Selection of SLM Technologies for Natural Disaster Risk Mitigation [ทาจิกิสถาน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: shane stevenson
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano, Joana Eichenberger
CAMP Kuhiston
approaches_2437 - ทาจิกิสถาน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของแนวทาง
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Pocheov Mirzokubon
+992 44 601 55 05
CAMP Kuhiston
Rudaki avenue, Dushanbe
ทาจิกิสถาน
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CAMP - Central Asian Mountain Partnership (CAMP - Central Asian Mountain Partnership) - คีร์กีซสถานชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์1.3 เงื่อนไขที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกไว้ผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล (ภาคสนาม):
10/06/2011
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การอ้างอิงถึงแบบสอบถามเรื่องเทคโนโลยี SLM
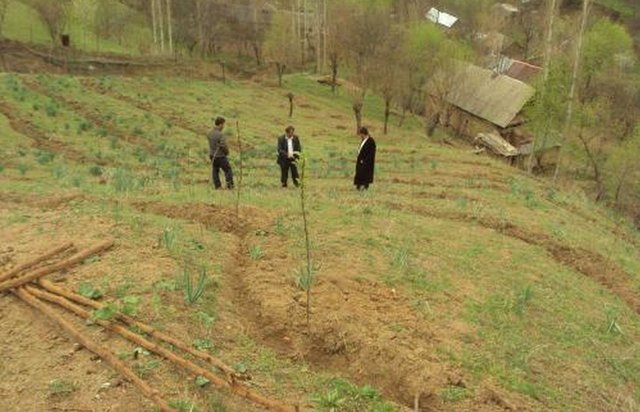

Planting of fruit trees to increase slope stabilisation [ทาจิกิสถาน]
Planting fruit tree orchards to increase the stability of the steep loess soil slopes.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Gulniso Nekushoeva
2. คำอธิบายของแนวทาง SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของแนวทาง
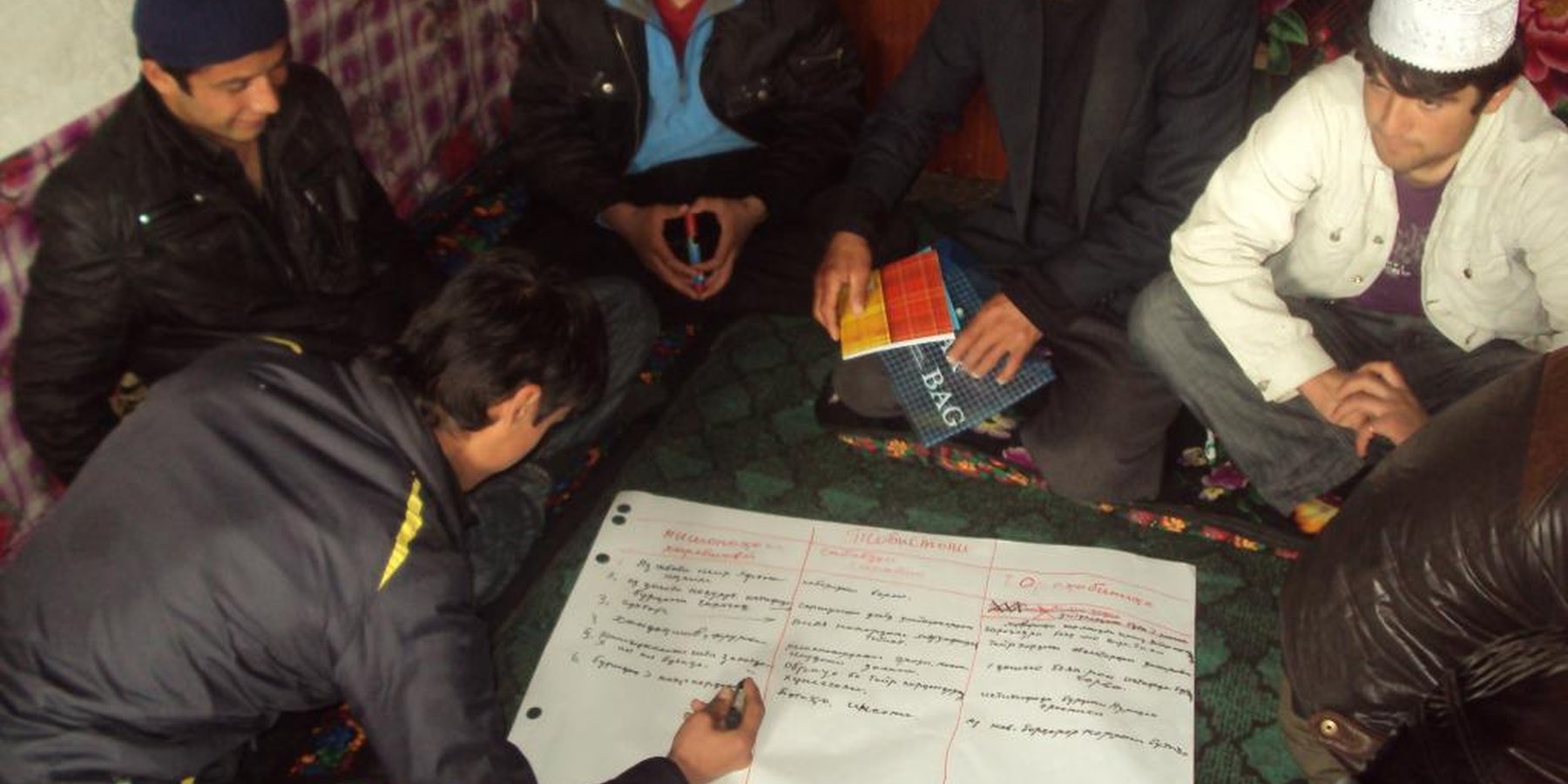
Community Based Natural Disaster Risk Management Workshops for identification of locations for the implementation of SLM technology to reduce the risk to the village from natural disasters.
2.2 การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง
การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง:
Aims / objectives: The main objective was to use a community based participatory approach to evaluate the risk from natural hazards and aid in the effective selection of location and types of SLM Technologies that could be implemented. The workshop systematically works through the natural disaster risk assessment process which includes evaluation of the natural and human triggers that can causes and contribute to specific natural disasters and subsequently rank the risk as either high/medium/low based upon a predetermined criteria. The assessment is repeated with the assumption the SLM mitigation has been implemented to evaluate whether the natural disaster risk would be reduced.
Methods: Several methodologies are used in this approach, these include the, display of posters and photos, watching documentary style DVD’s, playing awareness raising training games, and distribution of brochures to educate the communities on the causes and impacts of natural disasters so that they can then complete a systematic risk assessment process. This is undertaken within the community using interactive participatory training modules and experienced teachers. Once the technologies are decided upon a proposal form is completed and copies submitted to funding agencies and the local government. A Memorandum of Understanding is signed with the local government to endorse the approach and any subsequent implementation activities. The proposal is vetted by experts for modification and approval to ensure best practice and sustainable results.
Stages of implementation: The communities are selected based upon natural disaster statistics and a natural disaster workshop conducted for up to twenty members of the community. At the completion of the workshop the community produce several proposals for the implementation of SLM technologies that will reduce the risk from specific natural disasters. The proposals are reviewed by experts from the soil institute and horticulture institute to ensure they are practical, viable and effective before final submission to the donor for funding. The local government remains informed of the activities throughout the process and is provided with copies of the proposals.
Role of stakeholders: NGO CAMP Kuhiston were the overall project managers. CAMP designed and conducted training on Disaster Risk Reduction and developed the natural hazard risk assessment process that leads to the formulation of the SLM mitigation proposals. CAMP are also responsible for engaging the experts and providing information to the local government who are asked to support the process. The community has to actively be involved and design their own proposal and decide how they will contribute to the implementation process.
Other important information: Although this could potentially be a lengthy process it is important that the communities understand why they have chosen a specific SLM technology and the desired impact that will help secure their livelihoods.
2.3 รูปภาพของแนวทาง
2.5 ประเทศ ภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่ได้นำแนวทางไปใช้
ประเทศ:
ทาจิกิสถาน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด: :
RRS
ข้อมูลเฉพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง:
Nurabad
ความคิดเห็น:
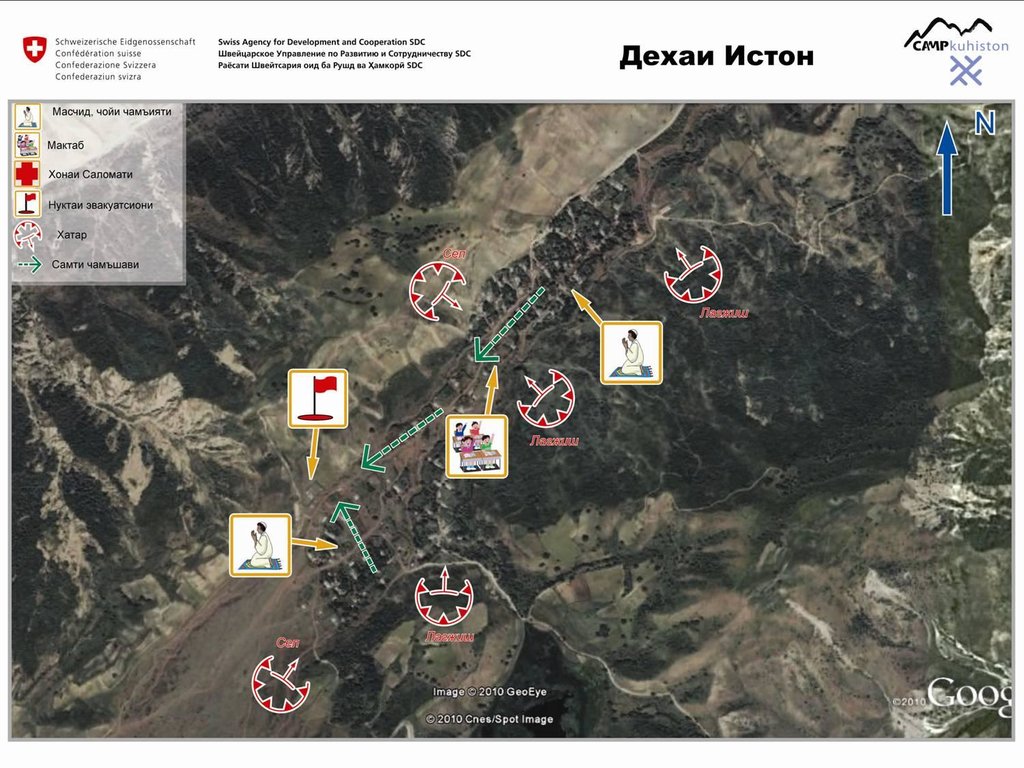
SLM was implemented in 7 different locations covering 5 villages within Mujiharf and Hakimi jamoats of Nurabad District. The two main watersheds are shown in the googleEarth file.
Map
×2.6 วันที่เริ่มต้นและสิ้นสุดของแนวทาง
ระบุปีที่เริ่ม:
2009
การสิ้นสุดลง (ถ้าแนวทางไม่ได้ใช้อีกต่อไป):
2011
2.7 ประเภทของแนวทาง
- ใช้โครงงานหรือแผนงานเป็นฐาน
2.8 เป้าหมายหรือวัตถุประสงค์หลักของแนวทาง
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (Natural Disaster Risk Mitigation)
The main objective was to educate the communities on the causes and triggers of natural disasters and how these triggers can be combated by SLM technologies. The approach concentrated on making the link between SLM technologies and causes of natural disasters. The risk assessment process helped communities understand how to evaluate the risk to their community from different types natural disasters and how these proposals would help reduce the risk presented by these types of natural disasters and also where is was the most effective and efficient use of time, finance and resources to reduce this risk.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The stabilisation of degraded slopes that increased the risk to communities from natural disaster such as mud flows, landslides, and avalanches.
2.9 เงื่อนไขที่เอื้ออำนวยหรือเป็นอุปสรรคต่อการนำเทคโนโลยีภายใต้แนวทางนี้ไปปฏิบัติใช้
บรรทัดฐานและค่านิยมทางสังคม วัฒนธรรม ศาสนา
- เป็นอุปสรรค
There were major problems incorporating women into the initial disaster risk management workshops and trainings. Therefore, there was limited input into the mitigation proposal development process.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: In some villages workshops were held separately from the men using female trainers. However, due to low educational backgrounds there was a limited the level of participation. The field training during the implementation stage managed to capture the women
การมีไว้ให้หรือการเข้าถึงแหล่งการเงินและบริการ
- เป็นอุปสรรค
There was initial concern that the farmers would not have finance to maintain the technology in the first year. The project was also conscious that fruit trees are subject to tax after three years.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Farmers were provided with a minimal payment at different stages as the SLM technology developed.
การจัดตั้งระดับองค์กร
- เป็นอุปสรรค
The Jamoat wanted to have more say in the land owners who received the trees.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: The Jamoat were taken on site visits and were explained that the land was selected because of the hazard risk, not the land owner.
กรอบแนวทางในการดำเนินการด้านกฎหมาย (การถือครองที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและน้ำ)
- เป็นอุปสรรค
There was no formal documentation to show who was the owner of the land.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: There was an informal agreement between the land user, village members and jamoat.
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights moderately hindered the approach implementation Although there are land use certificates available for farms, there are problems with allocating specific parcels of land to one particular land user. Therefore this issue needs to resolved before a technology can be implemented.
3. การมีส่วนร่วมและบทบาทของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้อง
3.1 ผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้องในแนวทางนี้และบทบาท
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น
Five local communities (20 people per community)
Individual land users were involved in workshops and planning of SLM Technology
Community were involved in workshops
Women particpitaed less, since there are noticeable gaps in the education levels of the genders and women fulfill a more traditional role centered around the household.
This area suffers from high levels of labour migration with many of the men working abroad in countries such as Russia. In particular separate workshops were held for women to ensure that they participated in the approach.
- ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM หรือที่ปรึกษาการเกษตร
Specialists were involved in selection of location of implementation
- องค์กรพัฒนาเอกชน
CAMP Kuhiston
CAMP Kuhiston developed the approach in collaboration with international support, land users, academic institutions, the local community and local government.
- รัฐบาลระดับท้องถิ่น
Jamoats, Khukhmats
- รัฐบาลแห่งชาติ (ผู้วางแผน ผู้ทำการตัดสินใจ)
Tajik Soil Institute, Horticulture Institute,
- องค์การระหว่างประเทศ
Voluntary Services Overseas, University of Bern
ถ้ามีผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียหลายคนที่เกี่ยวข้องให้ระบุหน่วยงานตัวแทน:
CAMP Kuhiston
3.2 การเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่นในช่วงต่างๆของแนวทาง
| ความเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น | ระบุผู้ที่มีส่วนเกี่ยวข้องและอธิบายกิจกรรม | |
|---|---|---|
| การริเริ่มหรือการจูงใจ | ไม่มี | |
| การวางแผน | ไม่มี | |
| การดำเนินการ | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | Involved in the workshops and the development of the proposals |
| การติดตามตรวจสอบหรือการประเมินผล | ไม่มี | |
| Research | ไม่มี |
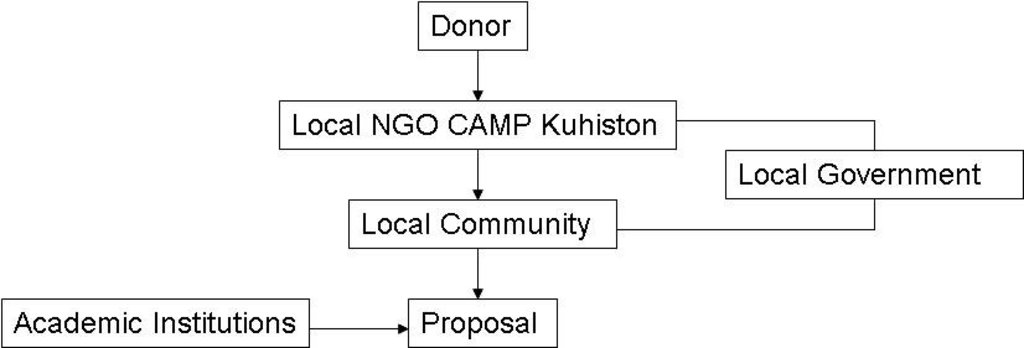
3.3 แผนผังแสดงขั้นตอนการทำงาน (ถ้ามี)
คำอธิบาย:
Organisation chart showing how the proposal for the SLM technology developed.
ผู้เขียน:
S. Stevenson (CAMP Kuhiston)
3.4 การตัดสินใจเลือกใช้เทคโนโลยี SLM
ระบุผู้ที่ทำการตัดสินใจเลือกเทคโนโลยีมากกว่าหนึ่งวิธีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
- ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM เป็นผู้ตัดสินใจหลัก ที่ติดตามให้คำปรึกษากับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
การอธิบาย:
SLM specialists made the decision on the SLM technology, but consulted with the land users before implementation.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by NGO CAMP Kuhiston. NGO CAMP combined two funded projects to develop the approach for the implementation to the SLM technology with consultation from the Tajik Soil Institute and the Horticultural Institute.
4. การสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค การสร้างขีดความสามารถ และการจัดการด้านความรู้
4.1 การสร้างขีดความสามารถ / การอบรม
ได้มีการจัดอบรมให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดินหรือผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียคนอื่น ๆ หรือไม่:
ใช่
ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้ได้รับการอบรม:
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
- 20 members of five communities received training.
ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง ให้ระบุ เพศ อายุ สถานภาพ ชาติพันธุ์ เป็นต้น:
The training on the risk assessment process included all members of the community, although due to the conservative nature of the community some trainings were divided between women and men.
รูปแบบการอบรม:
- กำลังดำเนินการ
- จัดคอร์ส
หัวข้อที่พูด:
The initial training were on natural disasters, their casues and impacts. Subsequent training is the communites covered soil and water conservation and fruit cultivation.
4.2 การบริการให้คำแนะนำ
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินมีการเข้าถึงการรับบริการให้คำปรึกษาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
4.3 การเสริมความแข็งแกร่งให้กับสถาบัน (การพัฒนาองค์กร)
สถาบันได้รับการจัดตั้งขึ้นมาหรือเสริมความแข็งแกร่งโดยแนวทางนี้หรือไม่:
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
ระบุระดับของสถาบันที่ได้รับการเสริมความแข็งแกร่งหรือจัดตั้งขึ้นมา:
- ท้องถิ่น
ระบุประเภทของการให้ความช่วยเหลือสนับสนุน:
- การสร้างขีดความสามารถ / การอบรม
ให้รายละเอียดเพิ่มเติม :
Two academic institutions were financially supported to undertake the review and evaluation process. Local NGO camp was supported by international finance to implement the approach and subsequent activities.
4.4 การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผล
การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผลเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ใช่
ความคิดเห็น:
no. of land users involved aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: The level of involvement in the workshops by the land users.
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: The level of engagement of the government and of the women in the process.
management of Approach aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: International staff provided informal monitoring of the approach.
technical aspects were ad hoc monitored by other through observations; indicators: The academic institutions reviewed the proposals.
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: The risk assessment process was simplified and the format of the proposals was made more understandable to the participants.
There were few changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: The monitoring of the SLM technology means that for replication of the technology there would be changes in tree species selected.
4.5 การวิจัย
การวิจัยเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ใช่
5. การสนับสนุนด้านการเงินและวัสดุอุปกรณ์
5.1 ระบุงบประมาณประจำปีสำหรับแนวทาง SLM นี้
ถ้าหากว่างบประมาณประจำปีไม่เป็นที่ทราบแน่นอน ให้ระบุช่วงลงไป:
- 10,000-100,000
แสดงความคิดเห็น (แหล่งของการระดมทุน ผู้บริจาคคนสำคัญ):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international non-government (International Consultants): 5.0%; international (Swiss Coorperation for Development and PAMS): 90.0%; local community / land user(s) (Local community support in kind): 5.0%
5.2 การสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินได้รับการสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ไปปฏิบัติใช้เทคโนโลยีหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.3 เงินสนับสนุนสำหรับปัจจัยนำเข้า (รวมถึงแรงงาน)
- วัสดุสำหรับการก่อสร้าง
| ระบุปัจจัยนำเข้าที่ได้รับการสนับสนุน | เห็นด้วยระดับไหน | ระบุเงินสนับสนุน |
|---|---|---|
| ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินบางส่วน | ||
| ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินบางส่วน | ||
- อื่น ๆ
| อื่นๆ (ระบุ) | เห็นด้วยระดับไหน | ระบุเงินสนับสนุน |
|---|---|---|
| training materials | ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินแบบเต็ม | posters, stationery and teachers salary |
ถ้าแรงงานโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินเป็นปัจจัยนำเข้าที่มีอยู่มากมาย ระบุด้วยว่าเนื่องจาก:
- สมัครใจ
ความคิดเห็น:
The approach was financed by funds from a donor.
5.4 เครดิต
มีการจัดหาเครดิตมาให้ภายใต้แนวทาง SLM หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 แรงจูงใจหรือเครื่องมืออื่น ๆ
แรงจูงใจหรือเครื่องมืออื่น ๆ ได้ถูกนำไปใช้ส่งเสริมการใช้เทคโนโลยี SLM หรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
Two academic institutions were financially supported to undertake the review and evaluation process. Local NGO camp was supported by international finance to implement the approach and subsequent activities.
6. การวิเคราะห์ผลกระทบและการสรุป
6.1 ผลกระทบของแนวทาง
ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ที่ดินนำเอาเทคโนโลยี SLMไปใช้และบำรุงรักษาสภาพไว้ได้หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
The approach provided the land users with training, saplings and construction material to use the land in a more sustainable way.
ทำให้กลุ่มด้อยโอกาสมีอำนาจทางสังคมและเศรษฐกิจหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
In some communities the women received specific training on the risk assessment process.
ปรับปรุงประเด็นของการถือครองที่ดินหรือสิทธิในการใช้ ซึ่งขัดขวางการนำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้ให้ดีขึ้น:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Where the technology was implemented, it made the community address the issue of land user rights. It is now apparent who is responsible for the SLM technology and for payment taxes on the land.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Trainings were provided to other NGO's on the Natural Disaster Risk Assessment process and the development of proposals. The success of this has not been monitored.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
It improved their knowledge through training on Natural Disaster and on fruit cultivation and through the distribution of accompanying brochures.
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
If the subsequently implemented technologies should help safeguard houses, land and livelihoods.
6.2 แรงจูงใจหลักของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเพื่อที่จะนำ SLM ไปปฏิบัติใช้
- การผลิตที่เพิ่มขึ้น
fruit crops within 3-5 years
- กำไร (ความสามารถ) อัตราส่วนค่าใช้จ่ายต่อผลประโยชน์ที่เพิ่มขึ้น
land previously had limited economic output.
- เกียรติภูมิ แรงกดดันทางสังคม ความเชื่อมแน่นทางสังคม
Government decree to plant trees
- จิตสำนึกด้านสิ่งแวดล้อม
To decrease the communities exposure to natural disasters.
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
SLM technology should improve the livelihood of the land users.
6.3 ความยั่งยืนของกิจกรรมของแนวทาง
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินสามารถทำให้สิ่งต่างๆ ที่ได้ปฏิบัติใช้โดยแนวทางนี้ยั่งยืนได้หรือไม่ (โดยไม่มีการสนับสนุนจากภายนอก):
- ไม่
ถ้าตอบว่าไม่หรือไม่แน่ใจ ให้ระบุและแสดงความคิดเห็น :
The land users are not in a position to mobilise all the parties involved in the approach.
6.4 จุดแข็งและข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทาง
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทางในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| The process allowed me to make decisions concerning my own village. |
| The training improved my understanding of human and environmental causes of natural disasters. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทางในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| The approach involved a range of stakeholders and experts who were all able to actively contribute. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: This could be enhanced by continued collaboration between all parties. ) |
| The approach included a community training element that benefited a broader range than just the land users. |
| The approach involved mobilisation of local government and community participation. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Further collaboration on technologies between the community and local government. The government to initiate replication in other communities. ) |
| The approach helped link the prevention of natural disaster with SLM practices. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: The community developing further proposals for technologies and seeking funding to implement them.) |
6.5 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบของแนวทางและวิธีในการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | สามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| To provide more support on alternatives for SLM technologies. There must be new technologies that we are not aware of. | Further develop the modul to provide further illustrations of best practice. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | สามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The approach covers only a one year period, therefore if the SLM technology has difficulties, such as disease which is highly prevalent in this area, the land owner may not be in a financial position to rectify the issue. | A longer monitoring and support period. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการหรือแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Planting of fruit trees to increase slope stabilisation [ทาจิกิสถาน]
Planting fruit tree orchards to increase the stability of the steep loess soil slopes.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Gulniso Nekushoeva
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล