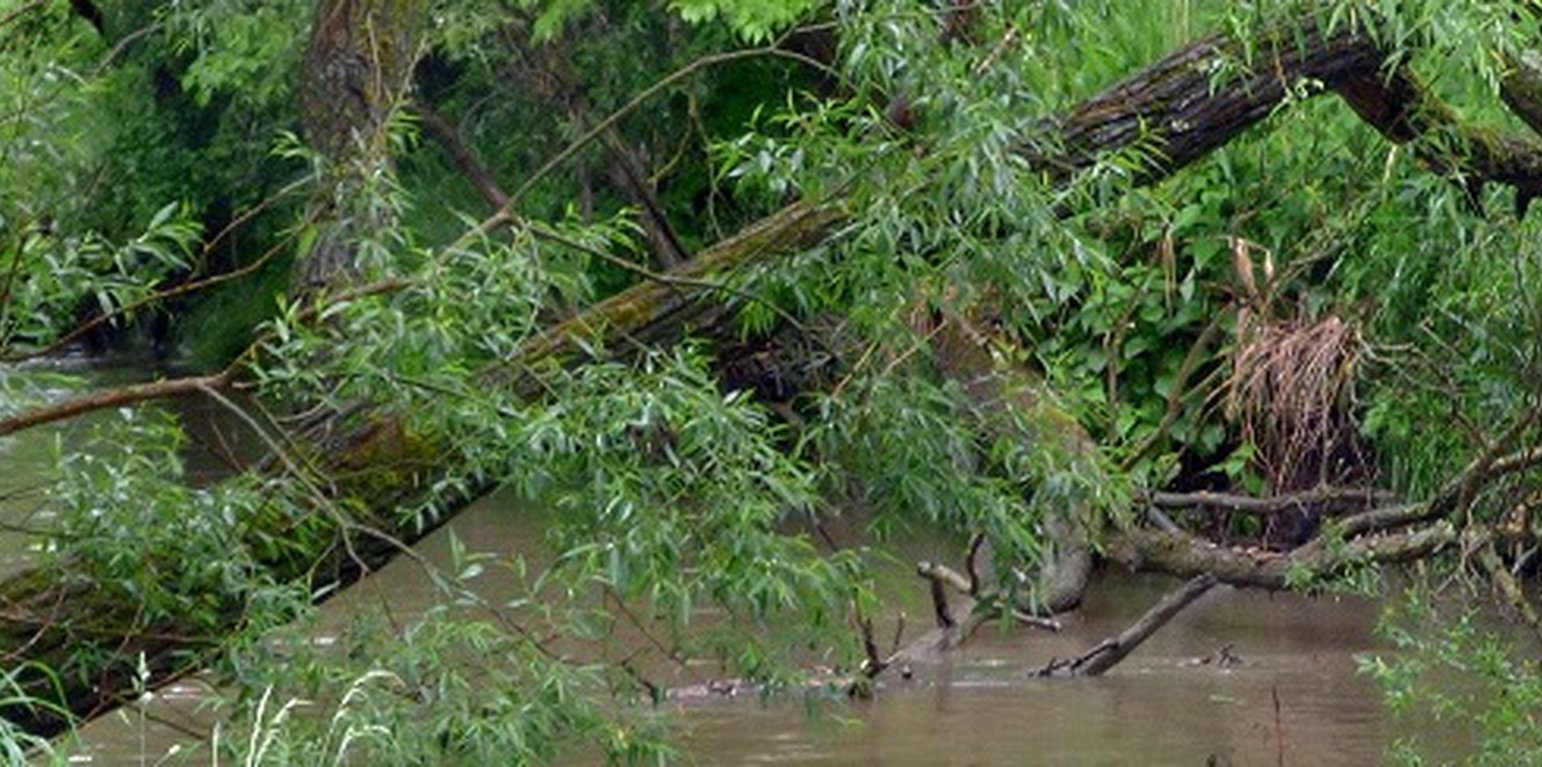




Allowing the accumulation of coarse woody debris in streambeds reduces flow velocity and levels of peak floods. This technology is applied in sloping landscapes, where runoff flows into streams/ gullies. The main function is to break the energy and reduce the speed of flow. Riparian trees or their branches are allowed to fall naturally into streams – through deliberate placement of wooden debris can contribute to the process. This may even create dams on steeper sections of the watercourses. Sediment loss will be reduced from the catchment area by deposition (sedimentation) of soil particles along the watercourses and on the plains lower in the valleys. In addition, slowing the flow results in a larger surface area of water and infiltration is increased. Wet spots created this way improve aquatic biodiversity and wildlife. A downstream benefit is that land users at a lower elevation are less affected by runoff, floods and sediment deposition. However a disadvantage is the risk of damage to surrounding fields - caused by wild animals attracted to the wet conditions and increased biodiversity.
สถานที่: The site where the technology is applied is situated within the catchment of Felső-Válicka stream, which belongs to the Balaton catchment area in western Hungary., Zala County, ฮังการี
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี: 2-10 แห่ง
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
In a permanently protected area?: ไม่ใช่
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: มากกว่า 50 ปี (แบบดั้งเดิม)
ประเภทของการแนะนำ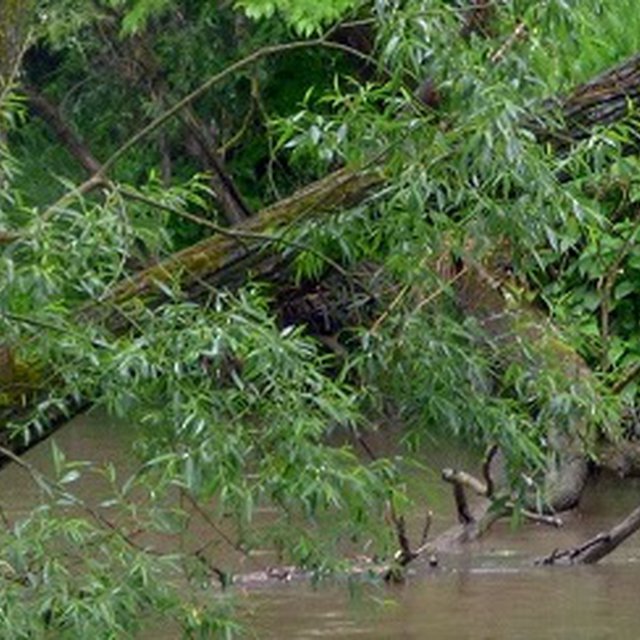





| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (USD) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (USD) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Cleaning (debris caught up behind the structure) | watercourse | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 50.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 50.0 | ||||
Woody debris slows the water during high flows. It does not collect water in a specific place, just keeps it longer in the upper area of the watershed.
Since the water moves more slowly, the rate of runoff also decreases.
Natural dams provide a new habitat for water wildlife.
Fallen trees are the basis of natural dams, they are no longer destroyed by storms, and new dams can be built from the newly fallen trees.
The natural dams can increase humidity in the forest.
As water is coming slower from the watershead upper part, water availability is much more balanced
Natural dams play a filtering role in the forest. Waste and debris must be regularly cleaned behind the structures.