Reduced contour tillage of cereals in semi-arid environments [สเปน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Joris De Vente
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Labranza reducida de cereal en contra de la pendiente en ambientes semi-áridos (ES)
technologies_939 - สเปน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
Ibáñez Torres Ascensión
Rural development service (CARM) - Consejería de Agricultura y Agua Murcia
สเปน
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Escamez Antonio
สเปน
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
EEZA-CSIC (EEZA-CSIC) - สเปน1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Regional rural development programme [สเปน]
Regional development programme to protect natural resources and stimulate rural economies.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Joris De Vente
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Reduced contour tillage in a rotational system of winter cereals and fallow land.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
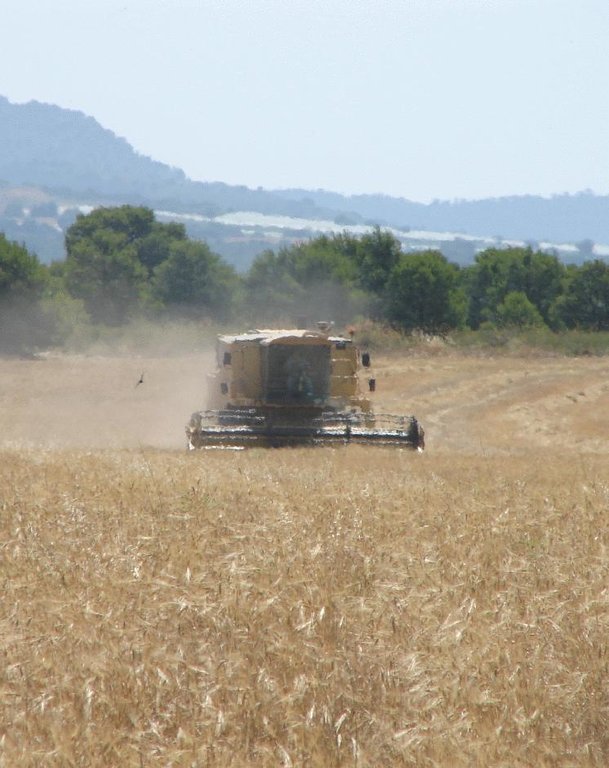
This technology is a type of conservation tillage with minimal economic effort and is adapted to semi-arid conditions. Tillage is reduced to a maximum of three times surface tillage (20-30cm) in two years with a disc- or a chisel-plough. The disc-plough is only used where there is a dense weed or crop residue cover. The disc-plough breaks-up the soil top layer better than the chisel-plough, while the chisel tends to plough slightly deeper (~30cm) than the disc-plough (~20cm). The advantage of the chisel-plough is that it leaves a higher surface roughness and is less destructive to soil aggregates. Under conventional tillage, fields are ploughed up to five times every two years, once with a mouldboard plough. In both systems, cereals are cropped in a rotational system with fallow land. Cereals are sown in autumn (October) and harvested in June followed by a fallow year. Under reduced tillage the crop residues are left on the field throughout the autumn and winter periods. This provides increased protection against soil erosion. Tillage is performed on fallow land in early spring (March-April) to prepare the land for sowing in October. With conventional tillage, fields are ploughed with a mouldboard plough in autumn. Traditional sowing machinery can be used so no investments are needed in specialised equipment. Tillage is performed parallel to the contour lines to prevent rill and gully formation. No herbicides are required since annual weeds are mixed with the upper soil layer during ploughing. Owing to increased organic matter content and a better infiltration capacity, soil water retention capacity, soil humidity and crop yields will increase within 3-5 years after implementation.
The aim of this technology is to increase the soil organic matter content by retaining it in soil aggregates and to reduce soil erosion by water and tillage. The higher infiltration capacity and better surface cover with crop residues in autumn and winter protects the soil against water erosion, reducing soil erosion by over 50% and runoff by 30%. In addition, the better organic matter content increases overall soil quality in terms of soil structure and water holding capacity. Compared to traditional multiple tillage operations with a mouldboard plough, under reduced tillage, tillage erosion is reduced by having fewer tillage operations, but also through tillage of fallow land resulting in lower tillage erosion rates than secondary tillage operations of already loosened soil. Fuel use by tractors is decreased, leading to a reduction of 40% in production costs and reduced CO2 emissions. Some studies showed that in first 2-3 years after implementation, the soil can be denser and have a lower infiltration capacity than under traditional tillage regimes. Yet, when the organic matter content and soil structure have increased, infiltration rates are higher than under traditional ploughing and result in increased soil water content and crop yields.
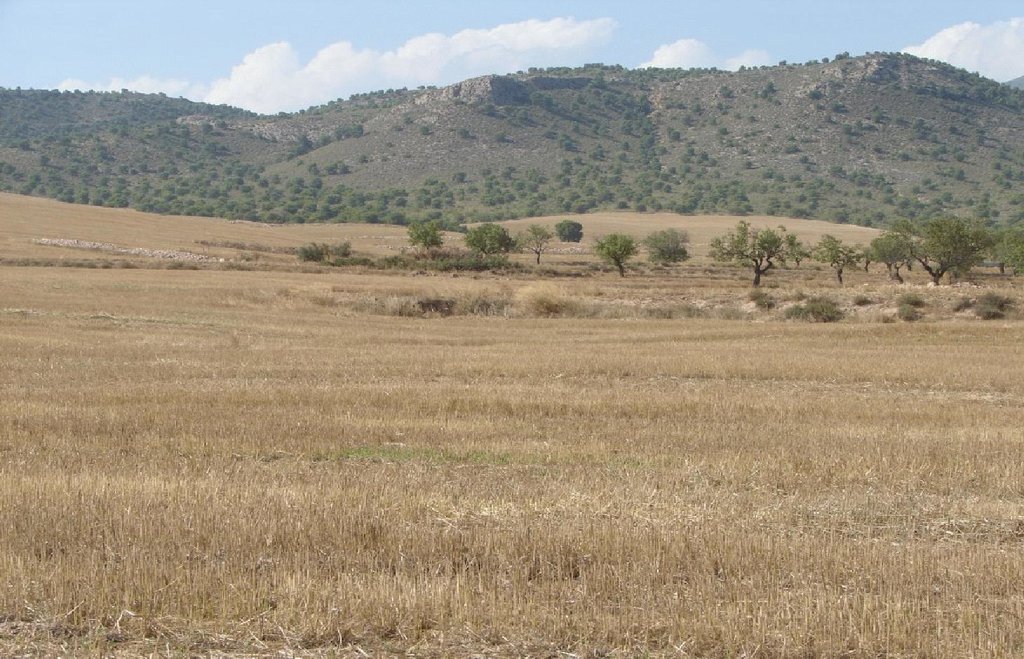
The technology is applied on loamy soils with a calcareous substrate, of shallow to medium depth, and slopes are gentle to moderate (5-15%). The climate is semi-arid with a mean annual rainfall of around 300 mm. Droughts, centred in summer commonly last for more than 4-5 months. Annual potential evapotranspiration rates greater than 1000 mm are common. The production system is highly mechanised and market oriented but depends strongly on agricultural subsidies.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
สเปน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Murcia
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Guadalentin catchment
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 10-100 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The exact area is not known, but the technology is widely applied throughout the province of Murcia and the district of the upper Guadalentin.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
- ในช่วงการทดลองหรือการทำวิจัย
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Conservation tillage is well-known from other areas around the world. Here, it was adapted to the semi-arid and low productivity conditions of this area.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 220 (Nov - Jun)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): There is a lack of water for irrigation of crops limiting the crop types that can be planted as well as the crop yield of dryland farming. A lack of water availability seriously limits the production potential of the soil and results in a low vegetation/crop cover. The relatively high soil erosion rates cause various off-site related problems (i.e. flooding, reservoir siltation) and on-site problems (i.e. gully formation and reduced soil depth).
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of water for irrigation of crops limiting the crop types that can be planted as well as the crop yield of dryland farming.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues.
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การรบกวนดินให้น้อยที่สุด
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A3: การรักษาหน้าดิน
- A4: การรักษาดินชั้นล่าง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Type of agronomic measures: rotations / fallows, breaking crust / sealed surface, breaking compacted topsoil, minimum tillage, non-inversion tillage, contour tillage
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pk (Slaking and crusting): การอุดตันของช่องว่างในดินหรือรูพรุน

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Pk: sealing and crusting, Ha: aridification. Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying.
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Crust formation, loss of soil organic matter, loss of soil structure, loss of available soil water and finally soil loss .), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Reduced infiltration capacity causing runoff and soil erosion), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Low market price of cereals)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (High intensity erosive rainfall is common), droughts (Dry periods and dry years require higher water availability), governance / institutional (Spatial planning of land use and control of soil management)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
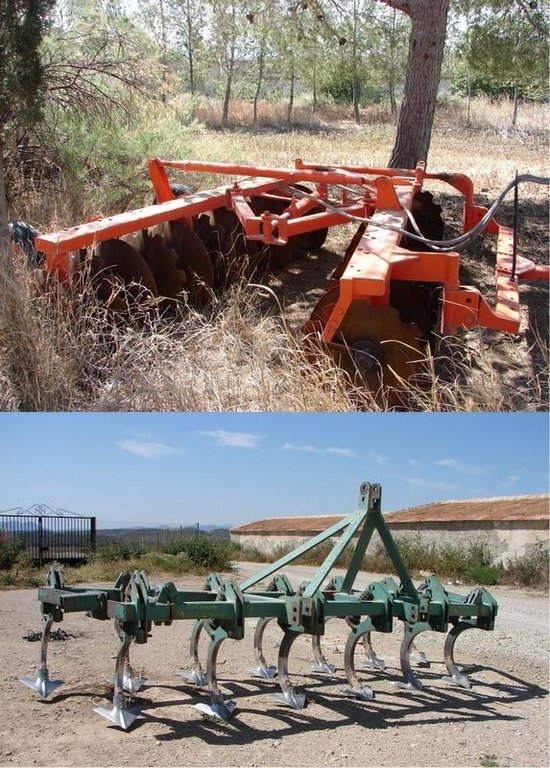
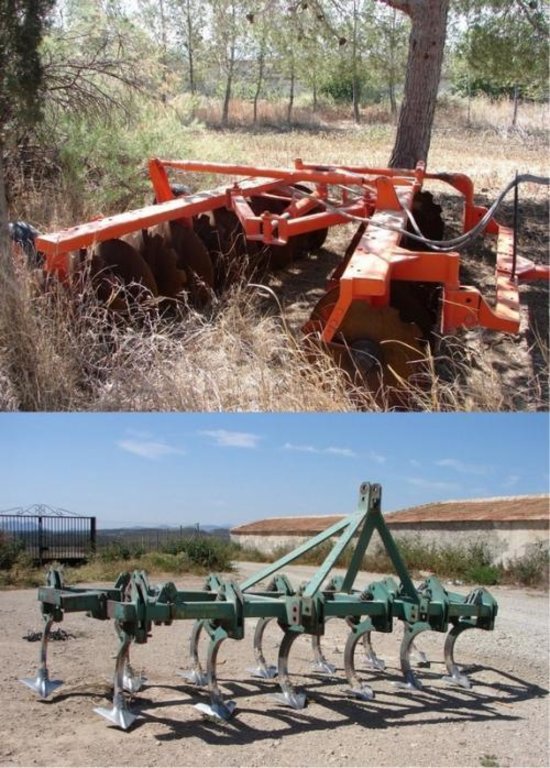
Photo of the disc-plough used for superficial ploughing (~20cm depth) where there is a large amount of crop residue and/or perennial vegetation. Bottom: Chisel-plough
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate. Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate.
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil. Secondary technical functions: increase of surface roughness, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Rotations / fallows: cereals are followed by 1-2 years of fallow
Breaking crust / sealed surface / compacted topsoi: Disc-plough or chisel-plough
Minimum tillage: Disc-plough or chisel-plough
Non-inversion tillage: Disc-plough or chisel-plough
Contour tillage: Disc-plough or chisel-plough
ผู้เขียน:
Joris de Vente
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Euro
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
0.63
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
79.00
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Disc plough | piece | 1.0 | 397.0 | 397.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 397.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 630.16 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The disc plough costs USD 7937, but assuming an average farm size of 10 ha, this means a per ha cost of $794 (Prices are for spring 2008). Two parties are sharing the costs. Initial investment per party = USD 397
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tillage with disc-plough | Before seeding once every 2 years in a rotational fallow system |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | 1.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 100.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Machine hours | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 99.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 62.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 98.41 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: Disc-plough and/or chisel-plough and tractor
The costs are indicated per ha of land where the technology is implemented.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Fuel price is the most determinate factor affecting the costs.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Dry period in summer during 3-4 months (June – August/September)
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
Thermal climate class: subtropics. The higher parts are generally somewhat colder
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
- ต่ำ (<1%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
There is a lowering of groundwater table due to overexploitation for irrigation purposes.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- > 50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users.
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Traditionally most agriculture is done by men in this region.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
15% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land. 80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 75% of the land. 5% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: There is no difference in the ones who apply the technology and those who do not. Most farmers do have an off-farm income for example from hunting, work in a factory or office.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- รายบุคคล
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
All cropland is privately owned. Water use is organised by permits to water extraction from aquifers on individual basis. Water rights are provided and controlled by the Water authority of the Segura river basin (CHS).
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Depending on local conditions yield may be the same or increase slightly. Sometimes in first year of implementation crop production is slightly reduced.
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Possible investment in a Disc-plough during first years
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Depends on crop yield. Gasoline use is decreasing.
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced labour: Less ploughing required.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
On the long term higher infiltration capacity of the soil
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
about 10% reduction
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
reduction by about 45%
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Less tractor use
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
ตะกอนที่ถูกพัดพามาโดยลม
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The crop type is sensitive to changes in water availability under the semi arid conditions.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
When a disc-plough was not already used in normal farming operations, this implies a slightly negative influence on farm income during establishment.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Reduced tillage is not subsidised and so is implemented 100% voluntary. However, there are subsidies for parts of the technology such as contour ploughing and rotational farming allowing a fallow period (1-2 years) after cereals. Practically 100 % of farmers use these subsidies.
There seems to be a growing public awareness of the fact that frequent deep rotational ploughing is not always necessary.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| The technology is low cost and even generates more farm income due to lower fuel use. The increased soil cover through winter and the contour ploughing have a notable positive effect on rill and gully formation in the fields. (How to sustain: The tillage between two fallow periods might be avoided to further reduce fuel use and maintain surface cover intact. However, in order to apply for subsidies for agricultural extensification, farmers are obliged to plough fallow land once a year in order to eliminate weeds.) |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| This is a low-cost technology that requires limited initial investments in equipment and potentially results in a slightly increased farm income, as well as a decrease in land degradation and an increase in soil quality and water-holding capacity. (How to sustain: In some higher areas with sufficient rainfall, the technology might be adapted to conservation tillage with direct sowing, reducing the tillage operations even more. However, this implies an important investment in machinery and a high level of organisation at the agricultural cooperation level.) |
| An increased soil surface cover throughout autumn and winter provides a good protection against soil erosion reducing rill and gully formation. (How to sustain: Sometimes a field is left fallow for two consecutive years, but it is still ploughed between them. This ploughing might be avoided as well.) |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| In order to apply for subsidies for cereal cultivation in a rotation system with fallow, farmers are obliged to plough after each fallow period to control weeds, even when two consecutive years of fallow are applied. This is considered unnecessary | It might be worthwhile to test the need for this and look for alternatives without ploughing. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The most important weakness of this technology is that it does not significantly improve farm income and so may not be stimulating enough for farmers to apply | Provide information on all the advantages of good soil management that include many costs for society (including floods, reservoir siltation, etc.) and stress the fact that reduced tillage will lead to less work for the same or slightly higher profit. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
12/06/2008
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Angás, P., Lampurlanés, J. and Cantero-Martínez, C., 2006. Tillage and N fertilization: Effects on N dynamics and Barley yield under semiarid Mediterranean conditions. Soil and Tillage Research, 87(1): 59-71.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Internet
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Holland, J.M., 2004. The environmental consequences of adopting conservation tillage in Europe: reviewing the evidence. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 103(1): 1-25.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Internet
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Hoogmoed, W.B. and Derpsch, R., 1985. Chisel ploughing as an alternative tillage system in Parana, Brazil. Soil and Tillage Research, 6(1): 53-67.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Internet
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Josa, R. and Hereter, A., 2005. Effects of tillage systems in dryland farming on near-surface water content during the late winter period. Soil and Tillage Research, 82(2): 173-183.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Internet
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Lampurlanés, J. and Cantero-Martínez, C., 2006. Hydraulic conductivity, residue cover and soil surface roughness under different tillage systems in semiarid conditions. Soil and Tillage Research, 85(1-2): 13-26.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Internet
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Lampurlanés, J., Angás, P. and Cantero-Martínez, C. 2002. Tillage effects on water storage during fallow, and on barley root growth and yield in two contrasting soils of the semi-arid Segarra region in Spain. Soil and Tillage Research, 65(2): 207-220
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Internet
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
López-Fando, C., Dorado, J. and Pardo, M.T., 2007. Effects of zone-tillage in rotation with no-tillage on soil properties and crop yields in a semi-arid soil from central Spain. Soil and Tillage Research, 95(1-2): 266-276.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Internet
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Martin-Rueda, I., Muñoz-Guerra, L.M., Yunta, F., Esteban, E., Tenorio, J.L. and Lucena, J.J., 2007. Tillage and crop rotation effects on barley yield and soil nutrients on a Calciortidic Haploxeralf. Soil and Tillage Research, 92(1-2): 1-9
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Internet
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Ozpinar, S., 2006. Effects of tillage systems on weed population and economics for winter wheat production under the Mediterranean dryland conditions. Soil and Tillage Research, 87(1): 1-8.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Internet
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Van Muysen, W., Govers, G., Van Oost, K. and Van Rompaey, A., 2000. The effect of tillage depth, tillage speed and soil condition on chisel tillage erosivity. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation(355-364).
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Internet
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Van Muysen, W., Govers, G., Bergkamp, G., Roxo, M. and Poesen, J., 1999. Measurement and modelling of the effects of initial soil conditions and slope gradient on soil translocation by tillage1. Soil and Tillage Research, 51(3-4): 303-316
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Internet
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Van Oost, K., Govers, G., De Alba, S. and Quine, T.A., 2006. Tillage erosion: a review of controlling factors and implications for soil quality. Progress in Physical Geography, 30(4): 443-466.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Internet
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
CARM 2008. Programa de Desarrollo Rural de la Región de Murcia 2007-2013 Tomo I. 508pp
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://www.carm.es/neweb2/servlet/integra.servlets.ControlPublico?IDCONTENIDO=4689&IDTIPO=100&RASTRO=c431$m1219
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Poesen, J., van Wesemael, B., Govers, G., Martinez-Fernandez, J., Desmet, P., Vandaele, K., Quine, T. and Degraer, G., 1997. Patterns of rock fragment cover generated by tillage erosion. Geomorphology, 18(3-4): 183-197.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Internet
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Regional rural development programme [สเปน]
Regional development programme to protect natural resources and stimulate rural economies.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Joris De Vente
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล