Mulching in rainfed vineyards on terraces in the loess hill zone [ทาจิกิสถาน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Qobiljon Shokirov
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Mulcha Sino
technologies_1111 - ทาจิกิสถาน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Boev Jahonbek
Tajik Soil Institute
ทาจิกิสถาน
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Tajik Soil Insitute (Tajik Soil Institute) - ทาจิกิสถานชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - คีร์กีซสถาน1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
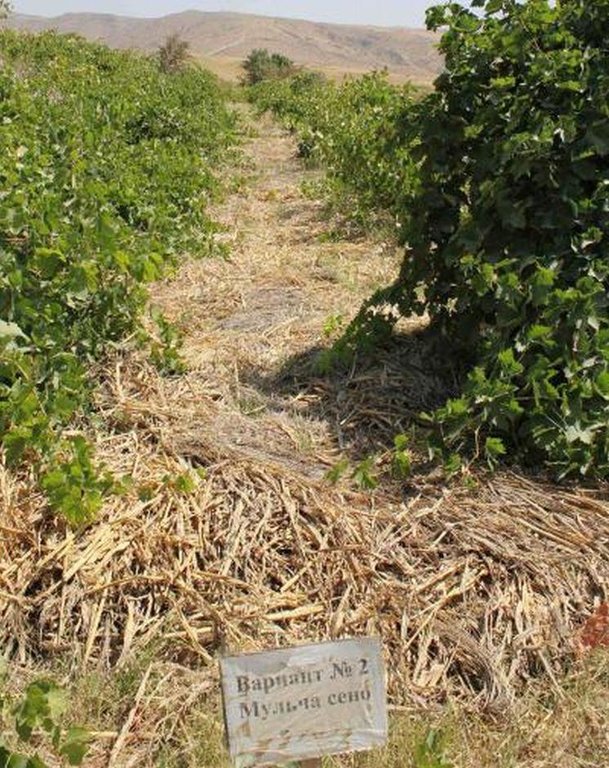
This technology consists of vineyards plots that are mulched with grass and established on terraced land in the loess hills of Tajikistan.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
On the terrain of the Tajik Soil Institut's research station in Karsang, Faizabad District, Tajikistan, a vineyard was established on forward sloping terraces with about 12° inclination on land formerly used as extensive pastures. This technology dates back to the times of the Soviet Union in 1968. Bulldozers were used to establish the terraces.
Before the planting of vines the soil was ploughed. Local vine sorts were used for the plantation and intercropping is done with wheat and fodder crops. About 1300 vine seedlings were planted per hectare.
