Hillside Terracing [เอธิโอเปีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Hans Hurni
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Yegara irken (Amharic), Kenetawi metrebawi zala (Tigrigna)
technologies_1388 - เอธิโอเปีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
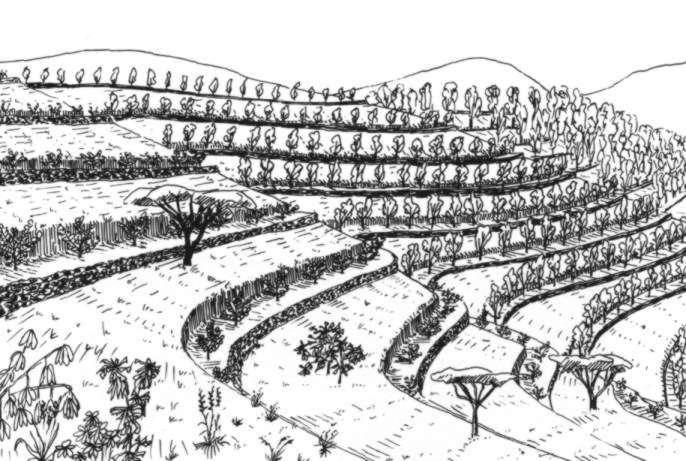
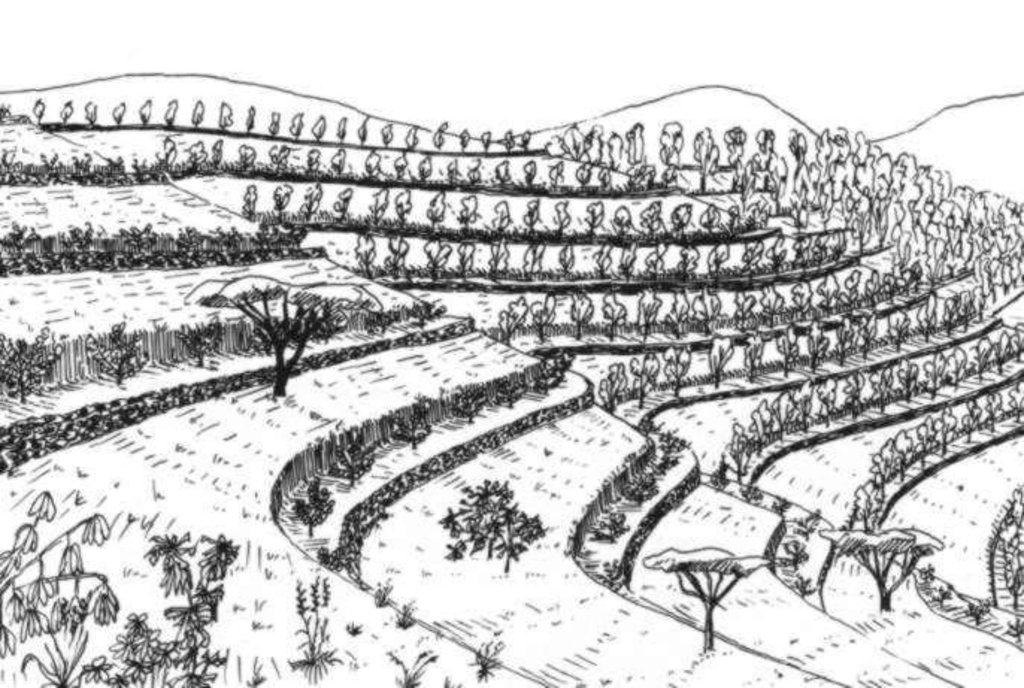
A hillside terrace is a structure along the contour, where a strip of land is levelled for tree planting.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
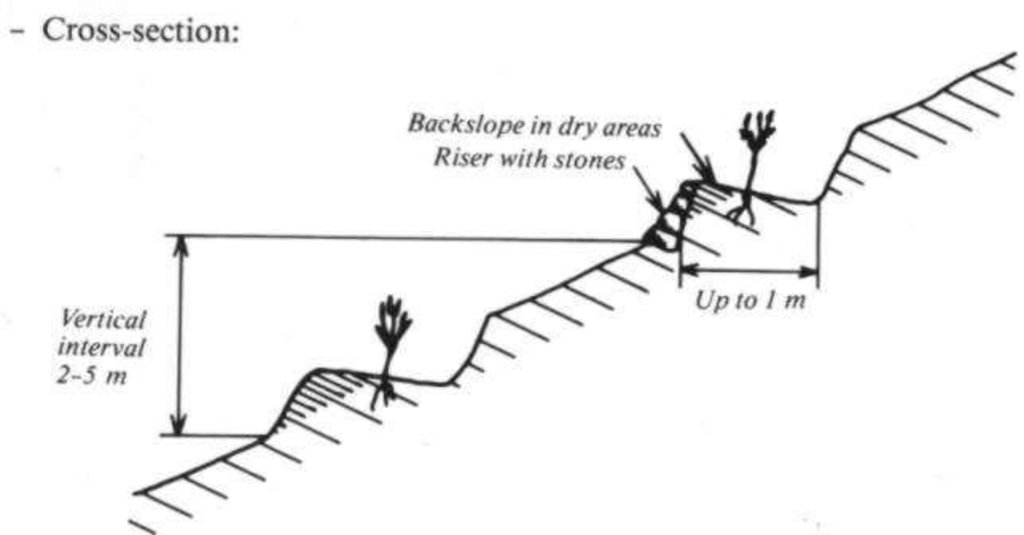
Hillside terraces are up to 1 metre wide and constructed at about 2-5 m vertical inteals. Hillside terraces should only be applied if there is a strong necessity of erosion control and/or water conservation justifying their construction. In Ethiopia and Eritrea, they have been mainly applied in the highlands, although the area of their applicability would be rather in the drier and lower lying agroclimatic zones. Slope range is 50-100%, soil range particularly on eavily degraded land. Hillside terraces are mainly used to prevent damage of flooding the area below steep slopes.
Hillside terraces help retain runoff and sediment on steep sloping land and to accommodate tree seedlings to be planted on them. They are also effective on badlands and in areas with low rainfall to conserve water. Hillside terraces are usually combined with area closure (against grazing). Little materials are needed for their construction: Line levels, digging instruments, stones, and other materials as needed for combined measures. Little management is needed for their maintenance, except for taking care of the tees planted, and for correcting damage that may be caused by livestock grazing.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
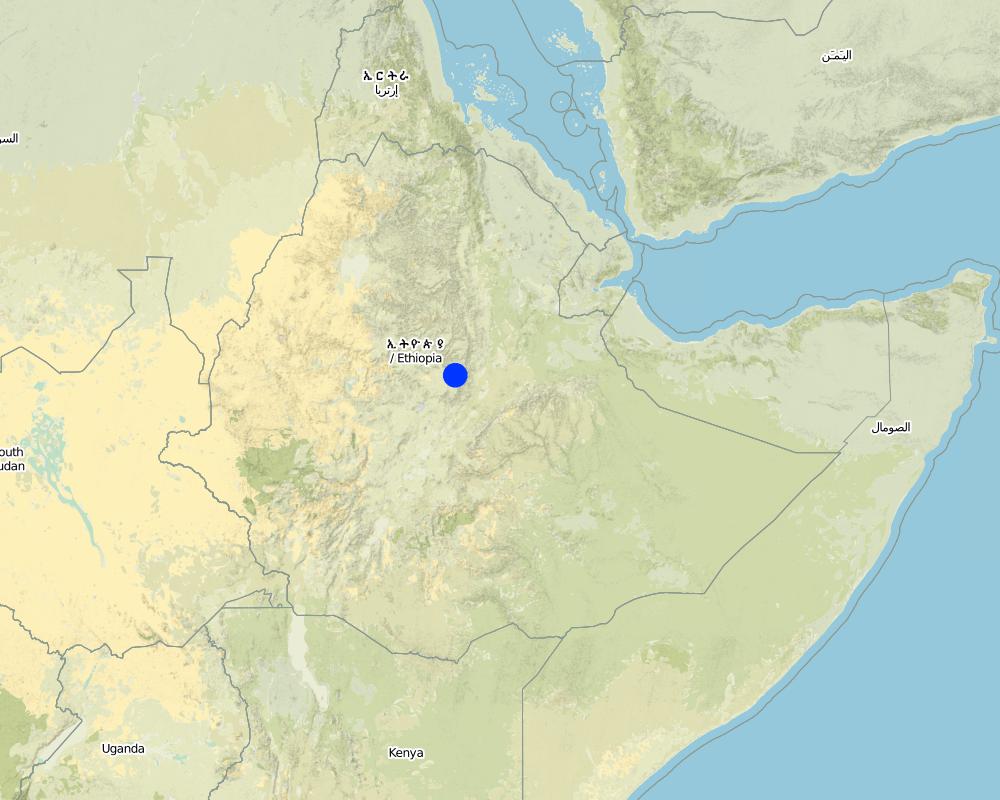
ประเทศ:
เอธิโอเปีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Harerge, Shewa, Wello, Tigray, Gonder, Sidamo, and Hamasien (Eritrea)
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 1,000-10,000 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1800 km2.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- มากกว่า 50 ปี (แบบดั้งเดิม)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Originated from engineering handbooks and Indian experience. Has been applied in Eritrea & Ethiopia since ~1978
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
- Eucalyptus, Cupressus, Juniperus

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- ไม้ที่นำมาทำเป็นเชื้อเพลิง
- ผลิตภัณฑ์อื่น ๆ จากป่า
- การแทะเล็มหญ้า / การเก็บกินหญ้า
- การอนุรักษ์ / ป้องกันธรรมชาติ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): High run-on from steep slopes onto cultivated land. Sheet and rill erosion from slopes, and subsequent gullying on cultivated land along footslopes. Lack of grass and woody biomass.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of grazing for livestock. Lack of cultivation land. General food deficiency.
Grazingland comments: Insuffient land at curent population density and low productive farming systems.
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Almost the natural forest is not exist. Low growing condition.
Type of grazing system comments: Insuffient land at curent population density and low productive farming systems.
Constraints of wilderness: these are mainly badlands which are totally degraded
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่มีการจัดการแบบเข้มข้นหรือการผลิตอาหารสัตว์:
- ตัดแล้วขนไป / ไม่มีการปล่อยแทะเล็มเอง (Cut-and-carry / zero grazing)
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Water supply: Also full irrigation
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S1: คันดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
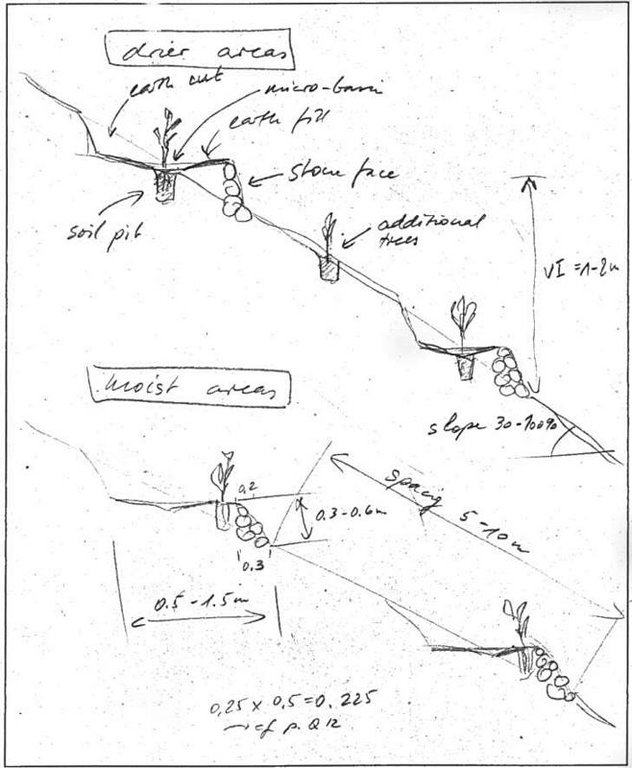
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Hillside terrace cross-section. Linied out along the contour, vertical interval between two terraces 2-5 m. (In: Soil Conservation in Ethiopia. CFSCDD, 1986)
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: reduction of slope angle, increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Trees/ shrubs species: Eucalyptus, Cupressus, Juniperus
Construction material (stone): Cut and fill with stone wall in front
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:10
Change of land use type: closed area
Other type of management: livestock management - prevention of grazing, cut and ary system
ผู้เขียน:
Joerg Wetzel, SCRP
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Ethiopan Birr
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
7.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
1.00
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Transplanting | beginning of rainy season |
| 2. | Seeding | nurseries |
| 3. | Construction | dry season |
| 4. | Planting | beginning of rainy season |
| 5. | Community guarding of closed areas | annual |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | rainy season /each cropping season |
| 2. | Control of grazing | always/annual |
| 3. | Care taking of seedlings | rainy season/each cropping season |
| 4. | communty guarding of closed areas | continuos / annual |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Length of structure on an average slope
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Slope, soil condition, length of terrace per hectare.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Annual rainfall: Also 1000-1500 mm
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- ชื้น
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
- แห้งแล้ง
Semi arid: Too little rainfall
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Slopes on average: Everything below 16 % is to genly sloping to be useful
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
- ต่ำ (<1%)
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- ยากจนมาก
- จน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land.
5% of the land users are rich and own 40% of the land.
20% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land.
60% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Labour offered to projects.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
60
หลังจาก SLM:
40
ดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
55
หลังจาก SLM:
30
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบ
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
30600
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
30000 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
2% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
600 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Very recently, some villages have begun to see the value of hillside terracing, afforestations and area closure if they are given full responsibility to manage the area by a group of land users.
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Hurni H. : Soil Conservation in Ethiopia. Guidelines for Development Agents.. 1986.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
SCRP Addis Abeba
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล