



Brittany is an area in the north-west of France. Brittany’s agriculture includes well-known products such as: fish, beef, pork, poultry, vegetables and milk. The technology is applied at Danilo Noël farm, located in the commune of Mauron in Morbihan. The region has an average annual rainfall of 650-700 mm and annual temperature of around 11°C. The climate of Mauron is warm and temperate, with the farm located in the basin known as Ploërmel. ‘Bocages’ in France refer to small forests and decorative elements such as hedgerows or ornamental garden structures that border agricultural fields .
The fields of the Danilo Noël farm are grouped together in a rotational system of fodder crop and short-term pastoral leys, divided into fenced paddocks. They are located between two ‘talwegs’, with slopes of 5 or 6 %. An analysis carried out in 2000 by the water management organization ‘Grand Bassin de l'Oust’, shows that 85% of the plots are at high and medium risk of plant protection product runoff due to the slope and water run-off.
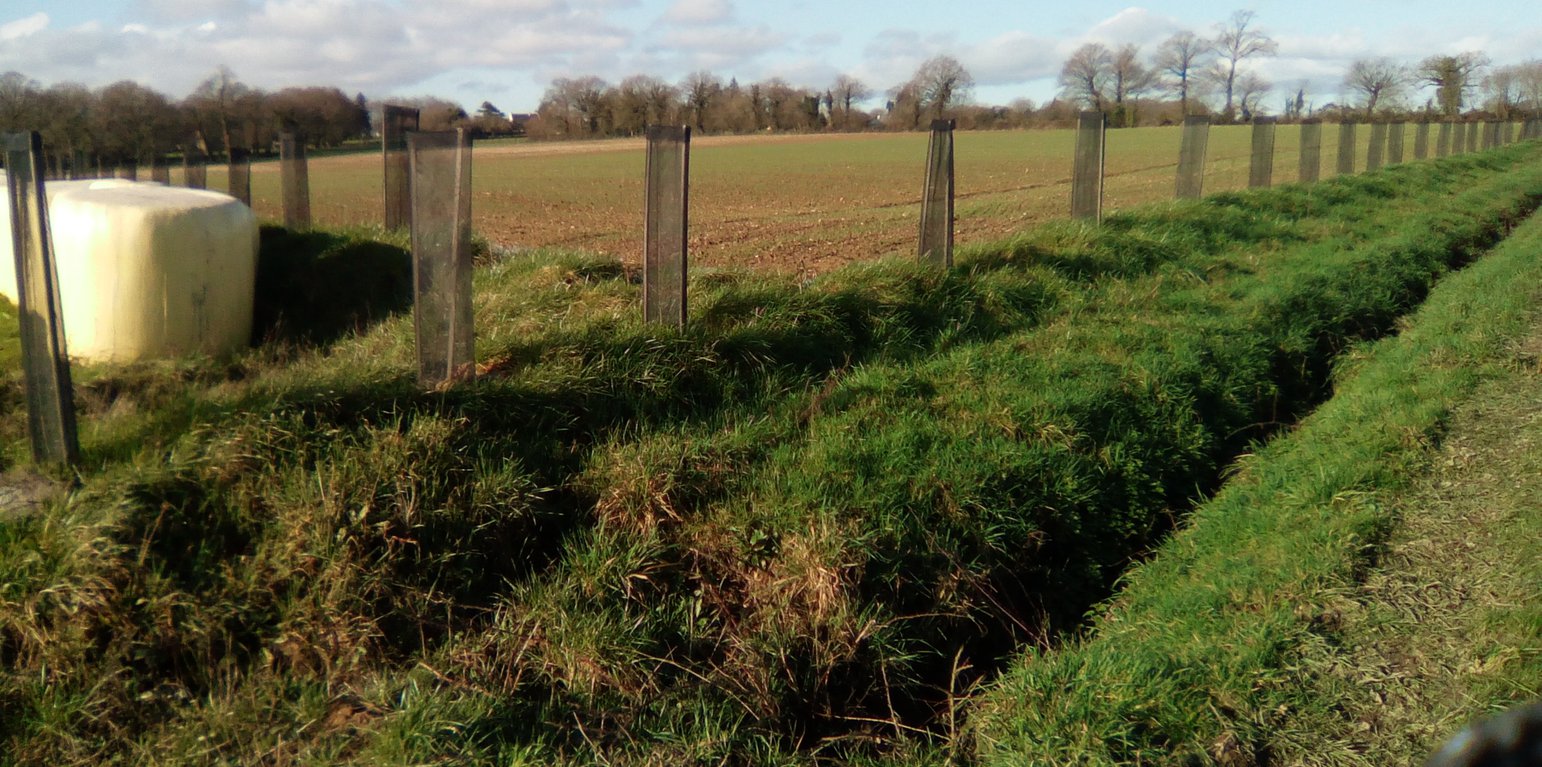
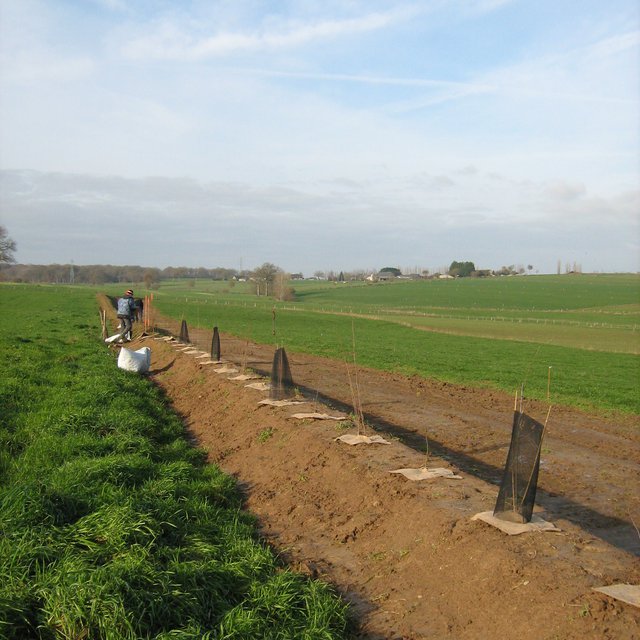
Following this evaluation of the farm, the ‘Bocage’ (small hedged pasturelands) was developed starting during the winter of 2003/2004, with the planting of 800 meters of woody features (hedges and trees) along the slopes of the talweg. Other slope plantings were carried out on the edge of the paddock in 2014/2015 (1500 meters) and 2018/2019 (1650 meters).
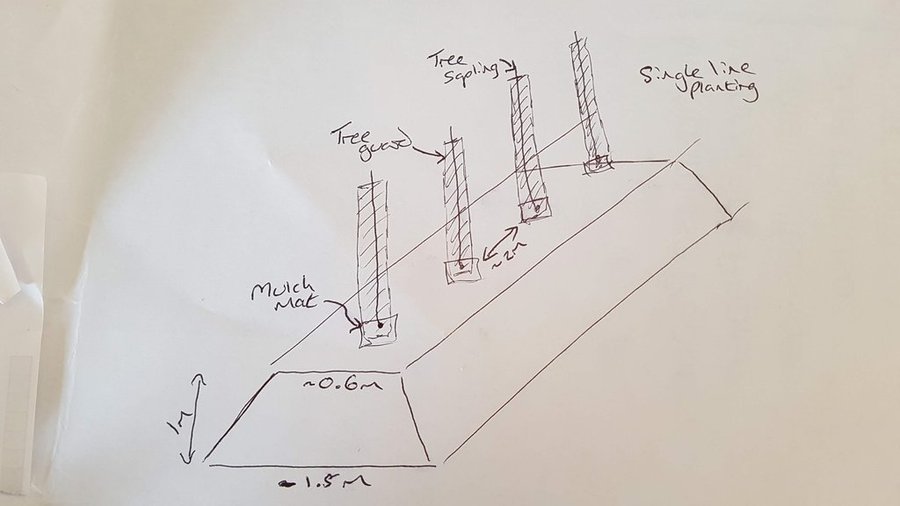
Earth bunds were established along the contour, either with a shovel (in 2003 and 2014) or with a forest plough (in November 2018), with hedge and tree whips (1-2 year old growth) planted 1 meter apart in single rows diectly into the shovel or plough furrow and a small amount of fertiliser and wire tree guards added. There was no irregation installed.
The technology was applied in three differnt phases combining to form one overall long-term plan. The tree species chosen for the hedgerow are local species (oak, beech, cherry, birch, myrobolan plum, chestnut, hazelnut, etc.). For the last two phases of the programs (2014 & 2018), emphasis was placed on the presence of melliferous species (for honey production) and the spread of flowering species (fruit trees, burdock, blood dogwood, medlar, etc.).
Buffering of fields with hedgerows aims to protect surface water quality and prevent land degradation by slowing surface water runoff and hence reducing soil erosion, nutrient and plant-protection product (pesticide) export and improving water infiltration into the soil and groundwater recharge. The reduction of soil erosion in turn improves productivity with a better surface cover and nutrient retention for improved plant establishment and growth. Additionally, maintenance and/or improvement of biodiverstiy can be attained as well as providing shelter for animals supports their well-being.
Major activities of the technology include: Tipping of trees (old and new) in spring/summer, soil preparation at the site of the future hedge in autumn and creation of the embankment (earth bund along the contour), tree planting over winter and laying of mulch and installation of game guards.
Benefits of the hedgerows/ shelter belts are reorganization and improvement of the field to reduce flooding, protect water quality , improve welfare of the livestock, Increase biodiversity of wildlife, including insects, birds and game. Additional honey bee forage supported the installation of an apiary (18 colonies) by a professional beekeeper in May 2019.
The only weakness of the technology in the eyes of the land owner was the extra cost/workload associated with the maintenance of the hedgerows.
The compilation of this SLM is a part of the European Interreg project FABulous Farmers which aims to reduce the reliance on external inputs by encouraging the use of methods and interventions that increase the farm’s Functional AgroBiodiversity (FAB). Visit www.fabulousfarmers.eu and www.nweurope.eu/Fabulous-Farmers for more information.
สถานที่: Brittany, ฝรั่งเศส
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี: พื้นที่เดี่ยว
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ (approx. 0.1-1 ตร.กม.)
In a permanently protected area?: ไม่ใช่
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: 2003
ประเภทของการแนะนำ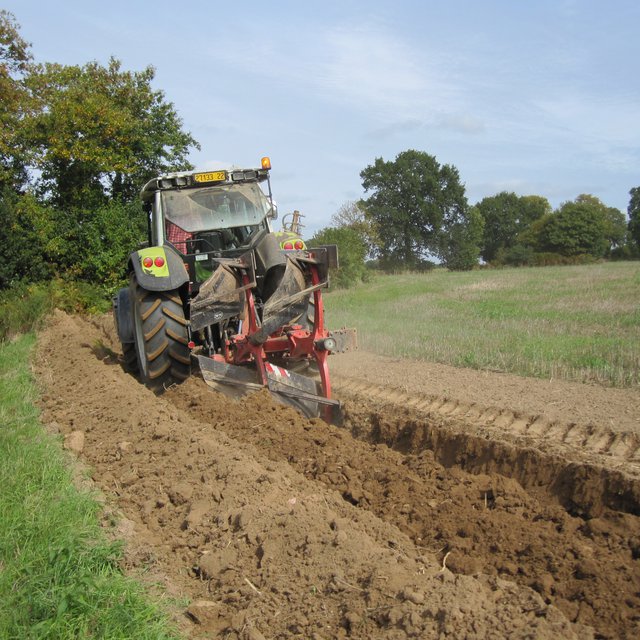



| Species | Count |
| cattle - dairy | 62 |





| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (€) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (€) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Tip saplings | metre | 1650.0 | 0.35 | 577.5 | |
| Soil preparation | metre | 1650.0 | 0.8 | 1320.0 | |
| Creation of the embankment & grass strips | metre | 1650.0 | 1.8 | 2970.0 | |
| Tree planting, mulching & protection | metre | 1650.0 | 2.0 | 3300.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Excavator / Forest plough | metre | 1650.0 | 0.5 | 825.0 | |
| Biodegradable mulch | metre | 1650.0 | 0.3 | 495.0 | |
| Tree guards | metre | 1650.0 | 0.7 | 1155.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 10'642.5 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 11'825.0 | ||||
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (€) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (€) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Hedge pruning and training | meter | 1650.0 | 0.25 | 412.5 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Mechanical intervention: annual clearing | meter | 1650.0 | 0.35 | 577.5 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | |||||
| Thermal brushcutter for landscaping and forestry work (investment to be amortized) | meter | 1650.0 | 0.6 | 990.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | |||||
| Maintenance of the embankment | meter | 1650.0 | 0.15 | 247.5 | 100.0 |
| od storage, chipping, transport of chips | meter | 1650.0 | 0.25 | 412.5 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 2'640.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 2'933.33 | ||||
diversification of production
remained same
Shelter belts protection of crops
remained same
Well-being improves production
New output product on land
Wood produced
Increased labour but more sustainable water and land management
New machinery and labour costs associated with diversified management
Increased output production
Addition of woody crop output
Increased workload with hedgerow management
quality of life
Improved water quality in streams due to reduced surface run-off with hedgerow buffer strips
Decreased run-off with hedgerow buffering
Rooting system reducing flooding
Reduced soil erosion from buffered strips
Hedgerow inceasing below ground C
longer cover of vegetation with hedgerows
hedgerows increase above ground C
Woody crops added
Biodiversity increases with hedgerow habitat creation
Bees, insects and birds as predators of pests
Habitat creation in hedgerows
cultivation aids
Buffer strips & rooting systems improving infiltration
Buffer strips limit water loss in drought
buffer strips provide crop and animal shelter
regulation of belt slope eriosion
Reduced soil, nutrient and plant protection run-off polluting watercourses
hedges slow flow as a buffer
shelter and sedimant capture
Intake from hedges