Purpose of the Technology: Mulching treatment with grass was initiated to increase soil moisture in the soil, improve soil quality such as soil organic matter and other elements and protect soil from erosion by water and wind.
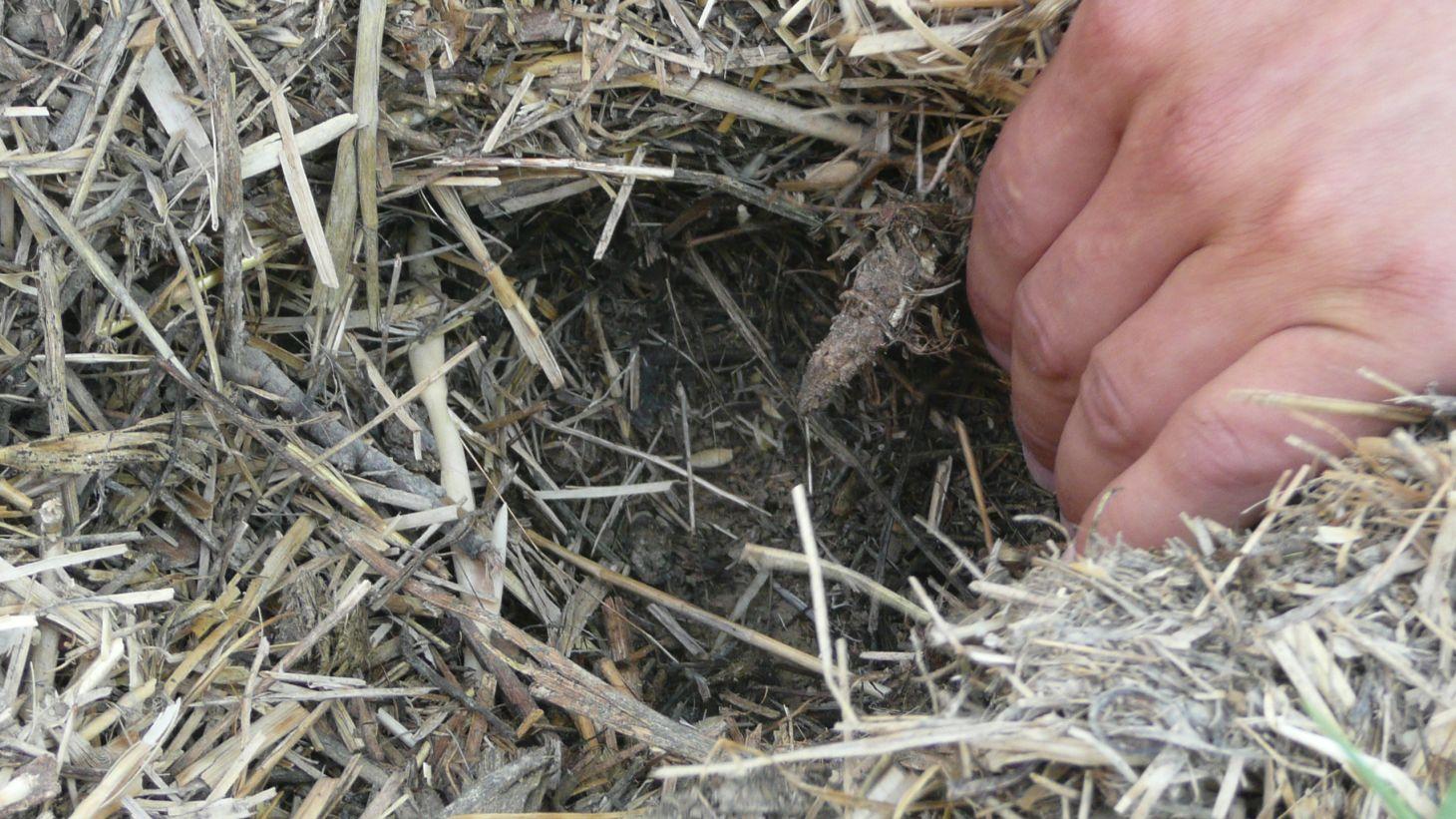
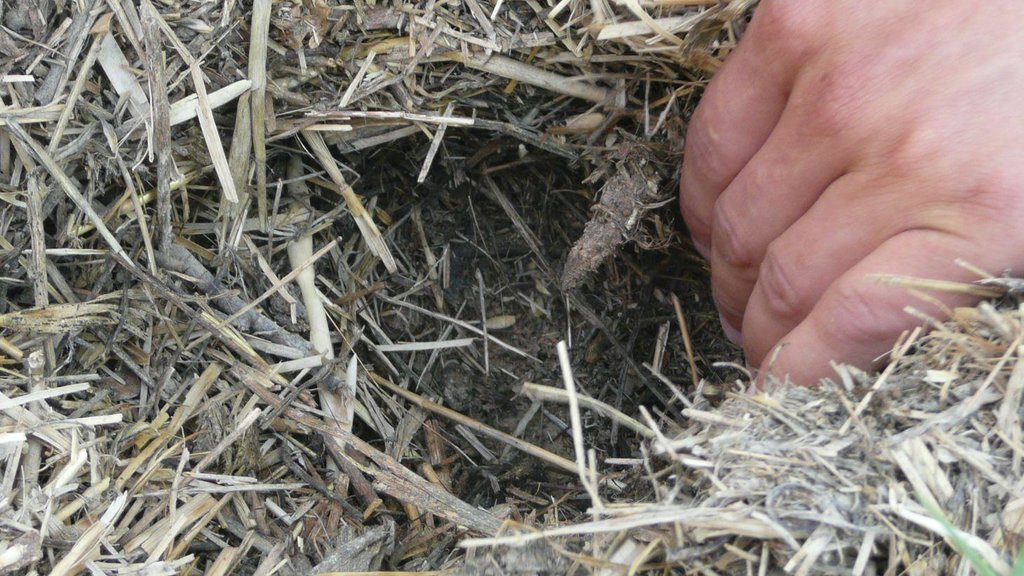
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Mulching with grass was set up by the Tajik Soil Institute and but has been maintained by the farmers who lease the land. Mulching with grass is relatively easy but can be very challenging; depending on the availability of resources. First, plots between the vineyard rows were ploughed by using animal power, in most cases horses. Natural grasses were cut from the property of the research station and applied as a mulch in between plots within the designated vineyard plots. Since then the experiment has been maintained by the farmers and over the last ten years layer of mulch with grass has been growing and building up the top soil layer. This layer of mulch prevents rainwater from eroding the top soil, improves soil organic carbon, provides shade to plant roots, and most importantly keeps soil moisture moderately in hot summer months, which is very essential in these rainfed areas.
Natural / human environment: The terraces have greatly helped to reduced soil erosion and the vines supported this effect in further stabilising the soil. Soil humidity has improved through increased soil moisture and reduced evaporation due to mulching throughout the year. As the vineyard was established on pasture land, a disadvantage is the reduced grazing land area. The disadvantage of mulching is that no inter cropping between the vines can take place for several years.
In summer of 2011, WOCAT questionnary was used to analyze and evaluate current conditions of the vineyard mulching treatment. At the same time proper soil samples were taken from the plots with mulch and control plots in 0-15 and 15-30cm for further comparison for soil organic carbon (SOC). All together 240 soil samples were taken from eight different plots and each have been analyzed for soil SOC content.
From this study it was revealed that plots with mulch has significantly higher SOC content than control plots. In average, plots with mulch consisted of 1.3% SOC and control plots in average contained 0.4% SOC within the 0-15cm depths. Average SOC content for plots with mulch and control plots were observed but there were no significant difference in 30cm depth, both contained 0.4-0.5% of SOC.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ทาจิกิสถาน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
RRS
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Faizabad, Javonon, Karsang
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.07 km2.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ในช่วงการทดลองหรือการทำวิจัย
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The vineyard was originally set up 60 years ago but the mulching experiment within the vineyard was introduced around 2000-2003.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- วนเกษตร (Agroforestry)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- grapes
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period from month to month: April to November

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): soil erosion through wind and water, soil moisture loss, soil nutrient mining
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): soil fertility and humidity decline, lack of technical equipment, low productivity of non-irrigated land on slopes when used in a conventional way as cropland of extensive pasture
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- วนเกษตร (Agroforestry)

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปลูกป่าร่วมกับพืช
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A3: การรักษาหน้าดิน
A3: Differentiate tillage systems:
A 3.1: No tillage

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S1: คันดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M1: การเปลี่ยนรูปแบบของการใช้ประโยชน์ที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures
Secondary measures: structural measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, breaking compacted topsoil, zero tillage / no-till
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Plowing), overgrazing, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts)
Secondary causes of degradation: wind storms / dust storms, droughts, governance / institutional (common grazing land in the vicinity of the village regulated management)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
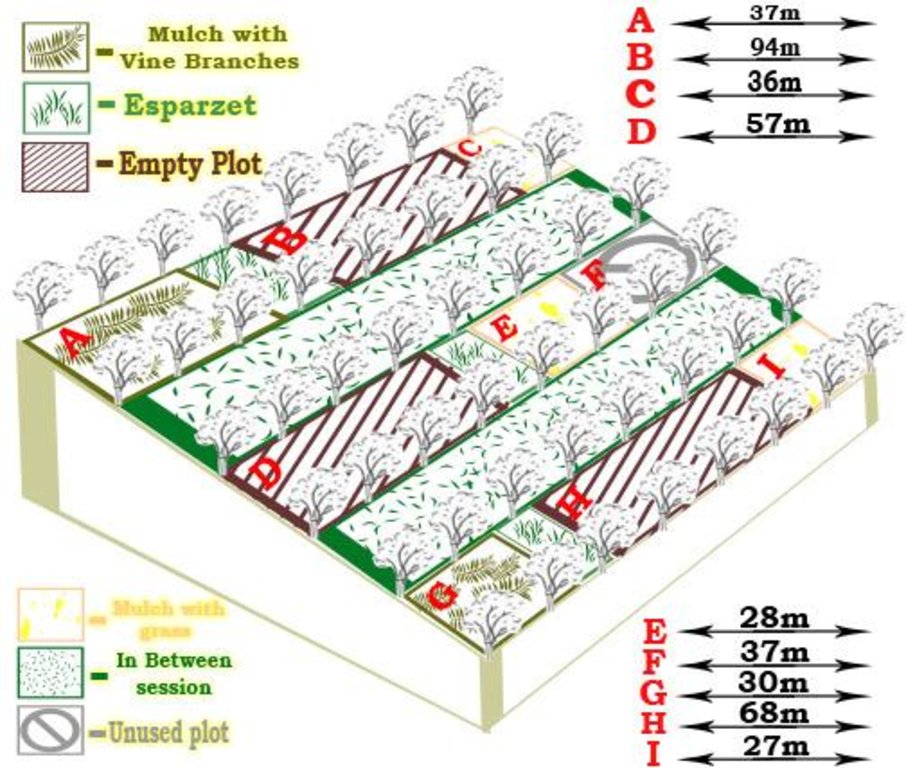
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
ocation: Faizabad, Tajikistan. RRS
Date: September, 2011
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply, increase of biomass (quantity)
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Material: earth
Mulching
Material/ species: grass
Quantity/ density: 15-20cm
Remarks: mulch layer thickness (15-20cm)
Breaking compacted topsoil
Material/ species: loosing of soil around vines, yearly
Zero tillage / no-till
Material/ species: zero tillage between the vines on the terraces
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 1300
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Fruit trees / shrubs species: vineyards "rosevitaiti", improved local sorts
Terrace: bench level
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
ผู้เขียน:
Ibrohimov Huseyn
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
-2.13
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
6.5
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting | |
| 2. | Terracing by bulldozer | late autumn / early spring |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Planting | Persons/day | 13.0 | 6.5 | 84.5 | |
| แรงงาน | Terracing by bulldozer | hours | 16.0 | 2.81222 | 45.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Bulldozer rent | hours | 16.0 | 0.8125 | 13.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seedlings | Seeds/ha | 1300.0 | 0.5 | 650.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Fertilizer | kg | 5.0 | 1.0 | 5.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Grass | tons | 1.0 | 165.0 | 165.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 962.5 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | -451.88 | |||||
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | cutting of grass | spring/once a year |
| 2. | soil loosening around the trees | |
| 3. | Mulching | spring (end of April/beginning of May) |
| 4. | Cutting the grass | 1 |
| 5. | Protecting the vineyard from animals | autumn to spring |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Cutting of grass | Persons/day | 5.0 | 6.5 | 32.5 | |
| แรงงาน | Soil loosening | Persons/day | 2.0 | 6.5 | 13.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Cutting the grass 2nd time | Persons/day | 4.0 | 6.5 | 26.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Mulching | tons | 1.0 | 86.0 | 86.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Scissors | ha | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 217.5 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | -102.11 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: scissors, hoes
The establishment of the vineyard took place in Soviet times and costs were born by the Soil Institute, which is a state institution. However, costs were calculated based on current costs (2011).
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- ลูกจ้าง (บริษัท รัฐบาล)
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
Subsistence (self-supply) is supported by the local Institution.
All three levels of mechanization are existing.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เช่า
- research
- research
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
harvest: 50% to state / 50% to land user
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
การระเหย
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
การอัดแน่นของดิน
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
ชนิดพันธุ์ที่ให้ประโยชน์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
earthworms
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
Hazards towards adverse events
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
drought
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Different types of mulching are currently being tested to increase soil moisture storage, to build up soil organic matter and thus infiltration capacity and soil fertility properties.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Farmers have noted that usually change can be seen within few years after the technology has established.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
10 households (3 percent of stated area)
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Overall acreage of the all field are roughly 3 hectares.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Vineyards are adapted to climate and give consistently good harvest. |
| Between the rows there is an additional harvest thanks to intercropping. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Efficient soil protection. |
|
Very practical and easily adaptable in villages, where grass is available. How can they be sustained / enhanced? At the same time grass can become deficit in villages, because of high number of livestock. In that cases small scale mulching is recommended with rotation system. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Technology is very practical but so far it has not been taken seriously by the farmers. | Probably, few educational days for knowledge sharing would be very helpful. |
| Grass might be available for small scale mulching but usually not for a big scale, because everyone in the region has high number of livestock and automatically grass is used as fodder for animals. | Maybe mulching can be applied around the trees and not so much for covering entire plots. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล