Planted Vegetative Strips (PVS) [ฟิลิปปินส์]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1105 - ฟิลิปปินส์
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Crisologo Victor
Cagayan Valley Integrated Agricultural Resources Research Center (CVIARRC)
ฟิลิปปินส์
1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
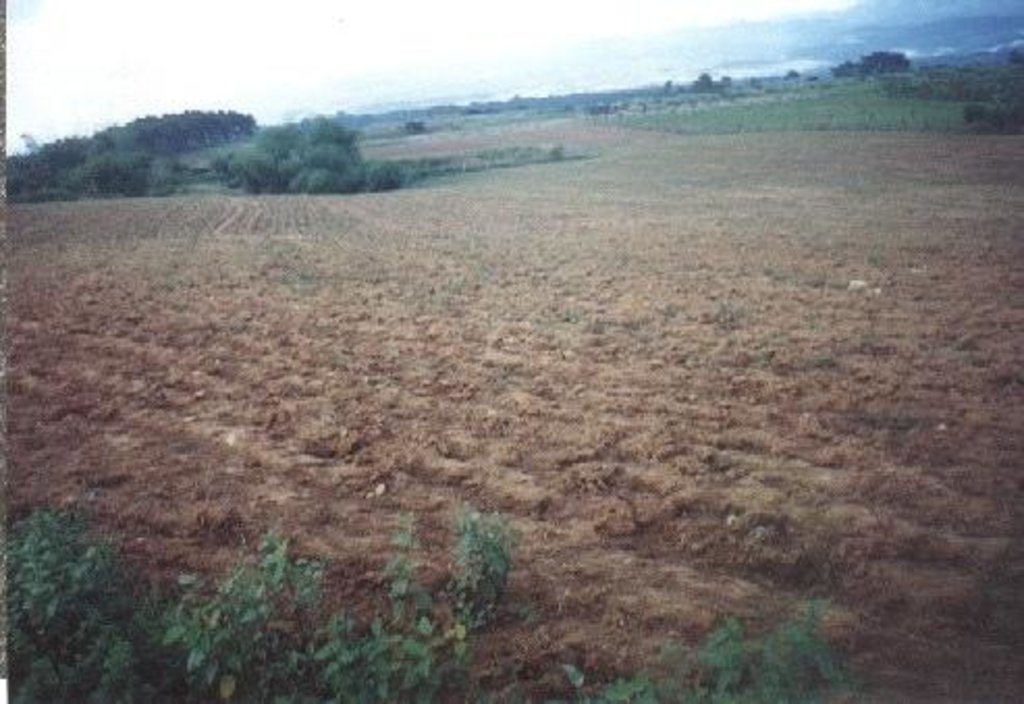
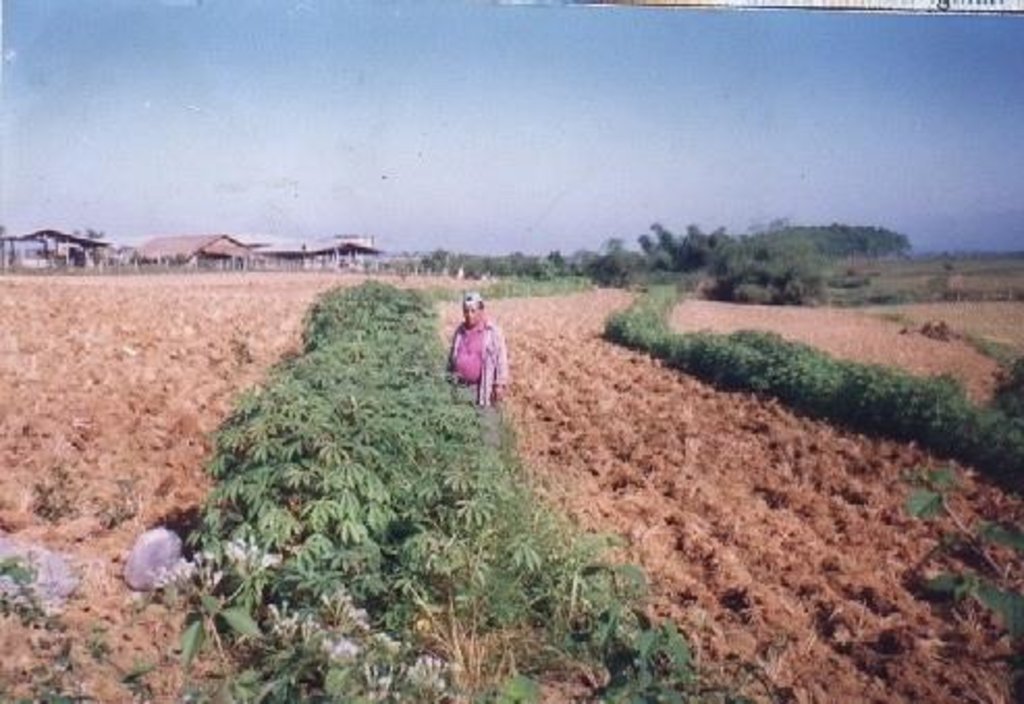
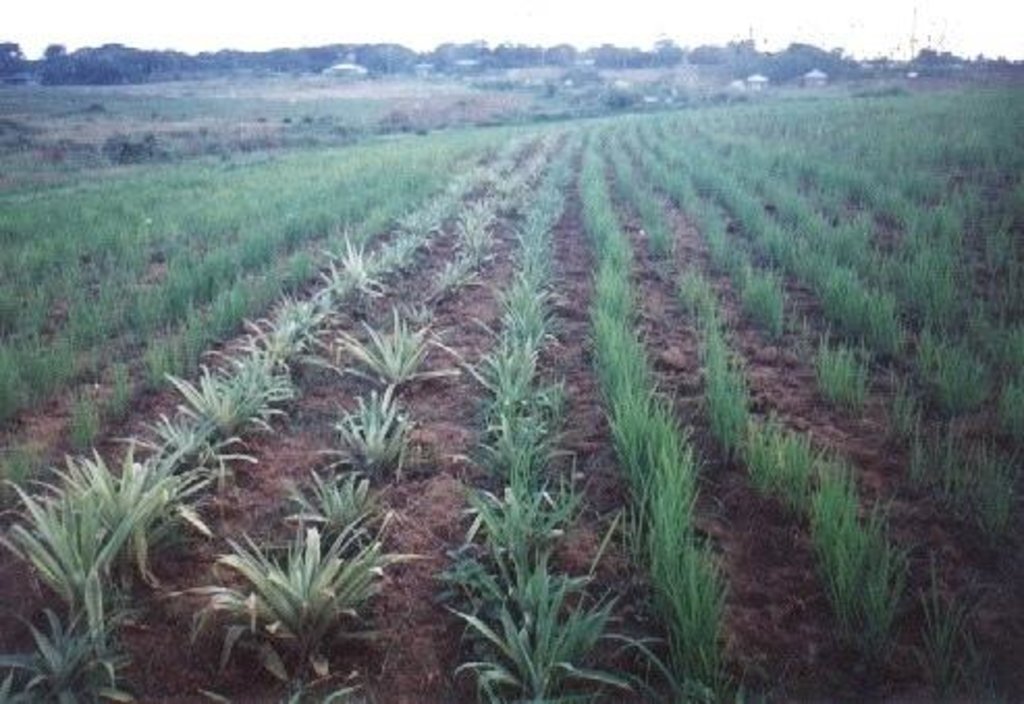
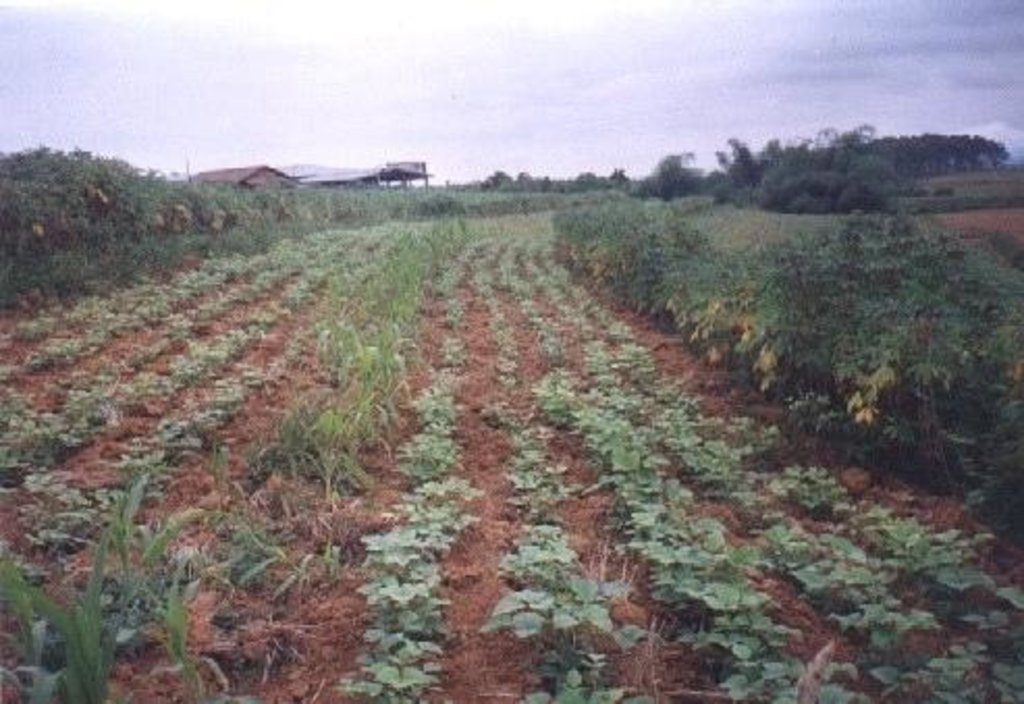
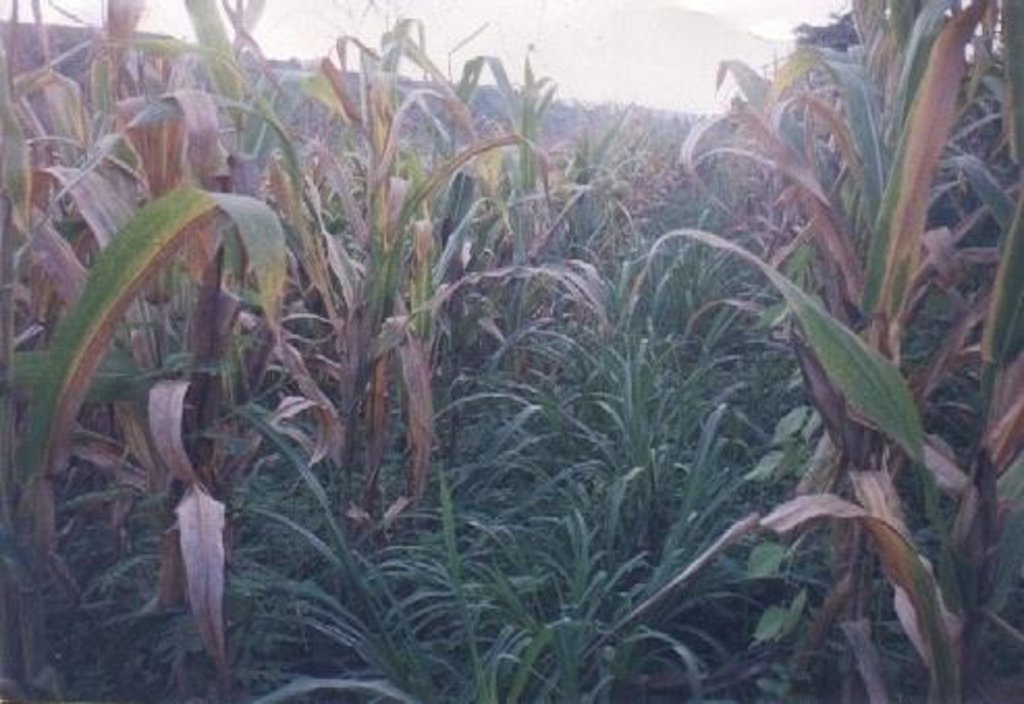
Planting of economic crops/forages in strips along the contour to control soil loss through erosion.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
The technology was introduced in the upland corn growing areas in Isabela province. The province is one of the main corn growing areas in the Philippines. As a means of minimizing/controlling soil erosion, economic crops like cassava and pineapple and forage grasses are planted in strips along the contour. Cassava and pineapple strips are established together with forage grass. When the cassava and pineapple is harvested, the forage will continue to provide protection against soil erosion. Planting of cassava is done yearly, while the replanting cycle for pineapple is 2 to 3 years. In some cases, forage grass is grown alone. It is more or less permanent and it is trimmed regularly. Overtime, natural terraces are formed and soil erosion is minimized. The system is advatageous in the economic benefit can be gained from both the alley crops is there on the contour strips.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ฟิลิปปินส์
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Isabela
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Isabela
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, specify area covered (in km2):
2.5
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 1-10 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 2.5 km2.
The technology was introduced in the upland corn growing area of Isabela. It was project-initiated
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Introduced by extension staff
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 240, Longest growing period from month to month: May - Dec; Second longest growing period in days: 180,Second longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Nov
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Severe soil erosion and fertility decline caused by intensive cropping (soil mining)
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Productivity decline - increased application of fertilizers to obtain the same yield level.
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A3: การรักษาหน้าดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Type of agronomic measures: contour planting / strip cropping, contour tillage
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
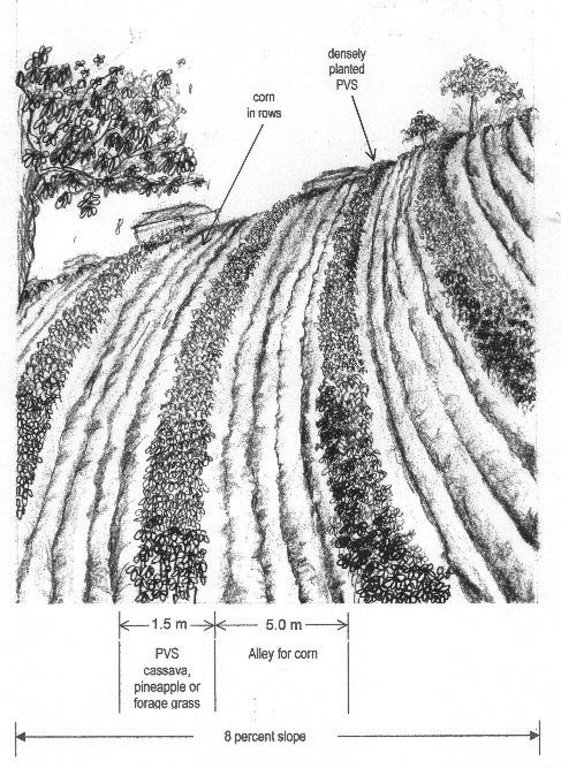
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Artist impression about planted vegetative strips (PVS) technology
Location: Isabela
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: seeds/seedlings
Quantity/ density: 4000
Remarks: in strips along the contour
Contour tillage
Remarks: strip cropping
Vegetative measure: contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 4000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.2
Vegetative measure: in rows
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 4000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.2
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Perennial crops species: pineapple
Grass species: napier
Other species: cassava
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 3.00%
ผู้เขียน:
Boyet Yambot-BSWM
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Philippine Peso
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
50.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
2.00
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | contouring | dry season |
| 2. | planting of vegetative strips (PVS) | onset of wet season |
| 3. | planting of alley crops | June/October |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | labour | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | seeds | ha | 1.0 | 80.0 | 80.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 32.0 | 32.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 144.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 2.88 | |||||
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting of vegetative strips (PVS) | onset of rainy season / once |
| 2. | Planting of alley crops | June/October / twice a year |
| 3. | Contouring | dry season / once |
| 4. | pruning/trimming (grass) | regular /every 2 weeks |
| 5. | fertilization (pineapple) | onset of rainy season /once a year |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | labour | ha | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 40.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 0.8 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The total area to be used for PVS which is approximately 2000 square meters.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Labor and inputs costs are the main factors involved.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- ชื้น
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
- ต่ำ (<1%)
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- > 50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
- รวย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
60% of the land users are very rich and own 60% of the land.
4% of the land users are rich and own 15% of the land.
1% of the land users are average wealthy and own 10% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Trading, working in other farms, carpentry or a family member working abroad
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Land subdivision due to inheritance
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Napier grass for work animals
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Napier grass for work animals
การผลิตไม้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
from the PVS
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ความเหลื่อมล้ำทางเศรษฐกิจ
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
PVS serves as barrier for field operation
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถาบันแห่งชาติ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
created awareness
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
70
หลังจาก SLM:
40
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
50
หลังจาก SLM:
10
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
PVS can harbor pests
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
Soil fertility
Production of extra food crops
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
from the PVS
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
20 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. They can clearly see the benefit of adapting SWC practices in terms of added benefits (additional products, ecological)
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Training and provision of planting materials/inputs |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Easy to establish and not capital intensive |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| PVS can harbor pests (e.g. rats) | Proper maintenance/cleanliness |
| Interfere with cultivation | Align PVS in a straight manner if the contour allows |
| Need additional capital | Provisions of incentives (e.g. subsidized inputs) |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Low effectivity of some PVS species/materials | Supplementary control measures (mulching, temporary barriers) |
| Yearly establishment (e.g. cassava) | Consider perennial species as PVS (e.g. forage grass) |
| Competition for nutrient and water | Application of fertilizer and use of water harvesting techniques. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
24/08/2001
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล