Dedha grazing system as a natural resource management technology [เคนยา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: IBRAHIM JARSO
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Caroline King-Okumu
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Hanspeter Liniger, Donia Mühlematter, Barbara *, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Alexandra Gavilano, Joana Eichenberger
Jars Dedha
technologies_3403 - เคนยา
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF เพื่อพิมพ์
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปหน้าเว็บ
- บทสรุปทั้งหมด (ไม่มีการจัดเรียง)
- Dedha grazing system as a natural resource management technology: 12 กรกฎาคม 2018 (inactive)
- Dedha grazing system as a natural resource management technology: 8 พฤษภาคม 2019 (inactive)
- Dedha grazing system as a natural resource management technology: 31 กรกฎาคม 2018 (inactive)
- Dedha grazing system as a natural resource management technology: 3 กันยายน 2018 (inactive)
- Dedha grazing system as a natural resource management technology : 13 พฤษภาคม 2018 (inactive)
- Dedha grazing system as a natural resource management technology: 2 พฤศจิกายน 2021 (inactive)
- Dedha grazing system as a natural resource management technology: 2 พฤศจิกายน 2021 (public)
- Dedha grazing system as a natural resource management technology : 27 เมษายน 2018 (inactive)
- Dedha grazing system as a natural resource management technology : 27 เมษายน 2018 (inactive)
- Dedha grazing system as a natural resource management technology : 20 เมษายน 2018 (inactive)
- Dedha grazing system as a natural resource management technology : 19 มีนาคม 2018 (inactive)
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Strengthening Adaptation and Resilience to Climate Change in Kenya Plus (StARCK+)ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Book project: Guidelines to Rangeland Management in Sub-Saharan Africa (Rangeland Management)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Resource Advocacy Programme (RAP) - เคนยา1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology is a sustainable land management practice that had been used for time immemorial by Boran pastoralists to manage land and land-based resources.
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
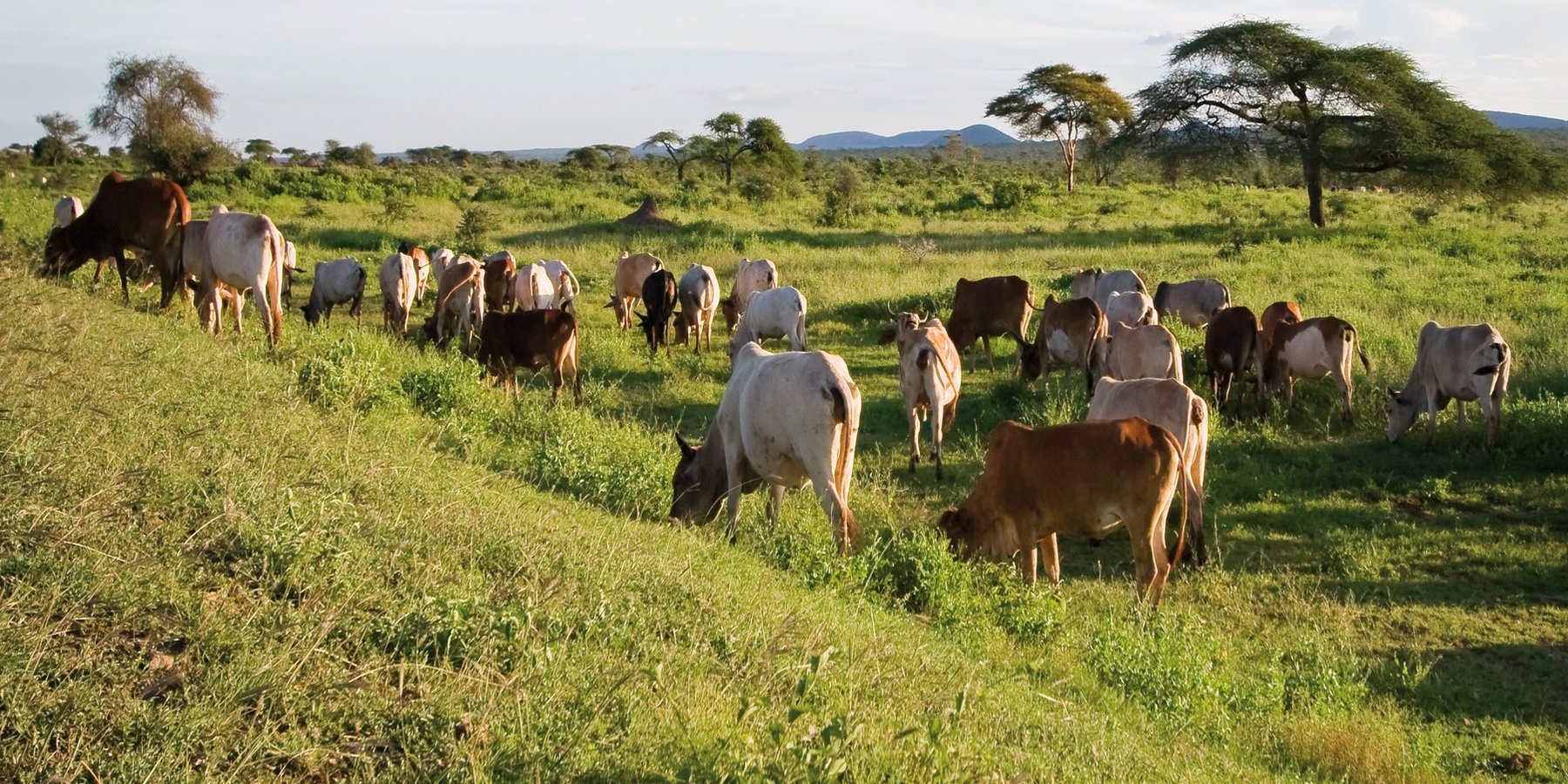
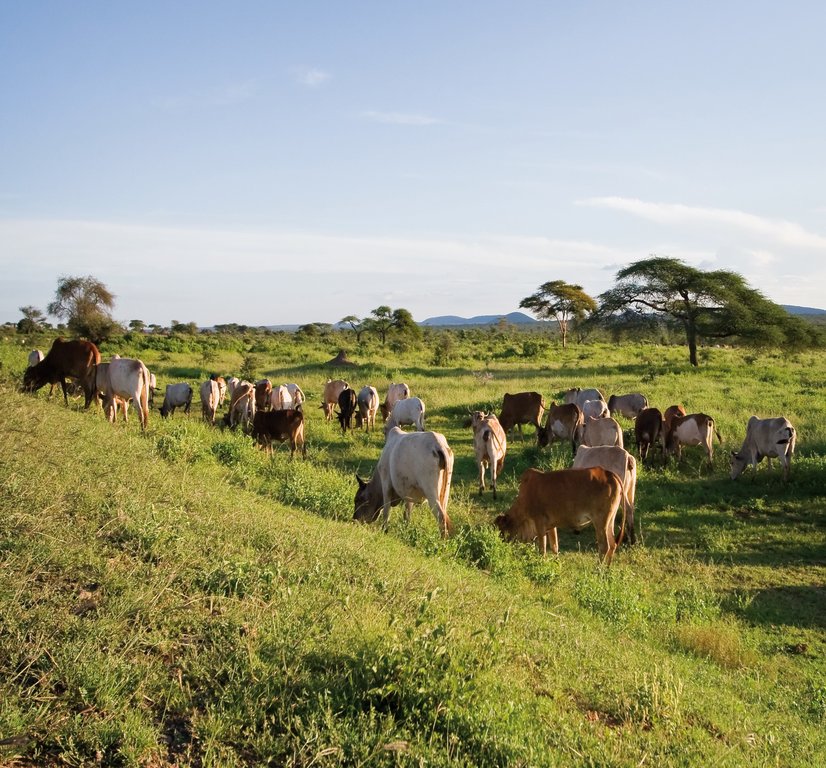
The Dedha grazing system is an ancient, traditional governance system for land and its resources practiced by Boran pastoralists. It carefully balances how pastoralists use rangeland resources. The basis of the technology is three grazing rangeland governance zones: wet season grazing, dry season grazing, and drought reserves. There is also water governance based on a traditional hierarchy of rights. Through this system, Boran pastoralists adapt to severe and recurrent droughts.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
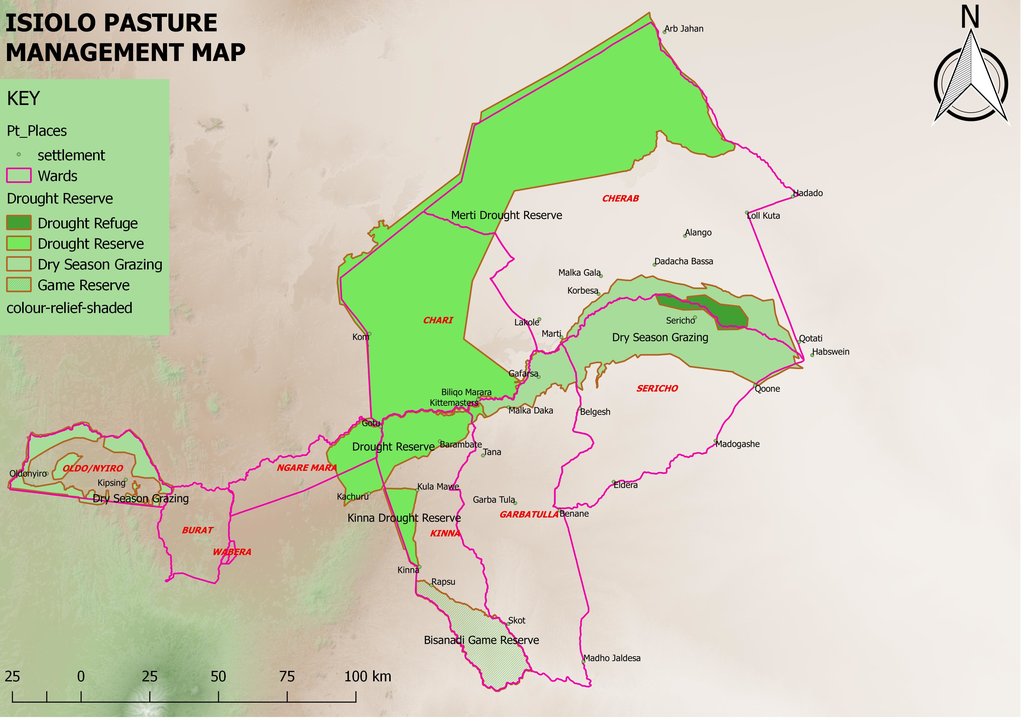
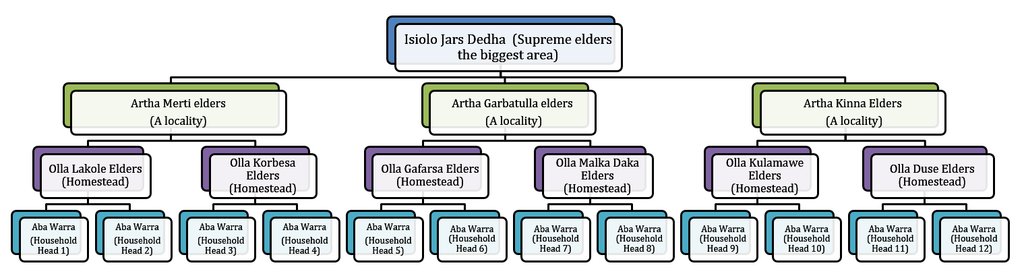
This grazing system is applied in Isiolo County, Northern Kenya. The Waso rangelands are inhabited by Boran pastoralists with Somali, Samburu, Rendille and Turkana herders sharing cross-border resources through negotiation. The technology is based on the maintenance of a delicate balance between livestock numbers, the supply of water, and the amount/ quality of standing pasture within the vast grazing area which is water scarce and prone to extreme seasonal variations. Through its main tenet of governing grazing patterns (wet, dry season grazing area and drought reserve) planned use of pasture is decided in large pastoralists’ assemblies attended by elders from a particular “Dedha” (a grazing area, which administratively can be as big as two wards). This process is complicated by dry seasons and droughts of unknown length, with pressure from the community to open grazing reserves. Wrong decisions can spell the end of livelihoods for some families. An ability, which has been gradually eroded over time and by external factors which don’t understand its enormous benefit but there is a project which is using an integrated approach to revive and empower this system.
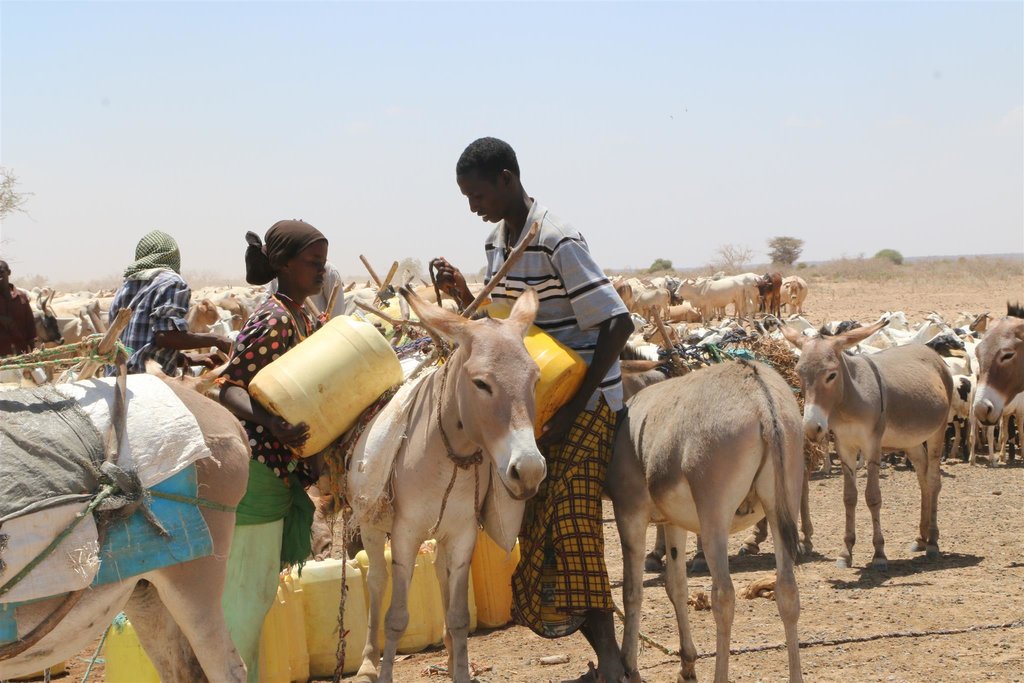
The Jars a Dedha use water points to manage grazing. Different types of water sources need specific forms of management. The most intensive management occurs during droughts at deep wells and boreholes which require the most labour to operate and maintain, and are the most reliable sources of water. Due to the strategic importance of these resources, management falls to the Jarsa Dedha (council of elders). The use of shallow wells is tightly controlled by both the aba ella (the person who first dug it) and aba erega (the owner of the rotter ) working together. Aba ella is assigned first rights to water. If there is spare capacity then ‘second rights’ are decided by aba erega. Second rights would typically fall to those of a different clan, while ‘third rights’ might fall to a different ethnic group. The Borana customs and culture defines both access to certain wells but also the order of priority for watering animals.
In addition, in consultation with the Dedha council of elders, aba erega manages the use of dams and access to rivers. Generally, use of flowing river water is restricted to the dry season and access is limited to designated watering points. These are located some distance downriver from settlements to minimize disruption to inhabitants and to reduce contamination. Temporary water sources during and after the rains are not subject to control except when their use conflicts with restrictions on grazing areas. After watering their livestock, pastoralists traditionally fill their troughs for wildlife at night. This is intended to prevent wildlife from falling into wells - and to seek God’s blessings.
The high variability of rainfall in pastoral areas leads to similarly variable pasture availability. Therefore, management of grazing resources needs to balance maximizing productivity while ensuring survival. Long-term viability of the system depends on the maintenance of adaptive traits within local breeds, and both maintaining and managing resources strategically. Only within these broader goals is the concept of ‘maximizing productivity’ meaningful.
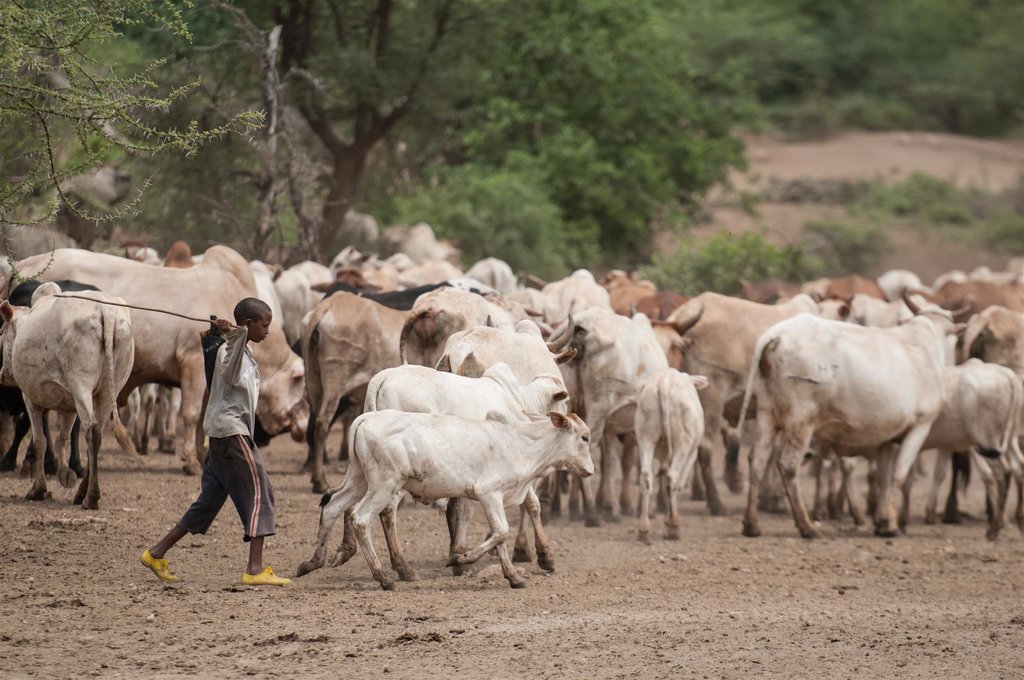
Mature livestock (gues) which are not lactating are moved to remote pastures. The gues, which make up the majority of community livestock, are herded by young unmarried men. By utilizing remote pastures, grazing resources closer to permanent water sources can be preserved for the dry season and droughts. Pasture within the vicinity of homesteads (maar qaae – literally ‘near grass’) is protected from grazing by non-lactating livestock (this is similar to kalo but a kalo reserve need not be next to the homestead ). This pasture is set aside for young animals (calves, lambs, and kids). Migrating livestock have predefined routes that maintain distance from maar qaae. The Dedha council of elders, therefore, controls settlement patterns to preserve key migratory routes. Movement of livestock between different Dedhas must be prearranged with the respective Dedha council of elders who assess spare capacity in terms of water and grazing.
The floodplain grazing area (chaafa) is crucial because it acts as a refuge for livestock during extreme drought. Grazing in chaafa is strictly prohibited during the wet season and one of the critical decisions for the Jarsa Dedha is when to open chaafa after rains have failed. Due to the relatively moist conditions in chaafa, there are additional challenges to animal and human health: namely trypanosomiasis, ticks, pneumonia, and malaria. Jarsa Dedha make decisions primarily concerning seasonal movements from wet to dry season grazing and also the opening of boreholes and chaafa. The overwhelming local consensus is that efficient resource use depends on the ability ofJarsa Dedha to enforce these regulations
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เคนยา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Isiolo
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Kinna town, Kinna Ward, isiolo County
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- > 10,000 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Kinna Town, Kinna Ward, Garbatulla Sub County, Isiolo County
Isiolo County has area of 25,000Km2 but 80% of the area is used for Nomadic pastoralism.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- มากกว่า 50 ปี (แบบดั้งเดิม)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
It is inherited from generations before.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
- ป้องกันพื้นที่ลุ่มน้ำ/บริเวณท้ายน้ำ โดยร่วมกับเทคโนโลยีอื่นๆ
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
- ชะลอการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลกและผลกระทบ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านสังคมที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Extensive grazing:
- การเลี้ยงสัตว์แบบเร่ร่อนไปตามที่ต่าง ๆ (Nomadism)
- กึ่งโนแมนดิซึ่มหรือแพสโตแรลลิซึ่ม (Semi-nomadism/pastoralism)
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่มีการจัดการแบบเข้มข้นหรือการผลิตอาหารสัตว์:
- ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่ได้มีการปรับปรุง (Improved pastures)
Animal type:
- goats
- camels
- sheep
- cattle
Species:
camels
Count:
39100
Species:
goats
Count:
399000
Species:
sheep
Count:
361900
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Number of growing seasons per year: 2
Grasses and shrubs which nourishes livestock grows during the rainy seasons
Livestock density: Isiolo county is endowed with a substantial livestock resource base that includes 198,500 cattle, 399,000 goats, 361,900 sheep and 39,100 camels
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The pastoralists depend on attendant pasture after the rains which are bi-modal in Isiolo County (Long and Short rains).
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการปศุสัตว์และทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
- M3: การวางผังตามสิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและสิ่งแวดล้อมของมนุษย์
- M4: การเปลี่ยนแปลงช่วงเวลาให้เหมาะแก่การทำกิจกรรม
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bh (Loss of habitat): การสูญเสียแหล่งที่อยู่
- Bf (Detrimenta leffects of fires): ผลเสียหายจากไฟ
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
- Hs (Change in quantity of surface water): การเปลี่ยนแปลงปริมาณของน้ำที่ผิวดิน
- Hp (Decline of surface water quality): การลดลงของคุณภาพน้ำที่ผิวดิน
- Hw (Reduction of the buffering capacity of wetland): การลดลงของความทนทานต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลง ของพื้นที่ชุ่มน้ำ
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ปรับตัวกับสภาพความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
The technology is implemented in a vast area of rangelands in Isiolo County which covers around 20,000 km2 inhabited by Boran pastoralists under common management of Isiolo Jars Dedha (Council of elders). The rangelands are subdivided into around 14 arthas (localities) which are separately managed by artha elders and within which there are also ollas (homesteads) which the elders oversee. The elders manage key resources that are essential for pastoral livelihood. The resources are; prime pasture/grazing areas, water points e.g. streams, rivers, springs, shallow wells and pans, wildlife, forests, minerals, sand and other valuable stones e.g. gemstones (bojimine) and quarry, Trees and their products e.g. makuti, medicinal herbs, wild, fruits, resins, gum arabic.
ผู้เขียน:
Ibrahim Jarso
วันที่:
02/05/2017
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
20,000km2
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
2,500 Kenya Shillings
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Dedha elders meetings | All seasons |
| 2. | Surveillance of grazing areas | Largely after the rains |
| 3. | Settling resource based disputes | Largely during dry seasons and drought |
| 4. | Deciding on when to access reserved pasture lands | Dry seasons and drought reserves |
| 5. | Negotiations on access to pasture within and across borders | Drought and Long dry seasons |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Regarding Surveillance of grazing areas, they observe pasture conditions and unwarranted access to preserved grazing areas and report on conditions. The surveillance is elevated after the rains as communities are in wet season grazing area depending on sub-surface water from the rains.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Meetings | All seasons |
| 2. | Surveillance of grazing lands | After the two rainy seasons |
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
This is a traditional technology of governing rangelands which was started and done voluntarily by the pastoralists. The costs considered are for subsistence of elders undertaking the meetings and discussions on range governance but the process still goes on even without the financial support as the actors involved do it for their own benefits.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
The rains are bimodal (Long rains of March-April-May and Short rains of October-November-December). The rains are unpredictable, erratic and not evenly distributed but pastoralists move to take advantage of difference in pasture quality and quantity.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Garbatulla automatic weather station
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
- แห้งแล้ง
5% of the area is Semi-arid and 95% is Arid.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
> 50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุ:
Many boreholes dug in the area is saline
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
เป็นครั้งเป็นคราว
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
The Ewaso Nyiro River floods every rainy seasons
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- กึ่งเร่ร่อน
- เร่ร่อน
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- ยากจนมาก
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
เพศ:
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- ผู้เยาว์
- วัยกลางคน
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดใหญ่
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
2
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The frequent and Severe drought has reduced the number of livestock and created a big group of pastoral dropouts but with improved rangeland management through the revived traditional systems animal production is gradually improving.
การจัดการที่ดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
2
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำดื่มไว้ให้ใช้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
1
การมีน้ำไว้ให้ปศุสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
2
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
2
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
2
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
2
พืชพันธุ์ต่างถิ่นที่รุกล้ำเข้ามา
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
1
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
2
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
-2
หลังจาก SLM:
2
ภูมิอากาศจุลภาค
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
2
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
2
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The preserved grazing lands regenerate and is less degraded. The improved environment in the preserved areas lead to less erosion and proper recharge of underground water. This was observed in Kinna Village where the Odha Springs improved its flow and also the recharge to Moliti shallow wells were improved with proper grazing management in Kinna.
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
2
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิตามฤดูกาล | ฤดูแล้ง | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดีมาก |
| ฝนตามฤดู | ฤดูแล้ง | ลดลง | ดีมาก |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดีมาก |
| ไฟบนบก | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ดี |
| น้ำท่วมฉับพลัน | ปานกลาง |
ภัยพิบัติทางชีวภาพ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| โรคระบาด | ปานกลาง |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ดีมาก |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- > 50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
80% of Isiolo County (Around 24,500 Households)
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าตอบว่าใช่ ให้ระบุว่าเงื่อนไขการเปลี่ยนแปลงใดที่ถูกปรับตัว:
- การเปลี่ยนแปลงแบบค่อยเป็นค่อยไปและสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ
ให้ระบุการปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี (การออกแบบ วัสดุหรือชนิดพันธุ์ เป็นต้น):
The grazing patterns were made more flexible and the rules made stricter.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| It is the cheapest and easiest way of managing the rangelands for now and for posterity. |
| It provides room for flexibility of decision making as seasonal variations occur. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| It is conservative and less costly to implement in the vast rangelands with few incentives. |
| It is a legitimate system recognized by all pastoralist for management of their rangeland resources. |
| It can easily be adapted to govern any pastoral rangelands all over the world (Universal). |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| There is no law protecting it. | Government needs to establish a law that recognizes and protects this technology. |
| Rich pastoralists can forego local rules and corrupt the systems overseeing the grazing plans. | Ensuring accountability for decisions made. As few lead elders can be corrupted and their decisions compromised but when the decisions on grazing are largely made in common meetings of all elders, the decisions are normally watertight and cant be influenced negatively. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Cross-border pastoralists are not aware of the Technology and tend to undermine it. | Improve awareness of the technology among the cross-border pastoralists that also access Isiolo rangelands. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
2
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
6
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
2
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
17/11/2017
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Evolving customary institutions by patison and tari
URL:
pubs.iied.org/pdfs/10076IIED.pdf
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Strengthening Customary institutions the case of Isiolo County Northern Kenya by Caroline, Tari and Jarso
URL:
www.celep.info/wp-content/uploads/2015/11/Strengthening-local-institutions.pdf
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล