



Precision Conservation Agriculture (PCA) is a combined technology that encompasses four basic principles: 1) minimum tillage – e.g. using planting basins which enhance the capture of water from the first rains and allow efficient application of limited nutrient resources with limited labor input; 2) the precision application of small doses of nitrogen-based fertilizer to achieve higher nutrient efficiency (from organic and/or inorganic sources); 3) combining improved fertility with improved seed for higher productivity; and 4) use of available residues to create a mulch cover that reduces evaporation losses and weed growth. Crop mixes are adapted to the local conditions and household resource constraints. Cereal/legume rotations are desirable. PCA spreads labor for land preparation over the dry seasons and encourages more timely planting, resulting in a reduction of peak labor loads at planting, higher productivity and incomes. Over four years these simple technologies have consistently increased average yields by 50 to 200% in more than 50,000 farm households. These strategies are promoted by ICRISAT, FAO and NGOs in Southern Africa focusing on low potential zones where most of the most resource-poor and vulnerable farm households exist.
Components of CF Planting Basins Package promoted in Zimbabwe:
1. Winter weeding: The first step in preparing a field using CF methods is to remove all weeds. This should be done soon after harvesting in May/June. Weeding is done using implements such as hand hoes and machetes that disturb the soil as little as possible. The importance of weeding before land preparation is to ensure that the plot is weed-free at basin preparation and also to prevent the dispersal of weed seeds.
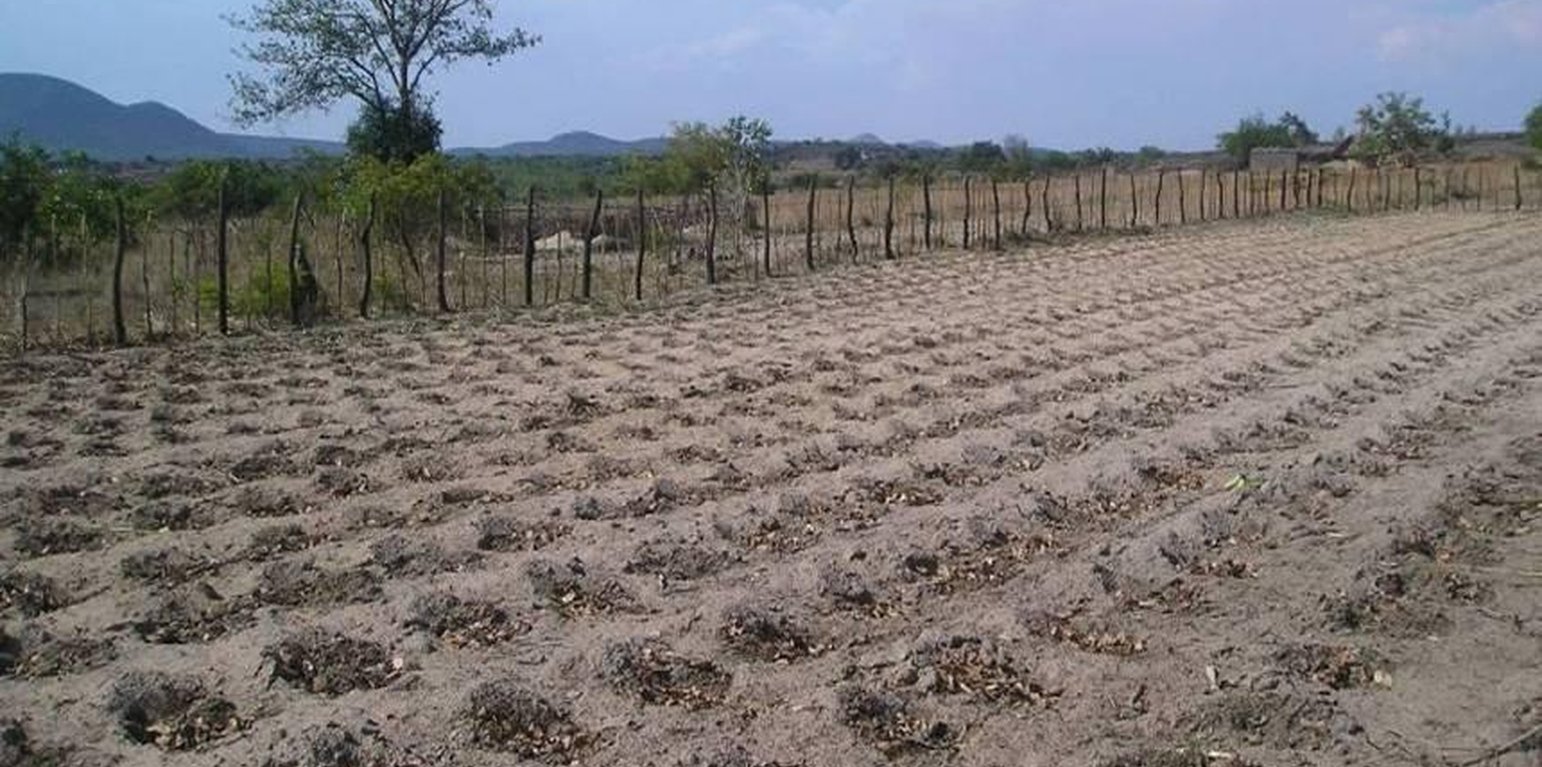
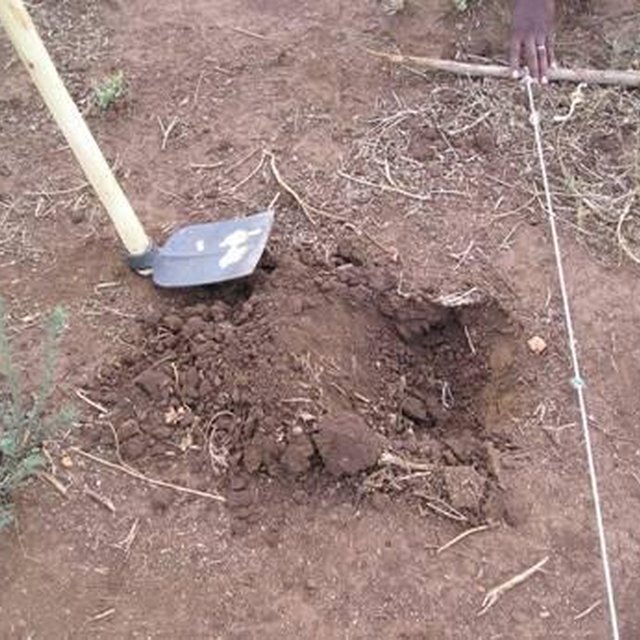
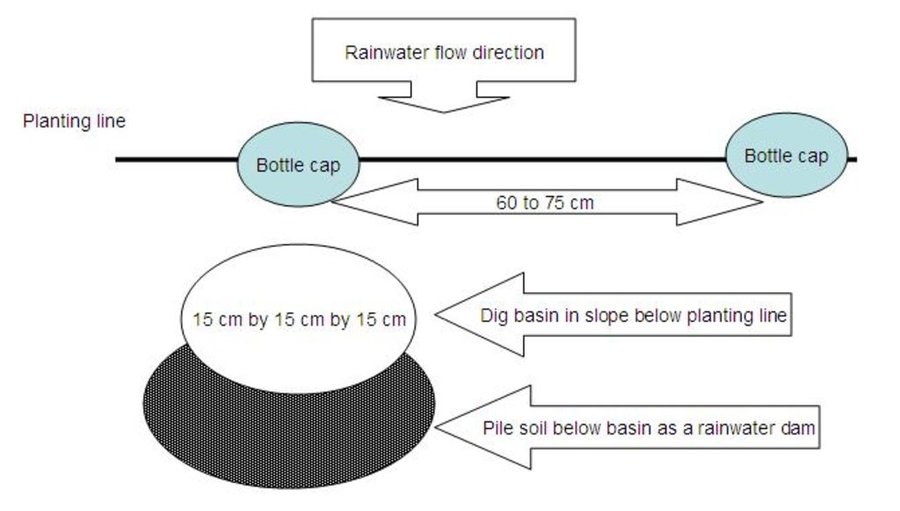
2. Digging planting basins: Planting basins are holes dug in a weed-free field into which a crop is planted. The basins are prepared in the dry season from July to October. The recommended dimensions of the basin are 15×15×15 cm, spaced at either 75×60 cm for rainfalls of 650 to 900 mm and either 75x75 cm or 90×60 cm for Natural rainfalls of 400 to 650 mm. The basins enable the farmer to plant the crop after the first effective rains when the basins have captured rainwater and drained naturally. Seeds are placed in each basin at the appropriate seeding rate and covered with clod-free soil. The advantage of using basins is that they enhance the capture of water from the first rains of the wet season and enable precision application of both organic and inorganic fertilizer as it is applied directly into the pit and not broadcast.
3. Application of crop residues: Crop residues are applied on the soil surface in the dry season, soon after harvesting if available. Ideally the residues should provide at least 30% soil cover. The mulch buffers the soil against extreme temperatures (thereby reducing soil evaporation), cushions the soil against traffic, and suppresses weeds through shading and improves soil fertility.
4. Application of manure: Fertility amendments are applied soon after land preparation in the dry season. In CF, the application of both organic and inorganic fertilizers is recommended as they complement each other. Organic fertilizers such as manure and/or composts are applied at a rate of at least a handful per planting basin. More can be used in wetter areas.
5. Application of basal fertilizer: Inorganic basal fertilizer is also applied soon after land preparation before the onset of the rains. One level beer bottle cap is applied per planting basin and covered lightly with clod-free soil. This is equivalent to 80 kg of compound fertilizer per hectare. Application rates can be increased in wetter areas and may depend on crop types.
6. Application of topdressing: Nitrogen fertilizer is applied to cereal crops at the 5 to 6 leaf stage soon after the first weeding at a rate of one level beer bottle cap per basin. This is equivalent to 80 kg of ammonium nitrate fertilizer per hectare. Application is done on moist soils. Precision application ensures that the nutrients are available where they are needed. Application rates can be increased in wetter areas and may depend on crop types.
7. Timely weeding: In conventional tillage systems, farmers plough/cultivate repeatedly in order to suppress weeds. With reduced tillage, weeds can be a problem requiring more effort initially. One strategy is to weed in a timely manner (ie, when the weeds are still small) preventing the weeds from setting seed. Timely weeding in combination with mulch should eventually lead to effective weed control.
8. Crop rotation: Rotating crops is one of the key principles of CF. Cereal/legume rotations are desirable because the cereal benefits from nitrogen produced by the Rhizobium associated with the legume, and the legume benefits from the residues produced by the cereal. The advantages of crop rotation include improvement of soil fertility, controlling weeds, pests and diseases, and producing different types of outputs, which reduce the risk of total crop failure in cases of drought and disease outbreaks.
สถานที่: Bulawayo, ซิมบับเว
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี:
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี:
In a permanently protected area?:
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
ประเภทของการแนะนำ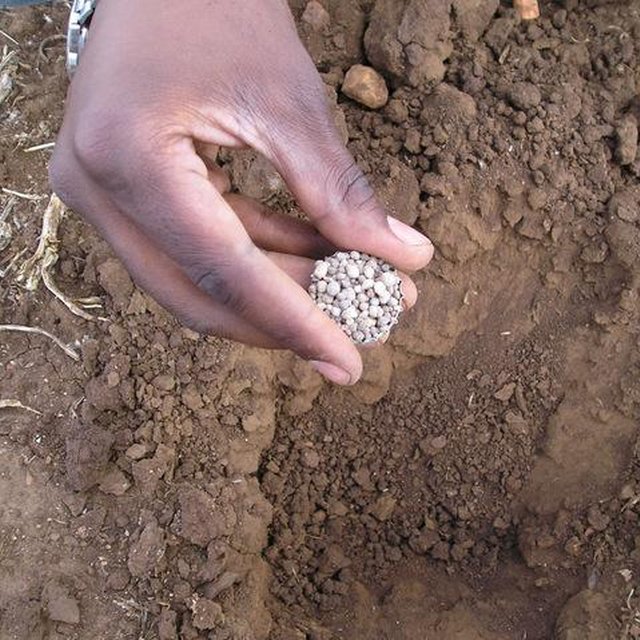









| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (n.a.) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (n.a.) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| labour | ha | 1.0 | 108.0 | 108.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| hand hoes | ha | 1.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | |||||
| fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 69.0 | 69.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 184.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 184.0 | ||||
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 400 kg/ha
หลังจาก SLM: 1520 kg/ha
increase varies between 50-200%, depending on rainfall regime, soil types and fertility, and market access
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 600 kg/ha
หลังจาก SLM: 2200 kg/ha
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 1.8 ha
หลังจาก SLM: 0.6 ha
Household meets food needs from less land
Community work groups using establishment
Dependent on number adopting in community/catchment