Permanent grassland on peaty and eroded soils [เอสโตเนีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Endla Reintam
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Ursula Gaemperli, Gudrun Schwilch, Alexandra Gavilano
Püsirohumaa turvas- ja erodeeritud muldadel
technologies_3113 - เอสโตเนีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Selge Are
Hummuli Agro
เอสโตเนีย
researcher:
Penu Priit
Agricultural Research Centre
เอสโตเนีย
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
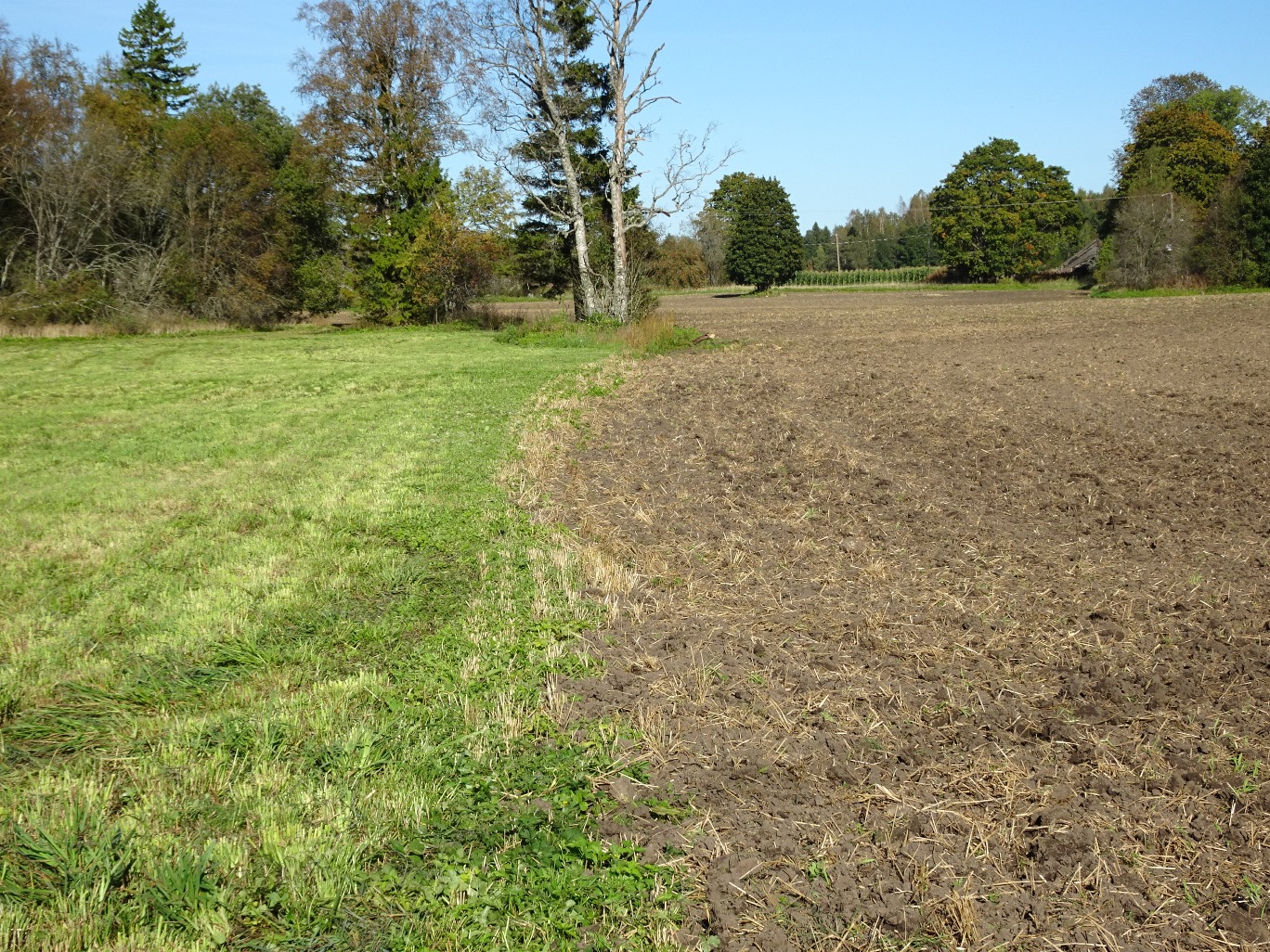
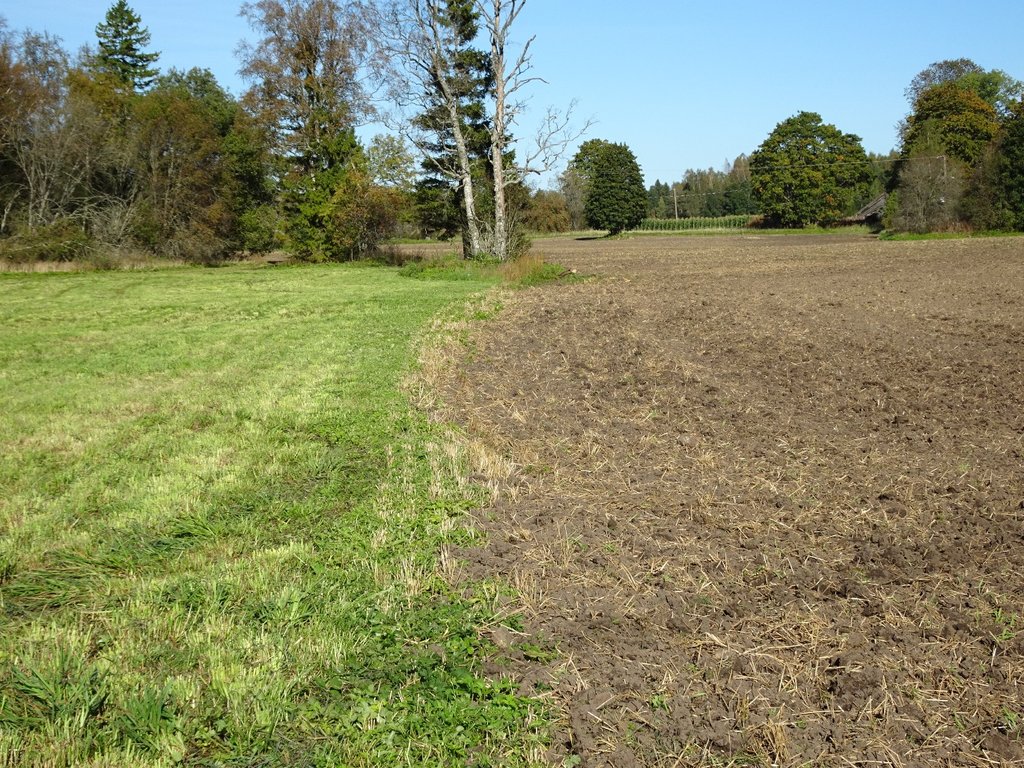
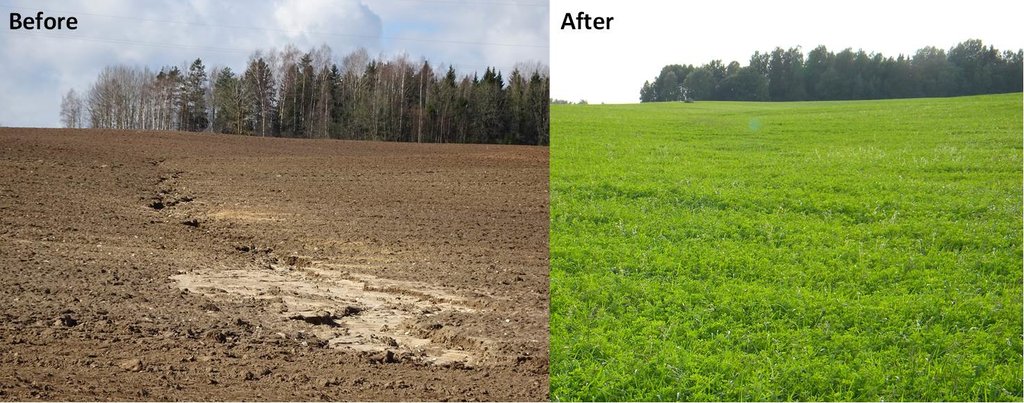
A permanent plant cover is maintained or established to protect soil against erosion or peat decomposition.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
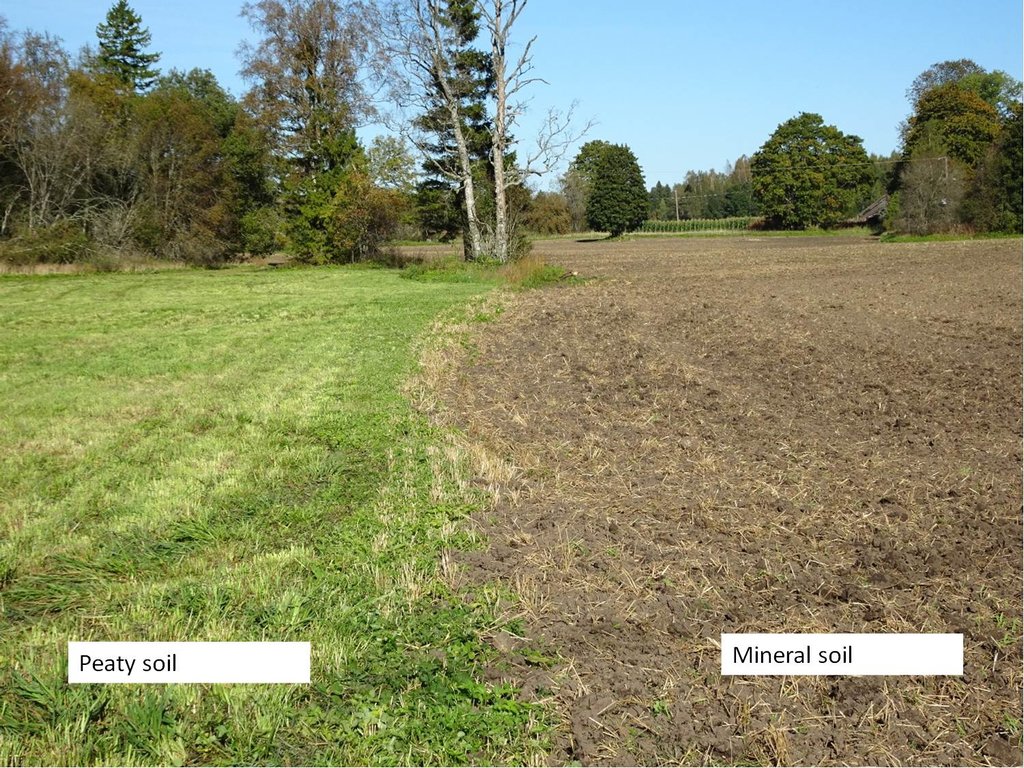
The technology is applied in sub-humid climate with an average of 696 mm of precipitations per year, from which more comes from July to October and less in March and April. Average annual temperature is +4 C, length of the growing period is 180-195 days. The territory is mostly flat to slopes of 6-10%. Average altitude from the sea level is 50 m. About half of the Estonian territory is above 50 m and half is below it. Soils are from very shallow (less than 0.1 m) inthe north to very deep (> 120m ) in the south. Soil cover is very variable. The peat cover of peatlands varies from 0.3 m to more than 10 m from well decomposed to poorly decomposed peat. On hilly areas the soils are medium textured with low (< 1%) organic matter in topsoil. Groundwater in near the surface in peatlands and deep in hilly areas. Biodiversity of these areas is medium. Market orientation of production system is mixed and off-farm income less than 10%. Relative level of wealth is average from individual households to cooperatives. Soil management is mechanized. Land belongs to land users but is leased also in case of bigger farms (over 1000 ha).
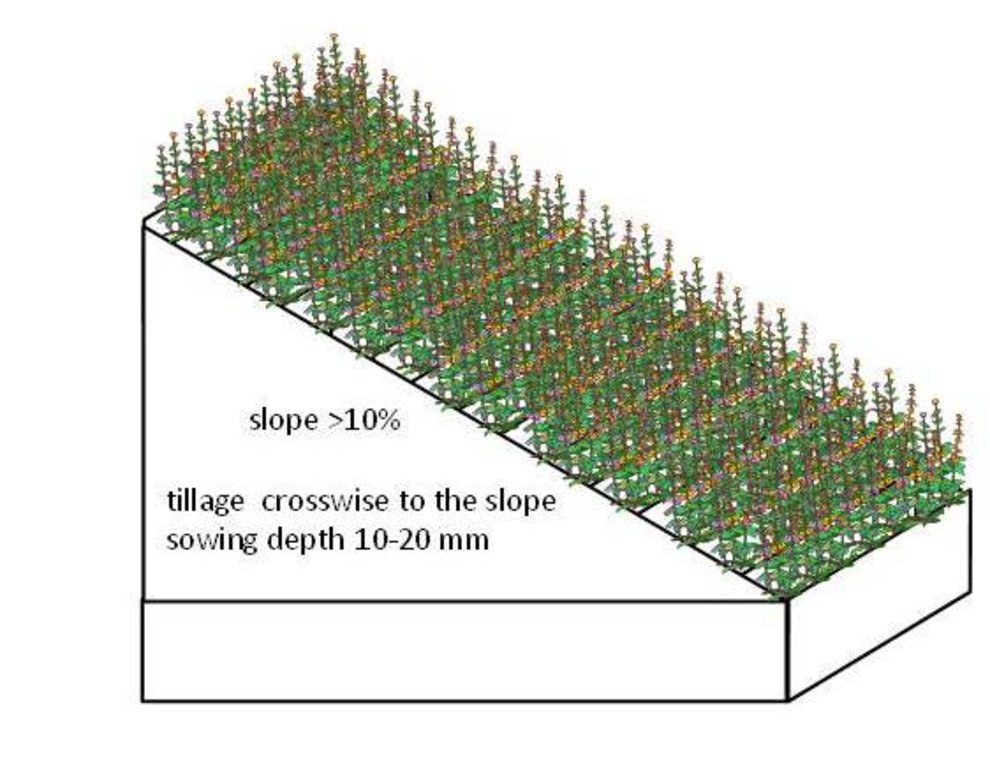
In the agricultural land the area will be excluded from intensive tillage by establishing a permanent plant cover, mainly with grass. The aim is to protect the slopes over 10% against erosion and peaty soils from further intensive decomposition of organic matter and with that the reduction of CO2 emission. The farmers should maintain permanent plant cover in the areas mentioned, or establish permanent plant cover. Renewing of the grassland is allowed from the top (without ploughing) once in a 5 year period. Government pays support of 50 EUR/ha if the area is bigger than 0.3 ha. The technology reduces intensively tilled area and thus the possibility to grow cash crops and/or reduces the yield from grassland. On the other hand it allows to still use wet areas for agriculture (i.e. fodder production).
The rules of the technology are fixed with the Estonian Rural Development Plan (ERDP) for 2014-2020 under activity "Support for regional soil protection" (https://www.agri.ee/et/eesmargid-tegevused/eesti-maaelu-arengukava-mak-2014-2020) related to the reguation of the European Parliment and of the Council 1305/2013, article 28. The regulation is relevant more to the South-Estonia in case to reduce erosion, as the landscape is more hilly there. The exclusion of peatlands from agricultural use is relevant more in West-Estonia where the share of peatlands of the total area is the highest. However, it can be applied in whole Estonia if the area of peatland is bigger than 0.3 ha.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เอสโตเนีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
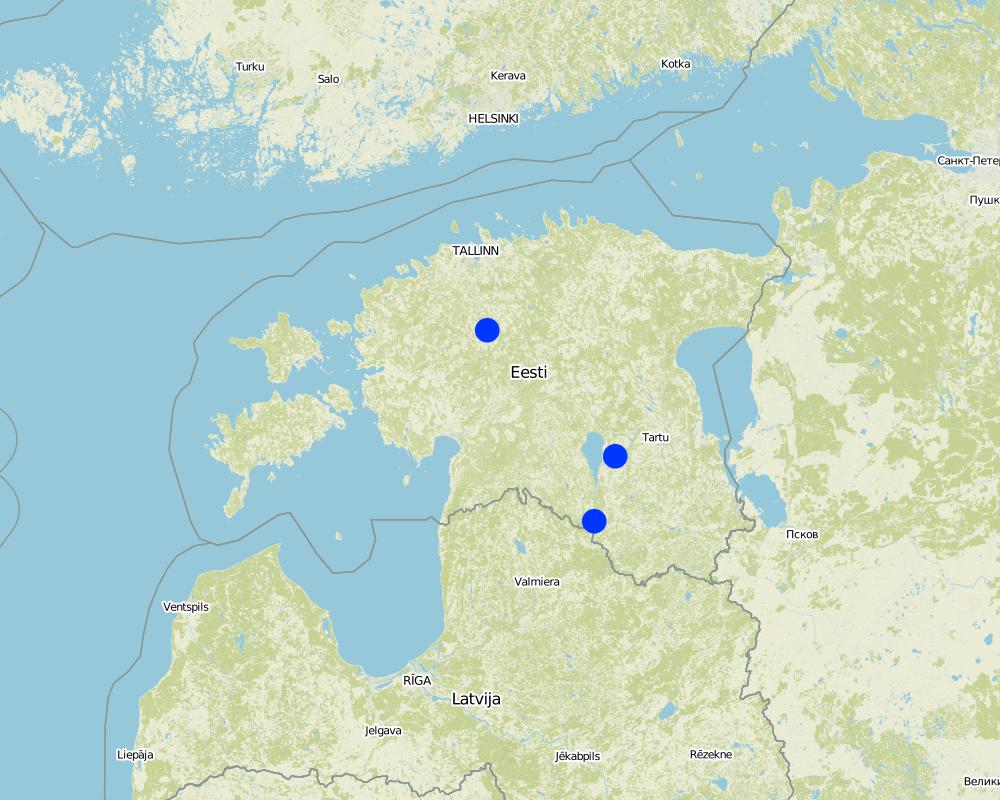
One site at Rapla, second at Tartu, third at Valga (erosion)
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
One site: Rapla county, Pae; second site Tartu county, Annikoru, third site Valga county, Hummuli
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 1-10 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
To get the governmental support the area should be larger than 0.3 ha. Othervise the size is not important, depending on the area covered by hilly area or wet soils in the landscape.
In 2016 it was 10554 ha Histosols and only 40 ha of eroded soils covered with this technology in Estonia. This area excludes grasslands on another soil types. On specific sites: in Rapla county in Pae the size of the field is ca 3.2 ha, at Tartu county, Annikoru 2.8 ha.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
- Governmental tool
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The tool is a part of Estonian Rural Development Plan (ERDP) for 2014–2020 for soil fertility.
The survey was done by the Soil Survey Bureau of the Estonian Agricultural Research Centre (http://pmk.agri.ee/). The results presented here are partly from this survey and from the work done by the project iSQAPER.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ชะลอการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลกและผลกระทบ
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agro-pastoralism (incl. integrated crop-livestock)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - barley
- cereals - maize
- cereals - oats
- cereals - rye
- legumes and pulses - beans
- legumes and pulses - peas
- oilseed crops - sunflower, rapeseed, other
- root/tuber crops - potatoes
- vegetables - leafy vegetables (salads, cabbage, spinach, other)
- vegetables - root vegetables (carrots, onions, beet, other)
- wheat
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
For the cereals one harvest per year, for grasslands 1-4 cuts per year. For hay 1 cut, for silage 2-4 cuts depending on the year

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Extensive grazing:
- การทำฟาร์มปศุสัตว์ (Ranching)
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่มีการจัดการแบบเข้มข้นหรือการผลิตอาหารสัตว์:
- ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่ได้มีการปรับปรุง (Improved pastures)
Animal type:
- cattle - dairy
- cattle - non-dairy beef
- sheep
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- meat
- milk
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Usually before the implementation of the technology the land was intensively tilled and used for annual crop plantation. After implementation the grasslands can be used for cutting and grazing.
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
On Histosols the groundwater is close to the surface.
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- การรบกวนดินให้น้อยที่สุด
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A3: การรักษาหน้าดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M1: การเปลี่ยนรูปแบบของการใช้ประโยชน์ที่ดิน
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม
- Et (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
The requirements to create a permanent grassland depends on soil type.
Species mixture suitable for the permanent grassland on wet soils (Histosols): Bromus sitchensis 30%, Phalaris arundinacea 45%, Phleum pratense 20%, Poa pratensis 5%. Sowing rate 20 kg/ha.
For the drier areas (eroded soils) the next mixture is suitable: Dactylis glomerata 65%, Phleum pratense 26%, Poa pratensis 9%. Sowing rate 23 kg/ha.
ผู้เขียน:
Endla Reintam
วันที่:
14/08/2017
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อหน่วยเทคโนโลยี
โปรดระบุหน่วย:
per hectar
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
EUR
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
1.18
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
36-40 EUR/day + taxes
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tillage (ploughing, cultivation) | in spring |
| 2. | Collecting stones, slip (by demand) | in spring |
| 3. | Fertilization | in spring complex fertilizer |
| 4. | Sowing | in spring |
| 5. | Rolling | in spring |
| 6. | Cutting the weeds | during growth (summer) |
| 7. | Fertilization during growth period | after every cut of grass, if cutted grassland, N-fertilizer |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
If renewing the grassland, there will be no ploughing, collecting the stones and sliping. Only chisel plowing and/or sowing with fertilization. If the grassland will be use for grazing, no need for fertilization during growth period.
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Driver (machinery work) | person day | 0.5 | 36.0 | 18.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Equipment (machinery) cost on establishment year | year | 1.0 | 207.0 | 207.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds | kg | 22.0 | 2.47 | 54.34 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Complex fertilizer | kg | 500.0 | 0.42 | 210.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Ammonium fertilizer | kg | 100.0 | 0.33 | 33.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 522.34 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 442.66 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
For tillage and other operations it is calculated 14-18 EUR/ha.
If to hire equipment the labour costs should be included to the machinery costs - for cutted grassland 225 EUR/ha, for grazed grassland 162 EUR/ha
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cutting or grazing the grass | 1-4 times per vegetation period |
| 2. | Fertilization | in spring in the beginning of season and after every cut N-fertilizer, after each second year complex fertilizer |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| อุปกรณ์ | Grasslands for cutting - machinery costs | year | 1.0 | 141.0 | 141.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Ammonium fertilizer | kg | 200.0 | 0.33 | 66.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Complex fertilizer | kg | 200.0 | 0.42 | 84.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Materials for hay making | year | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 306.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 259.32 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The governmental support to establish and to maintain the grassland is 50 EUR/ha.
If to use the land for the grazing, the machinery cost per year is 38 EUR/ha.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Fuel price.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
696.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Average 696 mm, almost equally spread over the year, more from July to October, less in March and April
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Tartu Tõravere
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
LGP 180-195 days
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- บริเวณสันเขา (convex situations)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- สูง (>3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Eutric Histosol, well decomposed peat, drained area.N 2.32%; C32.89%; C/N14.20%; P2,62 mg/100g; K 13.73 mg/100g; Ca 1762.32 mg/100g; Mg 166.98mg/100g
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
<5 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Histosols biodiversity depends on the base saturation and level of groundwater (degree of drainage). Diversity is higher at higher pH and better drainage.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
- สหกรณ์
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
- ผู้สูงอายุ
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดใหญ่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
There are also small-scale and medium-scale farms applying the technology. At Pae, the farm have 4900 ha of land, from which 1800 are grasslands, at Annikoru the farm have 2320 ha of land from which 390.5 ha are grasslands.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เช่า
- รายบุคคล
- individual/open access
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Groundwater belongs to the state. Smaller water bodies can be in individual use, larger are usually open access
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The area will be excluded from crop production and it means no cash crops can be cultivated on this area. Instead of crops hay or silage is possible to sell.
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As it is not allowed to renew these grasslands intensively, the quantity of grass will drop. For short term clover+grasses mixture the average yield is 16 tons/ha per year, for long-term grass mixtures 5.2 tons/ha per year.
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to the change of species in the mixture, the protein level will drop. Instead of red clover grasses will be used in the mixture of long-term grasslands.
การผลิตสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to the changes in silage/hay quality (protein) there can be reduction of milk and meat production if the differences will not be covered with other fodder.
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
In case of crop orientation, there are new products to sell - grass, hay, silage, or grasslands to rent.
การจัดการที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Depending on the farm it can be simplified or hindered. If focus was on crops, then new machinery is needed to manage grasslands (for cutting, hay or silage making).
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As renewing of grassland is after every 5 years, there is no need to buy seeds every year, as well as pesticides and to till the soil.
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to the reduction of the inputs costs, the income my increase. Also the government pays support 50 EUR/ha for the land under these measures.
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Next to the yield (grass, silage, hay) the support from the government (50 EUR/ha)
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
It may decrease due to no need of every year tillage and sowing and due to the change from 2 year short-term grasslands to the permanent grasslands. However, if not managed grasslands earlier it may increase the workload as cutting and collecting the grass is needed.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
More land under grasslands than under crops. Grasses are suitable for animals feeding, not for human direct consumption.
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
If land was eroded before and soil was on the road, everybody can see the differences after establishment of the grasslands. It is not so severe in case of peatlands, however, less tractors will stuck in to the mud on rainy period.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
In case of erosion, no soil will be washed down to the hill as plant cover protects soil surface and increases infiltration. In case of peatlands, grass cover creates better structure and increases water infiltration thus decreases surface runoff during heavy rainfall.
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Grass creates protection to the soil surface and raindrops can't destroy the soil structure any more. Also grass roots create better porosity and structure in the soil leading to better water drainage.
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The difference in soil moisture between mineral and organic soils under cereals and under grassland was ca 5% and 25%, respectively, in favour to the grasslands in autumn 2016.
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
40%
หลังจาก SLM:
100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Under spring cereals soil is covered only 4-5 months per year, under grasses soil is covered 100% of the year.
การสูญเสียดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
On the slopes depending o the crop and the amount of precipitations, the loss varied from 3 to 60 tons/ha, under permanent grass cover it is less than 0.05 tons/ha per year. Without every year tillage there is no intensive decomposition of the peat, as well as no wind erosion.
การสะสมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Under grasses we can increase the soil organic matter content by 0.35 t/ha in 5 year period in peatlands. In eroded soils we can increase 0.02% per year.
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As plants protect soil surface, raindrops can't destroy the soil structure and there will be no crust formation
การอัดแน่นของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Under the grasslands the bulk density was lower by 0.1-0.2 g/cm3 compared to tilled soil.
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As the intensive decomposition of the peat stops or there will not be any leaching by water, more nutrients remain in the soil. Also the permanent plant cover during the whole year stops nutrient leaching.
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Under permanent grasslands the Corg increases by 0.35 t/ha per 5 year period.
ความเป็นกรด
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Without periodic liming the acidity of peatlands starts to increase. If no CaCO3 in mineral part, also pH of previously eroded soils starts to decrease slowly, as organic acids form during decomposition process.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Thanks to the permanent plant cover there is no period of the year without vegetation.
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
If previously the plant residues were mixed with the soil by tillage, now there will always some extent of plant mass be left above ground (5-10 cm), even if the most is removed for hay or silage.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Long-term grassland includes at least 4 species in the mixture, short-term mixtures 2-3 species. However, compared with the cereals, the annual weeds will disappear and the diversity may decline.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There are more spiders, ants, beets.
ชนิดพันธุ์ที่ให้ประโยชน์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
2 species of earthworms
หลังจาก SLM:
3-4 species of earthworms
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Under grasslands were 1-2 more earthworm species than under tilled management. More spiders and ground beetles were found there compared to the tilled soil.
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Grasslands create untilled patterns to the landscape.
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Grasses surpress many soil born crops diseases and pests, also annual and perennial weeds.
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Grass roots go to the deeper soil and they are not so sensitive to the drought.
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Under permanent grasslands reduced CO2 emission by 1.10 t/ha per year compared to the tilled areas.
ความเสี่ยงจากไฟ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
If the grass will not be cutted before winter, the dry grass has the risk of higher landscape fires in the spring.
ภูมิอากาศจุลภาค
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The changes of soil temperature as well as moisture content are smaller under permanent grass cover than under tillage.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
All year plant cover helps to bind nutrients and stop their leaching from the soil. Higher amount of organic matter in the soil increases water holding capacity.
ตะกอนที่ถูกพัดพามาโดยลม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Organic peat particles are light and are easy subject of wind erosion in dry conditions by tillage. Permanent plant cover stops such kind of erosion
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
On hilly landscape no extra soil is flushed to neighbours fields. In case of peatlands no dust is carried around.
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
In case of erosion, no soil is carried by water or wind to the ditches and on the roads.
ผลกระทบของก๊าซเรือนกระจก
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Under permanent grasslands reduced CO2 emission by 1.10 t/ha per year compared to the tilled areas.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ปานกลาง | |
| อุณหภูมิตามฤดูกาล | ฤดูหนาว | เพิ่มขึ้น | ปานกลาง |
| อุณหภูมิตามฤดูกาล | ฤดูใบไม้ผลิ | เพิ่มขึ้น | ปานกลาง |
| ฝนประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ไม่ทราบ | |
| ฝนตามฤดู | ฤดูหนาว | เพิ่มขึ้น | ไม่ทราบ |
| ฝนตามฤดู | ฤดูใบไม้ร่วง | เพิ่มขึ้น | ไม่ทราบ |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ปานกลาง |
| พายุฝนฟ้าคะนองประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
| พายุลูกเห็บประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
| พายุหิมะประจำท้องถิ่น | ปานกลาง |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ทราบ |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| คลื่นความหนาว | ไม่ทราบ |
| สภาพอากาศฤดูหนาวที่รุนแรง | ปานกลาง |
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ปานกลาง |
| ไฟบนบก | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ปานกลาง |
| น้ำขึ้นจากพายุหรือน้ำท่วมชายฝั่ง | ปานกลาง |
| ดินถล่ม | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติทางชีวภาพ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| โรคระบาด | ดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- > 50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
In 2016 two hundred four households got the governmental support, in total 10554 ha
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 11-50%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Anyway, the use of Histosols and Gleysols is limited due to their properties and regular use of these soils is for grazing or grass cutting.
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Better soil protection |
| Possibility to earn money in unsuitable soil conditions. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Reduces soil erosion on hilly landscape |
| Reduces the decomposition of peat on Histosol |
| Reduces CO2 emission from agricultural land. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Loss of income | Governmental support (50 EUR/ha) |
| Problems with the grass (farms without animals) | Cooperation with neighbours, selling the hay for energy production |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Farmers don't want to use the technology | More effective lobbying |
| Wrong declaration of the land under the technology | Better advisory system and improvement of electronic databases |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
5 within iSQAPER project but more than 20 during another projects
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
10 within iSQAPER project but more than 20 during another projects
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
8
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
04/06/2017
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Bender, A. (koostaja) 2006. Eritüübiliste rohumaade rajamine ja kasutamine. I. ja II. osa. Jõgeva
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Bender, A. 2010. Heintaimede sordiaretus ja seemnekasvatus. Jõgeva Sordiaretuse Instituut
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Older, H. 2011. Kohalikud söödad. Eesti Rohumaade Ühing.
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Estonian Rural Development Plan (ERDP) for 2014–2020
URL:
https://www.agri.ee/en/objectives-activities/estonian-rural-development-plan-erdp-2014-2020
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Kattetulu arvestused taime- ja loomakasvatuses 2016. Koost: Marju Aamisepp, Helle Persitski. Maamajanduse infokeskus. 2017.
URL:
http://www.maainfo.ee/data/trykis/kattetulu/KATTETULU2016.pdf
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Statistics Estonia
URL:
https://www.stat.ee/en
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Eesti maaelu arengukava 2007-2013 2. telje ning Eesti maaelu arengukava 2014-2020 4. ja 5. prioriteedi püsihindamiseks 2016. aastal läbiviidud uuringute aruanne. Põllumajandusuuringute keskus. Saku 2016.
URL:
http://pmk.agri.ee/mak/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2016/09/aruanne_uuringud_2015.pdf
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Eesti tuleviku kliimastsenaariumid aastani 2100
URL:
https://www.envir.ee/sites/default/files/kliimastsenaariumid_kaur_aruanne_ver190815.pdf
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล