Cover crops in organic vineyard [สเปน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: CELIA BARBERO SIERRA
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Cubiertas vegetales en calles de viñedos
technologies_1162 - สเปน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Ruíz Colmenero Marta
Instituto Madrileño de Investigación y Desarrollo Rural, Agrario y Alimentario - IMIDRA
สเปน
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Bienes Ramon
Instituto Madrileño de Investigación y Desarrollo Rural, Agrario y Alimentario - IMIDRA
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
UNIVERSIDAD AUTONOMA DE MADRID (UNIVERSIDAD AUTONOMA DE MADRID) - สเปนชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
IMIDRA (IMIDRA) - สเปน1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Use of cover crops to prevent erosion and increase soil organic matter.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
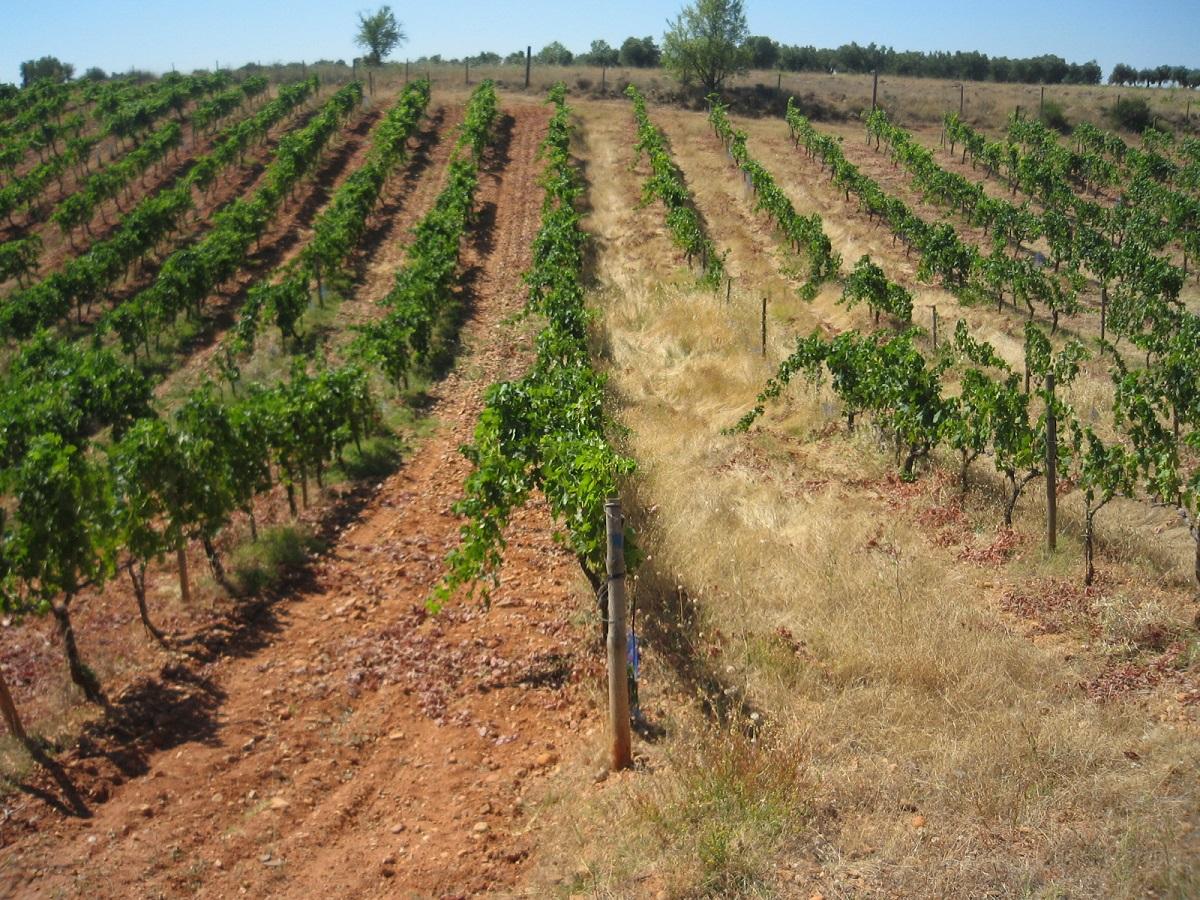
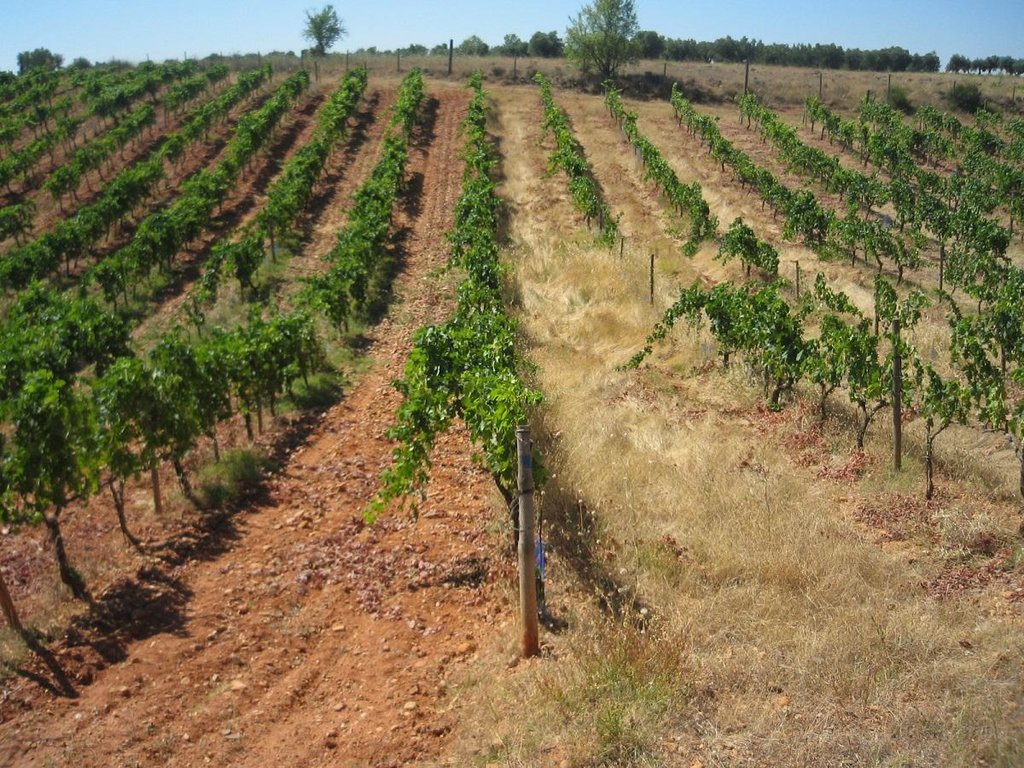
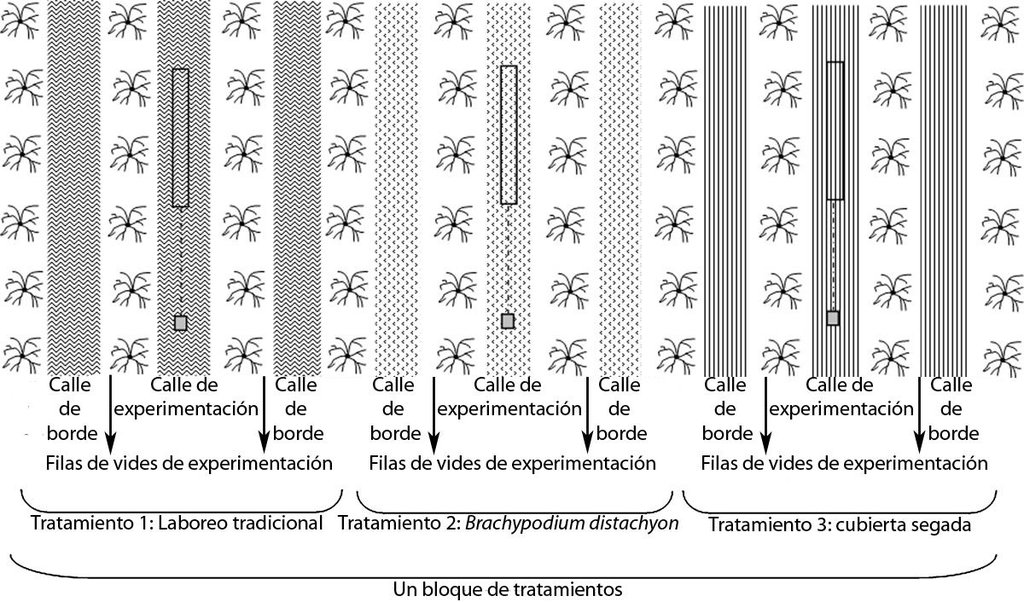
In total there were 66 rows of vineyards of the Tempranillo red variety, spaced 3 m apart with a distance of 2.5 m between vines. To date they have been worked using conventional tilling without herbicides: most of the work is done mainly in the winter, followed by two or three sessions in spring aimed at controlling the growth of weeds, which is conditioned by the spring rains.
The technology is based on minimum tillage and the use of Secale cereale L and Brachypodium distachyon (L.) as cover crops to protect the soil against erosion and to increase the organic matter.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purposes of this technology are to fight against erosion and water runoff and to increase soil organic matter.
Indirectly this technology contributes to increase biodiversity in the vineyards and it could have some positive effects on wine quality (related to the content of sugar and poliphenoles) as proved by some authors (Dry et al., 2001).
Cover crops usually increase the soil moisture but on the other hand, along the summer, the cover crops and the vines are in competition for the scarce water available in the area.
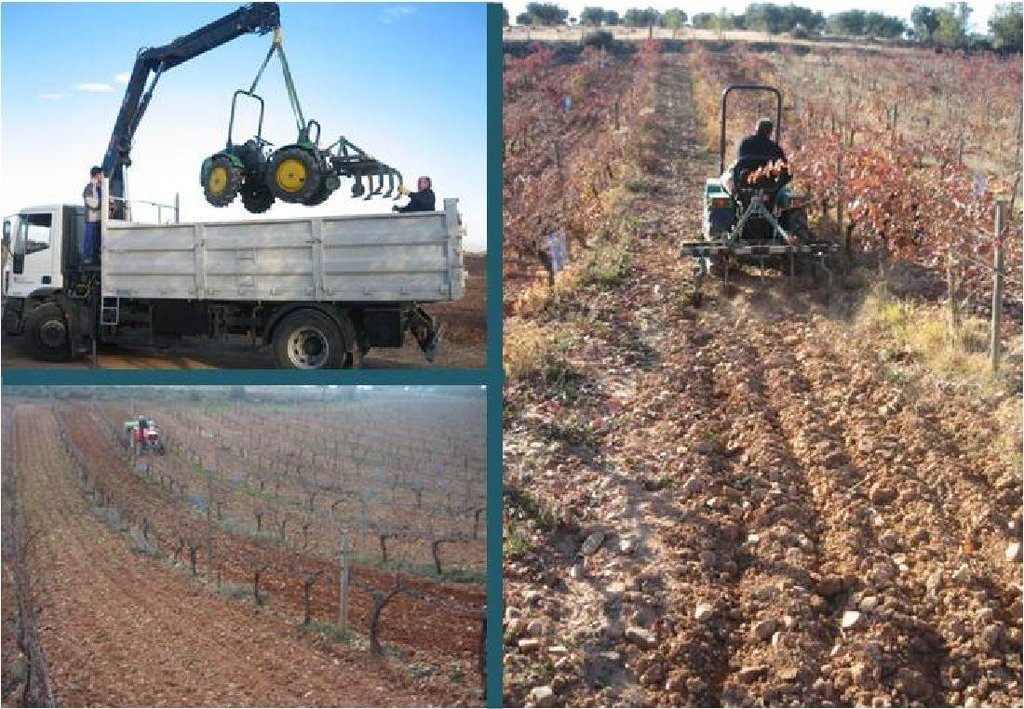
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The plant cover in the centre of the rows was sown in mid-November, following the copious rains in the autumn of 2006. A minimum tillage (15cm depth) is carried out before sowing. The seeding rates were 70 kg/ha for rye, Secale cereale L., and 40 kg/ha for purple false brome, Brachypodium distachyon (L.) P. Beauv. This latter cover had to be reseeded by hand since the seeds have to be buried at a very low depth. It sprouts in late winter or early spring and by late June it is already mature and dry, at which point it self-sows and it sprouts spontaneously again the following autumn. The Secale cover has to be cut in spring and re-sown in late autumn.
Once sown, the resulting vineyard was divided into alternating rows with three treatments: bare soil with traditional tilling, rows covered with Secale and rows covered with Brachypodium.
The maintenance activities consist of no tillage in winter and conservation of natural cover crops until spring.
Natural / human environment: The area is at an altitude of 800 m, in a semiarid Mediterranean climate where the recorded annual rainfall is below 400 mm and the average annual temperature is 14 ºC, with very hot and occasionally stormy summers and very cold winters. It rains primarily in spring and autumn.
The farmland is predominantly dry, especially where olives and vines are planted. Oaks (holm, Portuguese and hermes) can be found in nearby wild areas and in abandoned terrains. The study focused on the area of Campo Real in the southeast of Madrid, in the centre of Spain. The vineyard covers an area of some 2 ha of rolling hills and is located on top of limestone marl.
The farmer is the owner of the land where the technology was implemented as well as he owns other plots. The land user is one of the few organic producers in the region.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
สเปน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Madrid, Spain
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Campo Real
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.02 km2.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ในช่วงการทดลองหรือการทำวิจัย
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Projects FP 06-DR3-VID IMIDRA and RTA2007-86 INIA, Bodegas y Viñedos Gosálbez-Ortí.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agro-pastoralism (incl. integrated crop-livestock)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
- grass see
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 75Longest growing period from month to month: February-April (Secale cereale)Second longest growing period in days: 90Second longest growing period from month to month: February-June (B distachyon)

อื่น ๆ
ระบุ:
Grass species: rye (Secale cereale) and bromus (Brachypodium distachyon) (2m)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Erosion and low soil organic matter content.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Water scarcity, climatic extreme events, low agricultural income.
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
- A3: การรักษาหน้าดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, contour planting / strip cropping, cover cropping, mulching, manure / compost / residues, breaking crust / sealed surface, minimum tillage
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น
- Pk (Slaking and crusting): การอุดตันของช่องว่างในดินหรือรูพรุน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bl (Loss of soil life): การสูญเสียสิ่งมีชีวิตในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Pc: compaction, Pk: sealing and crusting, Bl: loss of soil life
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Bare soil by traditional tillage in sloping lands), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Lack of vegetation increases soil erodibility), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Increase the annual rate of rain infiltration due to high vegetation cover), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Extreme events- storms), droughts
Secondary causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Slope between 10 to 15%), land tenure (Uncertainties on future land tenure implies overexploitation of land in the short run)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Cover crops are sown in the middle of the strips of the lines of vineyard.(Bare soil under the vines: 50 cm wide; cropped strips: 2 m wide)
Location: Campo Real. Madrid, Spain
Date: 2008
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Selection of cover crops and management.
Botanical and agronomic knowledge required.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Use of appropriate machinery.)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater
Better crop cover
Material/ species: Secale cereale
Quantity/ density: 70 kg/ha
Remarks: decrease soil erosion and it does not compete for water.
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: Vineyard plus cereals
Remarks: bare soil under the vines: 50 cm wide; cropped strips: 2 m wide
Cover cropping
Material/ species: Brachypodium distachyon
Quantity/ density: 40 kg/ha
Remarks: best coverage and SOM increase, but reduces the grape production too much due to water competition
Mulching
Material/ species: Straw of Secale cereale
Remarks: Conservation of cut rye on site
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Secale cereale and Brachypodium distachyon
Remarks: roots and residues (straw) left in soil increase SOM
Breaking crust / sealed surface
Remarks: cover crops avoid soil crusting
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: up to 15 cm soil depth
Quantity/ density: 15 cm
Remarks: before sowing
Vegetative measure: in the middle of the lines of vines
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Grapes (50cm) /grass see G (cover crops) (2m)
Grass species: rye (Secale cereale) and bromus (Brachypodium distachyon) (2m)
ผู้เขียน:
María José Marqués, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
euro
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
1.34
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
46.90
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buy secale cereale seed, 70 kg per ha | |
| 2. | Buy B. distachyon seed, 40 kg per ha |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 140.7 | 140.7 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 51.46 | 51.46 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 354.43 | 354.43 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 546.59 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 407.9 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 6 month(s)
Life span of the product: B. distachyon seed, 4-5 years
Life span of the product: Secale cereale seed, 1 year
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Minimum tillage and seeding in one go (Secale cereale) | Annually in late autumn or winter |
| 2. | Seeding (B distachyon) | Every 5 years |
| 3. | Mowing Secale cereale 1 ha | Once a year |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 140.7 | 140.7 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 51.46 | 51.46 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 113.23 | 113.23 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 305.39 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 227.9 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: tractor, brushcutter
Grass strips per hectare in 2008.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Labour and price of B. distachyon seeds as it is not a commercial seed.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
400.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Autumn and spring
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- บริเวณแอ่งบนที่ราบ (concave situations)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Slopes on average: Rolling (10-14%)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil texture is medium (sandy loam)
Soil fertility is medium
Topsoil organic matter is medium (1.3%)
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Ground water table: No data avalilable
Availability of surface of water: During the maximum water requirements of vines (June-July) water is not available usually.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Traditionally vineyard sector in Spain is driven by men.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
Off-farm income specification: This information is not available.
Market orientation is commercial/market (wine).
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- รายบุคคล
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Depending on the cover crop (B. distachyon)
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
But not really used
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำไว้ให้สำหรับการชลประทาน
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับการชลประทาน
ความต้องการน้ำจากการชลประทาน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Related to the quality and price of wine
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
No tillage
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
Landusers perception of the landscape
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The farmers use to prefer the landscape of their vineyards with "clean" soil. They consider cover crops as weeds.
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
This SLM Technology contributes to soil improvement but has no direct impacts on human wellbeing of the land users. Due to organic labelling of the product, the price of wine may increase wich also increases farm income.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
More than 80% of runoff reduction in B. distachyon and more than 60% for Secale.
การระเหย
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Depending on the cover. B. distachyon increases soil moisture in autumn and winter. From May to July soil moisture heavely decreased, the rest of the year the cover crops increase soil moisture compared with bare soil
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
93% in permanent cover crops
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
การอัดแน่นของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to less use of heavy machinery
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
1.27%
หลังจาก SLM:
1.6%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
From 1.27% to 1.6% in three years for permanent covers
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
ตะกอนที่ถูกพัดพามาโดยลม
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The species were chosen to be tolerant to drought and poor soil conditions
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
This particular land user is an organic farmer and he is willing to change his manangament practices but tradtional farmers in the region have a very negative vision of this kind of SLM techs.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
1
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
Increase in wine quality How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintaining this SLM practice along the time |
|
Prevention of erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintaining this SLM practice along the time |
|
Decrease in intensity and frequency of tillage How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintaining this SLM practice along the time |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Increase of soil organic matter How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintaining this SLM practice along the time |
|
Prevention of runoff and soil erosion (change of bare (tilled) soil by cover crops) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintaining this SLM practice along the time |
|
Increase in biodiversity How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintaining this SLM practice along the time |
|
Increase in wine quality (related to the content of sugar and polyphenols), as proved by some authors (Dry et al., 2001) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintaining this SLM practice along the time |
|
The costs are reduced through reduced use of tractor (decreased intensity of tillage) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintaining this SLM practice along the time |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Lack of knowledge or training to adopt this technologies | Awareness raising campaigns |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Soil moisture decreases during certain months | Mowing the cover in spring |
| High costs of the most effective seed (8.04$/kg) (B. distachyon) | Using other similar and cheaper seeds |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
M.J. Marques , S. García-Muñoz , G. Muñoz-Organero , R. Bienes. 2009. Soil conservation beneath grass cover in hillside vineyards under mediterranean climatic conditions. Land Degradation and Development. 21: 122-131.
Ruiz-Colmenero, S; Bienes R.; Marques MJ. 2011. Soil and water conservation dilemmas associated with the use of green cover in steep vineyards. Soil & Tillage Research 117, 211-223.
Bienes R., Marques MJ, Ruiz Colmenero M 2012. Cereales, viñedos y olivares. El manejo tradicional del suelo y sus consecuencias en la erosión hídrica. La erosión y la hidrología en campos de cultivo en España. Cuadernos de Investigación Geográfica 38(1), 49-74.
Ruiz-Colmenero, M., Bienes, R., Eldridge, D.J. and Marqués, M.J. 2013. Vegetation cover reduces erosion and enhances soil organic carbon in a vineyard in the central Spain. Catena. 104, 153-160.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล