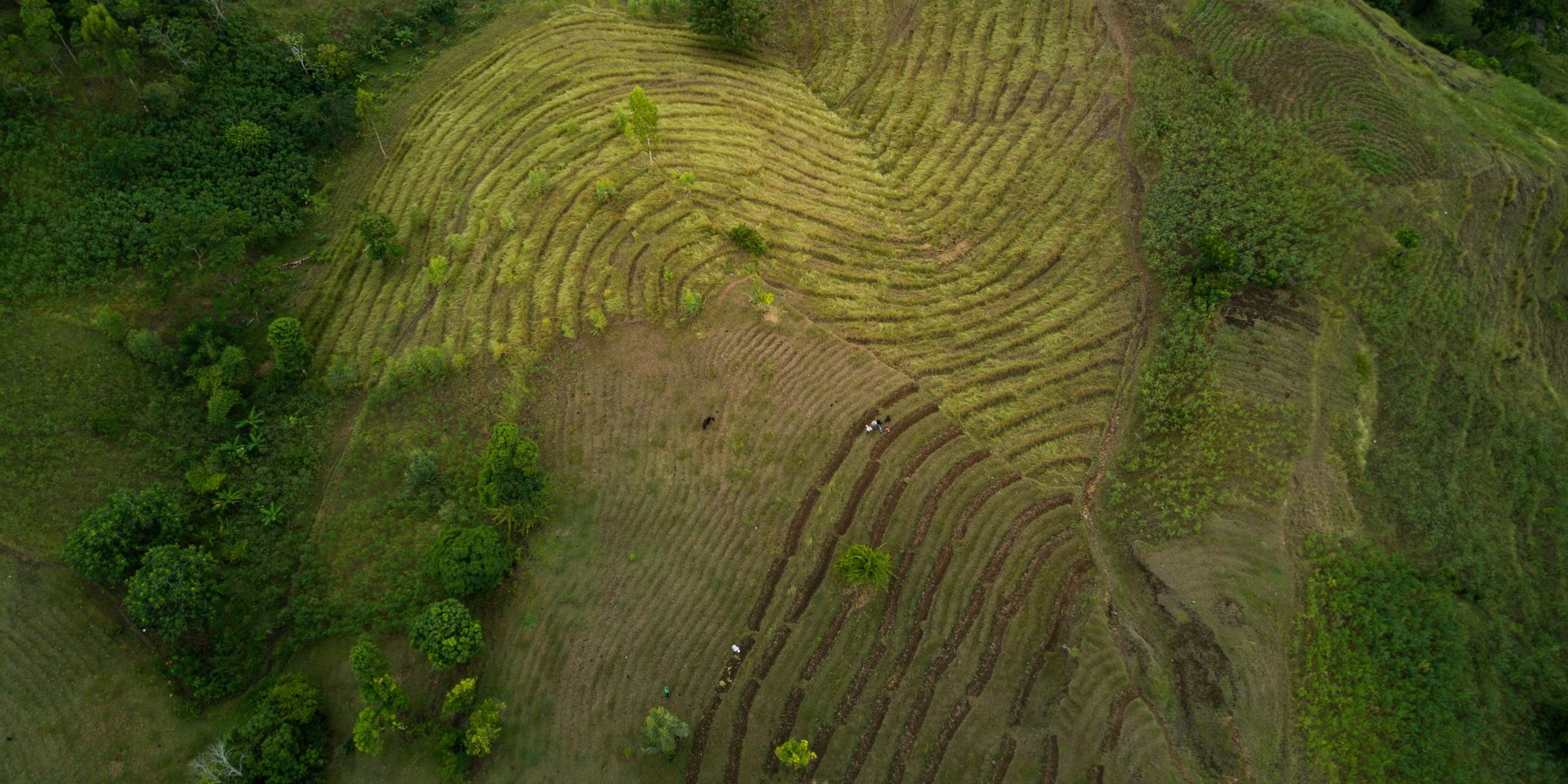
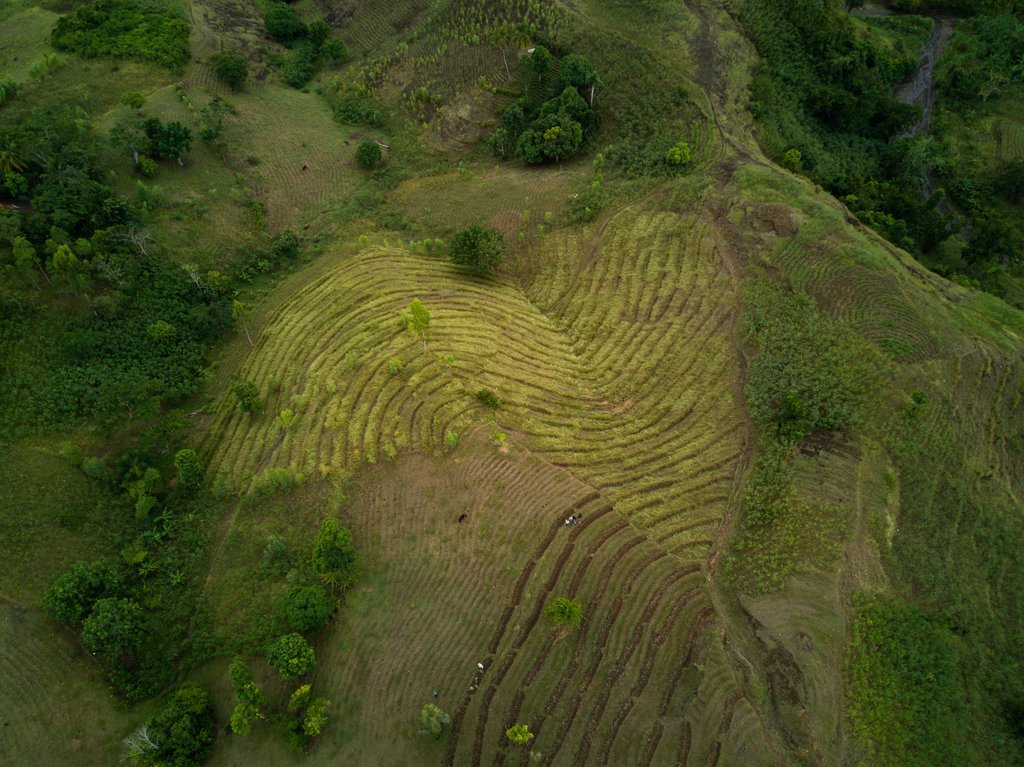
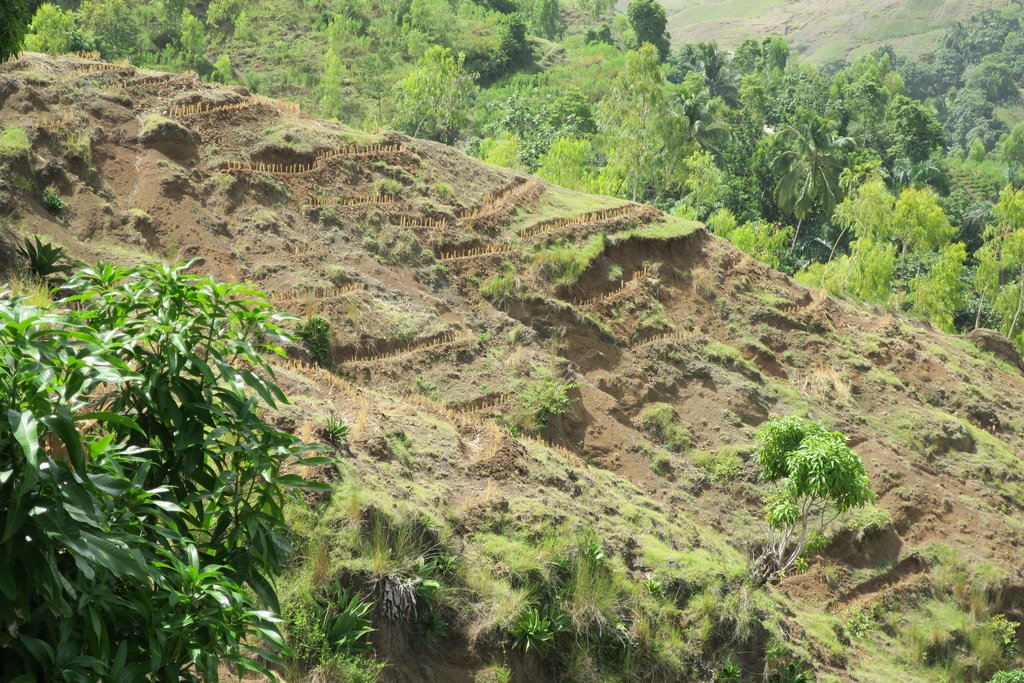
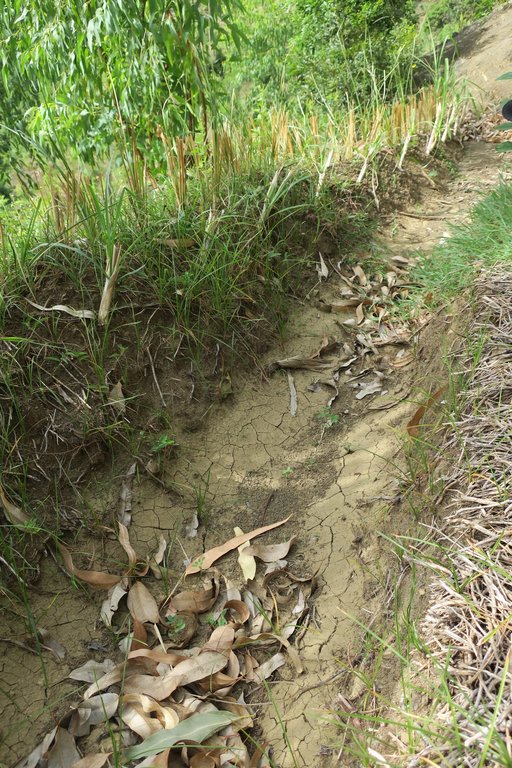
Progressive bench terraces formed by a vetiver hedge system and trees [เฮติ]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Joana Eichenberger
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Jean Carls Dessin, Hanspeter Liniger
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Hanspeter Liniger
Ranp vivan (fran. rampes vivantes)
technologies_3223 - เฮติ
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF เพื่อพิมพ์
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปหน้าเว็บ
- บทสรุปทั้งหมด (ไม่มีการจัดเรียง)
- Progressive bench terraces formed by a vetiver hedge system and trees: 23 กุมภาพันธ์ 2019 (inactive)
- Progressive bench terraces formed by a vetiver hedge system and trees: 16 มิถุนายน 2020 (inactive)
- Progressive bench terraces formed by a vetiver hedge system and trees: 16 เมษายน 2020 (inactive)
- Terrassement progressif à vétiver: 16 กุมภาพันธ์ 2019 (inactive)
- Progressive bench terraces formed by a vetiver hedge system and trees: 27 มิถุนายน 2021 (public)
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
Technician:
เฮติ
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Swiss Red Cross (Swiss Red Cross) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
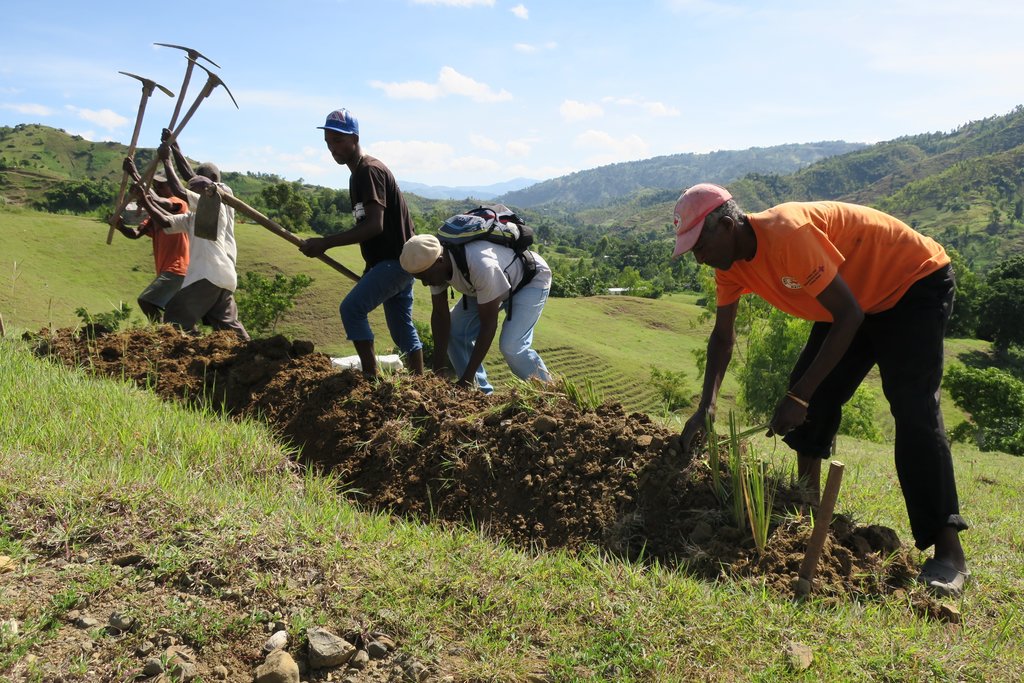
The progressive terracing technology results from successive deposits of sediments upstream of any other anti-erosional structure, in this case vetiver grass hedges (vetiveria zizanioides). To better stabilize the slopes in the long-term, new trees are planted downstream of the vetiver hedges.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
The technology can be implemented wherever slopes are being cultivated. Ideally, it would be applied as a preventive measure in lands where the land is still in good condition. In Haiti, however, the Swiss Red Cross (CRS) uses it instead as a restoration measure where soil has already been degraded by surface erosion. The principle of terracing consists of reshaping the terrain of a given slope into a succession of steep slopes and platforms with little or no gradient. Progressive terraces result from successive deposits of sediments upstream of any other anti-erosion structure. To make the anti-erosive structure, the CRS in Haiti uses mostly vetiver grass because vetiver 1) has deep roots, 2) can be cut and used as mulch and 3) is easily accessible and well known in Haiti thanks to the fragrance industry. Below (downstream) the vetiver hedges, tree seedlings are planted to better stabilize the soil in the long-term. Ideally, fruit trees would be planted so that land users could benefit more. However, if the soil is to degraded, forest trees are better suited since they are less demanding. Between the vetiver hedges, the landholders can cultivate crops. It is recommended not to use crops whose roots are consumed (potatoes, peanuts, cassava, etc.), but to plant legumes that fix nitrogen and / or perennial crops. From time to time vetiver can be cut and used as mulching.
The progressive terracing with vetiver has two objectives: On the one hand, by stabilizing the slopes with its deep roots and by retaining the rainwater runoff and the eroded sediments in the canals upstream the hedges, this technology protects communities and crops downstream against landslides, floods and siltation. On the other hand, the terraces are supposed to have a favorable effect on the water sources: by retaining it in the channels, the water can infiltrate more easily into the ground and recharge the aquifers. Like that, in times of drought, the water table has more reserve of water. In addition, this technique has the advantage of restoring degraded slopes since the sediments accumulated in the canals are fertile and allow agriculture between the terraces.
Unlike mechanical terraces, progressive terraces need less work for setting up. They are also less expensive than dry stone terraces and it is easier to transport vetiver plants than stones.
The disadvantage is that land users are afraid of losing arable land with this technology. They exploit their plots as much as possible and apply it only when the soil is completely degraded. Another disadvantage is that the oil extracted from the roots of vetiver is very sought-after in the fragrance industry. Therefore, from time to time there are people who dig up the vetivers in order to sell its roots.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เฮติ
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Département de l'Ouest
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Léogâne
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 0.1-1 ตร.กม.
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2014
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ป้องกันพื้นที่ลุ่มน้ำ/บริเวณท้ายน้ำ โดยร่วมกับเทคโนโลยีอื่นๆ
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
- adapt to steep slopes
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- oilseed crops - groundnuts
- cereals - maize
- root/tuber crops - sweet potatoes, yams, taro/cocoyam, other
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- banana/plantain/abaca
- sugar cane
- pigeon peas
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Mar-May and Sep-Oct
Is intercropping practiced?
ใช่
If yes, specify which crops are intercropped:
pigeon peas and sweet potatoes

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
- ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
Tree plantation, afforestation: Specify origin and composition of species:
- การปลูกหลายพันธุ์รวมกัน
Are the trees specified above deciduous or evergreen?
- deciduous
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- ผลไม้และถั่ว
- การอนุรักษ์ / ป้องกันธรรมชาติ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
This technology can be implemented wherever slopes are being cultivated. Normally the technology is used as a restoration measure when the soil has already been degraded by weeded/ ploughed crops.
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- oilseed crops - groundnuts
- cereals - maize
- root/tuber crops - sweet potatoes, yams, taro/cocoyam, other
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- banana/plantain/abaca
- sugar cane
- pigeon peas
Is intercropping practiced?
ใช่
If yes, specify which crops are intercropped:
pigeon peas and sweet potatoes

ที่ดินที่ไม่ให้ผลผลิต
ระบุ:
The soil has been too degraded by the weeded/ploughed crop practice and has become unproductive.
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
- การลดความเสี่ยงจากภัยพิบัติบนพื้นฐานของระบบนิเวศ
- In the long term: agroforestry
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S1: คันดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
A2: Vetiver grass can be cut and used for mulching.
V1: The SRC combines the technology of progressive terracing with vetiver hedges with reforestation.
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
- Wm (Mass movement): การเคลื่อนตัวของมวลดินหรือดินถล่ม
- Wo (Offsite degradation): ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
- Hs (Change in quantity of surface water): การเปลี่ยนแปลงปริมาณของน้ำที่ผิวดิน
- Hg (Change in groundwater): การเปลี่ยนแปลงของน้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
- Hp (Decline of surface water quality): การลดลงของคุณภาพน้ำที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Hg: assumption
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Ideally, the technique would be applied to prevent degradation, but in Haiti, it is used as a measure to reduce land degradation and to restore severely degraded land.
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
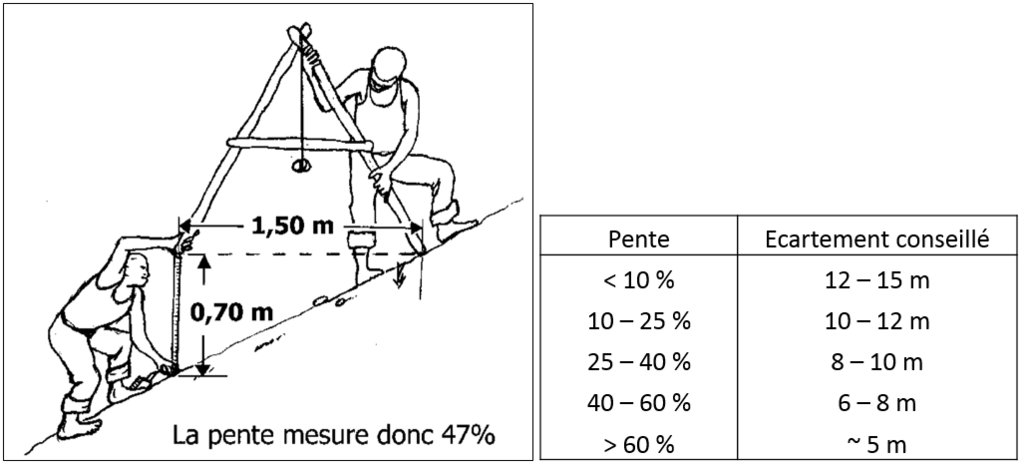
In order to implement this technology, the average slope has to be measured first. This is done with a "A-level"-called instrument. By placing one foot to the A-level and raising the lower foot (downstream in the direction of the slope), the A-level should be placed in a horizontal position. The slope corresponds to p=h/l*100, for p = slope, h = distance from the downstream foot of A-level to the ground, and l = distance between the two feet of level A. The average slope defines the distance between the vetiver lines. The steeper the slope, the smaller the distance.
ผู้เขียน:
Régis and Roy
วันที่:
1999
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
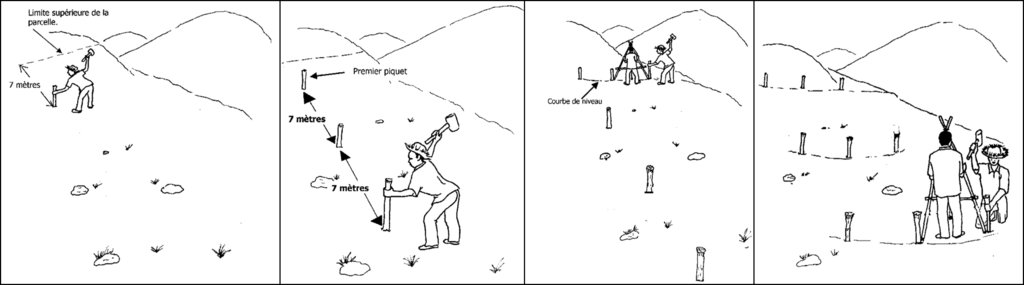
After having calculated the average slope of the terrain, one can start picketing the contour lines where the vetivers will be planted. First, an alignment in the direction of the slope from upstream to downstream is done by planting stakes. The first stake is placed at the upper limit of the plot, the distance the other stakes is a function of the average slope of the terrain (here: 50% --> 7m). This alignment forms the baseline. Once the baseline is set, the contour lines can be picketed. This is done again with the A-level instrument.
ผู้เขียน:
Régis and Roy
วันที่:
1999
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
In a third step, channels (about 30cm deep) are dug following the picketed contour lines. The material removed is used to form ridges downstream of the channels. On the ridges, vetiver cuttings are planted every 10-15cm.
ผู้เขียน:
Joana Eichenberger
วันที่:
03/10/2017
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
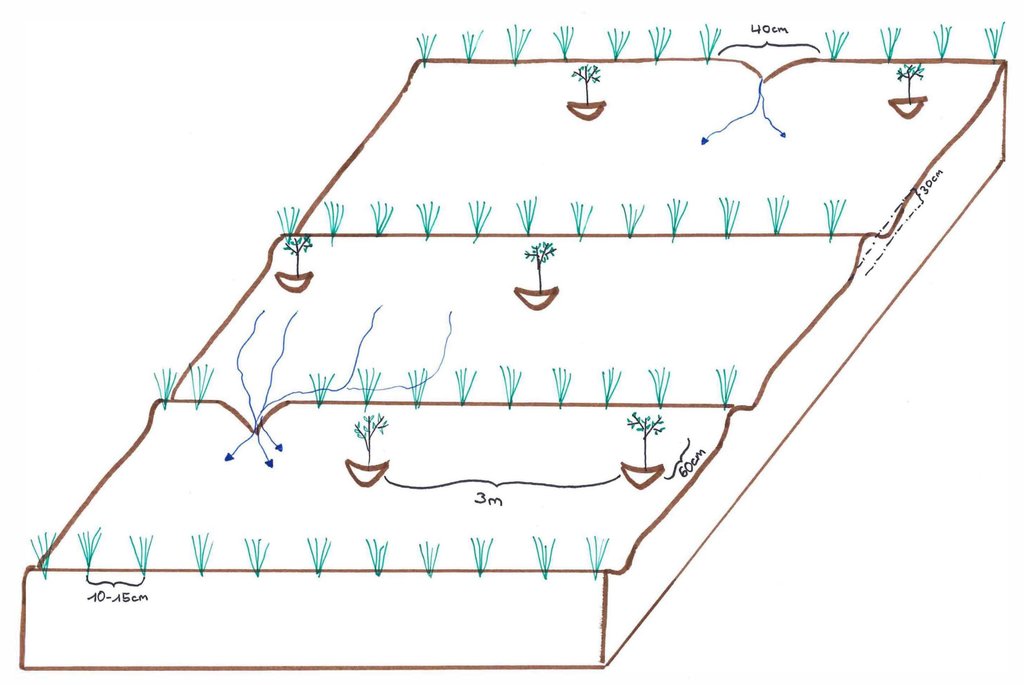
It is recommended to leave a space of approx. 40cm in each line (see drawing). These spaces a) facilitate the passage for the land users once the vetiver grass is high and b) make it possible for extra water to escape (if there is too much water accumulated in the channels, the ridgesmay break). 60cm downstream of the vetiver hedges, fruit or forest tree seedlings are planted every 3m. After about three months, the roots of the vetivers are deep enough. Depending on the soil degradation’s degree, land users may begin to cultivate the spaces between the lines.
ผู้เขียน:
Joana Eichenberger
วันที่:
29/06/2018
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อหน่วยเทคโนโลยี
โปรดระบุหน่วย:
Vetiver line
Specify dimensions of unit (if relevant):
200m
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
HTG
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
62.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
200 HTG per person and day
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | If necessary: deforest the plot | |
| 2. | Measure the slope with A-level and calculate the necessary distance between the lines of vetiver | |
| 3. | Mark out the contour lines (put a stake every 3m) | Beginning of the rainy season so that the vetiver can grow well -> March / April |
| 4. | Dig a channel following marked contour lines | March / April |
| 5. | Plant the vetiver seedlings every 10-15cm on the ridges of soil below(downstream) the canal | March / April |
| 6. | Plant the tree seedlings every 3m below (downstream) the vetiver lines | March / April |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Unskilled labourer | person-days | 20.0 | 200.0 | 4000.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Skilled labourer | person-days | 5.0 | 1000.0 | 5000.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Machete | pieces | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Pickaxe | pieces | 3.0 | 5.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | A-level | pieces | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Hoe | pieces | 5.0 | 5.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Vetiver grass | cuttings | 2000.0 | 2.0 | 4000.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Trees | cuttings | 67.0 | 50.0 | 3350.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 16400.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 264.52 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
Unskilled labour is provided by the community based organizations (OCB). The Swiss Red Cross offers a technician (skilled labor). The equipment (hoes, picks, ...) are provided by labouers themselves or the OCBs. Vetiver and tree cuttings are provided by the community.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Replant dead cuttings | 2 times a year |
| 2. | Reparing broken ridges | 2 times a year |
| 3. | Verify if ridges are ok | In the beginning once a month, after that only once every three months |
| 4. | Cultivate normally | From tree months after implementation |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Land user and his family (monthly check, 1/2 day of work for 200m) | person-days | 6.0 | 200.0 | 1200.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Replanting dead cuttings and reparing ridges (2 times a year total 5 working days for 20 people) | person-days | 100.0 | 200.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Hoe | pieces | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Vetiver cuttings replaced after rainy season (5%) | cuttings | 65.0 | 2.0 | 130.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Vetiver cuttings replaced after dry period (40%) | cuttings | 533.0 | 2.0 | 1066.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 22401.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 361.31 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
Labor is provided by the OCBs. The equipment (hoes, picks, ...) are provided by labourers themselves or OCBs. Vetiver and tree cuttings are provided by the community
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The costs depend a lot on the proportion of the damage and the damage depends on the weather. It is recommended to implement the measurement at the begining of the rainy season.
Land users have the necessary tools (the 5 HTGs are budgeted as compensation cost for using their own tools).
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
1) Skilled labourers
2) Maintenance costs depends very much on the weather: if it rains too much, runoff destroys the ridges by forms gullies and remove the vetiver cuttings which were not sufficiently rooted. If it does not rain enough during the first weeks, the vetivers can not form roots, dry out and must be replaced.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
The windward sides (north slopes) receive up to three times more rain than the lee sides.
Dry season1: Nov-Mar
Rainy season1: Apr-Mai
Dry season2: Jun-Jul
Rainy season2: Aug-Oct
(Due to climate change, the first rainy season tends to starts later than it used to)
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Mean annual temperature: 25-27°C
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
In Haiti this technology is applied on very degraded sites with very shallow soil. But normally it is advisable to have a ground of a minimum of 25cm of depth (Régis and Roy 1999).
The technology can be applied everywhere, therefore, the soil can be sandy, loamy/silty or clay
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- สูง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- สูง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- ผู้เยาว์
- วัยกลางคน
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users age: young, middle-aged and elderly.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
- ขนาดกลาง
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As the land was too degraded, one has to patient. But in the long run agricultural production will increase.
คุณภาพพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As the land was too degraded, one has to patient. But in the long run crop quality will increase.
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำดื่มไว้ให้ใช้
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As the land was too degraded, one has to patient. But in the long run farm income will increase.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As the land was too degraded, one has to patient. But in the long run food security will increase.
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
การระเหย
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
การสะสมของดิน
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากน้ำท่วม
ดินถล่ม/ ซากต่าง ๆ ที่ถูกพัดพามา
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
ผลกระทบของพายุไซโคลน พายุฝน
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
ภูมิอากาศจุลภาค
Specify assessment of on-site impacts (measurements):
The impacts are just estimates, they have not been quantified yet.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
Specify assessment of off-site impacts (measurements):
The impacts are just estimates, they have not been quantified yet.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุเขตร้อน | ดี |
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ดินถล่ม | ดีมาก |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The first period of rain is shifting (March-May -> April-June);
For vetiver grass, the first 3 months are decisive: there must be neither too much nor too little rain. After these three months, the drought has a negligible impact.
The SRC receives many positive feedbacks on this technology. The communities appreciate its benefits.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
If the slopes were too degraded, it is necessary to wait a few months / years until land users can enjoy the benefits of this technology.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ใช่
อื่น ๆ (ระบุ):
Terrain conditions
ให้ระบุการปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี (การออกแบบ วัสดุหรือชนิดพันธุ์ เป็นต้น):
The Swiss Red Cross has tried out this technology by using sugar cane instead of vetiver. But since vetiver has deeper roots and is more resistant to dry periods, the SRC abandoned the variation with sugar cane.
If the ground is too degraded it is not necessary to make long lines of vetiver with always the same distance between one and the other (see the photo under description). We must adapt to the terrain.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| vegetable matter for mulching |
| sediment retention |
| increased soil moisture |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| smoothens the slope |
| recuces soil erosion |
| improves soil fertility |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Land users believe this technology recuces the arable surface. | It is necessary to increase the land users awareness regarding the benefits of the technology, like for example the productivity which increases. |
| The implementation of the technology is very labour-intensive. | Show that other technologies give even more work (e.g. progressive terraces with dry stones) |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The technique with vetiver grass depends on rain and as a result it is more vulnerable than dry stone technology. | The dry stone technology is only applied where there are stones locally available. Otherwise buying the stones and transporting them would cost too much. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
28/09/2017
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล