



The state of Madhya Pradesh (India) has an average annual rainfall of around 1170 mm. However, data shows a declining trend. It is characterized by a monsoon period from July to September. Winter is from December to January and the summer is from February to March. The rainfall is irregular, resulting in crop failures, land degradation, nutrient leaching and shortened growing seasons. This constrains the agricultural sector, upon which 74% of the population is either directly or indirectly dependent. 38% of the agricultural area is intensively/conventionally irrigated. The majority of the water is obtained from groundwater which has led to over-exploitation.
To sustainably improve the agricultural sector, the International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) introduced Supplemental Irrigation (SI). This is a practice in which essentially rainfed crops are cultivated rather than more water demanding crops. SI ensures a sufficient amount of water as rainfall satisfies the majority of the crop water demand. Water availability is not sought in (fossil) groundwater extraction, thus avoiding over-exploitation, but rather through rainwater harvesting (RWH), using the rainfall optimally. In addition, SI prolongs the growing season and enables more diverse farming systems by crop rotation and inter-cropping.
In 2018, a reservoir was constructed, with a 900,000 litres capacity. Every rainy season groundwater rises to the surface, indicating that the soil is fully saturated. The reservoir is filled by pumping the surface water from shallow wells. This is considered sustainable RWH as it assumed the pumped water is solely rainwater. An additional benefit of this approach is that no large catchment area is required. The building of the reservoir consists of 1) excavating the soil; 2) stone pitching the excavation; 3) installing polysheet to avoid water losses through infiltration. The water from the reservoir is distributed over the field by a portable (wheeled) sprinkler irrigation system. Hence, pumping from the reservoir is required.
The water from the reservoir allows for crop rotation with a winter crop, namely chickpeas. This crop grows from November till March, outside of the rainy season. Without SI, chickpea yield is poor as farmers must wait until sufficient rain has fallen before sowing, limiting the growing period. SI can provide the necessary water for the chickpeas to germinate well, ensuring a sufficient growing period. The chickpeas are manually harvested in March. Besides increased income for the farmer, chickpeas also provide valuable soil improvement as the plant fixes atmospheric nitrogen in the soil.
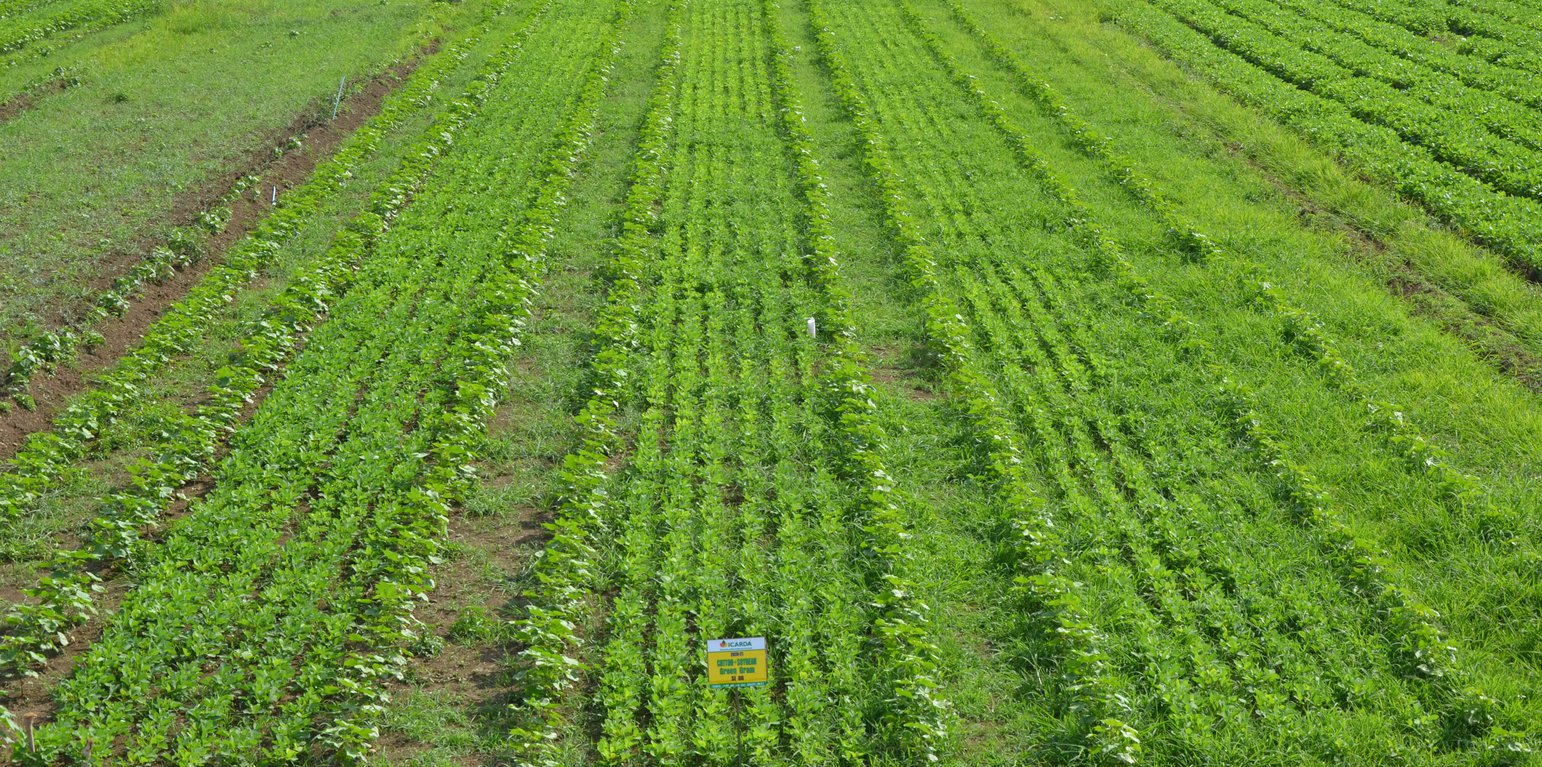
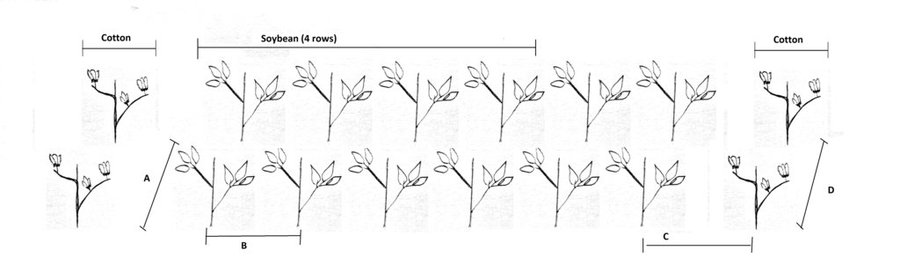
In additional to crop rotation, SI and water harvesting allows for a more intensive cropping system in which cotton and soybean are intercropped. These crops are planted in June-July. The intercrop ratio is two rows of cotton and six rows of soybean. Soybean and cotton are respectively threshed and harvested in October. Consequently, the plants are grown mainly in the rainy season. Fertilizer (80 kg nitrogen, 100 kg phosphorus and 60 kg potassium per hectare) is applied directly after sowing, hence June-July. In the same period the field is manually weeded. Micro-Nutrients (a mixture of B, Zn, Mn) are applied if needed. On average, this corresponds to one kilogram per hectare. Mechanical pesticide application is done from July to August by a sprayer, consisting of herbicides, fungicides and insecticides.
The frequency and amount of irrigated water through SI is unpredictable as it compensates rainfall irregularity. Nevertheless, it is advised to irrigate less than the infiltration rate of the soil, to avoid deep percolation of water and nutrient leaching. That is, it is better to irrigate small doses multiple times. For this reason, sandy soils are unsuitable as they have relatively high infiltration rates and low water holding capacity. On average, one hectare of this particular production system is irrigated through sprinklers thrice by 250 cubic meters of harvested water.
A great advantage of SI is that it leads to a year-round income through a diversified production system with an additional winter crop. Farmers also value SI ensuring stable yields, thus making them less vulnerable to rainfall irregularities. Also, the diversified system protects the crops better against epidemics. And as there are legumes included in the system, the soil quality is improved, lowering the required amount of nitrogen fertilizer.
Nevertheless, SI has some weaknesses. For example, the implementation of SI is difficult for smallholder farmers as they lack the area for a reservoir. In addition, the initial costs are high, so adoption may be restrained by the lack of available funds, especially for smallholder farmer. This specific SI, by water harvesting (extracting shallow groundwater) is not suitable in areas of poor groundwater recharge. But the concept of SI can be applied. To conclude, where it is technically and financially feasible, SI allows for more intensive, diversified and stable production system under climate change induced risks, hence supplemental irrigation is an important technique to improve the livelihoods of farmers exposed to climate change.
สถานที่: Madhya Pradesh, Central India, อินเดีย
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี: พื้นที่เดี่ยว
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ (approx. < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์))
In a permanently protected area?: ไม่ใช่
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: 2018
ประเภทของการแนะนำ












| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (INR) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (INR) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Pond Excavation | m2 | 53.0 | 4000.0 | 212000.0 | 100.0 |
| Sprinker Operation | Person Hour | 1.0 | 37.5 | 37.5 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Zero Tillage Seed Drill | Machine | 1.0 | 55000.0 | 55000.0 | 100.0 |
| Sprinkler System (portable) | System | 1.0 | 28300.0 | 28300.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | |||||
| Micron-Geo-Membrane | m2 | 2857.0 | 105.0 | 299985.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | |||||
| Tax (18%) | Total | 1.0 | 38160.0 | 38160.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 633'482.5 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 8'616.46 | ||||
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (INR) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (INR) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Total Labour (inc sowing, fertilizer, irrigation, threshing, etc) | Peron-Hours | 640.0 | 37.5 | 24000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Sowing (Zero-Tillage Seeder) | Machine-Hours | 57.0 | 500.0 | 28500.0 | 100.0 |
| Threshing Soybean (Thresher) | Machine-Hours | 51.0 | 300.0 | 15300.0 | 100.0 |
| Sprayer (weeding) | Machine-Hours | 51.0 | 300.0 | 15300.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | |||||
| Chickpeas Seeds | Kilogram | 448.0 | 450.0 | 201600.0 | 100.0 |
| Cotton Seeds | Kilogram | 10.0 | 1400.0 | 14000.0 | 100.0 |
| Soybean Seeds | Kilogram | 256.0 | 150.0 | 38400.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | |||||
| Micro-Nutrients (mixture of B, Zn, Mn) | Kilogram | 6.4 | 900.0 | 5760.0 | 100.0 |
| Nitrogen (Urea) | Kilogram | 510.0 | 6.0 | 3060.0 | 100.0 |
| Phosphorus (DAP) | Kilogram | 640.0 | 25.4 | 16256.0 | 100.0 |
| Potassium (MOP) | Kilogram | 380.0 | 36.0 | 13680.0 | 100.0 |
| Herbicide | Liter | 6.4 | 470.0 | 3008.0 | 100.0 |
| Fungicide | Liter | 3.2 | 570.0 | 1824.0 | 100.0 |
| Insecticide | Liter | 3.2 | 580.0 | 1856.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | |||||
| Cost Irrigation | Total | 6.4 | 250.0 | 1600.0 | 100.0 |
| Irrigation Events | Event | 19.0 | 100.0 | ||
| Water (depth) per irrigation event | mm | 300.0 | 100.0 | ||
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 384'144.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 5'225.03 | ||||