


Aims / objectives: As part of the Community Agriculture & Watershed Management Project (CAWMP), this approach helped beneficiaries and project partners allocate grants and manage the flow of funding while promoting fairness, transparency, and ownership. It facilitated appropriate SLM choices across the highly variable agricultural, climatic and geographic conditions. Almost 4000 rural investments including SLM technologies were implemented, resulting in over 96,000ha under improved land management practices and benefits for more than 43,000 households in Tajikistan’s uplands.
Methods: This approach set a fixed budget per village, limited the grant value received per household as well as the total size of any one grant, required minimum levels of beneficiary contributions, and provided grant money to beneficiaries, enabling them to purchase the inputs.
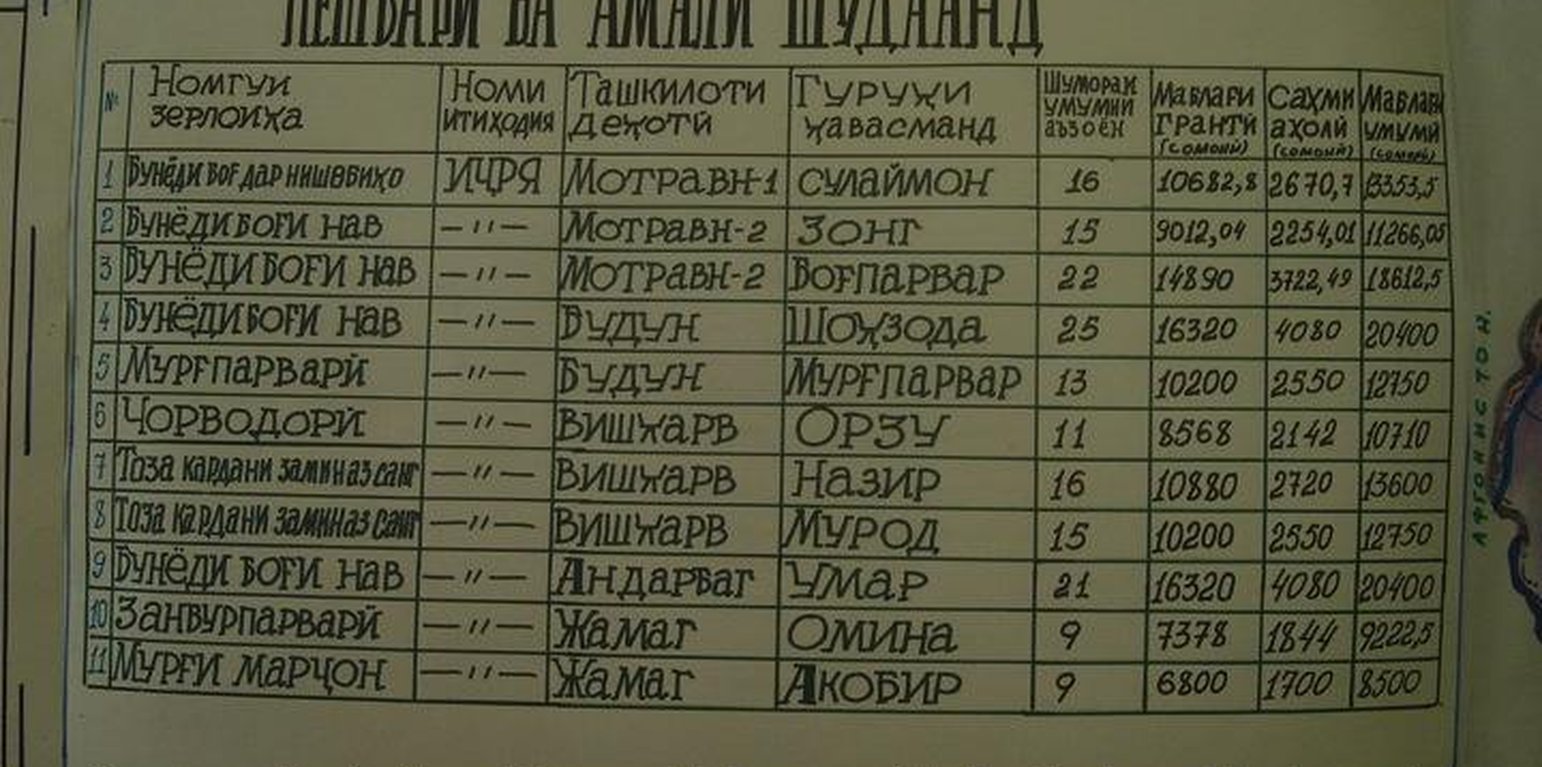
Stages of implementation: Fixed village budget: In their Community Action Plans (CAP) villages assigned priorities to grants within a set budget amount for the entire village. Project guidelines specified a formula for this budget based on amounts per investment type per household excluding beneficiary contributions ($30/household for farm productivity, $74/household for land management, and $30/household for rural infrastructure). The number of households in a village multiplied by these per-household-amounts determined the overall size of the grant funding for that village. Grant allocation limits. The villages were informed of their overall budget as well as the household limits for each category. They chose investments for groups of households (Common Interest Groups, CIGs) and allocated grant funds to subprojects accordingly. The household limits ensured that collectively at least 50% of the families would benefit directly. In practice, about 75%, of a total of about 57000 households in the project sites participated in the farm productivity and land resource management investments, and 60% in rural infrastructure investments. Grant size. Except in a few cases requiring special approval, the Project-financed grants for each subproject were lower than US$5,000, which reduced risks of the funds being used for purposes for unrelated to the Project. Beneficiary Contribution. Beneficiaries were required to contribute a minimum of 25% of the grant amount in labor, materials or cash which increased their stake in the investment, thereby strengthening ownership and sustainability. At least 5% of the grant amount for rural infrastructure had to be contributed in cash at the start in order to demonstrate financial sustainability.
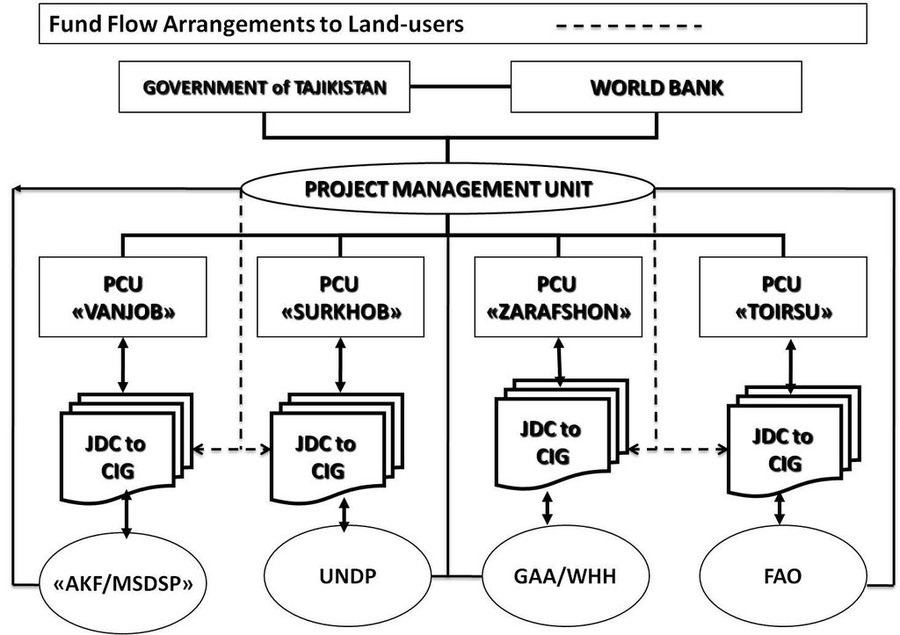
Role of stakeholders: Fund flow. Once a grant proposal was approved, the PMU transferred the grant amount to the local savings bank according to the schedule specified in the agreement between Jamoat Development Committee (JDC) and CIGs. The JDC accountant transferred the funds fromthe bank to the CIGs. The CIGs then had the responsibility for purchasing inputs, which created an incentive for selecting cost-effective inputs.
สถานที่: Jirgital, Tajikibad, Vanj, Aini, Matcha, Penjikent, Danghara, Sughd, Region of Republican Subordination, Khatlon, GBAO, ทาจิกิสถาน
วันที่ริเริ่ม: 2005
ปีที่สิ้นสุด: 2012
ประเภทของแนวทาง
| ผู้มีส่วนได้เสียหรือองค์กรที่นำไปปฏิบัติใช้มีส่วนเกี่ยวข้องกับแนวทางนี้อย่างไร | ระบุผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสีย | อธิบายบทบาทของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสีย |
| ผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น | CIGs (Groups of households) Local cultural and social conditions determined the extent to which women took part in the grant allocation decision-making, and as members of CIGs managing small grant funds. In some more remote communities, it was not generally acceptable for women to be active participants. In other areas, women only CIGs were formed. Marginal groups within a generally poor upland rural population participated in grant allocation decisions and as CIG members in managing small grant funds. In some villages, vulnerable and poor households were targeted as priority recipients of grants through the allocation mechanism. | Participated grant allocation decision making and fund management |
| องค์กรพัฒนาเอกชน | JDCs – locally registered NGOs | JDCs managed fund transfers to CIGs based based on formal agreements |
| รัฐบาลแห่งชาติ (ผู้วางแผน ผู้ทำการตัดสินใจ) | Project Management Unit |
CAWMP - Implementation Arrangements and Fund Flow Arrangements to Land-Users
การตัดสินใจถูกทำโดย
การตัดสินใจถูกตัดสินอยู่บนพื้นฐานของ
Grant allocation mechanisms. Fund flow arrangements and management.
The grant allocation mechanism fostered multi-factor decision-making, including consideration of local environmental conditions, by villagers. Fund flow arrangements enabled JDCs to manage about $7.4 million in small grants to about 4000 CIGs for rural production investments.
The project population is considered generally poor or very poor. Within this population, particularly vulnerable groups participated in rural production investments.
: Portions of the approach and associated guidelines have been adopted in other donor-funded projects.
Grant allocation mechanism was understood and could be used for other sources of financing for groups of households at the village level. Fund flow mechanisms will require a sub-district presence to support transfers to village-based groups.: