Integrated stone wall and poplar tree perimeter fencing [ทาจิกิสถาน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Habib Kamolidinov
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Alexandra Gavilano, David Streiff, Joana Eichenberger
technologies_1107 - ทาจิกิสถาน
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF เพื่อพิมพ์
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปหน้าเว็บ
- บทสรุปทั้งหมด (ไม่มีการจัดเรียง)
- Integrated stone wall and poplar tree perimeter fencing: 21 มีนาคม 2017 (inactive)
- Integrated stone wall and poplar tree perimeter fencing: 23 กรกฎาคม 2017 (inactive)
- Integrated stone wall and poplar tree perimeter fencing: 14 สิงหาคม 2019 (inactive)
- Integrated stone wall and poplar tree perimeter fencing: 2 พฤศจิกายน 2021 (public)
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
GITEC/ADB/DMC Rural Development Project Land Management Institute - ทาจิกิสถาน1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
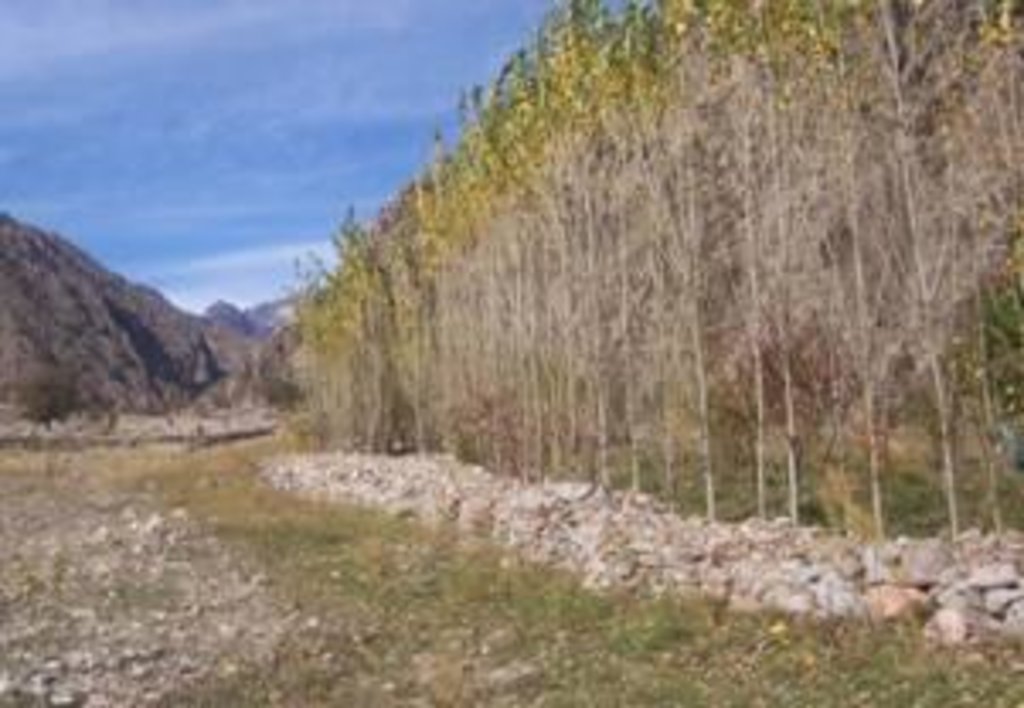
Stones cleared from land within a narrow valley floor where flat land is at a premium, was used to construct a perimeter stone wall which was subsequently supplemented with a row of poplar tree to protect an agro-forestry area with small scale supplementary irrigation.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
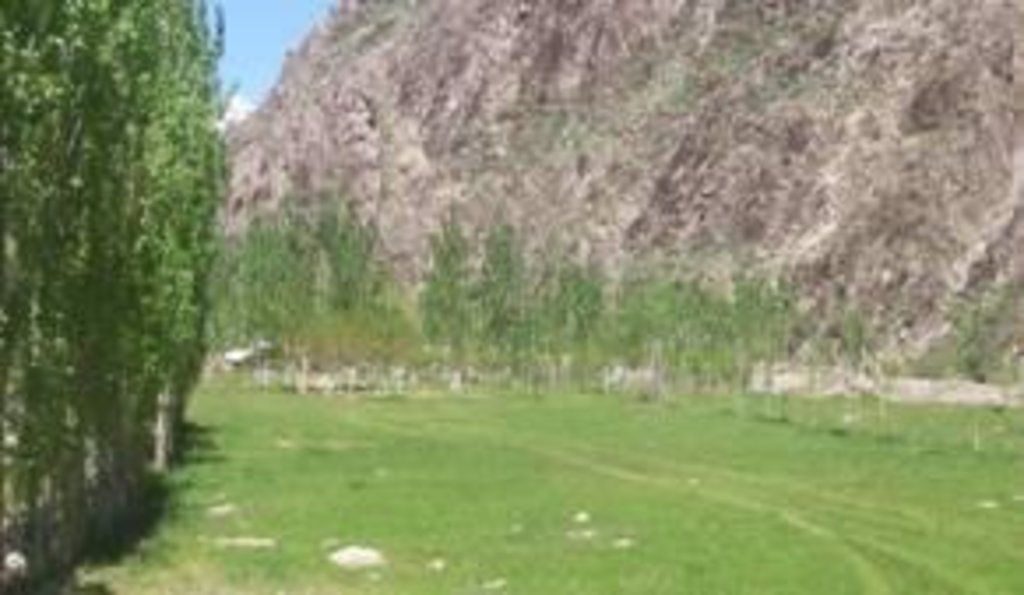
The area in question is a very narrow, flat valley floor, 95% of which was covered in stones and boulders, and devoid of vegetation, both grass and trees/shrubs. The stones in the area were cleared and used to build a protecting, perimeter wall (approx. 1.5 m high). This was then supplemented by an inner row of fast growing poplar trees. The stone clearing has resulted in deeper soil within the protected area that has led to far greater vegetation coverage, such as grass (that can be cut and used as fodder), forest and orchard trees and vegetable gardens. Irrigation was provided to the area by a small diameter poly pipe from a permanent spring. The area is now being extended to almost double the size of the initial walled agro-forest area.
Purpose of the Technology: The farmer’s primary aim, in initiating and continuing this SLM approach, was to “leave a legacy of improved land” for future generations, recognising how little flat and potentially productive land there is in this high, narrow valley location. Clearing the land of stones and building a walled enclosure that was irrigated greatly assured the quantity and quality of fodder for his animals, as they remain fenced in beside his village home almost all year. Fruit and vegetable production was also greatly improved.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The family commenced stone clearing and wall construction in 2005. The next task was tree planting; poplar trees were planted around the wall's perimeter. The irrigation source was tapped into using a poly pipe. The vegetable gardens are seasonal and their plants change with the seasons and the family’s needs. Stone removal continues even now, to improve the soil in the walled area. The farmer hopes to extend the walled area in the future.
Natural / human environment: Before the family began clearing stones and building the wall, this land had almost zero productivity. This area has a shortage of cultivated land and with increases in popluation and continued food insecurity, cultivated land is at a premium.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ทาจิกิสถาน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Central District of Tajikistan
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Kushon village, Romit Jamoat, Vahdat
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
A small area was all that the family could manage as there was an initial large workload, clearing stones and fence building, etc
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The initiative began in 2005 and has been ongoing ever since, it continues to improve, at least up to 2010 when reviewed.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- increase size of agrictultural land
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- วนเกษตร (Agroforestry)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- stone fruits (peach, apricot, cherry, plum, etc)
- pome fruits (apples, pears, quinces, etc.)
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: April to September

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Animal type:
- cattle - dairy
- sheep

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- ไม้ที่นำมาทำเป็นเชื้อเพลิง
- ผลไม้และถั่ว
- ผลิตภัณฑ์อื่น ๆ จากป่า
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): This area is strongly dependent on the extremely limited flat, valley bottom land for the production of pasture, 'cut and carry' fodder, orchards and vegetable production. 95% of this land is covered in stones that require removal before any productive capacity can be achieved. Even when cleared of stones the soil is still very shallow (< 20cm) and requires irrigation to ensure plants survive the hot summer months
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Same – the above words were used by him in the on-farm interview
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: sheep/cattle
Plantation forestry: The Poplar trees they planted are pruned and thinned for firewood and construction materials
Other type of forest: orchard species: Apple, Apricot, Cherry
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, fruits and nuts
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Grazing land: Gi: Intensive grazing/ fodder production
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์

อื่น ๆ
ระบุ:
wastelands, deserts, glaciers, swamps, recreation areas, etc
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปลูกป่าร่วมกับพืช
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S6: กำแพง สิ่งกีดขวาง รั้วไม้ รั้วต่างๆ

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M1: การเปลี่ยนรูปแบบของการใช้ประโยชน์ที่ดิน
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
- M3: การวางผังตามสิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและสิ่งแวดล้อมของมนุษย์
- M4: การเปลี่ยนแปลงช่วงเวลาให้เหมาะแก่การทำกิจกรรม
- M5: การควบคุมหรือการเปลี่ยนแปลงขององค์ประกอบของชนิดพันธุ์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, structural measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, mixed cropping / intercropping, cover cropping, retaining more vegetation cover, furrows (drainage, irrigation)
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary, in blocks
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bh (Loss of habitat): การสูญเสียแหล่งที่อยู่
- Bq (Quantity/biomass decline): การลดลงของปริมาณหรือมวลชีวภาพ
- Bl (Loss of soil life): การสูญเสียสิ่งมีชีวิตในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bh: loss of habitats, Bq: quantity / biomass decline, Bl: loss of soil life
Secondary causes of degradation: land tenure (The lack of good quality available land puts pressure on the lower grade land.), poverty / wealth (People still need land to harvest to survive.)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
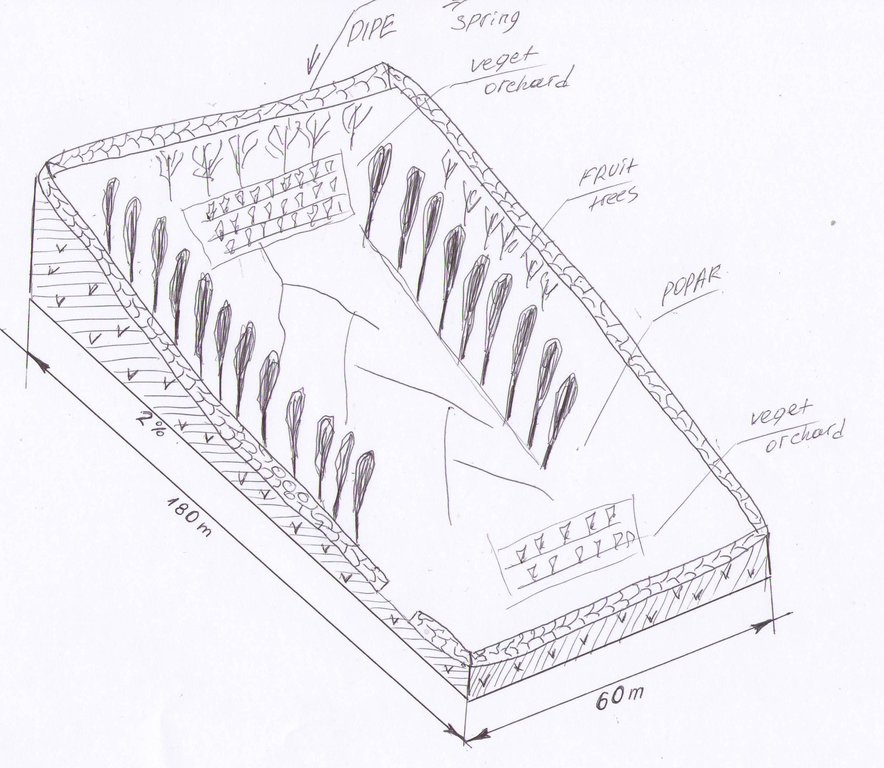
The drawing shows a 1.5m high stone wall, lined with poplar trees on a gentle slope. The site is located in the valley floor and has access to a naturally occuring spring. The enclosed land is now used mainly for fodder production, intercropped with fruit trees and vegetable patches.
Location: Khatlon province. Kushon village, Romit jamoat, Vahdat raion
Date: 21.04.2011
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (The farmer has a good understanding of farming techniques.)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, reduction in wind speed, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Better crop cover
Material/ species: Perennial pasture (grass) for fodder
Quantity/ density: 100 %
Remarks: covers 1.3 ha
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Forest and orchard trees with fodder grasses and vegetable gardens
Quantity/ density: 100
Remarks: dramatically increased
Cover cropping
Material/ species: Perennial grass is the cover crop
Quantity/ density: 100
Remarks: dramatically increased
Retaining more vegetation cover
Material/ species: Land previously bare and stony
Quantity/ density: 100
Remarks: vegetation cover increased
Furrows (drainage, irrigation)
Material/ species: Irrigation via hand cut 20cm cube ditches and poly pipe from nearby spring
Agronomic measure: Stone removal and clearance
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 1200
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
In blocks
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 60% cover
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): About 0.5 ha planted
Trees/ shrubs species: Poplar trees - planted
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Apple, cherry, apricot - planted
Grass species: Grass - natural
Other species: Vegetable garden - planted
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 0.00%
Wall/ barrier
Vertical interval between structures (m): Wall around area
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.7
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 500
Construction material (stone): Stone wall – from stones removed from within area
Lateral gradient along the structure: 3 degrees%
ผู้เขียน:
Des Mcgarry, Land Management Institute, Giprozem 15, Dushanbe, Tajikistan
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
somoni
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
4.5
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
4.50
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Stone clearing | On initial set up |
| 2. | Wall building | On initial set up |
| 3. | Tree planting | annually |
| 4. | Irrigation pipe | On initial set up |
| 5. | Vegetable garden | annually |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Stone clearing | Persons/day | 15.0 | 50.0 | 750.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Wall building | Persons/day | 15.0 | 50.0 | 750.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Tree planting | Persons/day | 10.0 | 25.0 | 250.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Vegetable garden | Persons/day | 20.0 | 15.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | Pieces | 6.0 | 16.66666666 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Trees | Pieces | 100.0 | 10.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Plants for vegetable garden | - | 1.0 | 450.0 | 450.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Irrigation pipe | meter | 700.0 | 3.0 | 2100.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Wall | meter | 500.0 | 7.0 | 3500.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 9200.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 2044.44 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Stone clearing | Annually |
| 2. | Vegetable garden | Annually |
| 3. | Tree planting | Annually |
| 4. | Animal husbandry | Annually |
| 5. | Fertilising and cultivating (garden vegetables) | Annually |
| 6. | Tree planting | Annually |
| 7. | Vegetable planting | Seasonally |
| 8. | random stone removal | Annual |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Stone clearing | Persons/day | 10.0 | 25.0 | 250.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Vegetable garden | Persons/day | 50.0 | 25.0 | 1250.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Tree planting | Persons/day | 20.0 | 15.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Animal husbandry | Persons/day | 40.0 | 15.0 | 600.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Labour: Fertilising and cultivating | Persons/day | 20.0 | 15.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Labour: Random stone removal | Persons/day | 10.0 | 15.0 | 150.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 2850.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 633.33 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: All works done manually., all done manually, All work done manually.
Wall – length; all money spent in first 1 or 2 years
Trees – per unit tree; initial start up and annual costs, now ongoing.
Vegetable seeds – per packet, annually
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The human labour costs involving the family were nothing as they willingly gave of their time to clear the land and build the wall, plant trees and create vegetable gardens. The real labour cost were the few days when the farmer paid 3 men to help build the wall.
The cost of the wall cost was also nothing as all materials came from on site.
Trees – there was an initial start up cost and the farmer said he tries to plant at least 20 new trees each year to maintain and enhance productivity
Grasses (fodder) – are self regenerating and local. The farmer has never bought grass seed or used fertiliser on the grass
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Dominate in Spring (March-May) The period June to September is very hot and dry (almost no rain).
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Altitudinal zone: The centre of the site is at 1,305 meters a.s.l
Landforms: The site is slightly sloped, north to south.
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- สูง (>3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil depth on average: Before intervention the soil was <1cm in depth. Now 20-30cm average depth.
Soil texture: Loess soil – silty loam
Soil fertility is high and with proper management/intervention these soils are very fertile. Before the intervention they were virtually infertile.
Topsoil organic matter is medium with intervention (<1% before).
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium because loess soils are low in clay (high in silt) – so have moderate PAWC.
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Availability of surface water: Also medium
Water quality (untreated): The spring water is almost pure water
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Not a large difference. The farmer’s wife shares the workload but tends to focus more on the garden, fruit production, household duties and bee keeping. The farmer conducts hay cutting and gathering, stone removal, fence upkeep and animal tending (feeding and slaughtering when required).
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
100% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: The issue is that the older and the very young family members (ie the farmer and his wife are in their late 50s ) stay on the farm. The rest (18 to 50 yrs ) have paid employment in Dushanbe and Russia, and only visit the farm, occasionally. However, it is believed they part-finance (contribute) to the upkeep of the family farm.
Market orientation of production system: All of the farm produce stays on the farm for home consumption, but they do eat well and very healthy (fresh and organic) food. Their cattle are also well fed and healthy .
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Is 1.5 ha
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
- This is jamoat land (local village land). The farmer has no certificate but is now applying for one
- This is jamoat land (local village land). The farmer has no certificate but is now applying for one
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Not yet an issue – as he is the only one with access to the spring water
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Before the Technology this land was almost 95% covered in rocks with almost zero carrying capacity, no productivity and no water supply. So the % increase as a result of the Technology is all related to this increase from nothing.
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
การผลิตสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
2
การผลิตไม้
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
การจัดการที่ดิน
การผลิตพลังงาน
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำดื่มไว้ให้ใช้
การมีน้ำไว้ให้ปศุสัตว์
การมีน้ำไว้ให้สำหรับการชลประทาน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
ภาระงาน
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
Livelihood and human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The primary aim of the farmer in introducing the technology was to improve the family’s lifestyle (livelihoods) and well being. He has easily achieved this and it seems to be getting better, year on year.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
คุณภาพน้ำ
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
การระเหย
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
การอัดแน่นของดิน
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
Hazard towards adverse events
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ทราบ |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The Technology (stone clearing, wall building, tree planting, vegetable production and grass (fodder) production) is vastly more tolerant to extremes of climate than what existed before.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The establishment and ongoing costs are very small compared to the returns both long and short term gained from introducing the Technology
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- ครั้งเดียวหรือเป็นการทดลอง
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
1 household
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material suppor
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Unsure how many such walled agro-forests are in this region. Would need to consult with Jamoat leader. There are quite a few walled areas. But unsure about the number and content (ie technologies inside).
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There seem to be quite a few enclosures in this area – but we have not conducted a formal survey.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| As above, as these words were transcribed during the farmer interview, on site. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
The stone clearing and wall building underpins the whole SLM initiative. That it was achieved by only 3 or 4 people, in under a year and at such a low cost (with minimal paid labour) adds to the strengths. The wall is also critical to keep animals out of this now richly vegetated area, not only sheep and goats but also wild pigs and even wolves. The stone clearing “created” soil which is critical for all the vegetation growth within the walled area. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The farmer is in the process of expanding the stone cleared area, and is using the stone to build a larger perimeter fence, aiming for a larger plot of 2 or 3 ha. |
|
Bringing water to the site (at his own cost) by poly pipe was a critical part to the technology. The walled agro-forestry area would have struggled without this extra and constant water supply – as the soil is so shallow (all the rock remains below the soil surface). Now he can have good fodder grass, trees, orchard and vegetables with a guarenteed regular supply. Getting the plants and trees through the hot summer months is the key use of the water. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The farmer wishes to source a 2nd spring to water the extended (2 - 3 ha) site. |
|
The rich mix of vegetation on the site (trees, perennial grasses and vegetable production) not only ensures the intervention remains viable but also ensures a continuous, rich, healthy food supply to the family and their animals year round. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The farmer has already started to plant new fruit trees outside the original walled area, in readiness for moving the fence to encompass a 2 -3 ha site. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| As above; as these were the sentiments of the farmer during the on site interview. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| None really. What the farmer has achieved is most impressive. Particularly as his Technologies were all self-financed and conducted slowly and carefully, hence with no financial burden to the family and no interruption or lessening of their food supply. | If costs / budget permit (unlikely) to bring some power-type assistance to stone removal (like a small tractor) or a solar powered pump to increase irrigation water pressure. However, the farmer may not wish to be reliant on such items, as if they breakdown, his whole enterprise (currently so successful) may suffer. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
There is no relevant documentation
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล