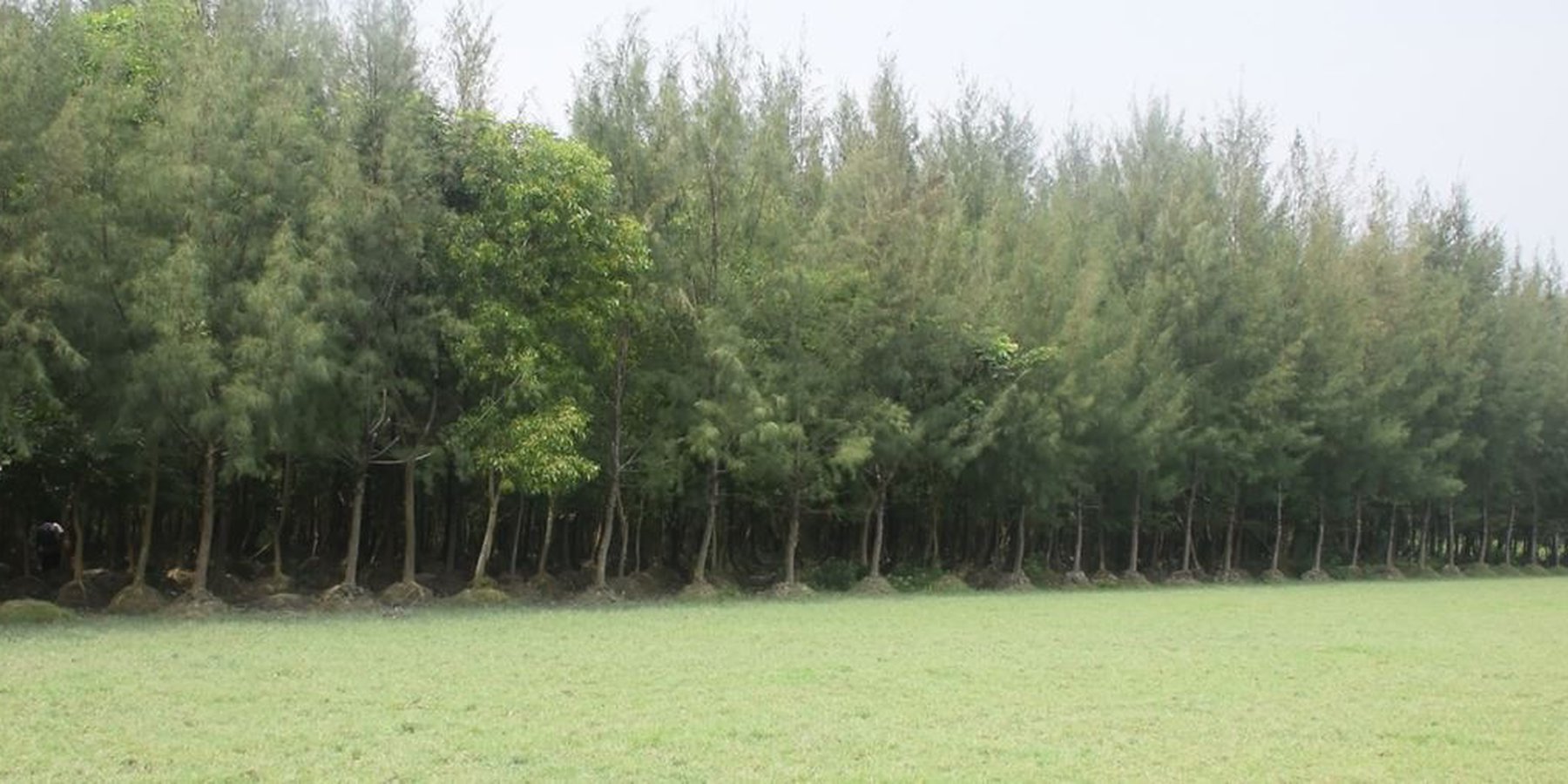
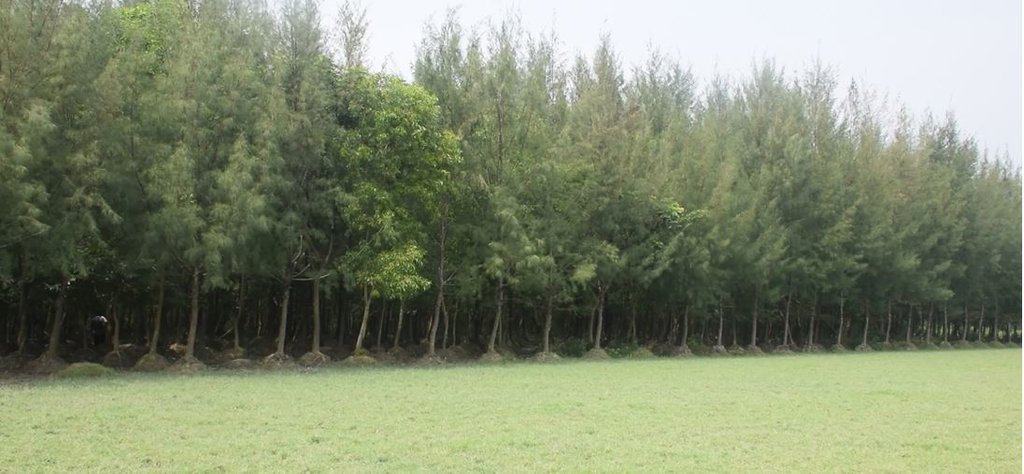
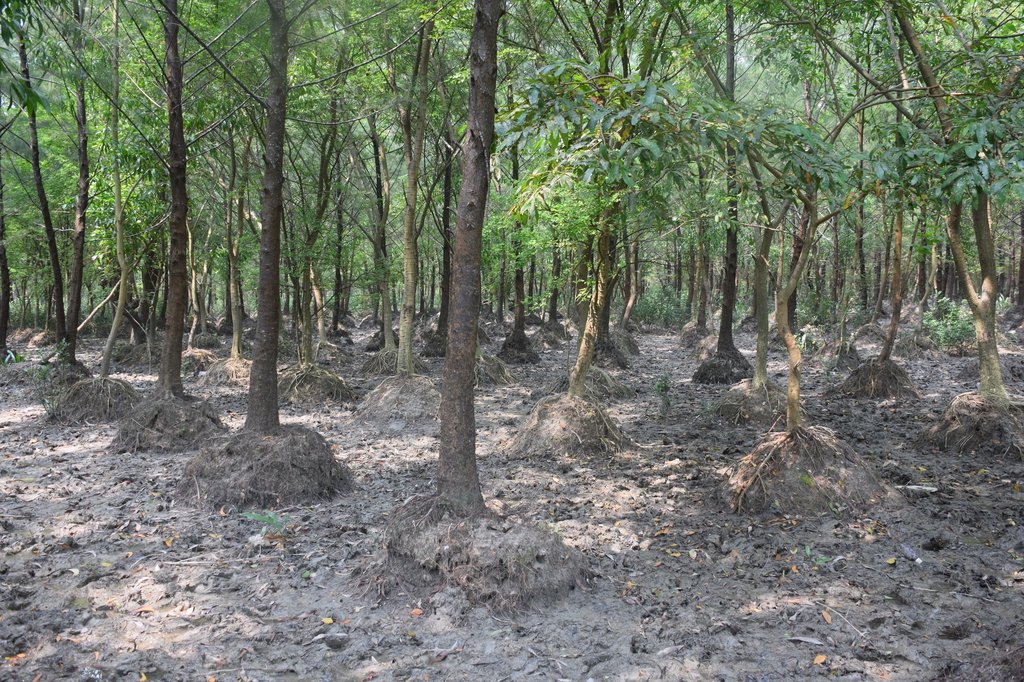
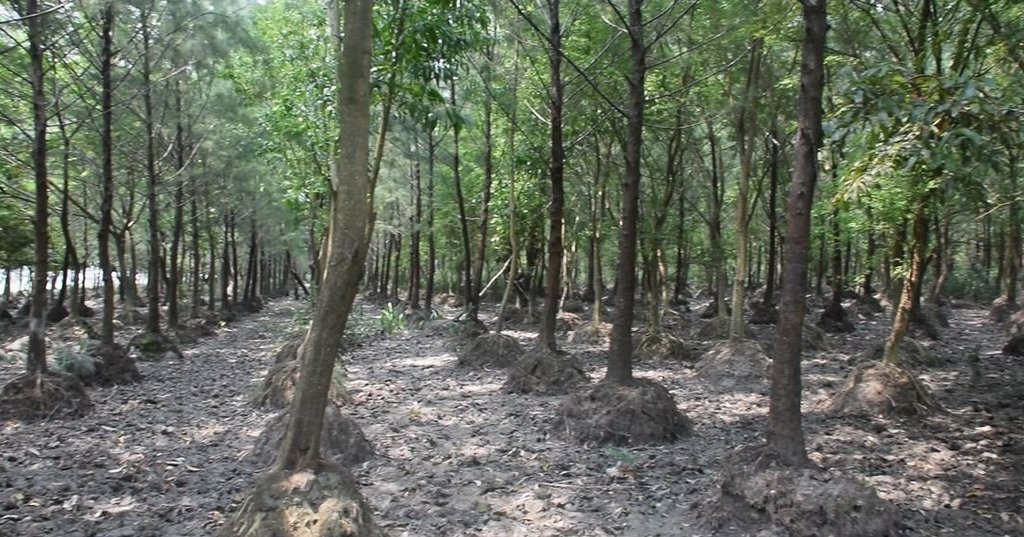
Mound plantation in coastal area with non-mangrove plant species for land stabilization [บังกลาเทศ]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Fazlay Arafat
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Mutasim Billah, Md. Jakir Hossain, Md. Arfanuzzaman
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Nicole Harari, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Ursula Gaemperli
Mound plantation
technologies_4732 - บังกลาเทศ
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Md. Anowar Hossain
Bangladesh Forest Department
บังกลาเทศ
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Mohammad Rahman
Local community people
บังกลาเทศ
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Bangladesh Forest Department (Bangladesh Forest Department) - บังกลาเทศชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
FAO Bangladesh (FAO Bangladesh) - บังกลาเทศ1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Mound plantation with non-mangrove species to transform mono-culture plantations subsequently into more ecologically resilient, mixed species plantations and as well as to accelerate natural processes of accretion and land stabilization in coastal areas.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
Bangladesh has nearly five decades of experience of coastal afforestation and reforestation on offshore islands and newly accreted lands. Coastal plantations were originally planted mainly to protect coastal populations against tidal bores, cyclones and storm surges and as well as to speed up the stabilization of newly accreted lands that eventually protect interior agricultural land from saline intrusion. According to the historical approaches to coastal afforestation and reforestation in Bangladesh, only a few pioneer mangrove species are suitable for planting on newly accreted coastal lands. Mangrove plantations that were established with a handful of pioneer species require increasing levels of management to promote ‘artificial succession’. There is need to transform these predominantly monoculture plantations subsequently into more ecologically resilient, mixed species plantations. Mound plantation with non-mangrove species was introduced in some places to address this issue.
Under the ‘Climate Resilient Participatory Afforestation and Reforestation Project’ non-mangrove mound plantations were established in 2013 in South Salimpur area of Sitakundu upazila (administrative unit) in Chittagong district by the Forest Department. Earlier, in 1983 the newly accreted char land (river islands formed from sedimentation) was planted with mangrove species Keora (Sonneratia apetala). Mangroves are salt-tolerant trees that cope with salt water immersion and wave action and are adapted to life in waterlogged and harsh coastal conditions. Due to cyclones and illegal removal of trees the Keora plantations were destroyed in many spots. In the meantime, the mangroves had accumulated sediments and the land was raised as compared to the adjacent inland areas. This accreted and stabilized land is suitable for non-mangrove plantation as the water does not flood the raised land regularly.
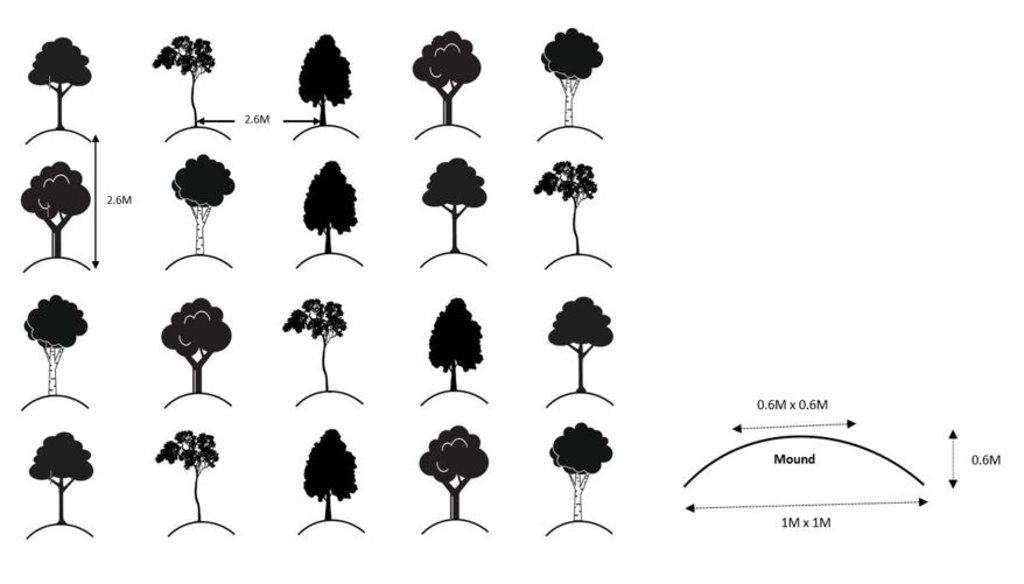
However, the area is regularly inundated by the tide during the monsoon. In addition storm surges flood the land and cause waterlogged conditions, which are not suitable for the survival of non-mangrove species. To successfully plant non-mangrove species along the coast, mound plantation is practiced. The mound served as a raised bed to protect the seedlings from waterlogged conditions in monsoon seasons. Akashmoni (Acacia auriculiformis), Jhau (Casuarina equisetifolia), Arjun (Terminalia arjuna), Rain-tree (Albizia saman), Babla (Vachellia nilotica) tree species are planted in mound. The major activities of this practice are cleaning of site from weeds & making of round shaped mounds. The diameter of the mound in the base is 1m and in top is 0.6m with a height of 0.6m. The mound is prepared through soil heaps from the plantation site. Inter and intra row spacing is 2.6m x 2.6m center to center of the mounds. 1500 mounds per hectare are constructed and one bamboo stick put inside every mound to support the plated seedlings to stand firmly.
The dimension of pit in each mound is 0.3m x-0.3m s 0.3m and the pit needs to be kept open for two weeks for drying before the one year old seedling can be transplanted in the pits. The seedlings were raised in the nursery of Forest Department under the project. While planting seedlings 0.5 kg compost and 0.5 kg loamy soil are mixed in the pit to increase the fertility of the soil. Vacancy filling is required in the next year and weeding practice continues till 3rd year of plantation.
Advantage of mixed-species over monocultures is the promotion of diversifying production under different rotation periods. Mixed-species plantations are more resistant to damage caused by storms, insects or diseases. Mound plantation with non-mangrove mixed species increased the diversity and ecological services. Mound plantations are vulnerable to a variety of threats from livestock grazing, mainly buffalo, to extraction of timber and outright conversion of plantations to other land uses such as agriculture, aquaculture and salt production.
However, the mound plantation practice contributes in coastal greenbelt species diversification along with speed up the natural processes of accretion and land stabilization.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
บังกลาเทศ
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Chittagong district
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Kattoli coast area
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 0.1-1 ตร.กม.
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Climate Resilient Participatory Afforestation and Reforestation Project’ by the Forest Department established the technology
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
- ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
Tree plantation, afforestation: Specify origin and composition of species:
- การปลูกหลายพันธุ์รวมกัน
- Coastal afforestation with non-mangrove plant species
Type of tree:
- Acacia auriculiformis
- Casuarina equisetifolia
- Terminalia Arjuna, Albizia Saman, Vachellia nilotica
Are the trees specified above deciduous or evergreen?
- evergreen
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- ไม้ซุง
- ไม้ที่นำมาทำเป็นเชื้อเพลิง
- การอนุรักษ์ / ป้องกันธรรมชาติ
- นันทนาการ / การท่องเที่ยว
- การป้องกันภัยธรรมชาติ
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่

ที่ดินที่ไม่ให้ผลผลิต
ระบุ:
Earlier the area was covered with mangroves species but due to cyclones and illegal logging the mangrove stand destroyed and the area turned to an unproductive land. However, the mangroves had stabilized the accredited land raised the land due to sediment deposition.
ข้อสังเกต:
Only some mangrove plant species found in scatter
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการสวนป่า
- แนวกันลมหรือแนวต้านลม
- การลดความเสี่ยงจากภัยพิบัติบนพื้นฐานของระบบนิเวศ
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wc (Coastal erosion): การกัดเซาะชายฝั่ง

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cs (Salinization/alkalinization): การสะสมเกลือหรือการทำให้เป็นด่าง
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Plant varieties that comes through natural succession process stabilize the newly formed coastal land. Mound plantation with non-mangrove species strengthen that process with other plantation services.
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
The dimensions of structures are explained in the description part
ผู้เขียน:
Md. Fazlay Arafat
วันที่:
06/05/2019
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
1 ha
If using a local area unit, indicate conversion factor to one hectare (e.g. 1 ha = 2.47 acres): 1 ha =:
1 ha=2.47 acres
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
BDT
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
84.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
500 BDT
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Nursery establishment | October-November |
| 2. | Raising seedlings | January-February |
| 3. | Site preparation: clearing of site and mound construction | April-May |
| 4. | Transplantation of seedlings | June |
| 5. | Fertilizer application: Compost mixed with loamy loamy soil | June |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Nursery preparation | person-days | 17.0 | 500.0 | 8500.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Earth clearing and mound preparation | person-days | 150.0 | 500.0 | 75000.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Plantation work | person-days | 25.0 | 500.0 | 12500.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Bucket | pieces | 15.0 | 250.0 | 3750.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Spade | pieces | 15.0 | 500.0 | 7500.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds for nursery bed | Lump sum | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Poly bags | Pieces | 1800.0 | 1.0 | 1800.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Bamboo stick to support seedlings | Pieces | 1600.0 | 2.0 | 3200.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Compost to apply in plantation | kg | 1000.0 | 4.0 | 4000.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Urea for poly bag seedling | kg | 4.0 | 35.0 | 140.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | TSP for poly bag seedling | kg | 4.0 | 40.0 | 160.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | MoP for poly bag seedling | kg | 4.0 | 30.0 | 120.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Bamboo for nursery fencing | pieces | 4.0 | 250.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Seedling transportation cost | Lump-sum | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 119670.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 1424.64 | |||||
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Vacancy filling | June |
| 2. | 1st year weeding | 3 times in a year |
| 3. | 2nd year weeding | 3 times in a year |
| 4. | 3rd year weeding | 2 times in a year |
| 5. | Fertilizer application to the newly planted trees | June |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Seedling transportation | person-days | 1.0 | 500.0 | 500.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Vacancy filling | person-days | 4.0 | 500.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Fertilizer application to the newly planted trees | person-days | 4.0 | 500.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Weeding | person-days | 40.0 | 500.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Bamboo stick to support seedlings | pieces | 350.0 | 2.0 | 700.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | NPK fertilizer | kg | 75.0 | 30.0 | 2250.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 27450.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 326.79 | |||||
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Labor
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- ชื้น
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
<5 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
เกินพอ
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
ใช้ประโยชน์ไม่ได้
Water quality refers to:
both ground and surface water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุ:
Due to regular tidal inundation the soil become saline and only support to grow mangrove plant species
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
เป็นครั้งเป็นคราว
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ต่ำ
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- ลูกจ้าง (บริษัท รัฐบาล)
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- ผู้เยาว์
- วัยกลางคน
- ผู้สูงอายุ
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Bangladesh Forest Department established the coastal plantation through participatory approach of co-management with adjacent local communities.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ไม่ใช่
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตไม้
คุณภาพป่า /พื้นที่ทำไม้
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to diversified non-mangrove species used in the plantation the risk of failure reduced
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Mound plantation increase production area through converting unproductive land areas
การจัดการที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Once established, the non-mangrove species do not require much silvicultural operation
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The spot become popular to tourist
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
surface runoff decrease as raised mounds acts as a barrier
การระเหย
ดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Soil loss with water decreased as mounds reduces surface runoff
การสะสมของดิน
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
ชนิดพันธุ์ที่ให้ประโยชน์
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากน้ำท่วม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
flood impact decreases as the mound forest act as a barrier and protect the raised land
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
ความเร็วของลม
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ตะกอนที่ถูกพัดพามาโดยลม
ผลกระทบของก๊าซเรือนกระจก
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี | |
| ฝนตามฤดู | ฤดูฝน | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุเขตร้อน | ปานกลาง |
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุฝนฟ้าคะนองประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำขึ้นจากพายุหรือน้ำท่วมชายฝั่ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติทางชีวภาพ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| โรคระบาด | ปานกลาง |
| การบุกรุกของแมลง / หนอน | ปานกลาง |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| การสูงขึ้นของระดับน้ำทะเล | ปานกลาง |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบ
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบ
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| The mixed plantation is now more pest resistance |
| The aesthetic beauty is increased and attract more tourists |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| The mixed stand with mound plantation supports more ecological services like supply of fuel wood, wildlife habitat, timber, tourism, greenbelt, etc. |
| Species mixtures maximize the use of resources, and consequently increase stand-level productivity and carbon sequestration. |
| Speed up the natural succession process. Otherwise it takes long period of time to grow non-mangrove species in coastal areas. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The mounds often requires to be repaired when it faces frequent tropical storms and storm surges | |
| Grazing hampers the stand at the initial stage | Community awareness |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Only salt tolerant plant species can be planted |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
Number of field visit:02
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
Number of informants: 03
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
Number of informants: 02
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
N/A
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
N/A
7.4 General comments
WOCAT questionnaire covers all the technical aspect of the practice
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล