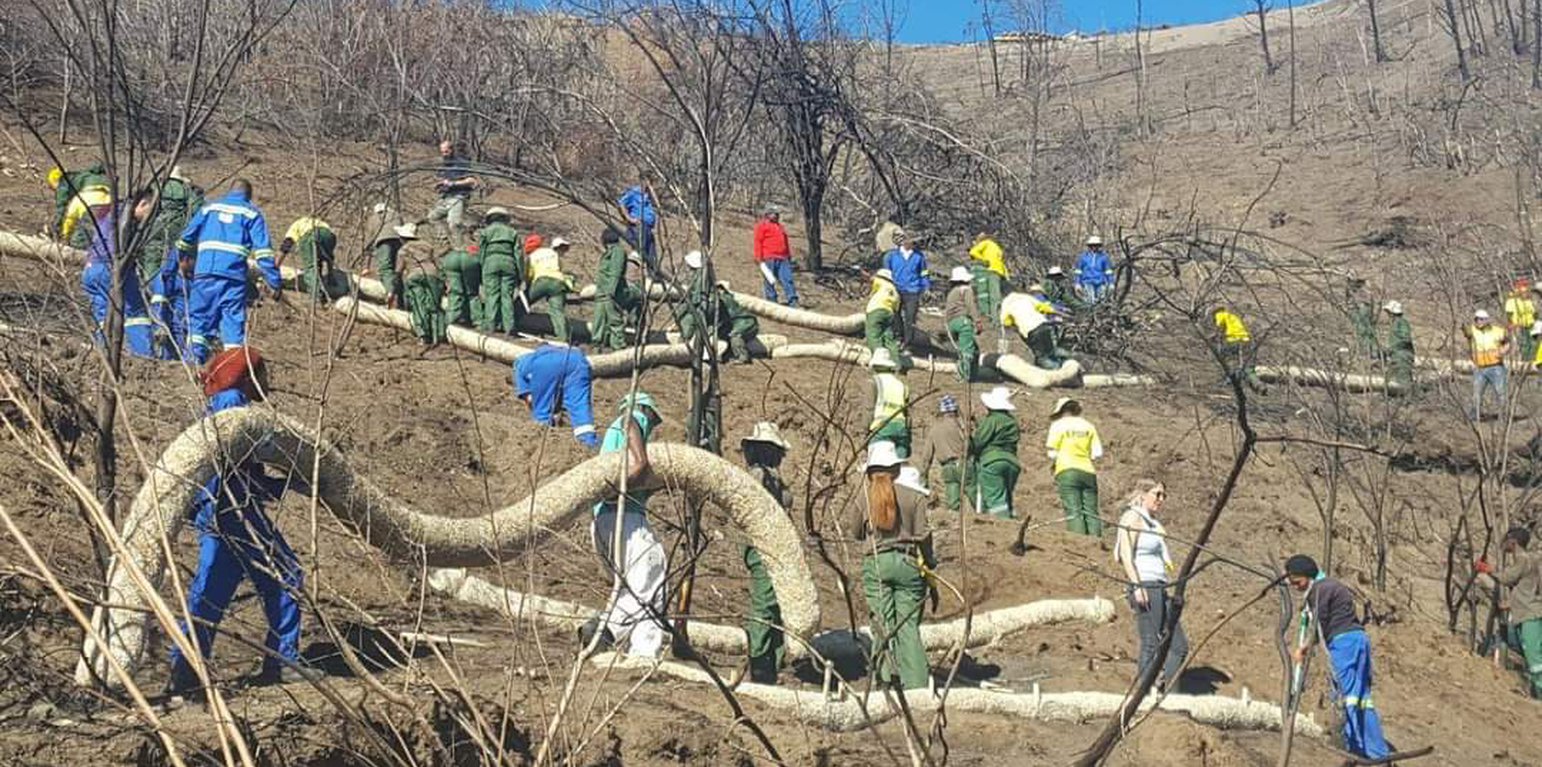




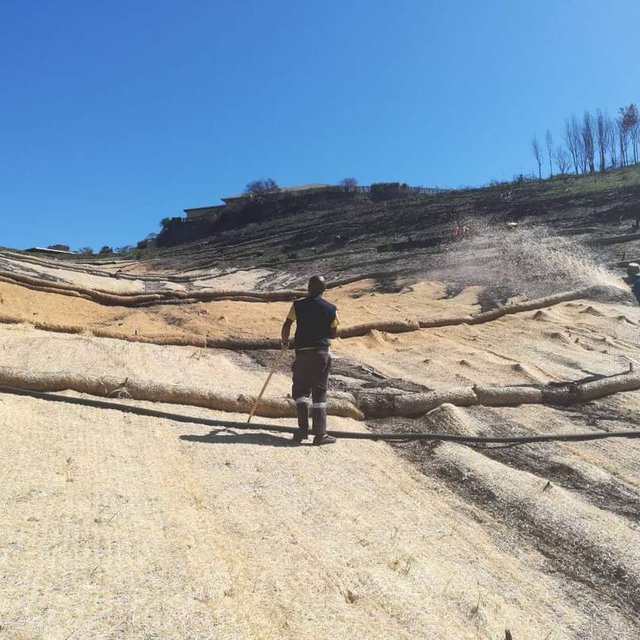
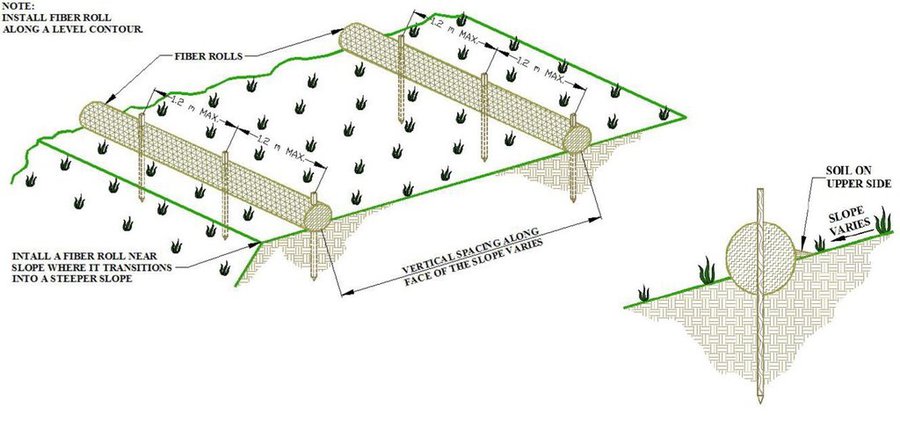
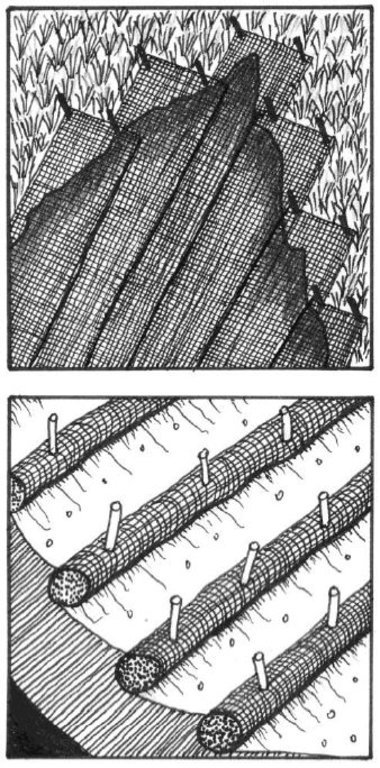
Sediment retention fibre rolls (SRFR) and erosion blankets were deployed near the town of Knysna in the Western Cape Province of South Africa to stabilise slopes after vegetation was destroyed by wildfires in 2017. The predominant geology is quartzite, shale, schist, conglomerate and dune sand. The soils of this area are generally acidic and nutrient-poor occurring, on moderate to steep slopes, ranging from 5 m to 1,220 m above sea level. The area receives summer and winter rainfall with an annual average of around 650 to 700 mm. The Knysna fires were the worst wildfire disaster in South African history (more than 21 000 ha were affected – destroying more than 800 buildings, 5000 ha of forest plantations and claiming the lives of seven people). Investigations reported that its severity was caused by a cocktail of factors, including drought, low atmospheric humidity, strong warm Bergwind conditions and abundant biomass. After the fires, the lack of vegetation cover on steep sandy slopes in the affected areas posed an immediate danger of erosion and landslides to downstream catchments, ravines and man-made infrastructure. Areas with high infestations of invasive alien plants required active re-establishment of indigenous plants and the removal of alien seedlings (popular and aspen) after germination. It is estimated that 53 km of wood fibre rolls (or "sausages") and 54 000 m² of erosion blankets (Woodwool fibre filled) have been installed on post-fire erosion mitigation projects. Furthermore hydroseeding was carried out with the annual grass "teff" (Eragrostis tef) to serve as an interim (annual grass) soil stabiliser. This will be replaced by indigenous plant growth in time. The project was implemented in the following stages:
1.Identification of priority areas where infrastructure was threatened (using GIS modelling)
2.Acquisition of restoration materials – SRFR and erosion blankets produced through secondary industries created through the removal of invasive alien plants (popular and aspen)
3.Training of local community members on implementation of restoration measures
4.Removal of all burnt woody material
5.Introduction of indigenous seed
6.Installation of erosion control blankets or hydroseeding (seeding using a slurry of seed and mulch)
7.Installation of SRFR
8.As part of maintenance, removal of invasive alien vegetation seedlings
สถานที่: Western Cape, แอฟริกาใต้
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี: 10-100 แห่ง
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ (approx. 10-100 ตร.กม.)
In a permanently protected area?: ไม่ใช่
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: 2018
ประเภทของการแนะนำ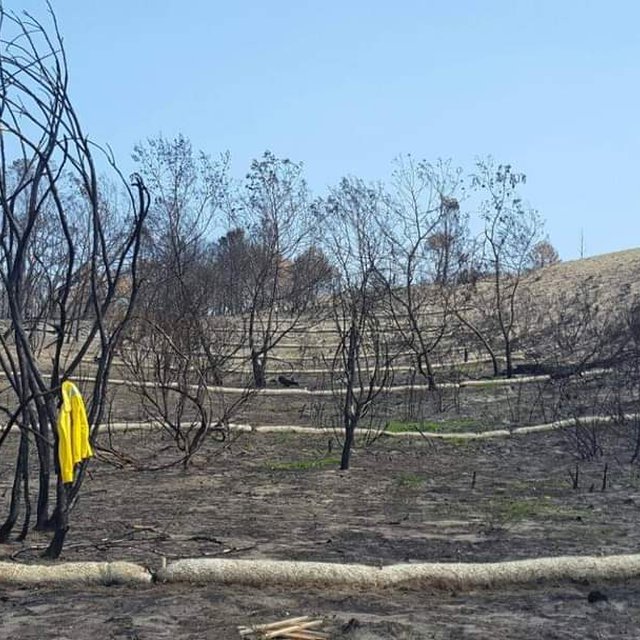









| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (Rand) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (Rand) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Unskilled labour (including transport) | per day | 84.0 | 260.0 | 21840.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Spades, hammer, scissors, rakes, hand saw | per day | 5.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | |||||
| Grass seed mix | kg | 50.0 | 100.0 | 5000.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | |||||
| SRFB 10m interval including stakes | per meter | 1000.0 | 50.0 | 50000.0 | |
| Erosion blankets | per square meter | 10000.0 | 13.0 | 130000.0 | |
| 1.0 | |||||
| อื่น ๆ | |||||
| Hydro seeding (including fiber, binding medium, seed and organic fertilizer) | per ha | 1.0 | 12000.0 | 12000.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 218'940.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 14'596.0 | ||||
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (Rand) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (Rand) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Restoration of site after flooding events | per day | 24.0 | 260.0 | 6240.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Tools to do restoration (same as installation) | per day | 3.0 | 30.0 | 90.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | |||||
| Removal of invasive alien vegetation | per day | 24.0 | 60.0 | 1440.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | |||||
| SRFR | per meter | 50.0 | 50.0 | 2500.0 | |
| Erosion blankets (only pegs) | per square meter | 300.0 | 3.0 | 900.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 11'170.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 744.67 | ||||
Restoration resulted in job creation for local communities
Improved ecotourism - land restored to natural state - hiking and cycling
Land without degradation more valuable for development
The introduction of structures and increased vegetation cover resulted in reduced runoff
The introduced technologies also improved excess water drainage and less flooding
Vegetation cover improved with the introduction of hydroseeding and retention of topsoil containing indigenous seed
Soil loss was reduced due to the introduction of the SRFR and improved vegetation cover
Vegetation cover improved due to the soil stabilisation and introduction of hydroseeding (annual grass protected soil until natural vegetation established)
Improved biomass due to the improved vegetation cover and reduction of soil loss (topsoil with high C content)
Maintenance of the applied technology included the removal of alien species
The technology resulted in the reestablishment of the natural vegetation and improved biodiversity
One of the main reasons for the introduction of this innovative technology is the reduction in flood impacts due to the inclusion of structures as well as improved vegetation cover
The added benefit of the technology is the reduction in the risk of landslides due to the inclusion of soil stabilising structures and improved vegetation cover
The introduction of the technology resulted in improved drainage and therefore less downstream flooding
The introduction of sediment trapping structures as well as improved vegetation cover resulted in less downstream siltation
The risk of damage to infrastructure was reduced due to the decrease in risk of flooding and landslides