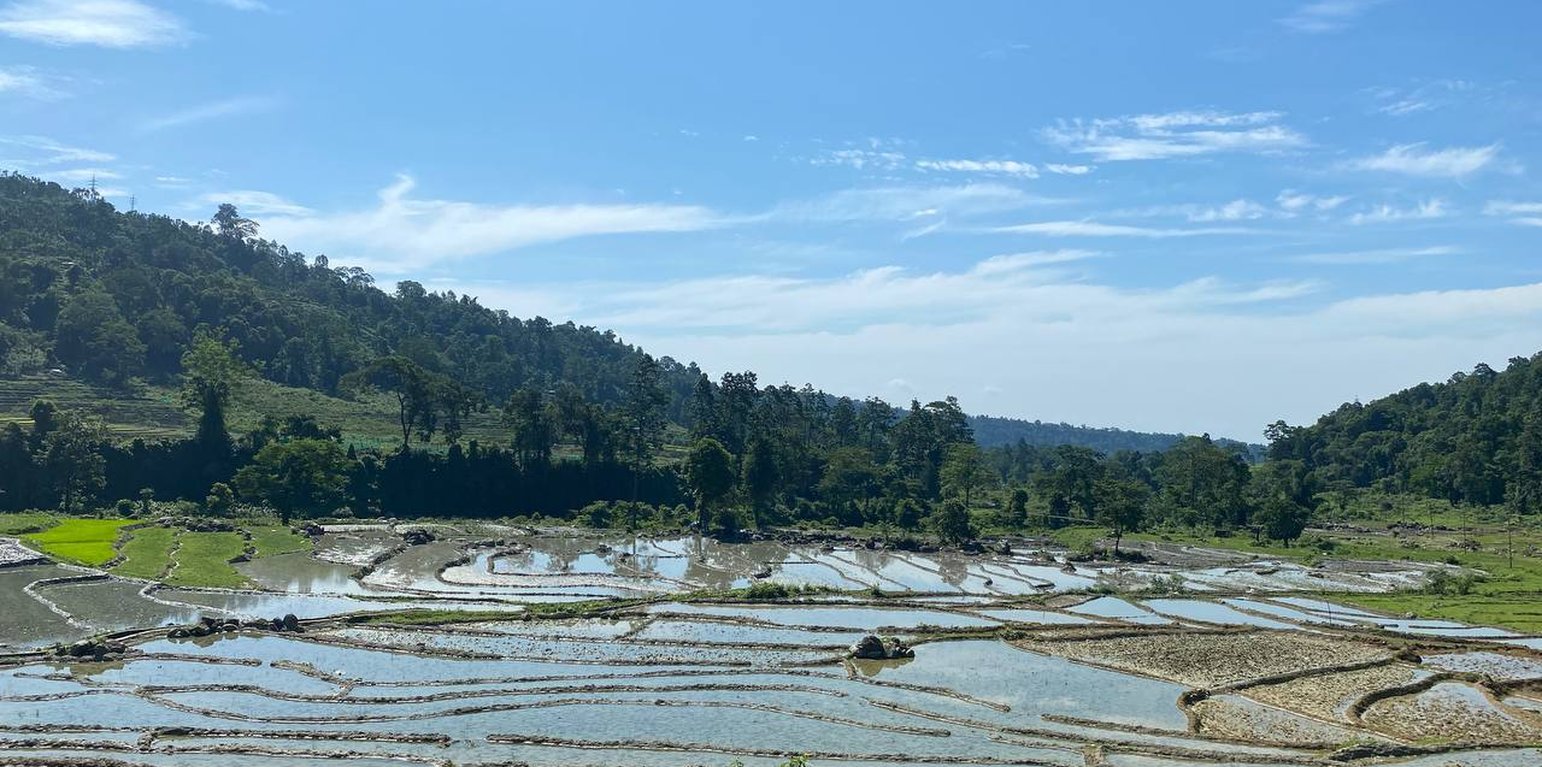




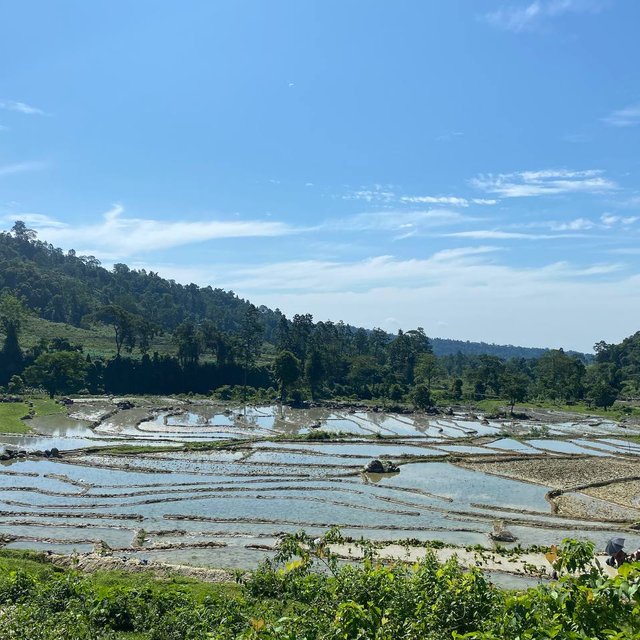
Terrace consolidation involves merging of small terraces into larger terraces using a machine to make more efficient use of land through farm mechanization, commercial farming and crop intensification. This technology is promoted as the existing terraces are generally narrow and this limits efficient operation and utilization of land and other resources.
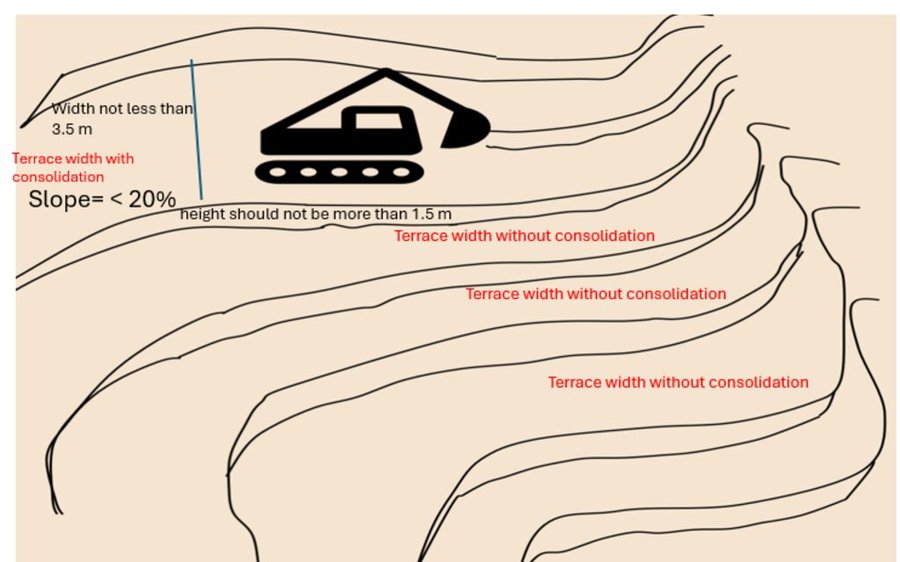
The consolidation of narrow terraces is recommended if the general slope of the proposed site is less than 20° (36%) with good soil drainage and low risk of land degradation. While consolidating narrow terraces, it is strongly recommended to remove the topsoil from the terraces and put it back once the levelling is completed. The consolidated terrace should maintain a maximum riser height of 1.5 m and bed width of 3.5 m. For slopes below 12° (21%), the bench width should not exceed 5–6 m.
Farmers can expand the amount of arable land available, maximize agricultural operations, and encourage sustainable farming methods for higher crop output and enhanced ecological resilience by converting narrower and more steep bench terraces into bigger ones (NSSC, 2020). A large portion of hillside farmers around the world rely on terracing. For the purpose of facilitating the growth of field crops, horticultural crops, fodder, and other crops that require specific management practices (e.g., irrigation), alone or in agroforestry systems, hilly or mountainous terrains are divided into narrow but graduated steps, typically 2-3 m wide and 50-80 m long across the slopes (Chapagain & Raizada, 2017).
Enlargement of terraces begins with a thorough survey and analysis of the topography and terrain. In order to build larger terraces with the least amount of environmental damage, this phase is essential. The next step in the construction process is to reshape the present, small terraces into larger, more open ones. To make wider terraced levels, this may entail moving soil and cutting through slopes. Furthermore, filling up the gaps and levelling the land's surface is required in order to reduce the number of risers and produce a continuous, gently sloping terrace. The installation of suitable drainage systems is also crucial to guarantee adequate water management and stop soil erosion.
Larger terraces enhance water management capabilities. With a more extensive surface area, water runoff is minimized, and the distribution of irrigation water becomes more even, promoting better soil moisture retention and reducing erosion. This, in turn, contributes to soil health and fertility, supporting sustainable farming practices. Moreover, the consolidation of smaller terraces into larger ones reduces the overall number of risers, thereby enhancing accessibility for farmworkers and farm machinery. This ease of access further optimizes the use of resources and fosters better crop management. Additionally, larger terraces can enable the implementation of crop diversification strategies, such as intercropping and crop rotation, promoting biodiversity and mitigating the risk of crop failure due to pests or adverse weather conditions.
However, the process of enlarging terraces involves altering the terrain, which can lead to soil erosion, habitat destruction, and ecological imbalances. This environmental impact may negatively affect local flora and fauna, reducing biodiversity and disrupting the delicate ecological equilibrium (Deng et al., 2021). Planning for safe discharge of excess water out of the terrace system effectively helps preserve soil fertility and reduces runoff. It is essential also to pay close attention to the preservation of the local ecosystem and biodiversity throughout the process.
สถานที่: Sang-Ngag-Chhoeling, Samtse, ภูฏาน
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี: 2-10 แห่ง
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ (approx. < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์))
In a permanently protected area?: ไม่ใช่
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: 2021
ประเภทของการแนะนำ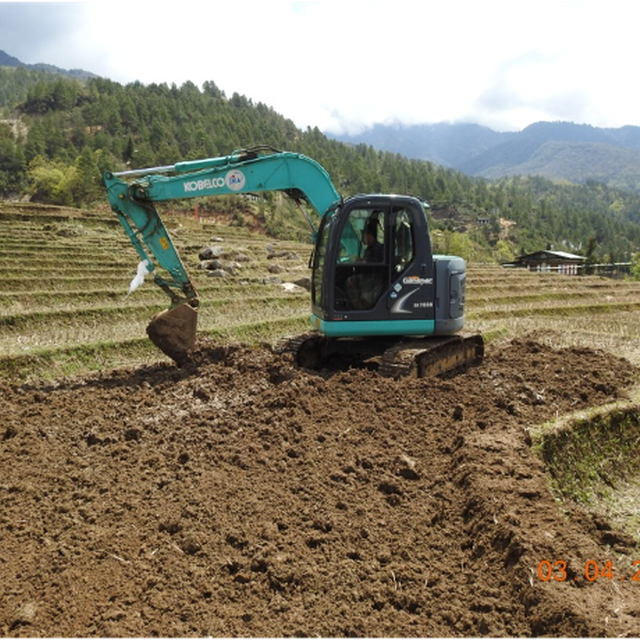




| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (Ngultrum) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (Ngultrum) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Assisting operator (reaching fuel) | no | 60.0 | 500.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| Labelling of terraces | no | 60.0 | 500.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | |||||
| Hiring of Excavator | day | 6.0 | 20000.0 | 120000.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 180'000.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 2'250.0 | ||||
Before the terrace consolidation they used to have minimum production but now they are producing for both self consumption and commercial purpose. these are expert estimates or data measured.
The merging of small terraces has increased the cropping area. These are expert estimates or data measured.
Overall Land management has become easier for them as they can use more machines due to larger flat terraces
The deployment of number of labor has reduced with the intervention of farm machineries, thus reducing the cost of production with reduced time and man power. These are expert estimates or data measured.
Farm income has increased compared to past as they have larger area of cultivation.
The time and resources saved from this technology intervention has been beneficial in for other use. These are expert estimates or data measured.
Due to mechanized farming favoured by terrace consolidation, the workload at an individual level has significantly reduced. These are expert estimates or data measured.
The increased cropping area and contributed in increase in production, thus enhancing the food and nutrition security. These are expert estimates or data measured.
The better crop productivity is found to be contributing better health quality of the farm household. These are expert estimates or data measured.
Could have better understanding on SLM and its benefits through the sensitization programs. These are expert estimates or data measured.
The flat terraces has been always been adventitious in controlling overall soil and nutrient loss. These are expert estimates or data measured.
Because of very minimum soil loss, the soil accumulation rate in these terraces has been very high. These are expert estimates or data measured.