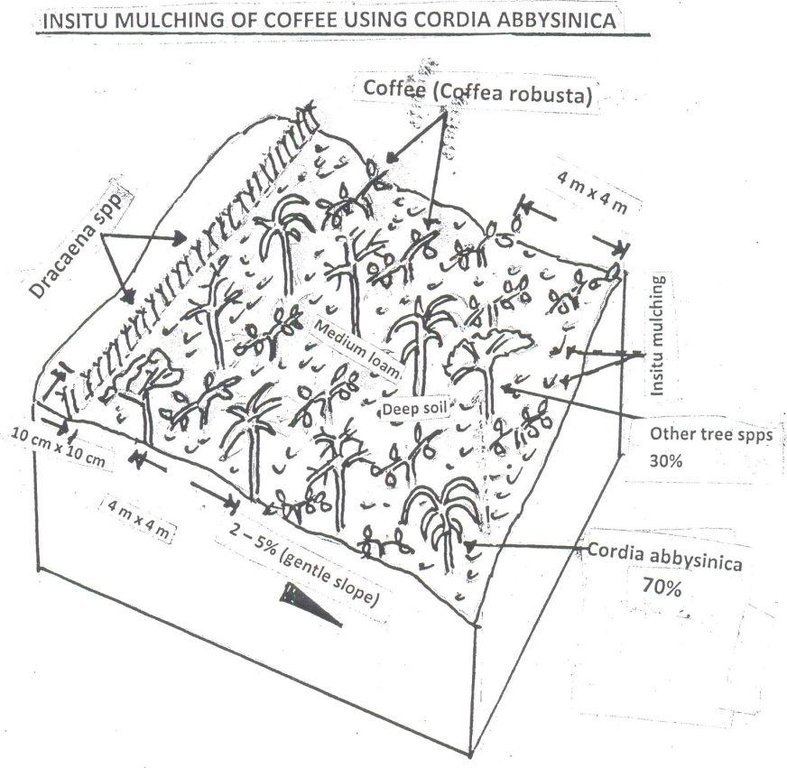
Establishment of Robusta coffee farms by an individual,on a cropland by mixing indigenous tree spp which provide a shade and dropping leaves save as natural mulch.The technology has been developed through land user initiatives over 40 years ago. Establishment activities include land clearing and preparation,preparation of holes,seed collection and planting which involve family labor Seeds are collected from neighboring village from mature trees. Holes are prepared randomly about 4 meters apart. No inputs are applied at the establishment stage only hand tools are used (hand hoe, matchet)
Shade trees are planted after establishment of coffee which are randomly planted, tree spp dominating is Cordia abbysinica which has broader leaves and easy to decompose.Other tree spp included are Erythrina,Meosopsis eminii,Ficus thornngii,Makhamia lutea and Tephrosia vogelii.
Maintenance include weeding which is done by pulling weeds by hand or using hand hoe at early stage after establishment because few leaves have dropped. The farm is mainly meant for coffee production however,few crops which are cassava bananas, fruit trees Jack fruit, Mangoes, Citrus spp which are planted in the peripherals,and Dracaena sppplanted to demarcate the farm along road side.
Pruning of tree branches is done before the shade is heavy as to allow ventilation.Coffee pruning is done to an individual tree depending on number of branches it has at time of harvesting, normally 4 branches are left. Bending of coffee branches is practiced to avoid branch breaking during harvesting.
Settlement is within the farm with few livestock which are sheep, cattle and chicken.
Purpose of the Technology: To increase coffee production by mixing coffee with indigenous tree spp which drop / shed its leaves.Selected trees are those broad leaved which its leaves decompose easily hence improve soil fertility and due to high accumulation of dropped leaves there is an increase in soil moisture content.
Trees act as wind break hence no flower drop.Dracaena spp are planted very close along the road side to demarcate his plot from neighbors and public infrastructure and this helps to reduce land conflicts among neighbors and community as well.
Hand weeding is done as the technology suppress weeds to the big shade.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: A farmer bought a piece of land from the village government.Establishment activities include land clearance by removal of shrubs using a matchet.This is followed by land preparations and planting holes which are 30cm depth and 30cm width. These activities are done from May to July by family labor.Planting is normally done between September and October by collecting seedlings from mature trees in neighbors fields.Planting of indigenous tree spp is done randomly after coffee planting to allow ventilation 80 different spps are planted in 1.5 acres. Seeds and seedlings are obtained from neighbors farms.Maintenance includes weeding which is done using family labor who use hand hoe. This is done twice a year in May and December to January. Pruning and bending of coffee tree branches is done once per year after harvesting of coffee as well as trees in June and July using a matchet. Each coffee tree is treated individually only 4 branches are allowed per tree. Bending is done to avoid breaking of branches during coffee harvesting.
Gap filling is done few months after transplanting between February and March at the beginning of long rains. and this was followed pruning and bending of coffee branches.
Demarcation of coffee farm using Dracaena (shrub) done on one side of his farm along the road.
Natural / human environment: Land use type: Establishment of coffee has been done on crop land.
Agronomic: Natural mulch from leaves falling on ground.
Vegetative: Demarcation of boundary using Dracaena spp.
Climatic zone: Sub humid more than 269 growing days.
slope: 2-5% gentle slope
Soil type: Clay loam
Soil depth: Deep
Tools and inputs: Hand hoes,bush knife,axe, seeds and cuttings.
Land ownership: Individually owned.
สถานที่: Ngara District, Tanzania, แทนซาเนีย
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี:
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ (approx. < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์))
In a permanently protected area?:
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: 10-50 ปี
ประเภทของการแนะนำ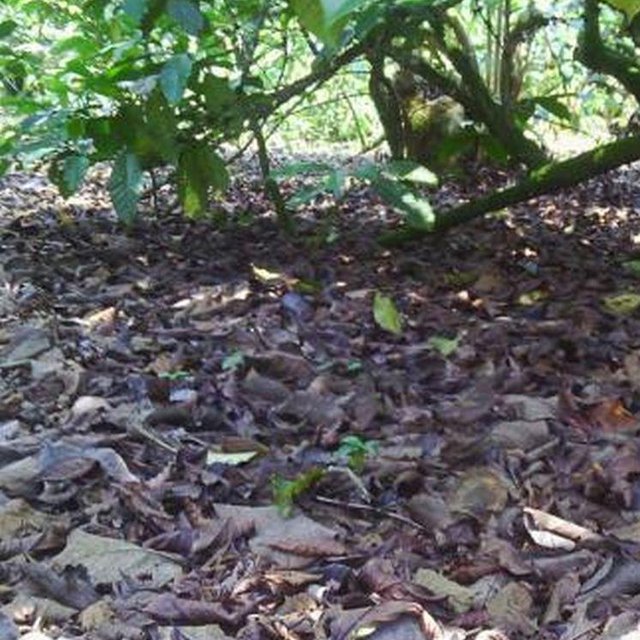








| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (Tanzanian shillings) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (Tanzanian shillings) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| labour | 1.0 | 2510.4 | 2510.4 | 100.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| tools | 1.0 | 21.88 | 21.88 | 100.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | |||||
| seeds | 1.0 | 31.25 | 31.25 | 100.0 | |
| seedlings | 1.0 | 61.73 | 61.73 | 100.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 2'625.26 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 1.64 | ||||
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (Tanzanian shillings) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (Tanzanian shillings) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| labour | 1.0 | 63.63 | 63.63 | 100.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | |||||
| seedlings | 1.0 | 33.05 | 33.05 | 100.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 96.68 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 0.06 | ||||
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 16bags/ha
หลังจาก SLM: 58 bags/ha
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 3cub.m/ha
หลังจาก SLM: 12cub.m/ha
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 62 kg/ha
หลังจาก SLM: 0 kgs/ha
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 15 md/ha
หลังจาก SLM: 2 md/ha
จำนวนก่อน SLM: low
หลังจาก SLM: improved
จำนวนก่อน SLM: little
หลังจาก SLM: inreased
จำนวนก่อน SLM: none
หลังจาก SLM: available
จำนวนก่อน SLM: none
หลังจาก SLM: available
จำนวนก่อน SLM: low
หลังจาก SLM: high
จำนวนก่อน SLM: low
หลังจาก SLM: high
จำนวนก่อน SLM: low
หลังจาก SLM: high
จำนวนก่อน SLM: low
หลังจาก SLM: high
จำนวนก่อน SLM: low
หลังจาก SLM: medium
จำนวนก่อน SLM: low
หลังจาก SLM: medium