



Introduction and Background
Intensive cropping systems coupled with monocropping and high usage of synthetic fertilizers have led to the degradation of soils and depletion of nutrients directly affecting agricultural productivity and farmers' income. Farmers in the Balangir district of Odisha are facing similar challenges. To address these issues and promote sustainable farming practices, a biochar production initiative was introduced by utilizing crop residues and waste material from forests to produce biochar, a carbon-rich material that enhances soil fertility and soil structure. The initiative is a part of the Pro-Soil Project of Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ), India and implemented by the International Centre for Research in Agroforestry (ICRAF). The technology (a kiln for biochar production) and technical inputs for biochar production were sourced from the Indian Institute of Soil Science, Bhopal.
Biochar is a type of charcoal produced from biomass like agricultural or forest waste or organic materials through a process called pyrolysis. The application of sustainable biochar technology in agroforestry systems can lead to better soil structure, increased water retention, reduced nutrient leaching, and improved crop yields. Moreover, it aids in mitigating greenhouse gas emissions by locking carbon into soil for an extended period.
In the project region farmers used crop residues such as rice straw, wheat straw and residue of other crops along with non-usable biomass from local forests, such as branches, twigs, and leaves, to supplement the feedstock for the pyrolysis. Since the District has large forest areas, the availability of forest waste is no problem. The biochar produced was applied into existing crops fields as well as into agroforestry system. Aiming to promote agroforestry, the project promoted the integration of trees (both fruits and timber) and shrubs into existing agricultural practices. Agroforestry offers multiple benefits such as improved soil health, biodiversity, and carbon sequestration. When sustainable biochar production is integrated into these systems, it can create a sustainable cycle where agricultural waste is converted into biochar, which then enhances soil fertility and sequesters carbon when added back into the soil.
The project has actively involved women farmers, entrepreneurial youth, and farmers' groups in the collection, production and application process of biochar thus promoting community participation and creating awareness about the benefits of biochar.
Implementation
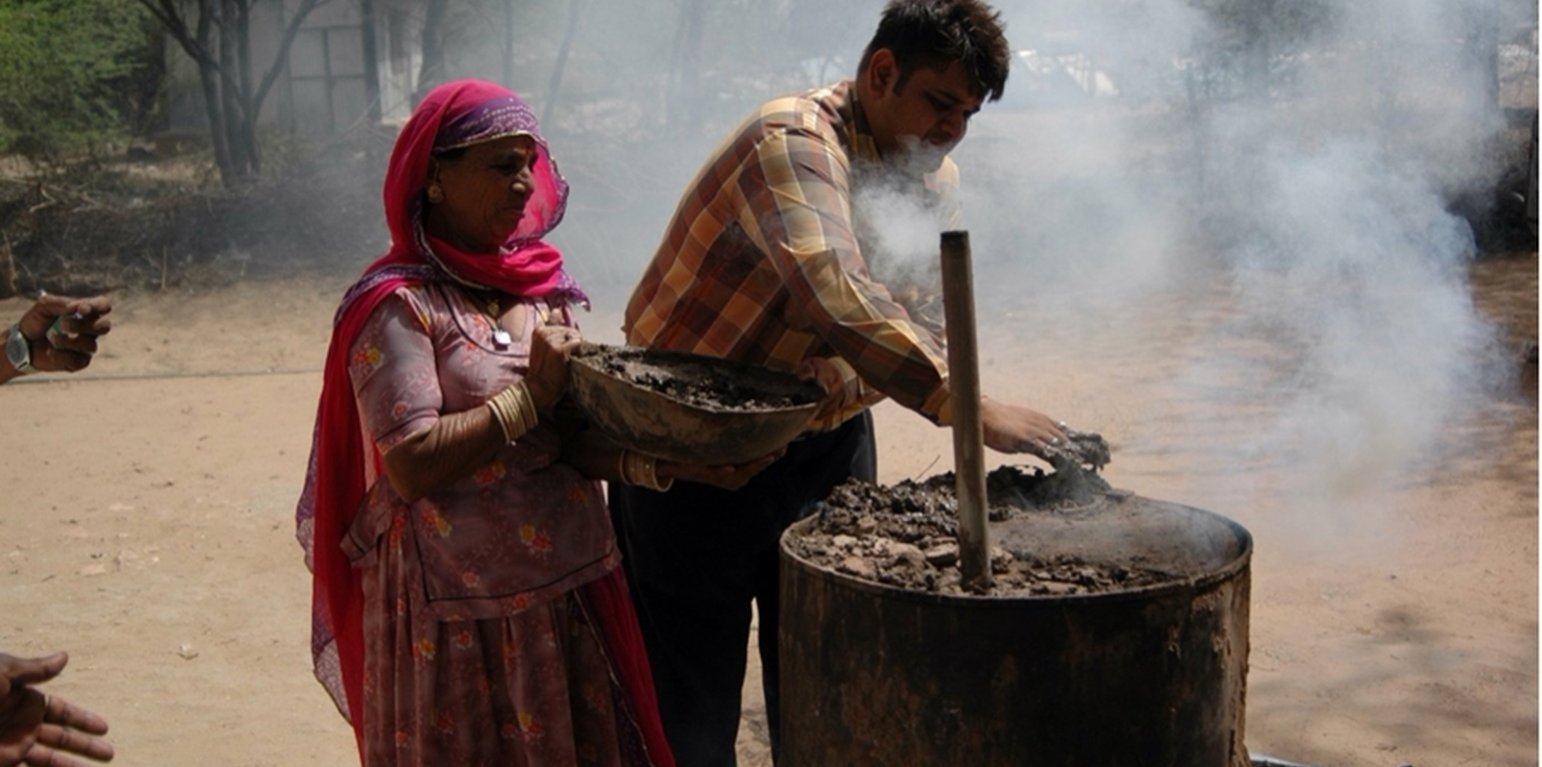
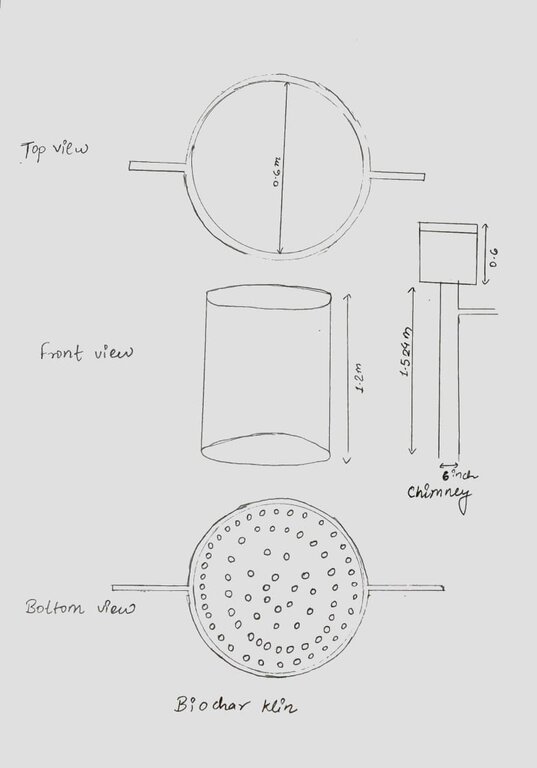
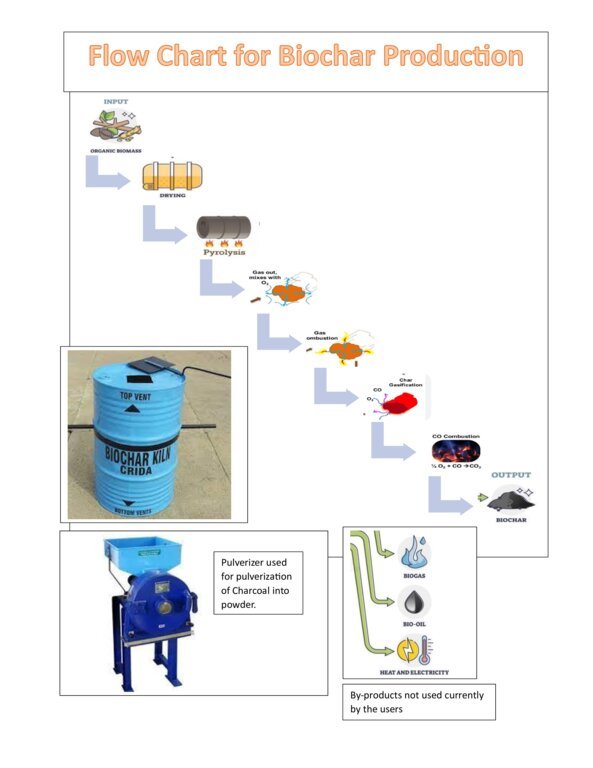
The biochar kiln technology, obtained from the Indian Institute of Soil Science, in Bhopal, is employed to convert biomass into biochar through pyrolysis. This technology ensures efficient and controlled production of high-quality biochar. The collected biomass undergoes a controlled pyrolysis process inside the biochar kiln, where it is burned in the relative absence of oxygen. Technical specialization during production includes kiln temperature control, feedstock preparation, and the management of pyrolysis gases to ensure efficient biochar production. This results in the conversion of biomass into biochar, also leaving behind bioenergy-rich gases. Quality control measures are implemented to ensure the production of biochar with optimal characteristics, including high carbon content, porosity, and stability.
The Biochar kiln used was designed with the aim to optimize temperature control and ensure efficient conversion of biomass. An efficient loading mechanism allows easy and controlled feeding of biomass into the kiln. This ensures a consistent flow of material during the pyrolysis process. Although local kilns are usually not equipped with temperature control mechanisms to regulate the pyrolysis temperature, the temperature in the kilns may alternatively be regulated through the rate of feeding biomass into the kilns. Such kilns usually have some safety features and proper ventilation so to prevent accidents.
To implement this technology the ICRAF conducted training sessions for farmers on the proper preparation and application of biochar. The trainings were focused on the following aspects:
-The collection and drying process for agriculture and forest waste
-The management of operations for the biochar kiln including the loading of raw material (feedstock) into the kiln, its burning, operation-timing, period check, volumes of raw material to be fed etc.
-Precautions to be taken during the process
-The quality check of prepared biochar charcoal and the process for pulverizing it
-Dosage recommendations for different crops as per local conditions
-The mixing of biochar with cow dung and cow urine before application
-Integration with existing farming practices and the long-term benefits of biochar on soil health
Impact and Knowledge Transfer
The biochar acts as a soil conditioner, enhancing water retention, nutrient availability, and microbial activity. The benefits and impacts on improved fertility, increased water retention, and reduced nutrient leaching, lead to higher crop yields and resilience against climate variability, carbon sequestration aids in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to global efforts to combat climate change, and utilizing agricultural residues reduces air pollution from open burning and provides a sustainable solution for organic waste disposal. Land users appreciated the enhanced soil productivity and environmental benefits brought by biochar. Overall, the Sustainable Biochar Production Technology represents a promising approach in sustainable agriculture and environmental stewardship.
The project team, in collaboration with local agricultural extension services and the Indian Institute of Soil Science, monitored the impact of biochar application on soil health parameters. This involved regular soil testing, crop yield assessments and feedback from participating farmers. In fact, they also measured the impact of biochar made from different feedstock (raw materials). Success stories were shared with neighboring communities, public stakeholders and researchers and encouraged the further adoption of sustainable soil management practices.
The biochar production initiative in the Balangir District of Odisha in India demonstrates a sustainable approach to addressing soil health issues using locally available resources. Through the collaboration between ICRAF and GIZ, this project not only improves soil fertility but also empowers local communities by providing them with sustainable solutions for agricultural challenges. The success of this intervention serves as a model for future initiatives aimed at promoting environmentally friendly and community-driven approaches to agriculture.
สถานที่: Odisha, อินเดีย
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี: 2-10 แห่ง
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
In a permanently protected area?: ไม่ใช่
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: 2021
ประเภทของการแนะนำ










| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (INR) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (INR) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Biochar Klin | Rs. | 1.0 | 7000.0 | 7000.0 | |
| Pulvariser unit | Rs. | 1.0 | 20000.0 | 20000.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 27'000.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 337.5 | ||||
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (INR) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (INR) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Preparation of biochar | Person-day | 2.0 | 200.0 | 400.0 | 100.0 |
| Application of biochar in the field | Person-day | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | |||||
| Farmyard manure | Rs. | 20.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizer | Rs. | 50.0 | 7.0 | 350.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 1'050.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 13.13 | ||||
The district is located in the interior parts of eastern India and considered as a backward district with poor access to infrastructure and other facilities
For Wood Biochar or Wood Coconut Husk Biochar (WCB), or Crop Residue Biochar (CRB) the highest grain yield of the crop was recorded with the highest dose of biochar, fertilizer, and manure application. Also, it's application significantly improved the straw yield
The application of Wood Biochar or Wood Coconut Husk Biochar (WCB), or Crop Residue Biochar (CRB) with manure also significantly improved the quality of the crop
It was found with significantly improved straw yield the availability of fodder for the livestock also increased
It was observed that the crop in which the application of biochar was with the manure and fertilizer, the crop had better adaptation and standing properties in comparison to another crop without the application of biochar.
The yield for the crop in which application was done was increased which led to an increase in income
Water retention from the soil increased because of the increase in soil organic matter and carbon content
The water holding capacity of the water increased leading to less surface runoff from the field.
With an increase in soil organic matter and improved soil texture the soil moisture increased
The semi-arid climate and limited rainfall, combined with sporadic and intense monsoons, can lead to soil erosion. When rainfall does occur, it can cause rapid runoff, carrying away the topsoil due to the lack of vegetation cover or inadequate soil conservation measures.
The application of biochar with manure and fertilizers not only increased the nutrients in the soil but also increased the nutrient uptake of plants from the soil.
Biochar can act as a soil amendment to moderate soil pH depending on the initial pH level. Scientifically, biochar tends to be pH neutral, so its impact on soil pH depends on the existing soil condition. The impact of biochar on pH is often gradual and depends on various factors like the type and composition of biochar, soil characteristics and environmental conditions. Biochar acts more as a buffer, stabilizing soil pH over time rather than making drastic immediate changes.
The plant biomass as well as the vegetative growth of the plant showed a significant positive reaction to the biochar application on crops
Resistance of the crop increases with better uptake of K from the soil. Plants become more resistant to disease and pests.