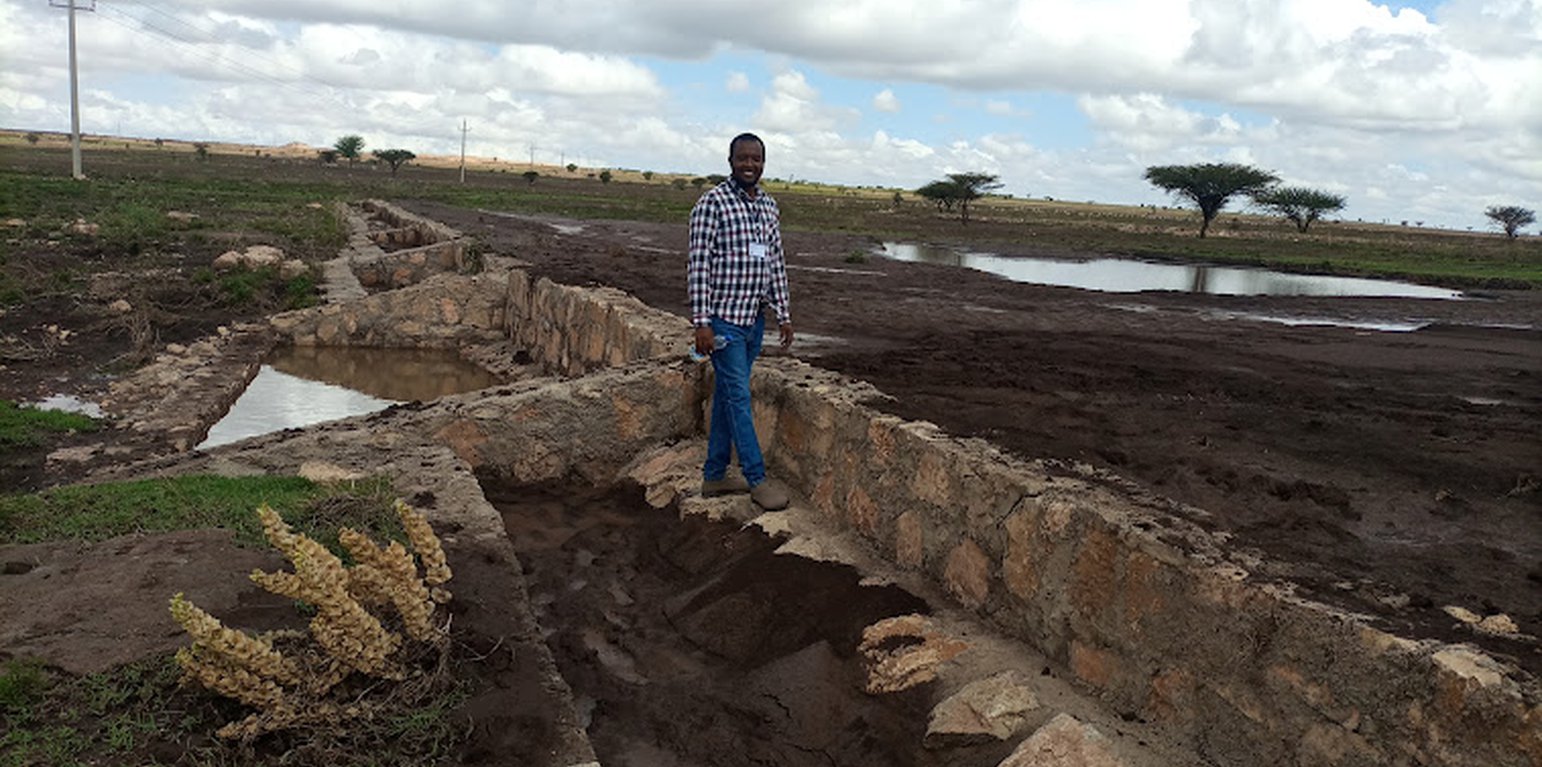




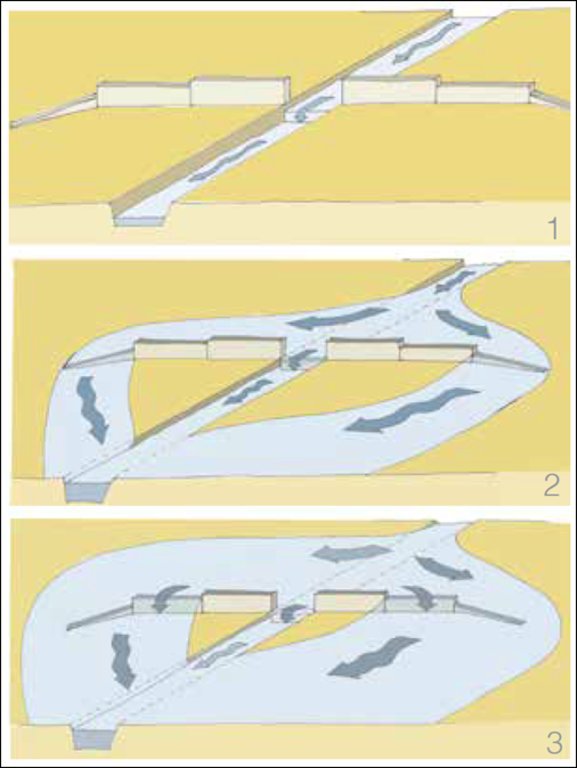
Water Spreading Weirs (WSWs) spread runoff water to the tips of the structure's wings, slowing down the speed of runoff and arresting the sediment pouring downstream. WSWs are applicable both on farmland and rangelands to improve the productive use of the land’s resources. They protect soil erosion and control gully development as well as increasing surface and sub-surface water availability. Activities such as mobilization of the community through awareness creation are among the numerous tasks implemented to put the technology in place. The community participates in site selection and participatory planning. Other stakeholders assist in area delineation, profiling the implementation area, and design. Labour and inputs such as surveying and construction materials, notably stone, sand, water, and cement, and equipment such as line levels, theodolites, spades, hoes, forks, string and measuring tapes etc. are required. On top of these, implementing the technology is supported by satellite images and ground validation exercises.
The main purpose of the technology is to reduce land degradation, harvest and use runoff water for spate irrigation and household uses, improve environmental resilience to the risks of drought, increase the depth and fertility of land behind the structure by capturing sediment washed away, allow infiltration of water and increase overall production of food and fodder crops. Also, the contribution to groundwater recharge is immense. Furthermore, it allows the agropastoral community to grow both cash and food crops which helps to ensure food security. Above all, the water harvested means people can remain in the area and that their livestock have access to drinking water for about three months after interception of rainfall. However, the agropastoralists may be discouraged by the size of the WSWs which can be from one hundred to over two hundred meters across. Care also must be taken that the structures do not cross livestock migration routes.
สถานที่: Amadle kebele, South Jijiga district, Somali, เอธิโอเปีย
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี: 2-10 แห่ง
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
In a permanently protected area?: ไม่ใช่
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: 2022; น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
ประเภทของการแนะนำ







It is the expert's conviction that crop production in the area increased with water harvest and spread over the farm for use as spate or supplementary irrigation to the seasonal rainfall.
As the moisture harvested by the structure is believed to add grain filling period, the crop quality is also expected to increase.
Fodder production also increases with the availability of good soil and moisture conserved in the farm behind the structure.
Increases with increasing availability of feed or fodder from either crop residue, natural grass or browse.
It rather improves crop resilience because of improved soil moisture.
Opportunities can be created to increase the size of land under farming with increasing availability of moisture and fertile soils.
Moisture availability eases the management operation.
Basically, quality is not a priority issue for agro pastoralists in dry valley areas.
As the structure reduces the degree of degradation, expense on agricultural inputs is believed to be reduced.
It promotes land users' understanding of SLM through training and exposure to the actual structure and soil and water harvested behind the structure.
They may manage to access water for livestock drink and/or household consumption.
The structure harvests soil moisture on the farm. It reduces the speed of runoff, stops, and spread over the farm.
Increased through production of more biomass.
The physical barriers stops the soil and water loss.
It is related to a warm climate that triggers evaporation and salinity development in the long run.
As the structure is recently constructed, it is dire to envisage the off-site impacts of the technology at this juncture. However, it has a positive contribution to the availability of groundwater in the adjacent farms.
Streams are less common in the dry valley.
It reduces the speed and volume of downstream flooding.
Need an investigation of its impact on the groundwater.
Believed to reduce it in the long run.