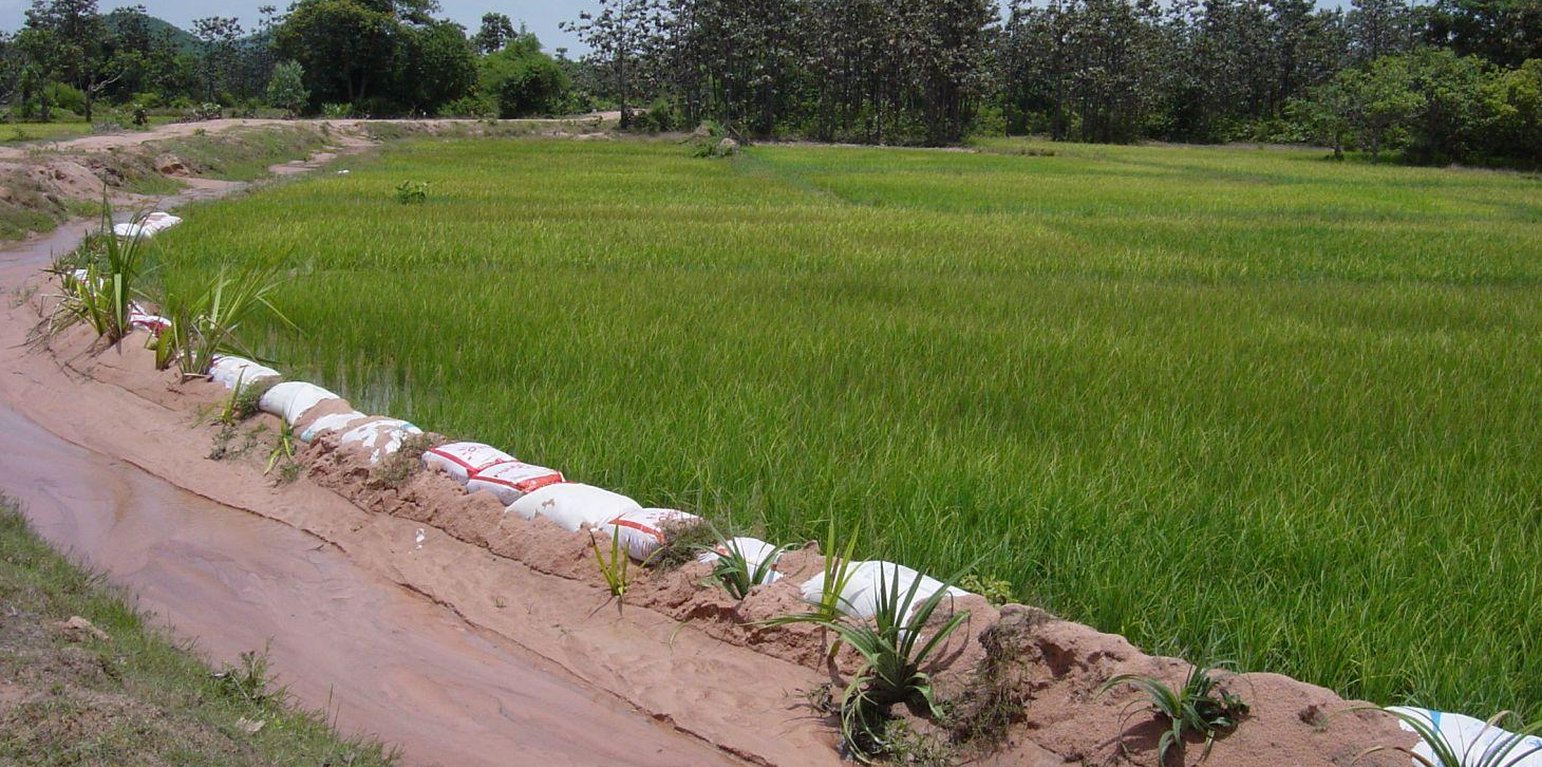




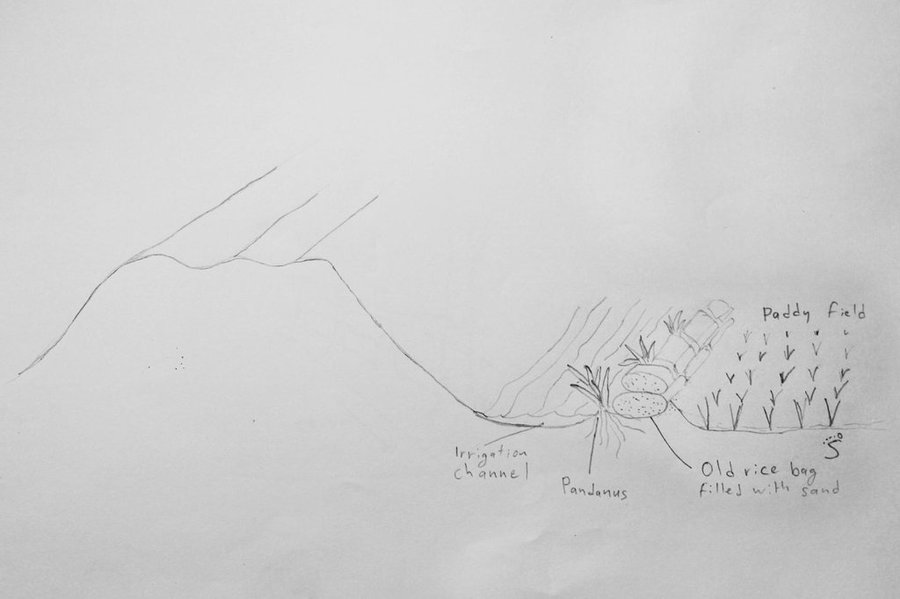
The paddy fields are surrounded by dikes and fed by local temporary streams and irrigation channels, as well as by rain. In sandy soils the dikes around the irrigation channels and fields cannot hold the water due to erosion. Old rice bags are filled with sand and piled up to form stable dikes on the short term, and Pandanus suckers are planted every 0.5 – 1 m to ensure a stability on the long term due to the root system.
The purpose of the dikes, stabilized for short and long term, is to ensure the flow of water to the paddy fields by reducing the riverbank erosion. It also helps to keep the water in the paddy fields. The Pandanus can be used to make mats and baskets, although this use diminishes due to the low cost of plastic. After a few years, the Pandanus on the dike is tall and spiky enough to fence off cattle and protect the rice from grazing.
To stabilize 50 m of dike, around 100 old rice bags are filled with sand and piled up on a height of 2 bags. Pandanus suckers are planted on the water side, between the bags, and sand is used to cover the plants and bags. Poles and sticks are used to stabilize the bags and plants until the root system is established. This is done in the beginning of the rainy season to ensure the growth of the sucker. In the first year, after each rain the eroded sand has to be added back to the dike. After the establishment phase, from the second year on, the Pandanus have to be cut back as they grow quickly and can grow tall.
The analysed area is flat (slope < 2%), with a tropical climate (dry season from November to May and wet season from June to October), and the soils are mostly sandy or loamy. The soil has a low fertility, contains little organic matter, and acidifies. The area has been deforested a long time ago, and the groundwater table is rather high (1-2 m during the dry season, on the surface during wet season).
Due to climate change, farmers notice more erratic rainfall, temperature rises and more recurrent droughts. Rice is the predominant crop grown in the area, since it serves as staple food (mix subsistence and commercial activities). Cattle are usually grazing on the fields after the harvest, without much control. Thus the cattle grazes too often and too much on the same spot, leading to degradation.
The increasing migration rate (the young generation leaves the villages to work in the cities, garment industry or abroad) results in a decrease of available labour force in the area which has detrimental effects on the agricultural activities. Furthermore, the civil war in the 1970s (Khmer Rouge) led to the loss of agricultural knowledge. Several NGOs are trying to re-establish the knowledge.
สถานที่: Chrey Bak/Rolea Pha’ear, Kampong Chhnang, กัมพูชา
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี:
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ (approx. 1-10 ตร.กม.)
In a permanently protected area?:
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: มากกว่า 50 ปี (แบบดั้งเดิม)
ประเภทของการแนะนำ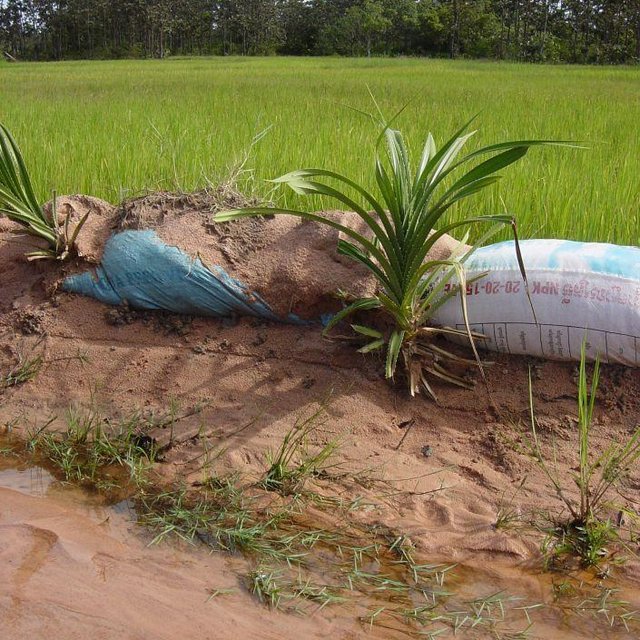






| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (Riels) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (Riels) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | |||||
| Construction of biodigester | 1.0 | 400.0 | 400.0 | 50.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 400.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 0.1 | ||||
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (Riels) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (Riels) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| labour | 1.0 | 121.5 | 121.5 | 100.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 121.5 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 0.03 | ||||
Dried residues are put in the garden (cucumber, pumpkin, watermelon) which increases nutrient availability.
Before the installation of the biogas system, the land user bought firewood.
He saves 50 $ on chemical fertilizer per year.
No smoke from open fire.
On the long term livelihood is improved, because he saves over 60 $ per year in firewood and battery charging for light, as well as 50 $ for chemical fertilizer.
Pollution of groundwater due to washing out of nutrients.
Most of the carbon is transformed into methane, not available as organic matter.
Compost usually not completely decomposed, as well as raw manure, contain lots of weed seeds.
Sludge is left to dry outside, nutrients washed out into groundwater. Not measurable.