Cultivation of blueberries on infertile/degraded soils using plant pots [บอสเนียและเฮอร์เซโกวีนา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Melisa Ljusa
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Donia Mühlematter, THEODORA FETSI, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Kontejnerski uzgoj borovnice na neplodnim ili degradiranim tlima
technologies_4126 - บอสเนียและเฮอร์เซโกวีนา
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Čustović Hamid
Universiyt of Sarajevo, Faculty of Agriculture and Food Sciences
บอสเนียและเฮอร์เซโกวีนา
co-compiler:
Agronomist of the Živinice Municipality:
Butković Mirsad
Municipality of Živinice - Department of Local Economic Development, Finance and Treasury
บอสเนียและเฮอร์เซโกวีนา
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Đogić Alija
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
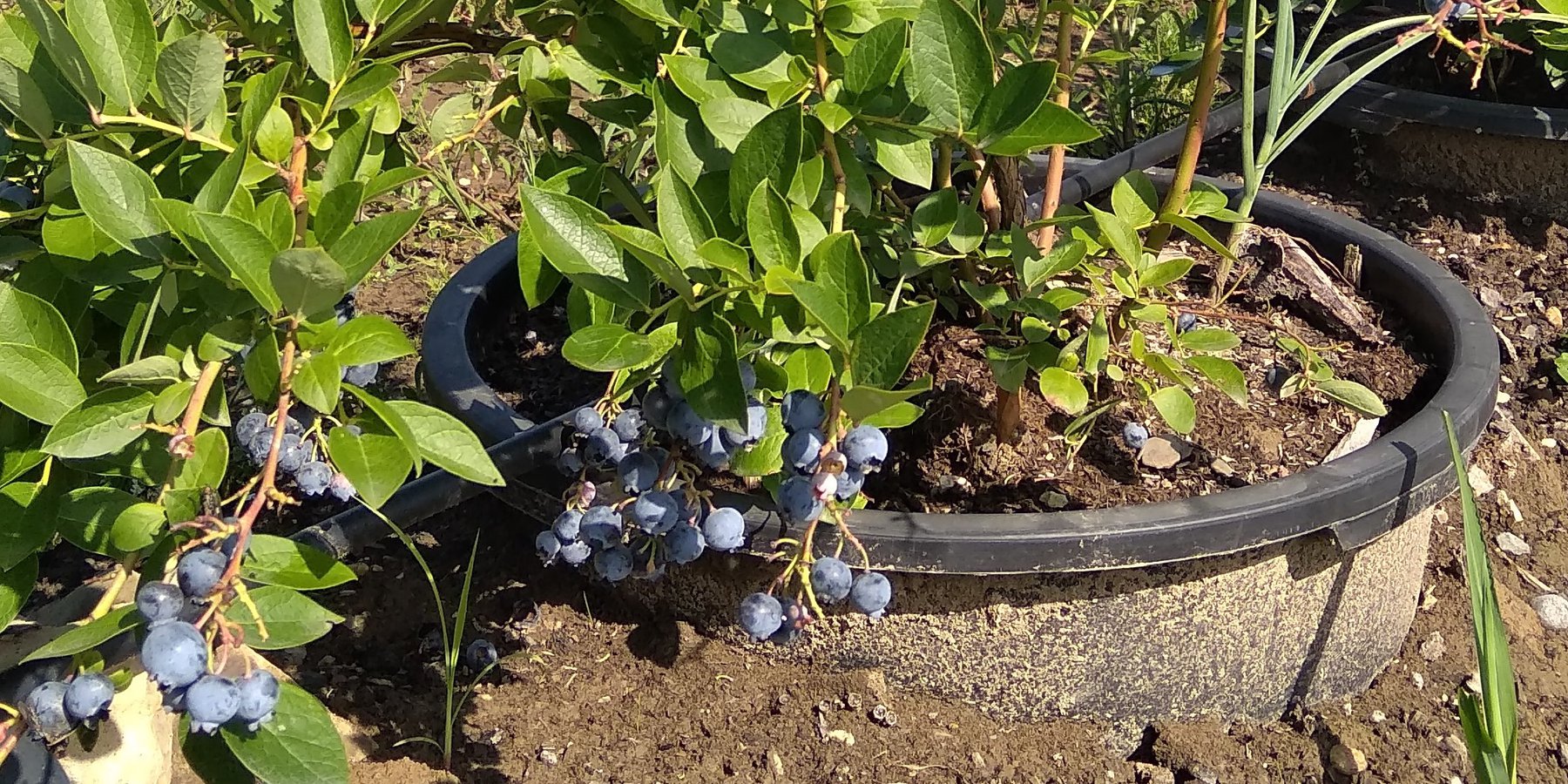
Establishment of blueberries cultivation in plant pots on soils with bad physical or chemical properties. The technology improves productivity and generates income for the farmers. The implementation requires drip irrigation system.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
The cultivation of blueberries in plant pots has been successfully implemented in the area of Živinice municipality - on soils of poor composition, physical properties and low fertility. Many efforts have been made to introduce a conventional production of blueberries but did not bring the expected results due to the bad soil quality.
The soil (Stagnogley) is poorly permeable to water, so even moderate rainfalls cause water remain on the surface, making it difficult or completely impossible to cultivate the land. In addition, soils of high acidity are required for the successful cultivation of blueberries. Planting blueberries in a conventional way is often carried out on soils where the acidity is increased by various additives (often with wood sawdust or similar wooden materials). Practical experience has showed that in the course of time the acidic properties of the soil in the zone of the development of the blueberry root change, i.e. soil/substrate acidity decreases due to resorption processes on the primary soil. Todays' market offers multi-component substrates for the cultivation of blueberries, which, in addition to their adequate acidity, have other properties necessary for a good development of the blueberry's root system. These substrates were also used in some localities of the municipality of Živinice in conventional or modified conventional planting of blueberries (on embankments using soil and commercial substrates). This technique did not yield satisfactory results, probably because of the loss of substrate properties (decrease of soil acidity) due to resorption to the nearby original soil. The substrate keeps its desirable properties much longer if it is put into the planting where blueberries are being planted.
The basic advantage of this technology is its ability to be applied on practically all soils of poor agricultural-productive properties, including heavily degraded and low water permeable soils. Even if the cost for introducing the technology is relatively high, its maintenance is reduced to standard agro-technology (fertigation, plant protection, weed control, harvesting, etc.) due to the type of crop. In the Živinica municipality, technology is currently being applied only in the cultivation of blueberries. The results have shown that the cultivation of blueberries in plant pots provides a yield of about 15 t/ha, which is about 5 t/ha (50%) higher than in the conventional cultivation of the blueberries. The farm on which the technology is described cultivated blueberries of the Duke variety on 8 ha whose fruits are sold at prices between 3.50 and 4.50 USD/kg. The estimated life span of the blueberries grown in plant pots under full yield is 15 years.
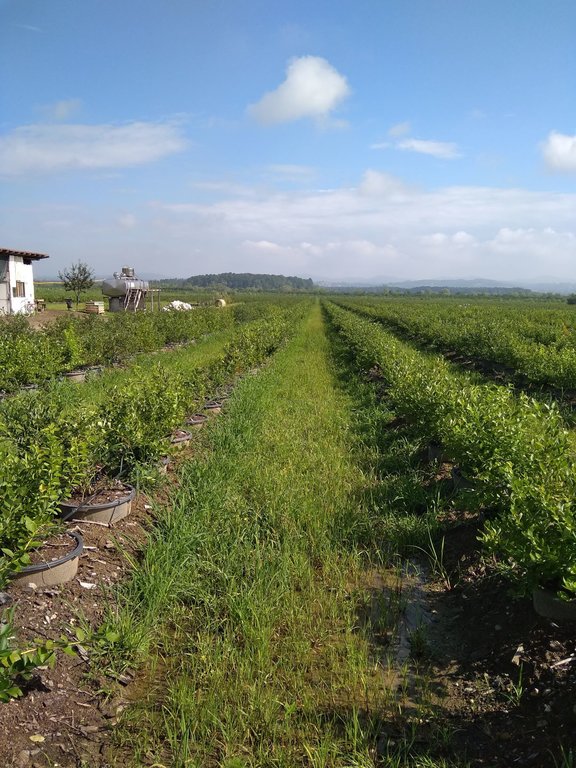
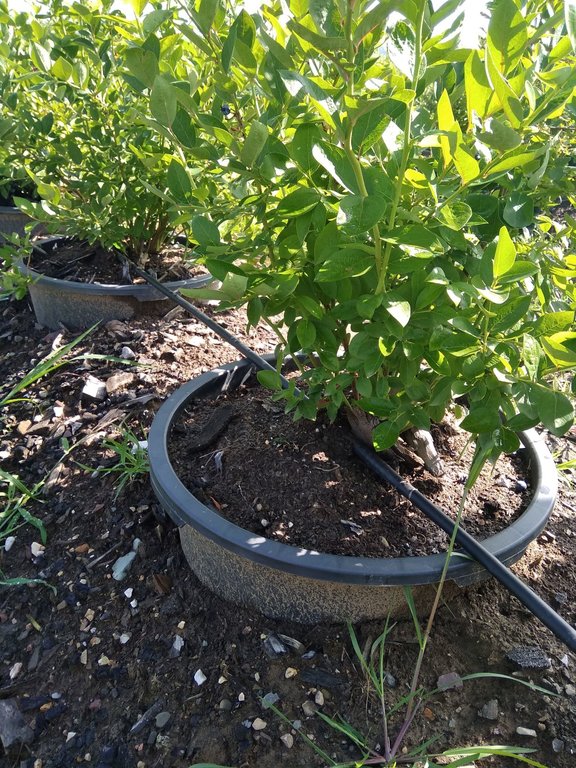
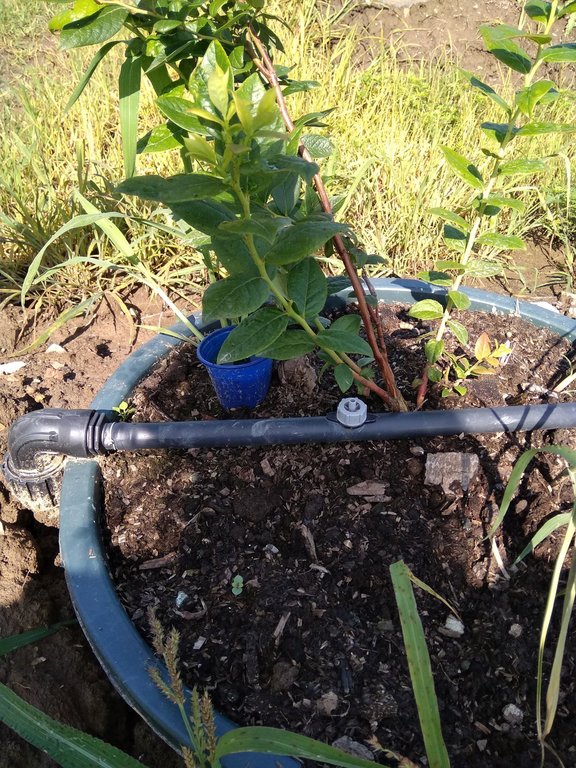
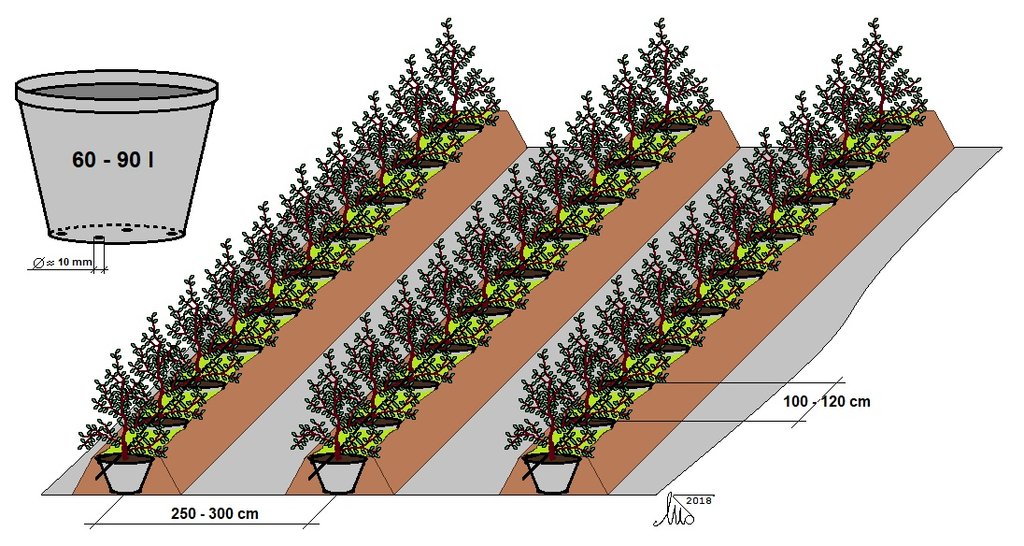
Regarding the technical characteristics of the SLM technology, the plant pots with blueberry plantings are placed in rows of low trenches with a distance of 100-120 cm between the plant pots (from center to center); and 250-300 cm between rows. The plant pots (60 to 90 liters) are placed in later formed embankments (trussing with the original soil), thus ensuring the stability of the plant pots (e.g. from wind) and more favorable temperature and humidity conditions of the substrate in the plant pots. The technology implies possession and use of the drip irrigation system, using the water collected in accumulations and distributed from tanks situated on the farm.
The technology offers relatively innovative use of infertile or degraded soils for the intensive and profitable production of blueberries or other crops, primarily berry fruits. Positive experiences from the implementation of the technology on about 8 ha, on the observed farm resulted in the replacement of the earlier conventionally planted and grown blueberries in the wider area of Živinice. By expanding blueberries cultivation in wider areas, the municipality is considered among the leading blueberry producers in the Balkans.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
บอสเนียและเฮอร์เซโกวีนา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Tuzla Canton
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Živinice municipality
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2014
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The technology was introduced by the endorsement of the Municipality.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The land, where the described technology is applied, is characterized by bad soil physical properties (heavy soils, poorly permeable to water, even moderate rainfalls do not allow movement of workers and mechanization).
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- การชลประทานแบบเต็มรูปแบบ
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- Crop management
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น
- Pk (Slaking and crusting): การอุดตันของช่องว่างในดินหรือรูพรุน
- Pu (Loss of bio-productive function): การสูญเสียหน้าที่การผลิตทางชีวภาพอันเนื่องมาจากกิจกรรม อื่นๆ

อื่น ๆ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology could be applied on practically all kinds of degraded lands if there is a possibility to provide (preferably) drip irrigation.
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ปรับตัวกับสภาพความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
1 ha
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
29.25 USD
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchasing of plantings | Any time |
| 2. | Purchase of substrate | Any time |
| 3. | Ground leveling (if necessary) | Any time |
| 4. | Filling the containers with substrate and planting blueberries in containers | Any time |
| 5. | Formation of rows of containers | Any time |
| 6. | Trussing of rows of containers by original soil | Any time |
| 7. | Installation of drip irrigation system | Any time |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Preferably blueberry plantings are 3 or 2 years old, in plant pots (containers) not smaller than 2 liters.
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Filling the containers with substrate and planting of blueberries | Person day | 28.0 | 29.25 | 819.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Forming and trussing the rows of containers (embankments) | Person day | 30.0 | 29.25 | 877.5 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | (Mecahnization for ground leveling - optional) | Hour | 4.0 | 70.2 | 280.8 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Blueberry plantings in containers (2 or 3 L plant pots) | Piece | 2800.0 | 5.26 | 14728.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Plastic containers (65 l) | Piece | 2800.0 | 5.47 | 15316.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Drip irrigation system (including water tank and pump) | ha | 1.0 | 13460.0 | 13460.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Multi-functional substrate for blueberries | L | 182000.0 | 0.07 | 12740.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 58221.3 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Ground leveling with use of mechanization is not necessary on plain or relatively plain terrains.
The cost of 2 or 3 years old blueberry planting in small (2 l) container include delivery (on farm) costs.
The costs of plastic plant pots (65 l) and substrate for blueberries include delivery (on farm) costs.
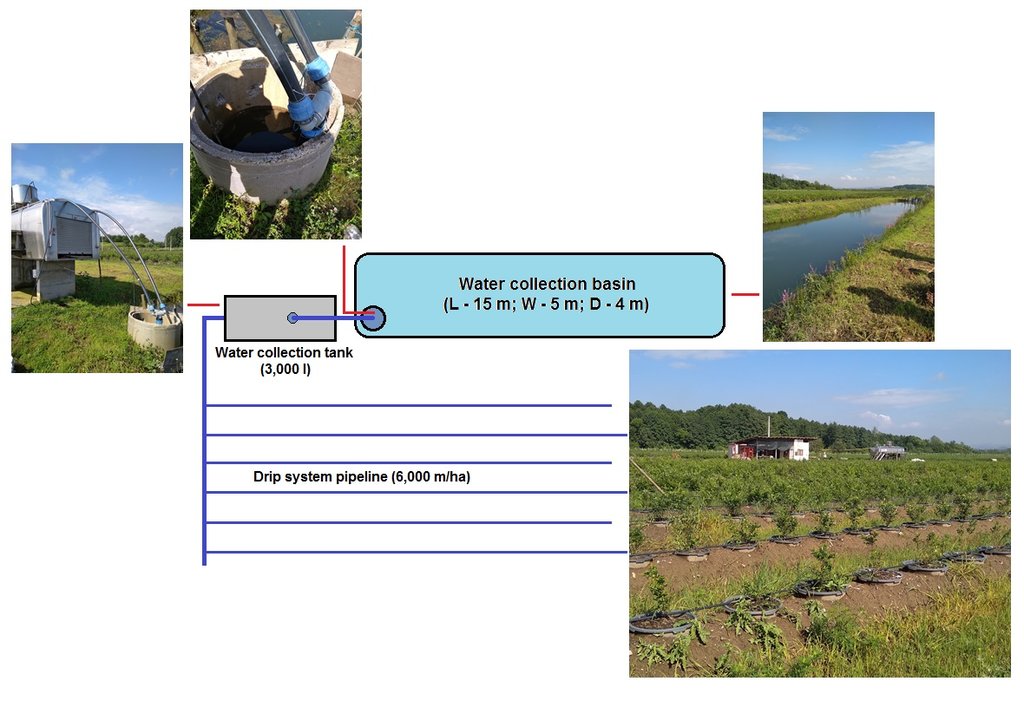
The price of drip irrigation system include delivery (on farm) and installation costs. It includes water reservoir (3,000 l), pump for water transfer from the basin to the reservoir and construction of well for pump in the basin. The costs of the irrigation system does not include construction of the basin for collection of water (it was constructed earlier, by previous land user), but one can calculate the costs of such structure (basin: L - 15 m, W - 5 m, D - 4 m) under local conditions. Current estimate of costs for such construction in Živinice municipality is around 4,000 USD. The total length of drip system pipeline per ha for the presented technology is 6,000 m.
Under the concrete conditions, the land user handles land leased from the municipality. The land rental charges are not included in the costs of establishing or maintaining the technology since they are, in this case, favorable (103 USD/ha/year) and can vary considerably under other conditions.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Checking and maintenance of embankments (rows of containers) | Once a year |
| 2. | Maintenance of drip irrigation system | During the growing season |
| 3. | Maintenance of blueberry orchard | During the growing season |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
During the exploitation of the technology ordinary agro-technical measures (plant protection, applied in growing of blueberries) are applied and they are not listed here as the technology maintenance activities.
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Checking and maintenance of embankments (rows of containers) | Person day | 10.0 | 29.25 | 292.5 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Maintenance of drip irrigation system | ha | 1.0 | 344.08 | 344.08 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Maintenance of blueberry orchard (lump sum) | ha | 1.0 | 20644.57 | 20644.57 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 21281.15 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The costs of maintenance of the blueberry orchard include all agro-technical measures and works (fertigation, plant protection, weed control, harvest) applied in growing of blueberry (Duke variety) in plant pots. The farm provide water free of charge, from its own drip irrigation system.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The prices of blueberry plantings, containers, and multi functional substrate for blueberries on the market.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
894.00
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
The highest precipitations appear during spring and early summer, (June 111 L/m2; February 55 L/m2). Heavy downpours during the summer are one of the climatic features of this area.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Tuzla
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
ที่ผิวดิน
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
เป็นครั้งเป็นคราว
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- รวย
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- ลูกจ้าง (บริษัท รัฐบาล)
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดใหญ่
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เช่า
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
คุณภาพพืชผล
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ความต้องการน้ำจากการชลประทาน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การอัดแน่นของดิน
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี | |
| อุณหภูมิตามฤดูกาล | ฤดูร้อน | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดีมาก |
| ฝนตามฤดู | ฤดูร้อน | ลดลง | ดีมาก |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology also copes very well with annual rainfalls which, due to gradual climate change, are characterized with extreme fluctuations (long dry periods, mostly during the growing season, and with intense short time rainfalls, mostly during early spring and late autumn).
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบ
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- ครั้งเดียวหรือเป็นการทดลอง
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Much more profitable agricultural production compared to previous use of the land characterized by heavy, less fertile soils unfovorable for most of agricultural crops growing. |
| Decreased workload compared to conventional cultivation of blueberries. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Possibility to organize profitable agricultural production on less fertile, non fertile or degraded lands. |
| Possibilities to apply the technology at the landfill sites of many coal mines in the region. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Relatively high costs of the technology introduction due to high prices of the inputs for blueberry cultivation in plant pots. | Cultivation in plant pots could be applied with other crops whose plantings are cheaper and which does not need specific, multi component, expensive substrate. |
| Necessity of drip irrigation system. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Relatively short period of the exploitation of the technology (an expert estimate: 15 years). | Producing of the goods (fruits in this case) with high market prices. |
| Due to the high introduction costs the technology could be reasonably applied in growing of highly priced crops. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
In total, three field visits and surveys were conducted from May to October 2018 during which blueberry production plots (fully conventional, modified conventional - embankments, and plant pot growing) were examined.
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
The most valuable information regarding the technology were provided by agronomist/technician Mr. Alija Đogić who manage blueberry growing plots on the spot where the technology was described.
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
Valuable information, especially about the possibility of spreading the technology to the degraded lands in the area of coal mining, were provided by the engineer Mr. Mirsad Butković from the Živinice municipality administration.
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
10/07/2018
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล