Tree windbreaks within irrigated agriculture in Central Asia [คีร์กีซสถาน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Niels Thevs
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_5861 - คีร์กีซสถาน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
International Centre for Research in Agroforestry (ICRAF) - เคนยา1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Agroforestry extension [คอสตาริกา]
Participatory extension of agroforestry systems, especially of shadegrown coffee, to promote sustainable and productive use of natural resources among small and medium scale farmers.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Olman Quiros Madrigal
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
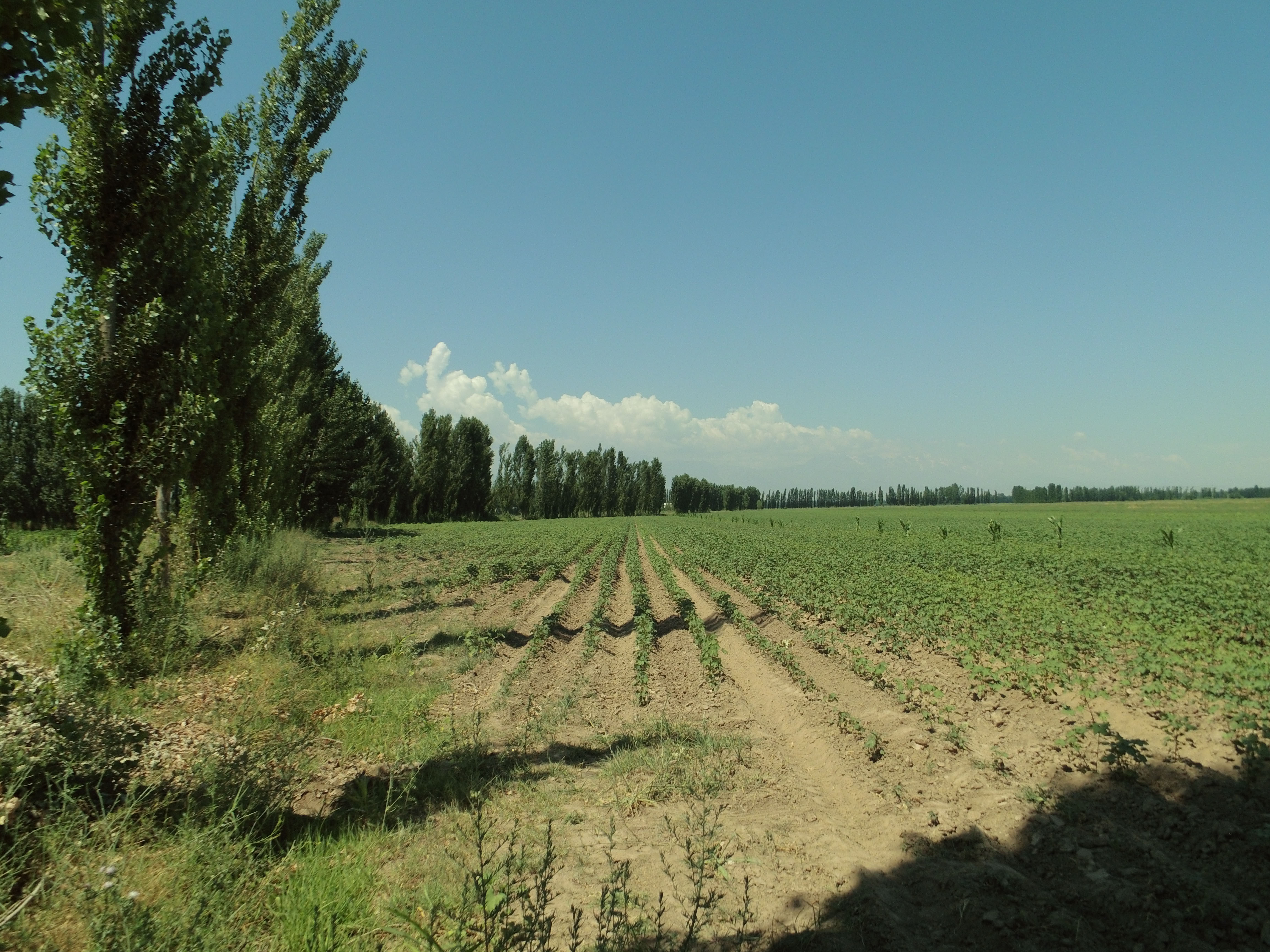
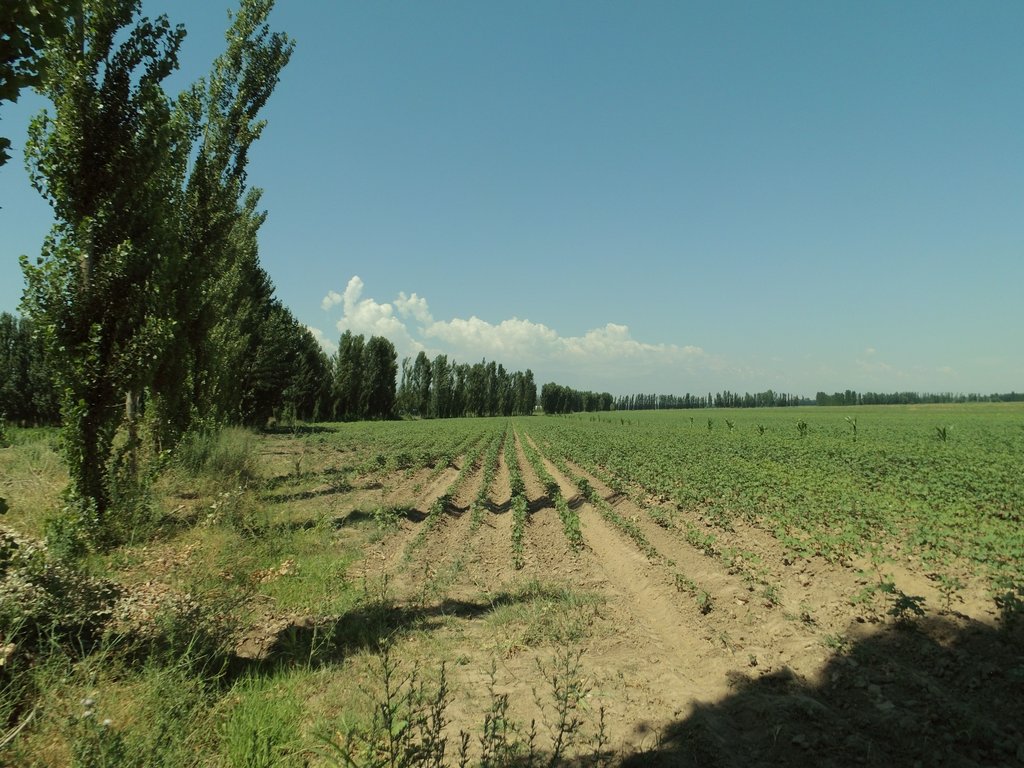
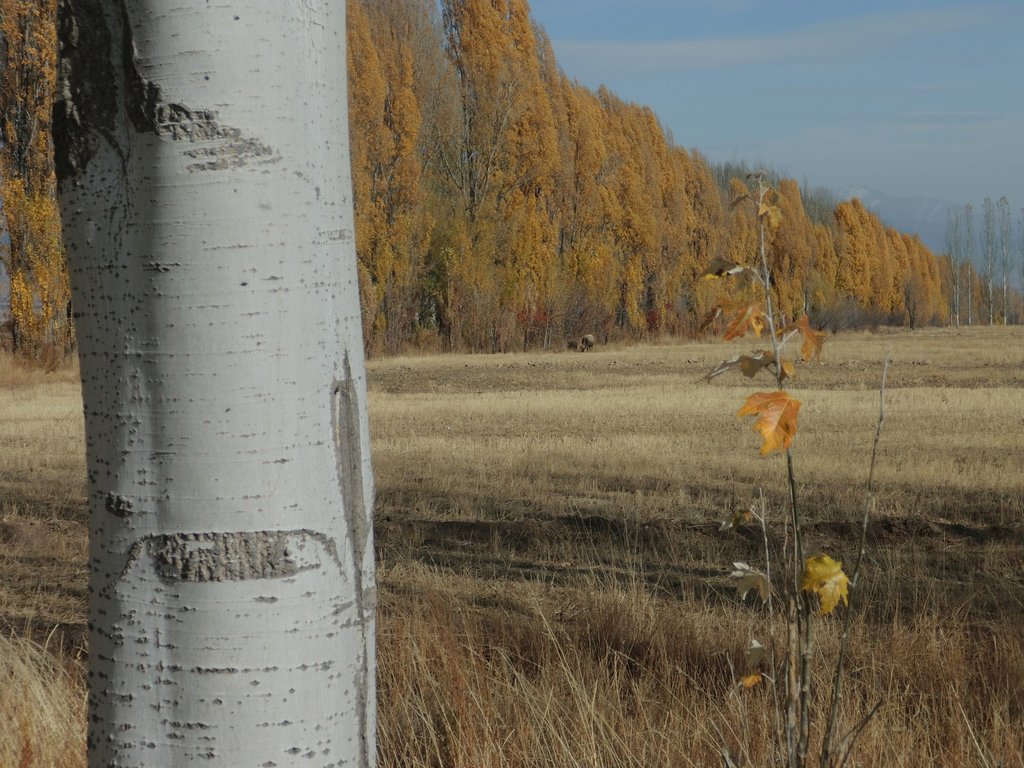
Windbreaks of poplar trees (Populus nigra pyramidalis) are a major agroforestry system in irrigated agriculture across Central Asia. Such windbreaks reduce the overall water consumption of irrigated agriculture by 10-20% and increase farm income by 10-15%.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
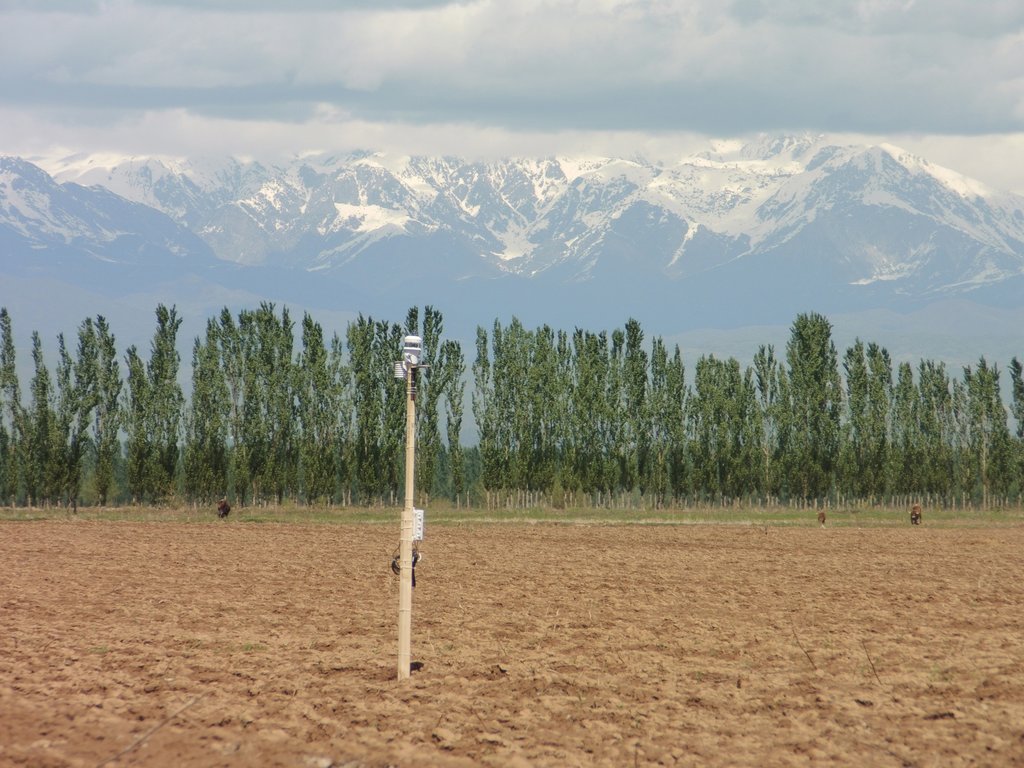
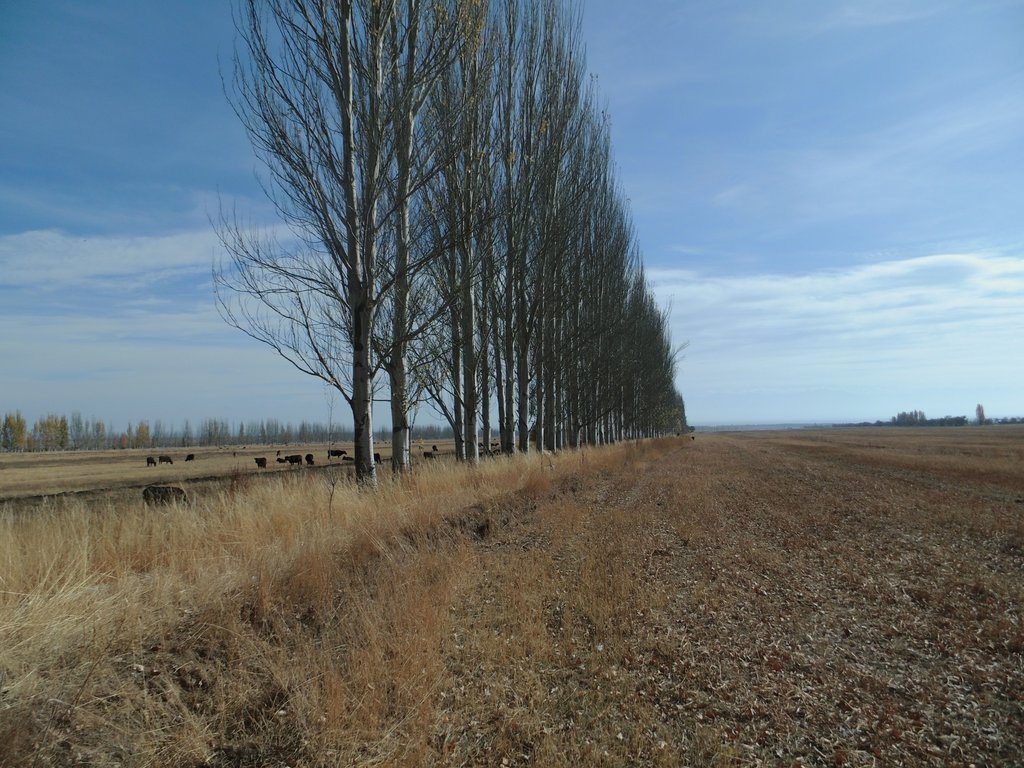
Windbreaks of trees are a major agroforestry system across Central Asia. The SLM technology presented here concentrates on windbreaks, chiefly of poplar trees (Populus nigra var. pyramidalis), within irrigated agriculture. These windbreaks of poplars have a long tradition as an agroforestry system in irrigated agriculture in the river basins of south and southeastern Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. In Kazakhstan and northern parts of Kyrgyzstan, poplars are partly replaced by Elm (Ulmus minor) windbreaks.
After those five countries had become independent, a large share of the windbreaks was cut down primarily for fuelwood and secondarily for timber, as the energy supply system had broken down in the course of the disintegration of the Soviet Union. Such windbreaks reduce the overall water consumption of irrigated agriculture by 10-20% compared to open field conditions, depending on crops and tree spacing (Thevs et al., 2019: doi:10.3390/land8110167). The trees serve as an additional source of income, chiefly from sustainable harvest of the trees for timber. Windbreaks also help to increase crop yields. In total, farm income is increased by 10-15% over the rotation period of the trees (Thevs and Aliev, 2021: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-021-00617-7). The rotation period of poplars is between 12 and 20 years, depending on the climatic conditions, e.g. poplars in the Ferghana Valles reach DBH (diametre at breast height) values of 22-27 cm and tree heights of 18 m after 13 years.
In this recent assessment, it was found that windbreaks of single tree rows with distances between trees of 1 m had the best effects on water saving and increasing farm income. The most suitable spacing between windbreaks was found to be around 200 m.
Windbreaks are perceived differently by land users depending on the region and knowledge (Ruppert et al., 2020: doi:10.3390/su12031093). For example, land users in the Ferghana Valley perceived windbreaks positively and were planting them primarily with the aim to have wood resources in the near future. In contrast, land users in the northern part of Kyrgyzstan were afraid firstly that windbreaks shaded their crops, consumed space, and competed for water and nutrients, and secondly that planting windbreaks may cause conflicts with neighbours due to those negative connotations. Farmers with larger field plots were more open towards them.
Windbreaks are planted with 2-year-old poplar saplings, which are locally available. The preferred place to plant is along irrigation ditches or other existing field boundaries. If windbreaks are planted along irrigation ditches, they simply tap water from the moist soil or elevated groundwater adjacent to those ditches. Otherwise, the trees need to be irrigated like the crops. As furrow irrigation is the dominant irrigation practice throughout Central Asia, poplars can be integrated without further adjustments in the field of irrigation. Alongside irrigation ditches poplars can withstand high water levels in those ditches as they occur during irrigation periods. If farmers switch to drip irrigation, and irrigation ditches are no longer present, the trees will need to be supplied with a dripline as well. The locally available poplar cultivars do not need additional fertilizer, but profit from the fertilizer applied to the crop. Only if high yielding modern cultivars were to be used, additional fertilizer application to the trees would be needed to unfold their full potential.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.4 วีดีโอของเทคโนโลยี
ความคิดเห็น/อธิบายสั้นๆ:
Video on Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2mAfQzO7MHg
This video provides a concise introduction into tree wind breaks, including their advantages with regards to water consumption, building resiliance against climate change, and income.
วันที่:
01/09/2019
สถานที่:
Ferghana Valley, Kyrgyzstan
ชื่อผู้ถ่ายวีดีโอ:
Gino Carlo Garcia
ความคิดเห็น/อธิบายสั้นๆ:
This video on Youtube, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Iv0VdPqBT9o, is part of a series on poplars. This part focusses on tree wind breaks with many statements of local acteurs. The other parts of this series introduce high yielding poplar cultivars and their options in agroforestry, woodlints, and value chains.
วันที่:
01/02/2020
สถานที่:
Kyrgyzstan
ชื่อผู้ถ่ายวีดีโอ:
Lea Gerster and Stefanie Breunlich
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
คีร์กีซสถาน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Jalalabad Region, Chui Region, and Issyk Kul Region
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 0.1-1 ตร.กม.
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Windbreaks are spread over large areas, but the spatial distribution can be described as pockets of between 10 and 1000 ha. Within those pockets, tree wind breaks are sometimes interrupted. Also outside those pockets with more or less contiguous windbreaks systems there are remnants of those systems.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- วนเกษตร (Agroforestry)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - barley
- cereals - maize
- cereals - rice (wetland)
- cereals - wheat (spring)
- cereals - wheat (winter)
- fibre crops - cotton
- fodder crops - alfalfa
- root/tuber crops - potatoes
- Poplars
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
Is intercropping practiced?
ไม่ใช่
Is crop rotation practiced?
ไม่ใช่
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- วนเกษตร (Agroforestry)
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- การชลประทานแบบเต็มรูปแบบ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
As the spatial distribution stretches over large parts of Central Asia, some locations where windbreaks are planted are rainfed and irrigated, but most parts need full irrigation.
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปลูกป่าร่วมกับพืช
- แนวกันลมหรือแนวต้านลม
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม
- Et (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบน

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
- Hg (Change in groundwater): การเปลี่ยนแปลงของน้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The main effect of windbreaks in the assessed areas is mainly reducing water consumption, and less wind erosion. Poplars could help to lower groundwater levels and thus contribute to combat salinization. But that did not play a role in the areas specifically assessed.
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
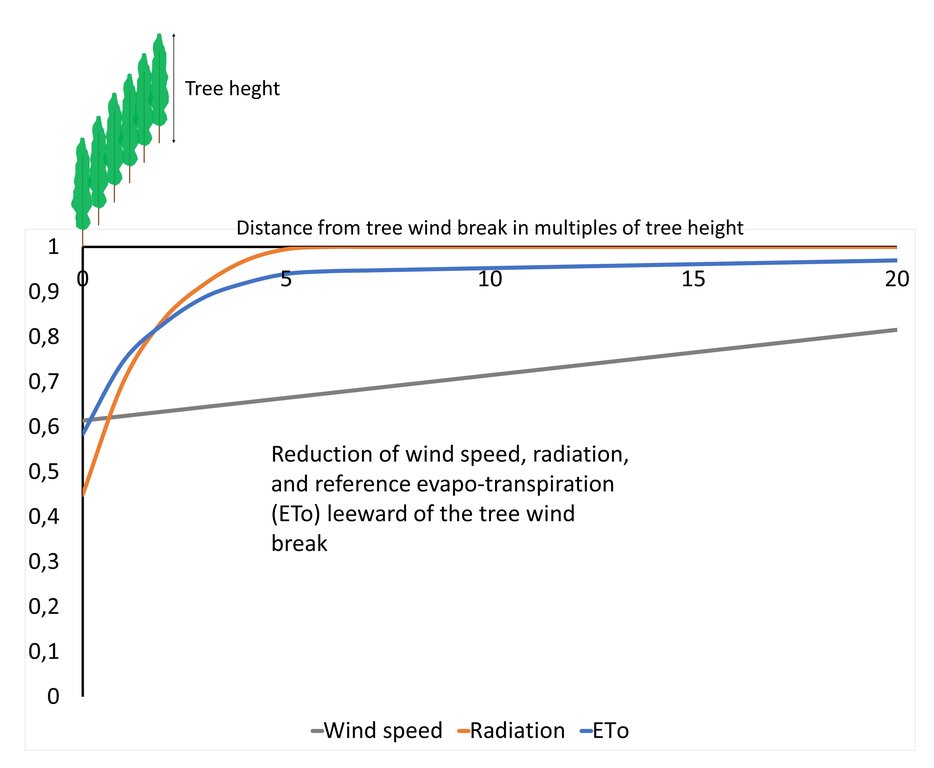
Windbreaks have their greatest impact when planted perpendicular to the main wind direction (or direction of the strongest winds). A whole grid of tree wind breaks running along all field plot borders will have a greater effect, as it prevents enhanced winds through a tunnel effect under changing wind directions. Tree wind breaks can be planted with distances of 50 m to 1000 m away from each other. The effect on the micro climate becomes less pronounced with increasing distance from tree wind breaks. Therefore, on a large field plot, say of 1000 m width between windbreaks, the micro climate averaged over the field plot will not differ much from the conditions without tree wind breaks. In contrast, on smaller field plots, say of 100 m width between windbreaks, the micro climate will differ significantly from open field conditions. This is also explained by the lines for temperature, air humidity, radiation, and in particular wind speed along an increasing distance from a given windbreak. Thereby, the distance from the windbreak is given in multiples of tree height.
In total, the best effects with regard to economic return and reduced water consumption come with a spacing of 200 m between tree wind breaks.
The best effects with regard to economic return and reduced water consumption were achieved with single tree lines. So, only one line of poplar trees is planted along the field borders. The planting distance between trees is 1 m to 1.20 m.
Poplar trees are locally available as trees with a length of 2 m to 2.50 m. Those trees are planted, best along the small irrigation ditches that run along the field borders. The local cultivar which is mainly used is a Populus nigra var. pyramidalis cultivar under the local name Mirza Terek. In principle, modern high yielding cultivars can be used as well; first research has shown a 2-3 times faster growth compared to the locally available cultivars at similar water and nutrient requirements.
ผู้เขียน:
Niels Thevs
วันที่:
25/03/2021
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
1 ha
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
KGS
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
68.87
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
750
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tree planting | March (first year) |
| 2. | Maintenance of trees | April to September (first and second year) |
| 3. | Harvest of trees | December to February (last year of tree rotation - after 15 years) |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
These entries refer to a windbreak system of poplars to be harvested at tree age of 15 years combined with cotton. Thereby, the activities related to trees, including the harvest, are considered as activities to establish windbreaks into an agrarian landscape where irrigated agriculture is ongoing. The annual crop related activities are therefore listed under maintenance. If cotton is rotated with corn or rice, the timing of the crop-related activities is similar.
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labor costs for tree planting and maintenance (first year) | man-days | 3.0 | 750.0 | 2250.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Labor costs for tree maintenance (second year) | man-days | 3.0 | 650.0 | 1950.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Labor costs to harvest trees (at tree age 15 years) | man-days | 3.0 | 70.0 | 210.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Poplar saplings | sapling | 116.0 | 20.0 | 2320.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Transport of saplings | 500.0 | 1.0 | 500.0 | 100.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 7230.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 104.98 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Costs had been retrieved for the year 2017. Costs that appear in the second year and later were discounted at a discount rate of 17.5% based on costs as of 2017.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Soil preparation and sowing of annual crop (cotton) | March to April / every year |
| 2. | Irrigation, fertilizer application and other farm operations for the crop | April to August / every year |
| 3. | Harvest of the crop (cotton) | September to October / every year |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labor costs for soil preparation | man-days | 6.81 | 750.0 | 5107.5 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Labor costs for sowing | man-days | 2.5 | 750.0 | 1875.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Labor costs for irrigation | man-days | 23.64 | 750.0 | 17730.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Labor costs to apply fertilizer and plant protection | man-days | 3.34 | 750.0 | 2505.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Labor costs for harvest (cotton) | man-days | 32.78 | 554.0 | 18160.12 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Machine costs (rent) for soil preparation | ha | 1.0 | 10021.0 | 10021.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Machine costs (rent) for sowing | ha | 1.0 | 1316.0 | 1316.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Machine costs for fertilizer application | ha | 1.0 | 1200.0 | 1200.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Seeds | kg | 50.0 | 101.0 | 5050.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Fertilizer | kg | 375.0 | 19.25 | 7218.75 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Plant protection | ha | 1.0 | 1517.0 | 1517.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Water fee | ha | 1.0 | 1014.0 | 1014.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 72714.37 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 1055.82 | |||||
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Labour costs are the largest single cost item. In fact, in the cotton system a lot of labour is unpaid family labour or mutual help among neighbours. All labour was calculated in monetary terms, as the share of unpaid labour differed much between farms. This cotton tree wind break system is wide spread in the south of Kyrgyzstan. In the north of the country, tree wind breaks are combined with wheat, barley, corn, or alfalfa (lucerne). There, labour costs are lower as more machines are used (e.g. for harvest).
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Precipitation maximum during spring and dry summers, which makes irrigation necessary.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Bazarkorgon, Kara Balta, Kemin
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
hot continental and semi-arid
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Tree windbreaks can be applied in a wide range of topographical situations. Though this particular entry focusses on windbreaks in irrigated agriculture so that the whole SLM technique, i.e. trees and crops, is distributed on flat land. As irrigation is tied to rivers as water sources, this SLM technique is distributed on river plains.
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Tree windbreaks per se are not limited to specific soil types. In the region considered here, the soils that are irrigated and therefore are sites for this SLM technique were mostly formed by riparian deposits. Those soils silty to loamy. On most of those areas, where irrigation takes place, soils are classified as Fluvisols. On few areas, the soils are classified as Gleysols.
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
<5 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
Water quality refers to:
surface water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Soil salinization and waterlogging do not play a role on the sites from where the information was collected for this introduction here. Though in parts of Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan, where this windbreak SLM technology is being applied and can be expanded as well, salinization and water logging do play a role.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
In Kyrgyzstan, the land users operate as households and can decide on their crops. Though, planting tree windbreaks does take place in agreement with neighbours. In Uzbekistan, where windbreaks are used as well, the freedom of farmers to chose their crops is limited, while tree windbreak planting partly follows governmental orders. In both countries as well as Tajikistan, labour migration is important for most rural families and remittances comprise a substantial share of the household income (off-farm income).
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เช่า
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ใช่
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There is agreement in the scientific literature that tree windbreaks cause crop yield increases of 10-15%. Some references even claim crop yield increases of up to 40%.
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The leaves of the trees are partly used as fodder. But that additional fodder only is a minor contribution to the overall fodder demand.
การผลิตไม้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
none
หลังจาก SLM:
53 m³/ha after 15 years
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Trees are harvested at an age of 15 years. Such trees have an average tree height and DBH of 19 m and 27 cm, respectively. Given a form factor of 0.42 one tree yields a stem volume of 0.457 m³. A number of 116 trees is assigned to 1 ha, which results in 53 m³/ha.
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
1 ha cropland
หลังจาก SLM:
0.9 ha cropland
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Tree wind breaks occupy space so that the area available to the crop gets reduced. While the trees do not occupy substantial space during their first years of growth, they occupy about 10% of the cropland at and age of 10-15 years. This calculation was made for a spacing between tree wind breaks of 200 m.
การจัดการที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Tree windbreaks at a spacing of 200 m do not impede farm operations, while narrower spacing may disturb farm operations, in particular with machines.
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ความต้องการน้ำจากการชลประทาน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
904 mm over the cropping season
หลังจาก SLM:
777 mm over the cropping season
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
ETc (water consumption) of cotton is 904 mm over the whole cropping season. Tree windbreaks (arranged as a rectangular grid with a spacing of 200 m) with cotton together consume 777 mm over the whole cropping season. (cf. comment below under evaporation)
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
There are expenses for tree planting material and labour associated to tree planting and maintenance during the first and second year.
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
Accumulated NPV after 15 years: 214,000 KSG/ha
หลังจาก SLM:
Accumulated NPV after 15 years: 232,000 KSG/ha
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The accumulated NPV over 15 years for cotton versus cotton and tree wind breaks were compared to assess the financial gain from tree wind break systems. 15 years is the tree age at which the tree wind breaks are harvested. Costs and revenues were discounted at a discount rate of 17.5%.
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Wood resources are added as additional income next to crops.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การระเหย
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
904 mm over the cropping season
หลังจาก SLM:
777 mm over the cropping season
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
ETc (water consumption) of cotton is 904 mm over the whole cropping season. Tree win breaks (arranged as a rectangular grid with a spacing of 200 m) with cotton together consume 777 mm over the whole cropping season. (cf. comment above under irrigation water demand)
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As tree wind breaks reduce evapotranspiration, they help to maintain soil moisture.
การสูญเสียดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Wind erosion did not play a role in this example of cotton combined with tree windbreaks. Though in other parts of Kyrgyzstan or Central Asia stronger winds prevail than in this very example. There, tree wind breaks do combat wind erosion.
ความเค็ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Salinity did not play a role in this example of cotton combined with tree windbreaks. Though in other parts of Kyrgyzstan or Central Asia salinity does play a role. There, windbreaks, in particular poplar trees, help to lower the groundwater levels due to their high water consumption, which helps to combat soil salinization.
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The leaves of the trees partly end up as litter on the soil surface. The trees' root systems add to the below ground biomass. Both contribute to the formation of soil organic matter. Though, this is limited to a small area adjacent to the tree wind breaks and does not translate into the area of the cropland.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
As the evapotranspiration (water consumption) and the demand for irrigation water are reduced, the general availability of water is increased.
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Neighboring fields are partly shaded.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| Glacier retreat which will result in reduced river flows and supply of water for irrigation |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
There are two major effects of climate change on the region Central Asia: 1. Glacier retreat through rising temperatures and 2. increasing rainfall during winter and partly reduced snow. Currently, the melting glaciers cause elevated river flows so that there is more water available for irrigation. But, once the glaciers have reached a new equilibrium with smaller glacier volumes, they will deliver less water so that river flows are expected to drop during the second half of this century. Then, the supply of water for irrigation will become constrained. Tree windbreaks are one option to adapt to those conditions in the future.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ใช่
ให้ระบุการปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี (การออกแบบ วัสดุหรือชนิดพันธุ์ เป็นต้น):
During the Soviet Union times, when tree windbreaks were promoted, multi-row tree windbreaks were planted. Today, farmers prefer single tree lines, in order not to sacrifice too much crop space.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Tree windbreaks deliver wood resources for self consumption or to be sold on markets. |
| In more windy parts of Kyrgyzstan or Central Asia, land users see the advantage of reduced wind speed for crop quality and snow trap to build up soil moisture. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Tree windbreaks provide additional income as they deliver wood resources. |
| Tree windbreaks reduce overall water consumption in irrigated agriculture. |
| In more windy parts of Kyrgyzstan or Central Asia, land users see the advantage of reduced wind speed for crop quality and snow trap to build up soil moisture. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Tree windbreaks shade the crop. | Capacity building and explain that this is a minor effect. |
| Tree windbreaks compete with the crops for nutrients and water. | Capacity building and explain that this is a minor effect. |
| Tree windbreaks disturb farm operations. | Capacity building and explain that this is a minor effect. |
| Tree windbreaks cause conflict with neighbours, as neighbours may share those negative perceptions. | Capacity building and explain that this is a minor effect and promote cooperation between neighbors to share benefits from tree wind breaks. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Financial resources are needed to establish tree windbreaks, while the revenue from the harvest of trees only can be realized in the future. | Access to suitable finance. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
Regular field visits (every 14 days) on three sites to collect climate, crop, and tree data to, among others, calculate crop and tree water consumption.
Field visit to two additional sites to collect data on tree growth.
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
62 household interviews to collect agro-economic numbers on crops and trees.
15 household interviews with wood traders and wood processors to collect information on markets and prices of wood from tree wind breaks.
80 semi-structured interviews on perception of tree wind breaks by farmers.
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
compilation of literature on tree windbreaks, from Soviet Union and recent international literature.
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
14/07/2017
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
July 2017 was the most busy time to collect the interviews on agro-economy and wood markets. The interviews on farmers' perceptions of tree windbreaks were collected during September and October 2018. Crop and tree data (growth, water consumption) were collected during 2017 and 2018.
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Thevs N, Aliev K (2021): Agro-economy of tree windbreak systems in Kyrgyzstan, Central Asia. Agroforestry Systems. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-021-00617-7
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Agroforestry Systems, EUR 37.40
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Ruppert D, Welp M, Spies M, Thevs N (2020): Farmers’ perceptions of tree shelterbelts on agricultural land in rural Kyrgyzstan. Sustainability 12:1093. doi:10.3390/su12031093
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/12/3/1093 - open access
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Thevs N, Gombert AJ, Strenge E, Lleshi R, Aliev K, Emileva B (2019): Tree wind breaks in Central Asia and their effects on agricultural water consumption. Land, 8: 167-183. https://doi.org/10.3390/land8110167
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://www.mdpi.com/2073-445X/8/11/167 - open access
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Strenge E, Thevs N, Aliev K, Eraaliev M, Lang P, Baibagysov A (2018): Water consumption of Populus alba trees in tree shelterbelt systems in Central Asia. Central Asian Journal for Water Resources 4, 48-62
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://www.water-ca.org/api/v1/articles/5955-water-consumption-of-populus-alba-trees-in-tree-shelterbelt-systems-in-central-asia.pdf - open access
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Thevs N, Aliev K, Lleshi R (accepted): Water Productivity of Tree Wind Break Agroforestry Systems in Irrigated Agriculture – an example from Ferghana Valley, Kyrgyzstan. Trees, Forests, and People
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
will be open access
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
UNECE (2019): Forest Landscape Restoration in the Caucasus and Central Asia – Challenges and Opportunities. Background paper for the Ministerial Roundtable on Forest Landscape Restoration in the Caucasus and Central Asia (21-22 June 2018, Astana, Kazakhstan)
URL:
http://www.unece.org/fileadmin/DAM/timber/publications/DP-72-flr-cca-en.pdf
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Agroforestry and Central Asia
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2mAfQzO7MHg
7.4 General comments
The questionaire guides the compiler through a number of questions through often standardized questions (ticking boxes). This is very helpful to avoid, possibly lengthy and not too concise descriptions. But with regard to agroforestry it should be made more clear where and how to address the trees.
In total it needs time to go through and fill in all sections, which surely is owed to the wish and need to collect information for a comprehensive description of each SLM technology. But, towards the end of projects, which have developed such technologies, the workload might be too high so that the entry into WOCAT is neglected. I guess one only can appeal to the motivation of projects or offer some sort of support for NGOs or so in need, but with very good SLM technologies to offer.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Agroforestry extension [คอสตาริกา]
Participatory extension of agroforestry systems, especially of shadegrown coffee, to promote sustainable and productive use of natural resources among small and medium scale farmers.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Olman Quiros Madrigal
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล