



The SmartAG model is mainly applied in the Montado (Portugal) and Dehesa (Spain) agroforestry systems which serve as a biodiversity oasis in the
Mediterranean region. They are currently being heavily impacted by climate change.
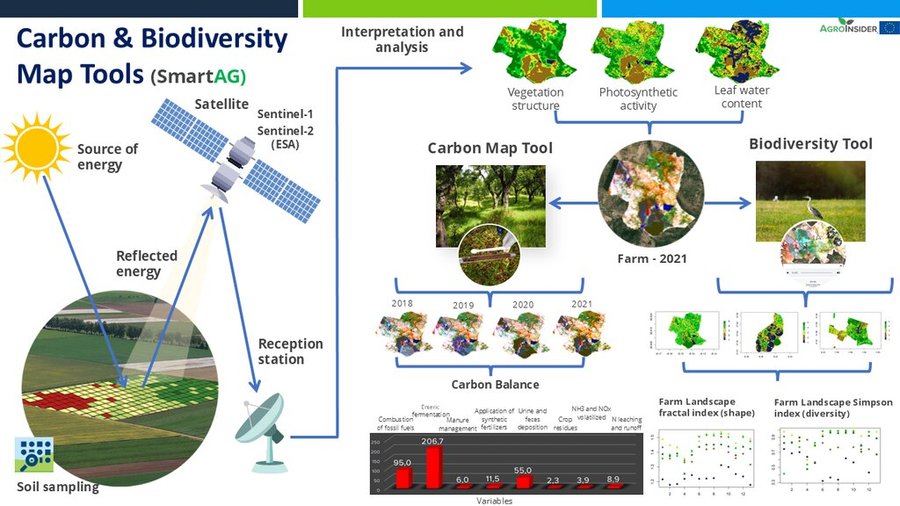
It contributes to achieving carbon sequestration potential. The SmartAG model is also applied in agriculture systems in Portugal, Spain, Greece, The Netherlands, Indonesia and Ukraine. Nevertheless, it can be applied in any part of the world. The SmartAG app provides accurate Agricultural Climate Services on a large-scale, available to farmers, producers, and stakeholders. The model analyzes agronomic anomalies to reduce CO2 emissions and promote CO2 sequestration in the soil, via remote sensing. Additionally, it seeks to remotely analyze farms by evaluating the spatiotemporal dynamics occurring in agroforestry activities for the same purposes.
Through data collection on land use, mapping, remote sensing and in situ data collection, an assessment of the initial state of the farm is carried out, along a carbon balance, to establish a reference scenario (baseline year). Future projections are made, and recommendations formulated.
Users appreciate this methodology because it helps them conserve or increase current carbon stocks, potentially creating a new source of income through the sale
of carbon credits. SmartAG is a highly user-friendly app which records georeferenced evidence of existing conditions and activities. It facilitates a transparent and participatory process in agroforestry ecosystem management.
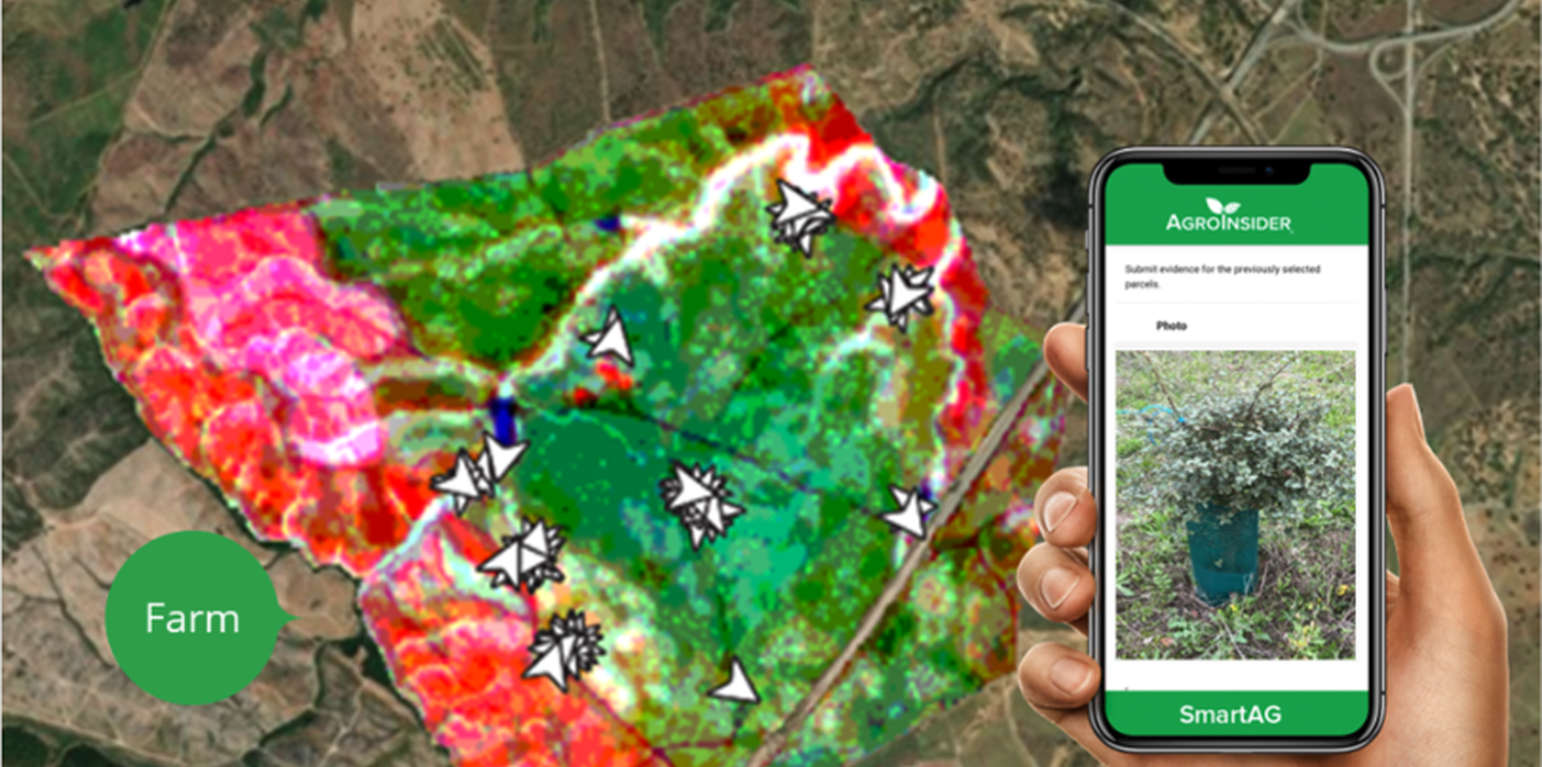
SmartAG automatically processes data from Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data, and LST data for thermo-climatic zoning. These data: i) allow monitoring, reporting and verification of farms; ii) provide machine learning capabilities in agroforestry and environmental data.
Based on Sentinel data, spectral vegetation indices are calculated to identify: i) crop anomalies related to soil-water-plant; ii) management zones to define different land uses, the selection of sampling locations and sensor installation sites, water sampling locations, and identification of species for biodiversity quantification.
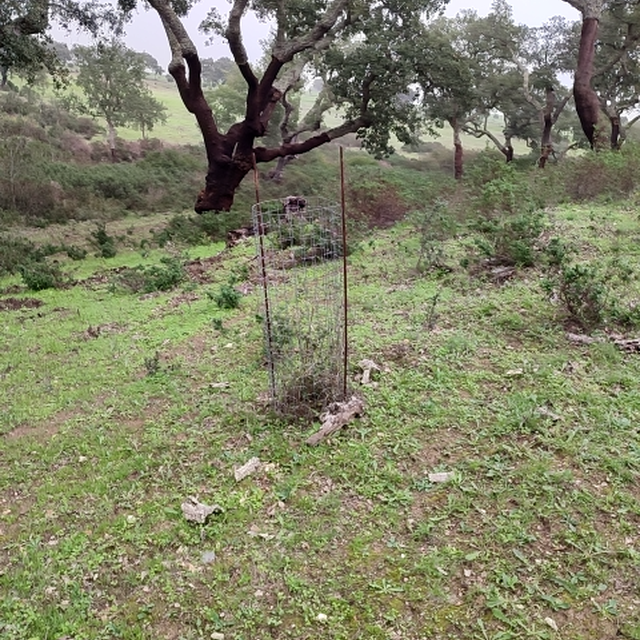
The Montado/Dehesa is a slow-developing and very complex agroforestry system meaning that differences will be observable only at the end of a year or longer. In addition, it is a highly stratified system, consisting of a complex arboreal structure with trees of different ages, shrubs, and herbaceous vegetation. Given the limitations of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 satellites it is essential to record georeferenced evidence of these. Using SmartAG app developed by AgroInsider allows the collection of georeferenced evidence (e.g., photos, audios, and videos) of
the vegetation structures, as well as documenting evidence of processes occurring such as ecosystem services and biodiversity. Georeferenced evidence is automatically uploaded into the system.
สถานที่: Alentejo, โปรตุเกส
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี: 2-10 แห่ง
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ (100000.0 km²)
In a permanently protected area?: ใช่
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: 2023
ประเภทของการแนะนำ


| Species | Count |
| sheep | 40 |
| cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu) | 40 |





| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (Euro (€)) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (Euro (€)) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Data preprocessing before heading to the field | Hour | 4.0 | 20.0 | 80.0 | |
| Field data collection | Hour | 24.0 | 20.0 | 480.0 | |
| Post-processing of field and satellite data | Hour | 4.0 | 20.0 | 80.0 | |
| Improvement suggestions | Hour | 8.0 | 20.0 | 160.0 | |
| Emission estimates | Hour | 40.0 | 20.0 | 800.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Car renting | Day | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | |
| Fuel | Km | 350.0 | 0.4 | 140.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | |||||
| Soil sampling | Samples | 3.0 | 70.0 | 210.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | |||||
| 1.0 | |||||
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 2'010.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 2'010.0 | ||||
Conservation and preservation of the Montado and Dehesa.
Estimated
Conservation and preservation of the Montado and Dehesa.
Estimated
Selling carbon credits in the voluntary market
Estimated
MRV and Implementation of improvements in Montado/Dehesa.
Estimated
MRV, Recording evidence and Implementation of improvements in Montado/Dehesa.
Measured
MRV, Recording evidence of reforestation of young growth and Implementation of improvements in Montado/Dehesa.
Estimated
MRV, Recording evidence and Implementation of improvements in Montado/Dehesa.
Estimated
MRV, Recording evidence, Calculation of emissions and Implementation of improvements in Montado/Dehesa.
Measured
MRV and Implementation of improvements in Montado/Dehesa. Estimated