



Perridge and Old Burford Farm is a 182 ha organic dairy and beef farm in Somerset. They established 43 ha of diverse herbal leys on their grazing platform between 2018 and spring 2021. There are a further 16 ha to be sown in autumn 2021 with further developments planned thereafter.
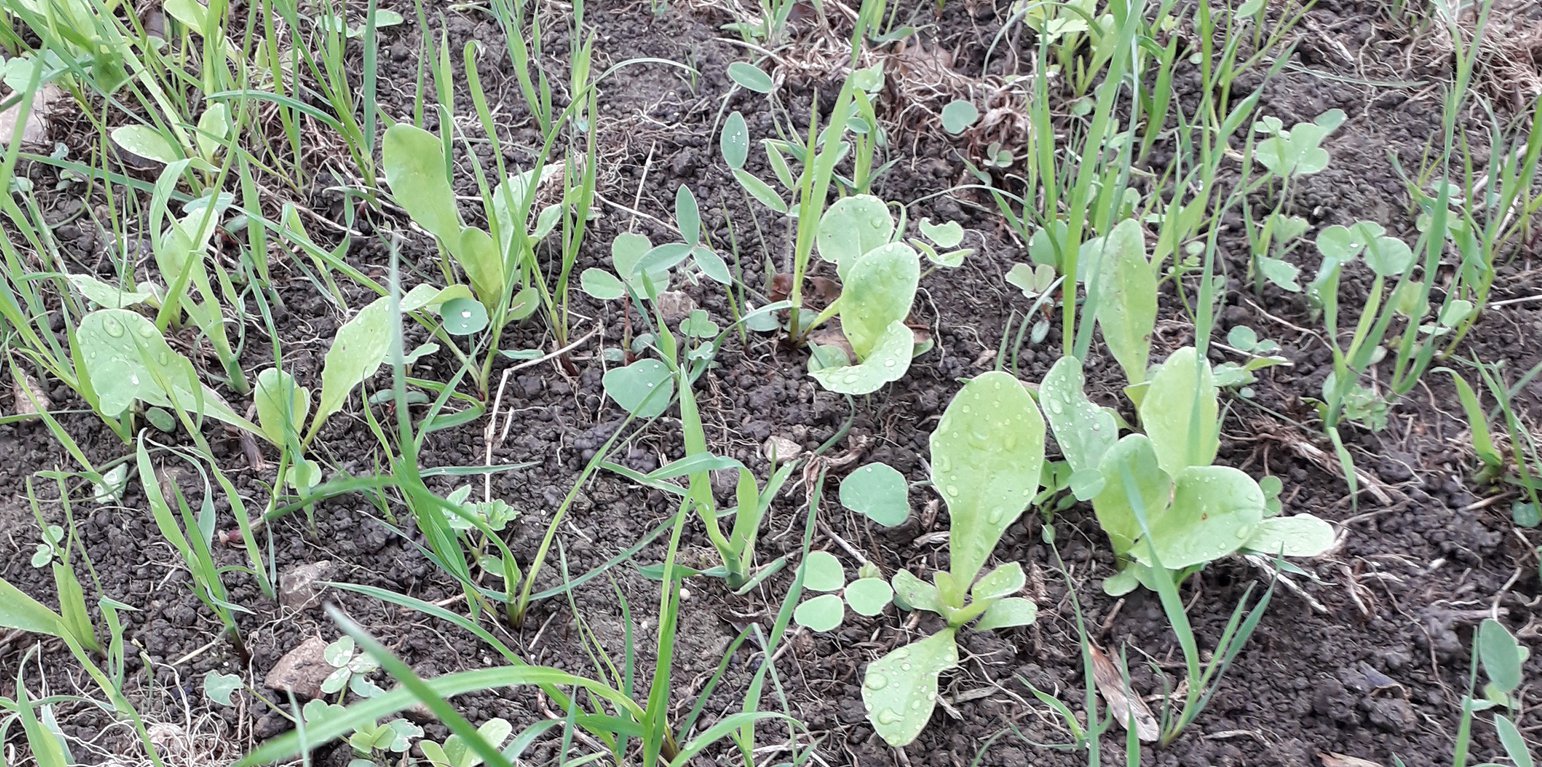
The system initially established a mix of chicory, plantain, ryegrass and clover in Autumn 2018, with further fields including a more complex mix of cocksfoot, Festulolium sp (a natural hybrid of ryegrass and fescue) , ryegrass, timothy, tall and meadow fescue, sainfoin; red, white, alsike and sweet clovers, sainfoin, lucerne, birdsfoot trefoil, burnet, chicory, ribgrass forage herb, yarrow and sheep’s parsley.
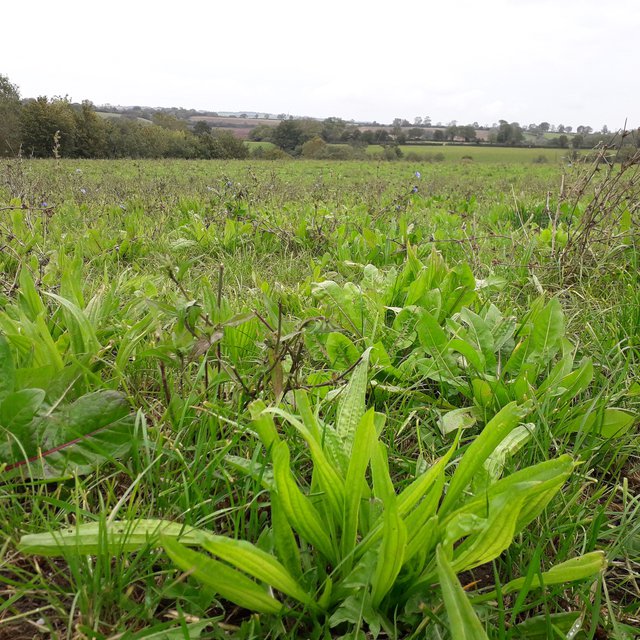
The most successful establishment has been from autumn sowing, following ryegrass, into a well prepared seed bed with shallow cultivation. This has led to three to four times more effective germination. To prepare the seed bed, a Cambridge roller was used to form a firm seed-bed and stop seeds going too deep, then seed was sown using a grass harrow and air seeder in August. Soil was rolled again with the Cambridge roller to break up clods of soil and then given a flat-roll to give tight soil-to-seed contact and to conserve moisture. The field is then left untouched until the following spring.
Once established by the following spring, the leys are grazed with 140 organic dairy cows, calves and beef animals. They are grazed using a strip rotation approach where they are moved daily at a target of 4,000kg dry matter (DM)/ha, and graze the herbage down to a residual of 1,800kg DM/ha (minimum residual of 10cm). The minimum full rotation is 35 days but this is often longer.
No artificial inputs are used with these diverse herbal leys, thus adhering to organic standards. The legumes (clover, lucerne, sainfoin and birdsfoot trefoil) are used to fix nitrogen, and with the grazing approach of “a third eaten, a third trampled and a third remaining as residual feed” soil organic matter is built up. In addition, the deep rooting species draw up minerals, improve soil structure and infiltration, and increase soil organic matter (SOM). Increasing SOM can also increase soil bacteria and microbe activity. Furthermore, managing the system with a rotational, cell grazing approach prevents selective grazing and increases species diversity and longevity of the sward.
Benefits:
Soil health – deep rooting species improve soil structure and infiltration, and through building up organic matter this improves soil carbon sequestration and leads to greater soil microbial activity and improved nutrient cycling. This is particularly important for this site due to mineral deficiency.
Resilient and persistent forage – deep rooting species bring up moisture from deep in the soil.
Mineral-rich forage – there is a high mineral content in ribwort plantain, chicory, sheep’s parsley, yarrow and burnet. Again, root structure helps, mining more minerals from deeper in the soil profile.
Biodiversity improvements - a wider species diversity of flowing plants is beneficial for biodiversity.
Animal health benefits – Anthelmintic properties of some species with a high tannin content, such as chicory, sainfoin and birdsfoot trefoil, reduce the parasitic worm burden. Also, the way livestock are grazed, with a good residual of forage, reduces soil contact and, therefore, worm risk
There are many positives to herbal leys and these have all been experienced to date, particularly resilient forage production in dry conditions. It currently is too early to see changes in soil structure and health.
The challenge with herbal leys are ensuring successful establishment and selecting the right seed mix. Establishment is reliant on conditions and preparations, with the lifespan of the ley managed through careful grazing by having long rotations and preventing selective grazing. Ensuring you have the correct mix of grasses, herbs and legumes to get the balance of energy and protein is key: there has been some anecdotal experience at this farm of cows not seeming “full” coming off herbal ley, this is thought due to dominance of chicory over grasses.
สถานที่: Shepon Mallet, Somerset, สหราชอาณาจักร
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี: พื้นที่เดี่ยว
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
In a permanently protected area?: ไม่ใช่
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: 2018
ประเภทของการแนะนำ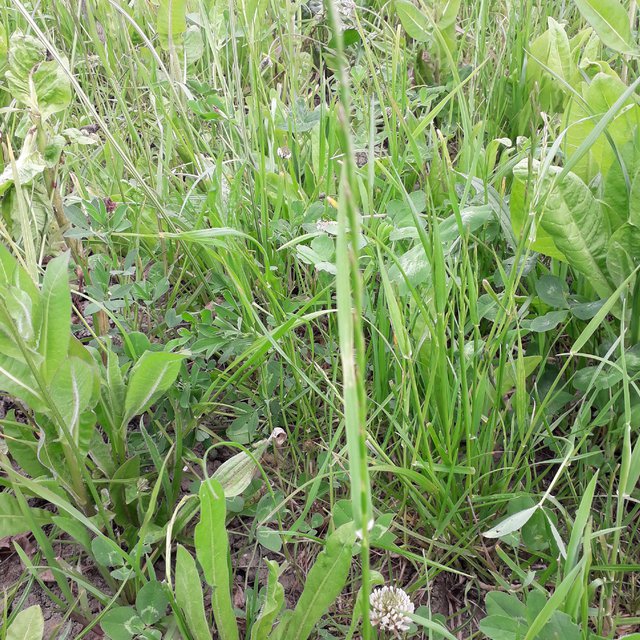


| Species | Count |
| cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu) | 140 |





| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (GBP) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (GBP) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Shallow cultivator (up to 4 passes) | Ha | 1.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 | 50.0 |
| Cambridge Roller | Ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 50.0 |
| Grass harrow and air seeder | Ha | 1.0 | 31.0 | 31.0 | 50.0 |
| Flat roller | Ha | 1.0 | 26.0 | 26.0 | 50.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | |||||
| Herbal ley seed mix | Ha | 1.0 | 218.0 | 218.0 | 50.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 330.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 440.0 | ||||
Good quality and diversity of fodder for grazing cattle. Similar production to grass ley achieved.
Good quality and diversity of fodder for grazing cattle
Cattle remained healthy and well fed on herbal ley
More resilient and diverse forage
Up to 16 species have been sown as a very diverse seed mix
Training and SLM expert support has transferred knowledge to land users
Deeper rooting and broader leaves have helped maintain soil moisture
No heavy machinery used after sowing in August through to grazing in May.
Deep rooting varieties can recharge nurtients from depth, while nitrogen fixers can support nutrient cycling
Up to 16 species have been sown as a very diverse seed mix
Plant diversity has attracted a greater abundance of beneficial species
Deeper rooting and broader leaves have helped maintain soil moisture and recycle from deeper soil water